Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 3
Uploaded by
Rhamadanny Omar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views32 pagesThe document discusses different types of flow diagrams used to communicate information about chemical processes: block flow diagrams (BFD), process flow diagrams (PFD), and piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&ID). It provides examples and conventions for each type of diagram. BFDs show the major process units and flow of materials using simple symbols. PFDs include more detailed equipment symbols and stream information. P&IDs provide specifications for engineering design and construction of the process.
Original Description:
Original Title
lec3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of flow diagrams used to communicate information about chemical processes: block flow diagrams (BFD), process flow diagrams (PFD), and piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&ID). It provides examples and conventions for each type of diagram. BFDs show the major process units and flow of materials using simple symbols. PFDs include more detailed equipment symbols and stream information. P&IDs provide specifications for engineering design and construction of the process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views32 pagesLec 3
Uploaded by
Rhamadanny OmarThe document discusses different types of flow diagrams used to communicate information about chemical processes: block flow diagrams (BFD), process flow diagrams (PFD), and piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&ID). It provides examples and conventions for each type of diagram. BFDs show the major process units and flow of materials using simple symbols. PFDs include more detailed equipment symbols and stream information. P&IDs provide specifications for engineering design and construction of the process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
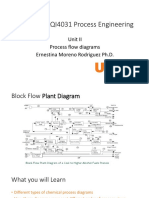
Conceptual Flow Diagrams
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.1/11
Un Croquis vaut mieux qu’un long discours
(A picture is worth a thousand words)
Napoleon Bonaparte
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.2/11
Understanding Chemical Processes
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.3/11
Understanding Chemical Processes
The most effective way of communicating information about
a process is through the use of flow diagrams
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.3/11
Understanding Chemical Processes
The most effective way of communicating information about
a process is through the use of flow diagrams
Block Flow Diagram (BFD)
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P & ID)
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.3/11
Example: Production of Benzene
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.4/11
Example: Production of Benzene
Toluene and hydrogen are converted in a reactor to
produce benzene and methane. The reaction does not go
to completion, and excess toluene is required. The
noncondensable gases are separated and discharged. The
benzene product and the unreacted toluene are then
separated by distillation. The toluene is then recycled back
to the reactor and the benzene removed in the product
stream.
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.4/11
Example: Production of Benzene
Toluene and hydrogen are converted in a reactor to
produce benzene and methane. The reaction does not go
to completion, and excess toluene is required. The
noncondensable gases are separated and discharged. The
benzene product and the unreacted toluene are then
separated by distillation. The toluene is then recycled back
to the reactor and the benzene removed in the product
stream.
Draw the BFD, PFD, and P & ID diagrams for this process.
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.4/11
Block Flow Diagram (BFD)
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.5/11
Block Flow Diagram (BFD)
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.5/11
Conventions and Format for BFD
Operation shown by blocks
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.6/11
Conventions and Format for BFD
Operation shown by blocks
Major flow lines shown with arrows giving direction of
flow
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.6/11
Conventions and Format for BFD
Operation shown by blocks
Major flow lines shown with arrows giving direction of
flow
Flow usually goes from left to right
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.6/11
Conventions and Format for BFD
Operation shown by blocks
Major flow lines shown with arrows giving direction of
flow
Flow usually goes from left to right
Light streams (gases) toward top with heavy streams
(liquids and solids) toward bottom
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.6/11
Conventions and Format for BFD
Operation shown by blocks
Major flow lines shown with arrows giving direction of
flow
Flow usually goes from left to right
Light streams (gases) toward top with heavy streams
(liquids and solids) toward bottom
Critical information unique to process
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.6/11
Conventions and Format for BFD
Operation shown by blocks
Major flow lines shown with arrows giving direction of
flow
Flow usually goes from left to right
Light streams (gases) toward top with heavy streams
(liquids and solids) toward bottom
Critical information unique to process
If lines cross, then the horizontal line is continuous and
the vertical line is broken
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.6/11
Conventions and Format for BFD
Operation shown by blocks
Major flow lines shown with arrows giving direction of
flow
Flow usually goes from left to right
Light streams (gases) toward top with heavy streams
(liquids and solids) toward bottom
Critical information unique to process
If lines cross, then the horizontal line is continuous and
the vertical line is broken
Simplified material balance provided
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.6/11
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.7/11
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.7/11
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
The location of all the major pieces of equipment in the
process are represented symbolically by icons.
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.8/11
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
The location of all the major pieces of equipment in the
process are represented symbolically by icons.
Each major piece of equipment is identified by a
number. A list of equipment numbers along with a brief
descriptive name of the equipment is printed on top of
the page. More details of the equipment are given in a
separate table (see Table 1.6 and 1.7 in TBWS).
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.8/11
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
The location of all the major pieces of equipment in the
process are represented symbolically by icons.
Each major piece of equipment is identified by a
number. A list of equipment numbers along with a brief
descriptive name of the equipment is printed on top of
the page. More details of the equipment are given in a
separate table (see Table 1.6 and 1.7 in TBWS).
All process flow streams are shown along with a
description of the process conditions and chemical
composition. Typically, this stream description is given
in a separate table (see Table 1.5 in TBWS).
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.8/11
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
The location of all the major pieces of equipment in the
process are represented symbolically by icons.
Each major piece of equipment is identified by a
number. A list of equipment numbers along with a brief
descriptive name of the equipment is printed on top of
the page. More details of the equipment are given in a
separate table (see Table 1.6 and 1.7 in TBWS).
All process flow streams are shown along with a
description of the process conditions and chemical
composition. Typically, this stream description is given
in a separate table (see Table 1.5 in TBWS).
All utility streams supplied to a major equipment are
shown.
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.8/11
Process Flow Diagrams (PFD)
The text-book distinguishes between a skeleton PFD and a
PFD. Compare Figures 1.3 and 1.5 for the difference
between the two PFDs.
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.9/11
Process Flow Diagrams (PFD)
The text-book distinguishes between a skeleton PFD and a
PFD. Compare Figures 1.3 and 1.5 for the difference
between the two PFDs.
In this course, when we say PFD, we mean skeleton PFD.
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.9/11
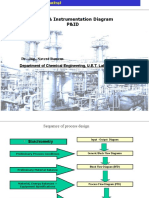
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.10/11
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.10/11
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Based on the information in this diagram:
Mechanical and civil engineers design and install
pieces of equipment
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.11/11
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Based on the information in this diagram:
Mechanical and civil engineers design and install
pieces of equipment
Instrument engineers specify, install, and check control
systems
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.11/11
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Based on the information in this diagram:
Mechanical and civil engineers design and install
pieces of equipment
Instrument engineers specify, install, and check control
systems
Piping engineers develop plant layout and elevation
drawings
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.11/11
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Based on the information in this diagram:
Mechanical and civil engineers design and install
pieces of equipment
Instrument engineers specify, install, and check control
systems
Piping engineers develop plant layout and elevation
drawings
Project engineers develop plant and construction
schedules
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.11/11
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Based on the information in this diagram:
Mechanical and civil engineers design and install
pieces of equipment
Instrument engineers specify, install, and check control
systems
Piping engineers develop plant layout and elevation
drawings
Project engineers develop plant and construction
schedules
We will talk more about P&IDs in ECH 4323
Conceptual Flow Diagrams – p.11/11
You might also like
- P&ID-Presentation (GOOD)Document104 pagesP&ID-Presentation (GOOD)alejandro inostroza100% (3)
- P & ID PresentationDocument104 pagesP & ID PresentationShaheer Shabbir100% (17)
- Working Guide to Pump and Pumping Stations: Calculations and SimulationsFrom EverandWorking Guide to Pump and Pumping Stations: Calculations and SimulationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Afs Map Pes 2013 Ps2Document11 pagesAfs Map Pes 2013 Ps2Sergio GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1 CEV602 Plant DesignDocument37 pages1 CEV602 Plant DesignSolehah OmarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Basics Lec (3) & (4) T. Alaa KhalidDocument40 pagesChemical Engineering Basics Lec (3) & (4) T. Alaa KhalidjoNo ratings yet
- Diagrams For Understanding Chemical Processes: This Chapter Is From The BookDocument4 pagesDiagrams For Understanding Chemical Processes: This Chapter Is From The Bookjane nizar rahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process DiagramsDocument52 pagesChemical Process DiagramsAasia FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Handout p3kDocument50 pagesHandout p3kAsha Herda AfiantiNo ratings yet
- Process Flow DiagramsDocument29 pagesProcess Flow DiagramsJaypal SindhaNo ratings yet
- DiagramasDocument7 pagesDiagramasAndrés BarretoNo ratings yet
- Process Design and EconomicsDocument16 pagesProcess Design and EconomicsNigel MitchellNo ratings yet
- PS TablesDocument2 pagesPS TablesjosebenedictNo ratings yet
- Flow Diagrams For Chemical Processes: Chemical Project Engineering and EconomicsDocument31 pagesFlow Diagrams For Chemical Processes: Chemical Project Engineering and EconomicsSandipSingNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Process Flow Diagram (PFD)Document20 pages1.2 Process Flow Diagram (PFD)م.احمد سالمNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Tony TroxNo ratings yet
- Penamaan PFD (Based On Turton Et Al.)Document15 pagesPenamaan PFD (Based On Turton Et Al.)Hardo NewbieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Process DiagramsDocument48 pagesChapter 1 - Process DiagramsHiep LeNo ratings yet
- AFT-Four Quadrant Pump Data - Theory Part 1 PDFDocument15 pagesAFT-Four Quadrant Pump Data - Theory Part 1 PDFSCR_010101No ratings yet
- Flowsheet LectureDocument23 pagesFlowsheet LectureAdolfo Perez MonteroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Diagrams: John Romar C. Panopio Che 413 Process Dynamics and ControlDocument29 pagesChemical Process Diagrams: John Romar C. Panopio Che 413 Process Dynamics and ControlEmmilio DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2Alexander EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Material On Process DigramsDocument47 pagesMaterial On Process Digramsram uoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Process DiagramsDocument61 pagesLecture 2 - Process DiagramsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture PFD & P &idDocument46 pagesLecture PFD & P &idsanjaykumarkadam2289100% (1)
- Process Diagrams Flow Sheet SynthesisDocument44 pagesProcess Diagrams Flow Sheet SynthesisAdeel Hussain ManjNo ratings yet
- Piping & Instrumentation DiagramDocument104 pagesPiping & Instrumentation DiagramSaz ZasNo ratings yet
- Diagramas de FlujoDocument6 pagesDiagramas de Flujolilith_08No ratings yet
- 1.2. Process Flow Diagram (PFD)Document13 pages1.2. Process Flow Diagram (PFD)Robin SimorangkirNo ratings yet
- CHE425CHAPTER1Document49 pagesCHE425CHAPTER1JuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2Halkawt G MuhammadNo ratings yet
- The Types of Process Flow DiagramsDocument5 pagesThe Types of Process Flow DiagramsMohd FarhanNo ratings yet
- Process Unit 2B Module 1Document27 pagesProcess Unit 2B Module 1Zabdi Paulina Pérez UrquietaNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Comparative Study On Analytical PI-IPR CorrelationsDocument19 pagesA Comprehensive Comparative Study On Analytical PI-IPR CorrelationsAgung Doank YessNo ratings yet
- Coordination System Piping ArrangementDocument29 pagesCoordination System Piping ArrangementAniekanNo ratings yet
- STATE of The Art Design FrancisDocument11 pagesSTATE of The Art Design FrancisearizabalNo ratings yet
- Piping & Instrumentation Diagram P&IdDocument41 pagesPiping & Instrumentation Diagram P&IdTg TarroNo ratings yet
- Piping Coordination Systems - Piping Arrangement - Double and Single Line PresentationDocument8 pagesPiping Coordination Systems - Piping Arrangement - Double and Single Line Presentationsowman tungNo ratings yet
- Designing Quieter Hydraulic SystemsDocument25 pagesDesigning Quieter Hydraulic Systemsbee140676No ratings yet
- Parametric Design of A Francis Turbine Runner by Means of A Three-Dimensional Inverse Design MethodDocument11 pagesParametric Design of A Francis Turbine Runner by Means of A Three-Dimensional Inverse Design MethodsandeshbhavsarNo ratings yet
- Daneshkah (2010) - Parametric Design of A Francis Turbine (Método Inverso)Document11 pagesDaneshkah (2010) - Parametric Design of A Francis Turbine (Método Inverso)HorácioNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Process Flow DiagramsDocument27 pagesChapter Three Process Flow DiagramsFarid DarwishNo ratings yet
- CTR 001 WWT Rev 1 (Without Pump, Tank, and Pipe Spec) Rev.1Document11 pagesCTR 001 WWT Rev 1 (Without Pump, Tank, and Pipe Spec) Rev.1rudiawanNo ratings yet
- Pse-801 Process Systems Theory: Dr. Muhammad AhsanDocument21 pagesPse-801 Process Systems Theory: Dr. Muhammad AhsanrehanNo ratings yet
- Pipe Sizing TechniquesDocument23 pagesPipe Sizing TechniquesmshNo ratings yet
- Lecture-II Flow SheetDocument35 pagesLecture-II Flow SheetChalachew NigussieNo ratings yet
- Turbodesign-Next Generation Design Software For PumpsDocument5 pagesTurbodesign-Next Generation Design Software For PumpsJun GWan ParkNo ratings yet
- Engineering Flow Diagrams and P&IDDocument38 pagesEngineering Flow Diagrams and P&IDvermaakash22No ratings yet
- Types of Piping Drawings: Piping and Instrumentation DiagramDocument18 pagesTypes of Piping Drawings: Piping and Instrumentation Diagramakash dawareNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids: Sylvain Tridon, Stéphane Barre, Gabriel Dan Ciocan, Laurent TomasDocument15 pagesEuropean Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids: Sylvain Tridon, Stéphane Barre, Gabriel Dan Ciocan, Laurent TomasIván David Flores ArteagaNo ratings yet
- NasbyG 2012 UsingFlowsheetsAsCommunicationTools AIChE-CEP Oct2012Document9 pagesNasbyG 2012 UsingFlowsheetsAsCommunicationTools AIChE-CEP Oct2012Henry Arenas100% (1)
- Aiaa 2004 3417Document11 pagesAiaa 2004 3417Fagner Goulart DiasNo ratings yet
- Flow Sheets As Communication ToolsDocument9 pagesFlow Sheets As Communication ToolsAída MuñozNo ratings yet
- L3 CL306 PDFDocument35 pagesL3 CL306 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Atv M 101 eDocument38 pagesAtv M 101 eLaurentiu GheorghitaNo ratings yet
- Pipelining (DSP Implementation) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesPipelining (DSP Implementation) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSubanth WiiliamsNo ratings yet
- Preparation of PFDDocument68 pagesPreparation of PFDkad-7No ratings yet
- Flow CorrelationsDocument13 pagesFlow CorrelationsKhalid sadratiNo ratings yet
- CTG 4080 Gypsum Board Systems Manual EngDocument52 pagesCTG 4080 Gypsum Board Systems Manual EngElmer Soroan BarrerasNo ratings yet
- La-Dimora Brochure PDFDocument23 pagesLa-Dimora Brochure PDFGaurav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Yarn RequisitionDocument8 pagesYarn RequisitionAzim UddinNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument73 pagesMarketingAse SharewNo ratings yet
- Basic English Language SkillsDocument59 pagesBasic English Language SkillsShane HtetNo ratings yet
- Python Odoo 14 NRW Version Book PDFDocument22 pagesPython Odoo 14 NRW Version Book PDFTree loveNo ratings yet
- Excel Property Management Invoice TemplateDocument10 pagesExcel Property Management Invoice Templatenull22838No ratings yet
- ForkJoinPool ExampleDocument6 pagesForkJoinPool ExampleionizareNo ratings yet
- Li Et Al-2018-The Structural Design of Tall and Special BuildingsDocument22 pagesLi Et Al-2018-The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildingsscri_kkNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Introduction To Finite Automata PDFDocument68 pagesUnit-2 Introduction To Finite Automata PDFnikhillamsal1No ratings yet
- Business Environment Q & ADocument16 pagesBusiness Environment Q & ASadaf NazneenNo ratings yet
- Elements of Workshop Technology by Hajra Choudhary PDFDocument4 pagesElements of Workshop Technology by Hajra Choudhary PDFShakeel Mohmand25% (12)
- Materilaspresentation 151211133439Document13 pagesMaterilaspresentation 151211133439Ethan HuntNo ratings yet
- Information Rich and PoorDocument2 pagesInformation Rich and PoorNur Aainaa HafizahNo ratings yet
- Ict351 4 Logical FormulasDocument32 pagesIct351 4 Logical FormulastheoskatokaNo ratings yet
- 077154C-000-STC-0490-000 - B - STD - Const. DrawingDocument79 pages077154C-000-STC-0490-000 - B - STD - Const. DrawingDarshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Executive Order No. 459, S. 2005 - Official Gazette of The Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageExecutive Order No. 459, S. 2005 - Official Gazette of The Republic of The PhilippinesCharlie AdonaNo ratings yet
- Hohner Accordions Nova III 96 Fingering ChartDocument4 pagesHohner Accordions Nova III 96 Fingering ChartFilipe Monteiro TavaresNo ratings yet
- Don - Nan Pump & SupplyDocument180 pagesDon - Nan Pump & Supplyjuliocanel2009100% (1)
- Time in Porphyry Cu - Au Development Corbett - Pacrim 2019 - BDocument5 pagesTime in Porphyry Cu - Au Development Corbett - Pacrim 2019 - BHumberto SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Sabiha Mid Term AssignmentDocument30 pagesSabiha Mid Term Assignmentanikb0% (1)
- INT402 Quiz (Unit 1 To 6)Document143 pagesINT402 Quiz (Unit 1 To 6)Hancy NixonNo ratings yet
- Sample Ss Learning TargetsDocument21 pagesSample Ss Learning Targetsapi-313968260No ratings yet
- Tabla Tension Correas GatesDocument4 pagesTabla Tension Correas Gatesvibrador0% (1)
- Audiolingual Method (Alm) : Elt MethodologyDocument11 pagesAudiolingual Method (Alm) : Elt Methodologyrm53No ratings yet
- CMC-Time Table 1st Year MBBS 150620Document1 pageCMC-Time Table 1st Year MBBS 150620KhanNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Stability Analysis of Microgrids Considering Comprehensive Load Models - A Sensitivity Based ApproachDocument7 pagesSmall Signal Stability Analysis of Microgrids Considering Comprehensive Load Models - A Sensitivity Based ApproachDIEGO ALVERNIANo ratings yet
- Introduction To SAP UI5Document11 pagesIntroduction To SAP UI5EugeneNo ratings yet
- Anti TBDocument44 pagesAnti TBLoreine Jane ClaritoNo ratings yet