Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advantages and Limitations of The Competency Based Curriculum 2012 2013
Uploaded by
Keith AugustineOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advantages and Limitations of The Competency Based Curriculum 2012 2013
Uploaded by
Keith AugustineCopyright:
Available Formats
Centre Régional des Métiers de l’Education et de la Formation 2012-2013
English Department Oujda A. Senhaji
Advantages and Limitations of the Competency-Based Curriculum and
Competencies Required in Classroom Teachers
The strengths of a competence-based/outcome-oriented curriculum
Learning outcomes are holistic (integrated) rather than fragmented,
Learning outcomes are more long term, flexible for future skills needs/ labour market needs,
Individual learners benefit,
Because learning outcomes are more application based learners are more motivated, understanding the
purpose,
Benefits all and particularly for disadvantaged students,
Benefits for teacher in new ways of working (including team working),
Benefits for the system by involvement of practitioners from the labour market,
The focus is on the success of each learner,
Participants build confidence as they succeed in mastering specific competencies,
More group work than individual work,
More efficient and effective as the teacher is a facilitator of learning as opposed to a provider of
information,
Specific and practical,
Judged by learners,
Can be mastered one at a time,
Student learning is enhanced because of the specification of expected outcomes and continuous
feedback ,
Quality of assessment and teaching improves.
The weaknesses of a competence-based/outcome-oriented curriculum
A risk of neglecting inputs and processes (a need for balance),
Teacher have to deal with it, and be properly trained (team effort),
Risk of atomized approach of formulating outcomes, can’t cope with complex situations,
Confusion around terminology ( outcome based, competence based learning) leads to different
approaches,
May detract from general academic excellence,
Tendency to generate inequity,
A risk that it is not flexible enough for further education or to switch to other professions,
There is a tendency to “teach as we were taught” and competency-based teachers quickly slip back into
the role of the traditional teacher.
Competencies Required in Classroom Teachers
Classroom teachers should be:
Equipped with in-depth knowledge of and about the English language, (Subject matter knowledge),
Communicate expected outcomes to students and provide feedback on student progress and mastery of
competencies using clear, simple language,
Learn and demonstrate effective techniques for teaching foreign languages in context,
Utilise innovative and/or exemplary teaching strategies and techniques in order to more effectively
meet the learning needs of individual students, groups and/or classes of students,
Engage in a variety of self-development activities, including a consistent high level of critical reflection
on one’s own teaching practice and teacher leadership, to sustain a high level of ongoing professional
growth,
Enhance professional knowledge and skills through employing effective development strategies,
Think systematically about their practices,
Display enthusiasm for teaching/learning foreign languages,
Believe that every student can learn when the environment is facilitative,
Flexible in mind, positive in attitude, critical in thinking,
Become skillful in developing appropriate assessment instruments,
Demonstrate an attitude that will convey to students the value of cross-cultural understanding and
foreign language learning,
Advantages and Limitations of the Competency-Based Curriculum Educational Psychology 1/2
Centre Régional des Métiers de l’Education et de la Formation 2012-2013
English Department Oujda A. Senhaji
Design lessons that connect to other content areas in school curriculum. (Interdisciplinary lessons),
Respond critically to the curriculum, to educational information technology innovations and pursue a
process of continuous improvement in their English language teaching career and their own learning,
Demonstrate sufficient responsibility in dealing with students and show trustworthiness,
Know how to create positive relationship between them and their students,
Know how to create a positive and supportive learning environment,
Know how to make their students aware of their own culture and values,
Be able to arise in their students the interest in other cultures and appreciate the differences,
Appreciate the role of theory and research in the teaching process.
Conclusion
The approach based on competency leads to a serious revision of the teacher’s profession. This implies a change
in the teacher’s attitude toward knowledge and towards teaching. The teacher will have to:
Do more than teaching as merely communicating knowledge.
Make the learner learn.
Quit his function of monitoring and evaluating in order to get involved in all activities.
Create various means of teaching.
Share his power, negotiate with the learners and accept their point their view.
Work on projects, and to do so, he must have a perfect knowledge of the project procedures.
Possess a complete knowledge of group dynamics.
Be able to conduct discussions, to act as a mediator between the learners and analyse the group
functioning.
Clarify the processes, the ways the learners think and act; thus the teacher displays greater transparency.
Encourage and guide the learner’s efforts by showing the learner that he is allowed to make errors and
to have doubts.
Enhance the value of co-operation between the learners.
Proceed to formative evaluation in working situations.
Open to other disciplines and have discussions with his colleagues about methods and interdisciplinary
concerns.
Combined & Adapted, Abdelouahab Senhaji
Advantages and Limitations of the Competency-Based Curriculum Educational Psychology 2/2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Valedictory Speech23Document2 pagesValedictory Speech23Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Elementary Instructional Walk-Through Observation Checklist Look Fors - . - Examples - .Document1 pageElementary Instructional Walk-Through Observation Checklist Look Fors - . - Examples - .Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- EDR 10 Maternity LeaveDocument2 pagesEDR 10 Maternity LeaveKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- BNTU Overview 2020Document4 pagesBNTU Overview 2020Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Plan For Covid 19 HolidayDocument5 pagesPlan For Covid 19 HolidayKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Case Study KeithDocument2 pagesCase Study KeithKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Course Two Final Assignment Report Template FinalDocument13 pagesCourse Two Final Assignment Report Template FinalKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- IntrinsicDocument3 pagesIntrinsicKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Respect All Cultures and DiversityDocument2 pagesRespect All Cultures and DiversityKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Flower KeithDocument1 pageFlower KeithKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.4.4.4 EthicsDocument6 pagesActivity 1.4.4.4 EthicsKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
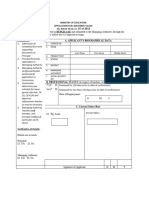
- Educational Visit ApplicationDocument4 pagesEducational Visit ApplicationKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Bntu Information Bulletin 2019-1Document2 pagesBntu Information Bulletin 2019-1Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Agenda For AGM October 2Document1 pageAgenda For AGM October 2Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- 2008 English - Science Paper 1Document40 pages2008 English - Science Paper 1Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Exit CardDocument1 pageExit CardKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Stress Management PlanDocument3 pagesStress Management PlanKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- PSE Answer SheetDocument2 pagesPSE Answer SheetKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Letter For WorkshopDocument2 pagesLetter For WorkshopKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
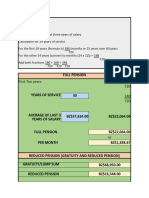
- Pension CalculatorDocument3 pagesPension CalculatorKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Classroom Checklist 2023Document7 pagesClassroom Checklist 2023Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Setting Up The Classroom Environment-JayDocument1 pageSetting Up The Classroom Environment-JayKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- LA and Science Weekly Scheme Package 1Document8 pagesLA and Science Weekly Scheme Package 1Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- History of UWG SpeechDocument3 pagesHistory of UWG SpeechKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Science Package #2 Cycle 1Document3 pagesScience Package #2 Cycle 1Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Belize Guidelines For School Reopening and Operation - 2021-2022Document30 pagesBelize Guidelines For School Reopening and Operation - 2021-2022Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Reading Intervention Abridged MASTERDocument185 pagesReading Intervention Abridged MASTERKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- BDAT Administration Instructions Guidelines ManualDocument38 pagesBDAT Administration Instructions Guidelines ManualKeith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Commuting Allowance Form Revised - 2019-Dario-Vasquez-2021Document2 pagesCommuting Allowance Form Revised - 2019-Dario-Vasquez-2021Keith AugustineNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Safe Operations of Carmelita GovernmentDocument21 pagesGuidelines For The Safe Operations of Carmelita GovernmentKeith AugustineNo ratings yet