Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.1-Molecules To Metabolism
Uploaded by
Priyani GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.1-Molecules To Metabolism
Uploaded by
Priyani GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
● Molecules to metabolism(P62 to P67)
● Carbon atoms are important because they form four covalent bonds and form many
different stable compounds
● Carbon compounds form the basis for life
● Metabolism is defined as a series of reactions catalysed by enzymes that occur in living
organism
● Macromolecules are built up from monomers during condensation reactions
● Macromolecules are broken down to monomers during hydrolysis reactions
Understandings:
● Molecular biology explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved
● Define ‘Molecular biology’
● Compare the benefits of a reductionist vs systems approach to studying biology
● Recognise common functional groups
● Draw skeletal molecular structures from full structure diagrams
● Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism
● Define metabolism and catalysis
● State the role of enzymes in metabolism
● Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the
formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions
● Define anabolism
● Define monomer
● Define polymer
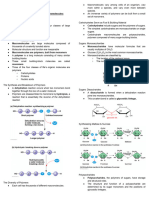
● Describe condensation/Dehydration reactions
● Using simple shapes to represent monomers/a condensation reaction
● Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the
hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers
● Define catabolism
● Contrast anabolism and catabolism
● Hydrolysis reactions
● Using simple shapes to represent monomers/draw a hydrolysis reaction
Applications
● Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organism but can also be
artificially synthesised
● Draw the molecular structure of urea
● Describe how urea can be synthesised by living and artificial mechanisms
● The molecular diagram of ribose
● The molecular diagram of alpha-glucose
● The molecular diagram of a saturated fatty acid
● The generalised structure of an amino acid(Label the amino group, carboxyl group,
alpha carbon and R group on an amino acid)
● Identify the four major classes of carbon compounds used by living organisms
● State the generalised chemical formula of the carbohydrates
● Identify the following carbohydrates from molecular drawings:D-ribose, alpha glucose,
beta glucose, cellulose, glycogen, amylose starch and amylopectin starch
● Compare the relative amount of oxygen atoms in lipids to the amount in carbohydrate
● Triglycerides
● Phospholipids
● Steroids
You might also like
- Module 1 - General Biochemistry (Chem.2)Document31 pagesModule 1 - General Biochemistry (Chem.2)Demeiape Veras BagalayNo ratings yet
- IB Biology HL NotesDocument154 pagesIB Biology HL NotesBobby McFerrin100% (1)
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument1 pageChemical Basis of LifeChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Lec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesDocument32 pagesLec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument39 pagesBiological MoleculesJennifer Fabia100% (1)
- Overview of Metabolism-1Document17 pagesOverview of Metabolism-1gospel munkondyaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule Summative TestDocument6 pagesMacromolecule Summative Testapi-2670792390% (2)
- Topic 2 - Molecular BiologyDocument140 pagesTopic 2 - Molecular BiologyyourstrulyrahulNo ratings yet
- BiopolymersDocument23 pagesBiopolymersAnubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Drilling FluidsDocument60 pagesPolymers in Drilling FluidsMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FileDocument17 pagesChemistry FilePrakhar33% (3)
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Topic 2: Molecular BiologyDocument30 pages2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Topic 2: Molecular BiologyHelena GlanvilleNo ratings yet
- B. BiochemistryDocument22 pagesB. BiochemistryRadhika SarawagiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 1 Molecular Biology-ChecklistDocument3 pagesTopic 2 1 Molecular Biology-Checklistapi-263323894No ratings yet
- Chapter Five Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesChapter Five Lecture NotesAla EnbayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Biological MoleculesDocument15 pagesTopic 1 - Biological MoleculesannabelbithellNo ratings yet
- MBC 201 Nature of Biomolecules, Basic Concept of Metabolism, Integration of Intermediary Metabolism and Energy Generation.Document13 pagesMBC 201 Nature of Biomolecules, Basic Concept of Metabolism, Integration of Intermediary Metabolism and Energy Generation.Aina AdesolaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument4 pagesCARBOHYDRATESALLYSON GENE GULANESNo ratings yet
- Proc2048 Biochemical Engineering: Week 2Document77 pagesProc2048 Biochemical Engineering: Week 2Ann mariaNo ratings yet
- دكتوره اطيافDocument12 pagesدكتوره اطيافbf28215No ratings yet
- Ap Biology MockDocument33 pagesAp Biology MockNabila Osama Al ZeinNo ratings yet
- BiologicalmoleculesDocument58 pagesBiologicalmoleculesrhaineNo ratings yet
- Lectures by Tariq Alalwan, PH.D.: Biology, 12/e Mader & WindelspechtDocument74 pagesLectures by Tariq Alalwan, PH.D.: Biology, 12/e Mader & WindelspechtSulaiman Dawood Saif AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Option B SyllabusDocument10 pagesOption B SyllabusToman Chi To LamNo ratings yet
- Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis: Chapter OverviewDocument5 pagesAnabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis: Chapter OverviewElishae SamonteNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument120 pagesCarbohydratesEmmaNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument32 pagesBiological MacromoleculesAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Metabolism: An Overview: Prof. Dr. Gerhard GrüberDocument57 pagesMetabolism: An Overview: Prof. Dr. Gerhard GrüberBS1009 group5No ratings yet
- Macromolecules Project 1Document10 pagesMacromolecules Project 1api-550561599No ratings yet
- CH 3 NotesDocument40 pagesCH 3 Notesbaileigh5995No ratings yet
- Module 9Document29 pagesModule 9Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocument62 pagesThe Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesOussema Ben KasdallahNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Molecules To MetabolismDocument46 pages2 1 Molecules To MetabolismGeronimo StiltonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Cells: Chapter 2, Section 3Document40 pagesChemistry of Cells: Chapter 2, Section 3idreesnazimNo ratings yet
- 2022C Biochemistry Le 3 Objectives ListDocument1 page2022C Biochemistry Le 3 Objectives ListManila MedNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT, CssoDocument77 pagesCarbohydrates: By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT, CssoTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument71 pagesMetabolismBabylyn Austria100% (1)
- Block 3Document112 pagesBlock 3NumayrNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids AS and A Level Biology CambridgeDocument44 pages2.2 Carbohydrates and Lipids AS and A Level Biology CambridgeImran fazalNo ratings yet
- Proteins PDFDocument7 pagesProteins PDFAshley ArnoldNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument24 pagesChemistryLee LuceroNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates BKSDocument45 pagesCarbohydrates BKSAjmain ShakibNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: by Peyton Kinon, Timothy Cushman, and David WeildDocument36 pagesBiochemistry: by Peyton Kinon, Timothy Cushman, and David WeildCharles IppolitoNo ratings yet
- Asam Amino Dan Protein: Irvandi 406138063Document9 pagesAsam Amino Dan Protein: Irvandi 406138063Evelyn PatriciaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To MetabolismDocument7 pages2.1 Molecules To MetabolismDayoun SongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology MidtermDocument35 pagesAnatomy & Physiology MidtermZNo ratings yet
- Week 2 3 - Molecular DiversityDocument61 pagesWeek 2 3 - Molecular DiversityhhhhNo ratings yet
- What Are Macromolecules???Document120 pagesWhat Are Macromolecules???Nurfarahain ZolkeflyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of Cells Year 11Document20 pagesChemical Composition of Cells Year 11Dyah AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Reviewer - Exam 1Document2 pagesBiochemistry Reviewer - Exam 1Ian IglesiaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Tarawally - 045400Document11 pagesMrs. Tarawally - 045400koromamoses235No ratings yet
- Molecules: The Building Block For ComplexityDocument23 pagesMolecules: The Building Block For ComplexityChristhoper26 TañoNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument43 pagesCarbohydratesMarwanNo ratings yet
- Educ 202 Week 1 (Carbon-Molecules of Life)Document52 pagesEduc 202 Week 1 (Carbon-Molecules of Life)Genel YutucNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6,7 - Biological MacromoleculesDocument34 pagesLecture - 6,7 - Biological MacromoleculesSharmin SultanaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 and 3 NotesDocument15 pagesTopic 2 and 3 NotesvDraqNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN (Biology Report) .PPTX FinalDocument20 pagesPROTEIN (Biology Report) .PPTX FinalHanz NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFDocument23 pagesStructures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFMark Bryan TolentinoNo ratings yet
- BIO-103: Biological Macromolecules: LECTURE: 06-07Document34 pagesBIO-103: Biological Macromolecules: LECTURE: 06-07behtuNo ratings yet
- General Biology: First Stage Lab 6Document13 pagesGeneral Biology: First Stage Lab 6IraqiNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Carbon ElementDocument23 pagesBiomolecules - Carbon ElementRyan S. CutamoraNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesBiomoleculesAdul basit mughalNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Grade 11 Second SemDocument8 pagesPhysical Science Grade 11 Second SemCons vf.No ratings yet
- Biology A Level SpecDocument32 pagesBiology A Level SpecszyzypNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3335.001.07f Taught by Lawrence Reitzer (Reitzer)Document5 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3335.001.07f Taught by Lawrence Reitzer (Reitzer)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Properties Evaluation of Chitosan-Coated Cassava Starch FilmsDocument19 pagesPreparation and Properties Evaluation of Chitosan-Coated Cassava Starch FilmsAthiyah IskandarNo ratings yet
- Photochemistry of Azobenzene-Containing PolymersDocument11 pagesPhotochemistry of Azobenzene-Containing PolymersKaio MaxNo ratings yet
- Tips &tricks For Isolation of DNA and RNA From Challenging SamplesDocument81 pagesTips &tricks For Isolation of DNA and RNA From Challenging SamplesAbhay Kumar100% (2)
- Biophysics Handout Bits PilaniDocument3 pagesBiophysics Handout Bits PilaniAryaman MandhanaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Spoolman 1133940137 9781133940135Document36 pagesTest Bank For Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Spoolman 1133940137 9781133940135StacyOdomtsixq100% (21)
- Big 4 MacromoleculesDocument91 pagesBig 4 MacromoleculesSophea Mercer Anais100% (1)
- Molecular Biology: The Central Dogma: Patricia J PukkilaDocument5 pagesMolecular Biology: The Central Dogma: Patricia J PukkilaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Mišel VuittonNo ratings yet
- (Basic Concept of Organic Chemistry) OrganicDocument33 pages(Basic Concept of Organic Chemistry) Organicrabiullah.edu987No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Biology 11Document46 pagesChapter 10 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Biochem SyllabusDocument14 pagesBiochem SyllabusLymberth BenallaNo ratings yet
- Honors Unit 2 Biochemistry Study Guide S23Document6 pagesHonors Unit 2 Biochemistry Study Guide S23realsteelwarredNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesEnvironmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions ManualCassieTurnerqszj100% (52)
- Objective Life ScienceDocument913 pagesObjective Life ScienceCBSE UGC NET EXAMNo ratings yet
- DDCArv Solutions OddDocument221 pagesDDCArv Solutions OddHuu Tri NguyenNo ratings yet
- Biopolymers LectureDocument23 pagesBiopolymers LectureNneka Okafor-EzeaniNo ratings yet
- Importance of Biological MoleculeDocument3 pagesImportance of Biological MoleculeMary Antonette LucioNo ratings yet
- Edu 214 Biological JeopardyDocument51 pagesEdu 214 Biological Jeopardyapi-438884957No ratings yet
- About The Various Definitions of Life - Pier Luigi LuisiDocument10 pagesAbout The Various Definitions of Life - Pier Luigi LuisiKris Cowell LlorensNo ratings yet
- Polymer Course Lec. 1-1Document10 pagesPolymer Course Lec. 1-1hadeerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Components of A CellDocument3 pagesChemical Components of A Cellapi-421872899No ratings yet
- Eng. Kap. 1-Bch-Chemical Composition of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesEng. Kap. 1-Bch-Chemical Composition of Living Organismskriss WongNo ratings yet
- BIO Prac Proj.Document11 pagesBIO Prac Proj.Sham PhadtareNo ratings yet