Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology 2
Biology 2
Uploaded by
Nitin DassOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology 2
Biology 2
Uploaded by
Nitin DassCopyright:
Available Formats
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
RESPIRATION
2
CHAPTER
E
T
CONTENTS
• Respiration
U
• Breathing
IT
• Respiration in Plants
• Respiration in Human
T
• Mechanism of Respiration
Figure : EPIBLEMA AND ROOT HAIR TAKE PART
IN EXCHANGE OF GASES DIRECTLY IN YOUNG
RESPIRATION
S ROOTS
By Leaves :
IN
It is a biochemical process of enzyme including
oxidative breakdown of organic compounds • Leaves and Young Stems. Leaves and young
inside living cells releasing energy in the form of stems are ideally suited to quick exchange of
ATP. gases. The organs have a covering of nearly
impermeable epidermis for reducing loss of water.
E
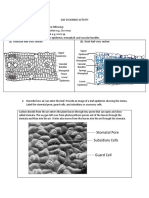
BREATHING The epidermis of leaves bears a number of
The process of intaking O2 & releasing of CO2 aerating pores called stomata (singular stoma or
N
known as breathing . stomata, Gk. stoma-mouth). Each aerating or
stomatal pore is bordered a pair of guard cells. In
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS
most of the plants, the guard cells are kidney or
-O
By young roots : bean shaped with inner walls being thicker and
• Air occurs in soil interspaces. Root hairs as well less elastic than the outer walls.
as epiblema cells of the young roots are in contact • When the stomata are open, gases diffuse into and
with them. They are also permeable to metabolic out of the leaf as per their concentration gradient.
gases. Oxygen of the soil air diffuses through root A gas which has come from outside first reaches
A
hair-epiblema cells and reaches all internal cells substomatal chambers. From here, it diffuses to
of the young root. Carbon dioxide produced by all the intercellular air spaces present in between
root cells diffuses in the opposite direction. the mesophyll cells. If the stomata are open
Respiration 9
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
during night, oxygen from outside will Trachea (Wind pipe) :
diffuse into the leaves and young stems • It is long, tubular structure which runs downward
while carbon dioxide will diffuse out. It is
through the neck in front of oesophagus. It is
due to respiratory gas exchange.
supported by cartilage to prevent collapse.
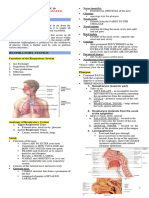
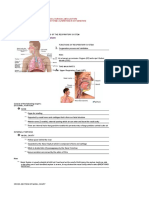
MAMMALIAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Primary bronchi :
E
The mammalian respiratory system consists of
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi,
• These are one pair of small thin walled tubular
structure formed by the division of trachea. It
T
bronchioles and alveoli.
further divides and end at alveoli.
Nostril :
U
Lungs :
• It is also called external nares.
• lungs are present in thoracic cavity on either side
Nasal Chamber :
IT
of heart. covered by pleural membrane.
• Nasal septum divides nasal cavity into two nasal
chamber by the nasal septum. Epiglottis
T
Internal nares : Larynx
•
Trachea
There are posterior opening of nasal chambers
that leads into pharynx.
S
Bronchus
Pharynx :
IN
Cut end Pleural
• The pharynx provides passage to both air and of rib membranes
food. Alveoli
Lung Pleural fluid
Bronchiole
Laryngopharynx : Diaphragm
•
E
It is the lower part of pharynx and has a slit like
aperature called glottis, which can be closed by a Figure : HUMAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
N
leaf like bilobed cartilage epiglottis, during
swallowing of food bolus. MECHANISM OF RESPIRATION
Larynx :
-O
Respiratory centre is in Medulla Oblongeta.
• It is also called voice box or adam's apple or Mechanism of breathing involves Two Phases.
pomas adami. (A) Inspiration
(B) Expiration
Vocal cord :
In larynx, 2 pairs of vocal cord is found outer pair Inspiration :
A
is false vocal cord whereas, inner pair is true
• Intercostal and phrenic muscles of diaphragm
vocal cord when air is forced through the larynx
contract to increase thoracic cavity, therefore
it cause vibration of true vocal cords and sound is
outside rushes inside.
produced.
Respiration 10
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
Expiration :
• Intercostal & phrenic relex muscles.
• Due to decrease of thoracic cavity air pressure
within lungs increase, the greater pressure within
lungs force ful air from lungs to outside of body.
E
Gaseous Exchange :
• Gaseous exchange occur in Alveoli following
T
pressure gradient O2 from high pressure in alveoli
diffuse into blood & CO2 from blood in alveoli.
U
Gaseous Transport :
• O2 is carried by haemoglobin (in RBC). 100 ml of
IT
blood can carry ~20 ml of O2 max, CO2 is
transported in form of bicarbonates in plasma.
T
S
IN
E
N
-O
A
Respiration 11
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
EXERCISE # 1
A. Single Choice Type Questions
Q.9 Covering of lungs is -
Q.1 Which one is anabolic process - (A) Pleura (B) Pericardium
(A) Respiration (B) Digestion (C) Epiglottis (D) Capsule
E
(C) Photosynthesis (D) Ascent of sap. Q.10 Gaseous exchange occurs in the lungs in the
Q.2 A catabolic process is - region of -
T
(A) Absorption of minerals (A) Trachea (B) Bronchi
(B) Ascent of sap (C) Bronchioles (D) Alveoli
U
(C) Respiration Q.11 Trachea and bronchi have -
(D) Assimilation (A) C-shaped cartilaginous rings
(B) Complete cartilaginous rings
Q.3 Exchange of gasses ouccurs through
IT
(C) Complete chitinous rings
(A) Stomata
(D) C-shaped chitinous rings
(B) Lenticles
(C) Root surfaces Q.12 Respiratory tract is lined by ciliated
(D) All of the above epithelium. The function of cilia is to -
T
(A) Trap dust
Q.4 Glycolysis occurs in - (B) Trap germs
(A) Cytoplasm (C) Push out mucus with trapped germs and
(B) Mitochondria
S dust
(C) Chloroplasts (D) Push in air vigorously
IN
(D) Golgi complex
Q.13 If the thoracic wall but not the lungs is
Q.5 Krebs cycle operates in - punctured -
(A) Endoplasmic reticulum (A) The lungs get inflated
(B) Chloroplasts (B) The man dies as the lungs get collapsed
(C) Golgi bodies (C) The breathing rate decreases
E
(D) Mitochondria (D) The breathing rate increases
Q.6 Which one is a product of glycolysis - Q.14 Skin is an ideal respiratory organ in frog
because it is -
N
(A) Oxaloacetate
(B) Pyruvate (A) Highly vascular
(C) Ethyl alcohol (B) Kept moist
(C) Devoid of hair and scales
-O
(D) Lactic acid
(D) All the above
Q.7 Adam's Apple occurs in -
Q.15 Respiration is -
(A) Buffaloes
(A) Anabolic and exergonic
(B) Dogs
(B) Anabolic and endergonic
(C) Human males
(C) Catabolic and exergonic
(D) Human females
(D) Catabolic and endergonic
A
Q.8 Muscular partition present between thorax Q.16 Glycolysis occurs in -
and abdomen is - (A) Anaerobic organisms
(A) Pericardium (B) Pleura (B) Muscle cells
(C) Epiglottis (D) Diaphragm (C) Prokaryotic cells
Respiration 12
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
(D) Almost all the cells
Q.17 The blood coming out of lungs is richer than
that entering into lungs in -
(A) CO2 (B) O2
(C) Both (D) None of these
E
Q.18 Anaerobic respiration is likely to occur in -
(A) Ants (B) Earthworms
(C) Echinoderms (D) Tapeworms
T
Q.19 Respiratory quotient is -
(A) CO2/O2 (B) O2/CO2
U
(C) CO2/N2 (D) N2/CO2
Q.20 Epiglottis guards the opening of -
IT
(A) Eustachian tube (B) Glottis
(C) Lungs (D) Internal ear
Q.21 Skin is an accessory respiration in -
(A) Humans (B) Frog
T
(C) Rabbit (D) Lizard
Q.22 The process of respiration is -
(A) Anabolic (B) Catabolic
S
(C) Metabolic (D) Anaerobic
IN
Q.2 3 Lungs are covered with the covering of -
(A) Pleural membrane
(B) Pericardium
(C) Peritoneum
(D) Mucous membrane
E
N
-O
A
Respiration 13
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
EXERCISE # 2
A. Very Short Answer Type Questions C. Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1 What is respiration ? Q.20 Name the respiratory organs in the following :
(a) a fish (b) a bird (c) an earthworm
E
Q.2 What are stomata ?
Q.21 How is respiration different from breathing ?
Q.3 Name the energy currency of living system.
T
Q.22 Explain the processes of 'aerobic' respiration
Q.4 What is respiratory organ ? and 'anaerobic' respiration.
U
Q.5 What is diaphragm ? Q.23 Draw a diagram showing 'human respiratory
system'. Label its following parts
Q.6 Define glottis. (i) Larynx (ii) Trachea
IT
(iii) Primary Bronchus (iv) Lungs.
Q.7 What is epiglottis ?
Q.24 Why do the walls of the trachea not callapse
Q.8 Define breathing
when ther is less air in it & write its
T
importance ?
Q.9 What is inspiration ?
Q.10 Define expiration.
S
Q.11 Name the common passage for food and air.
IN
Q.12 What is the shape of diaphragm during
expiration ?
Q.13 What is the shape of cartilaginous rings in
trachea ?
E
B. Short Answer Type Questions
N
Q.14 Differentiate between photosynthesis and
respiration.
-O
Q.15 Distinguish between breathing and respiration.
Q.16 Differentiate between bronchioles and
tracheoles.
Q.17 What is the composition of inhaled and
exhaled air ?
A
Q.18 Differentiate between inspiration and
expiration.
Q.19 What are the functions of nasal passage ?
14
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
You might also like
- Generator Principles Generator Construction Excitation System Operational Aspects Generator ProtectionsDocument50 pagesGenerator Principles Generator Construction Excitation System Operational Aspects Generator Protectionsvasanth11kv100% (1)
- Developing Thinking in Geometry by Sue Johnston-Wilder, Professor John Mason PDFDocument285 pagesDeveloping Thinking in Geometry by Sue Johnston-Wilder, Professor John Mason PDFpietro265No ratings yet
- Elementary French The Essentials of French Grammar With Exercises 1000090314Document555 pagesElementary French The Essentials of French Grammar With Exercises 1000090314Brinzea Laura100% (1)
- Cat Caterpillar D4 D4B Dozer Operation Maintenance Manual DownloadDocument3 pagesCat Caterpillar D4 D4B Dozer Operation Maintenance Manual DownloadDaniel Marin Morales100% (1)
- Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument75 pagesAnatomy of Respiratory SystemAnonymous aqeaNUn83% (6)
- 7.1 (LEC) - Functional Anatomy of Respiratory System and Mechanics of BreathingDocument9 pages7.1 (LEC) - Functional Anatomy of Respiratory System and Mechanics of BreathingKenneth TorresNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument16 pagesRespiratory PhysiologyYsabel Salvador DychincoNo ratings yet
- D5490 93 Standard Guide For Comparing Groundwater Flow Model Simulations To Site Speci C Information PDFDocument9 pagesD5490 93 Standard Guide For Comparing Groundwater Flow Model Simulations To Site Speci C Information PDFVictor KlassenNo ratings yet
- Effects of Planetary Gear Ratio On Mean Service LifeDocument6 pagesEffects of Planetary Gear Ratio On Mean Service LifeasdNo ratings yet
- Iready at Home Activity Packets Student Math Grade 6 2020Document31 pagesIready at Home Activity Packets Student Math Grade 6 2020ceci100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Lecture 234 Pages Pg. 333 566Document189 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Lecture 234 Pages Pg. 333 566Crystal Ann TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical TransesDocument144 pagesMedical Surgical Transesmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Pocket Handbook For Arc Welding SteelDocument18 pagesPocket Handbook For Arc Welding SteelixoteeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Clips 1-5Document1 pageRespiratory System Clips 1-5api-552227798No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemAmore BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Final pt.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Final pt.2Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- (Transes) Human Histology - 14 Respiratory SystemDocument17 pages(Transes) Human Histology - 14 Respiratory SystemReina CastronuevoNo ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument24 pagesOxygenationJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange ActivityDocument3 pagesGas Exchange ActivitySophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Ms Lec 2 Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesMs Lec 2 Respiratory SystemLabinnah MoresNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Lecture 234 Pages Pg. 333 566Document242 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Lecture 234 Pages Pg. 333 566ShiraishiNo ratings yet
- Review On Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesReview On Respiratory Systemsecondacvalo123No ratings yet
- Anaphy-Respiratory HandoutDocument7 pagesAnaphy-Respiratory HandoutAEGEL DARO TORRALBANo ratings yet
- Medterm RespiratoryDocument17 pagesMedterm RespiratoryVince BalloriNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemden mNo ratings yet
- Bree Final Pulm ReviewDocument46 pagesBree Final Pulm ReviewAnna StacyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document7 pagesLecture 4cejix87209No ratings yet
- Lec 1 Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesLec 1 Respiratory SystemfaiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System BAYLONDocument17 pagesRespiratory System BAYLONElijah Joaquin Payumo BaylonNo ratings yet
- 8.respiration 2023Document12 pages8.respiration 2023Alina AtherNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationDocument44 pagesMedical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationYman Gio BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Reviewer (Prelim)Document71 pagesMedsurg Reviewer (Prelim)JOANA MARIE MAE SANTOS BASILIONo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument25 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeTyrsonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders (Completed)Document55 pagesRespiratory Disorders (Completed)Czejan Rae TabaranzaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System - Tran LoanDocument22 pagesThe Respiratory System - Tran LoanLoc HuynhNo ratings yet
- KINE 2031 Test 4 NotesDocument16 pagesKINE 2031 Test 4 NotesnokiaNo ratings yet
- Complete Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument20 pagesComplete Breathing and Exchange of GasesANo ratings yet
- Topic 11Document15 pagesTopic 11Lorraine RiegoNo ratings yet
- MTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesMTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Respiratory SystemJaeri HuangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Handout # 15 Respiratory System-1Document8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Handout # 15 Respiratory System-1Jounri Arsted Dimabuyu (Kaiz)No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory System: O CO O CO O CODocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Respiratory System: O CO O CO O COAJ BayNo ratings yet
- Midterm 3 Anatomy PDFDocument364 pagesMidterm 3 Anatomy PDFaidanNo ratings yet
- EAR-4 Year PresentationDocument133 pagesEAR-4 Year Presentationeiuj497No ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument9 pagesRespiratoryAhmad NoorNo ratings yet
- Ch. 29 StudyDocument6 pagesCh. 29 StudyPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- SEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch14 RespirationDocument56 pagesSEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch14 Respirationmiki leeNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument15 pagesGen BioCAMILLE JELLA ALZOLANo ratings yet
- Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument4 pagesNose and Paranasal SinusesAlloiBialbaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 New Biology NotesDocument181 pagesClass 10 New Biology Noteskaziamna62No ratings yet
- Respiratory System HandoutDocument11 pagesRespiratory System HandoutJohn Carlo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory Systemadelina.jianu9991No ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument3 pagesRespiratoryJehira OcampoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10-Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 10-Respiratory SystempraiseginelcNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesOrgans of The Respiratory SystemCrystal Kaye RecasaNo ratings yet
- Nose and Parasinuses: I. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. II. A. B. C. D. IiiDocument3 pagesNose and Parasinuses: I. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. II. A. B. C. D. IiiKenneth TorresNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemAdit KumarNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Revision QuizDocument80 pagesForm 4 Revision QuizEnvira LeeNo ratings yet
- 12 Respiratory System - ATFDocument43 pages12 Respiratory System - ATFLucas BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 1Document8 pagesRespiratory System 1Jann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 FinalDocument10 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 FinalJann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- Rle 070722Document14 pagesRle 070722kyla arachelleNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORYDocument32 pagesRESPIRATORYJulia BascoNo ratings yet
- RT 105 Prefinal NotesDocument24 pagesRT 105 Prefinal NotesLouiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Part 2Document35 pagesChapter 5 Part 2Leorey Evaristo AjeroNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesGroup 3 - Respiratory Systemvina1598No ratings yet
- M7 RespiratoryDocument6 pagesM7 RespiratoryNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- Producción de Urea Por Carbonatacion de AmoniacoDocument17 pagesProducción de Urea Por Carbonatacion de AmoniacoTatiana HoyosNo ratings yet
- WI-NG-6460-002-036 Commissioning of XLPE Power Cables (From 69kV To 380kV) Rev01Document16 pagesWI-NG-6460-002-036 Commissioning of XLPE Power Cables (From 69kV To 380kV) Rev01Makesh Indhu0% (1)
- 5.1-5.5 Guided Notes: If 15° and 52°, What Is ?Document3 pages5.1-5.5 Guided Notes: If 15° and 52°, What Is ?2020 MistakesNo ratings yet
- Tips and Tricks Using EnergyplusDocument64 pagesTips and Tricks Using EnergyplusBasil OguakaNo ratings yet
- Simple Phenomena of Magnetism 1 QPDocument11 pagesSimple Phenomena of Magnetism 1 QPnssNo ratings yet
- Coffe Can Radar MejoradoDocument13 pagesCoffe Can Radar MejoradoDaniel Alejandro Almela0% (1)
- The Internet: ITS323: Introduction To Data Communications CSS331: Fundamentals of Data CommunicationsDocument43 pagesThe Internet: ITS323: Introduction To Data Communications CSS331: Fundamentals of Data CommunicationsNatnael KetemaNo ratings yet
- Guide 7 ADocument21 pagesGuide 7 AengsamerhozinNo ratings yet
- Pos 0,5 DatasheetDocument7 pagesPos 0,5 DatasheetDoğa Tuğçe DurmuşNo ratings yet
- Differential Relations For Fluid FlowDocument11 pagesDifferential Relations For Fluid FlowBenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1 (MMW)Document3 pagesAssessment Task 1 (MMW)Wendelyn JimenezNo ratings yet
- EC68651 TLRF Big Questions All UnitsDocument2 pagesEC68651 TLRF Big Questions All UnitsDhanaraj P100% (1)
- KSB Sicca Valves For The Ansi World: PDF Processed With Cutepdf Evaluation EditionDocument36 pagesKSB Sicca Valves For The Ansi World: PDF Processed With Cutepdf Evaluation EditionPravin KohaleNo ratings yet
- MIB 303 - 503 - Separation System - Safety - 2018Document10 pagesMIB 303 - 503 - Separation System - Safety - 2018Centrifugal SeparatorNo ratings yet
- Thermo Scientific Cimarec Series-1Document2 pagesThermo Scientific Cimarec Series-1Dini DarmawatiNo ratings yet
- Inventor 2014 Application OptionsDocument21 pagesInventor 2014 Application OptionsDobrica PetrovicNo ratings yet
- 498 110 Falk Wrapflex Type R10, 31, 35, Sizes 2 80 Elastomeric Couplings Installation ManualDocument8 pages498 110 Falk Wrapflex Type R10, 31, 35, Sizes 2 80 Elastomeric Couplings Installation ManualDiego Madrid MirandaNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Activity On Coordination CompoundsDocument5 pagesSelf-Learning Activity On Coordination CompoundsAbigail CalalangNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Precast Multistoreyed Building - A Case Study: I J I R S E TDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Precast Multistoreyed Building - A Case Study: I J I R S E TalexanderNo ratings yet
- MC9S12C Family MC9S12GC Family Reference Manual: HCS12 MicrocontrollersDocument680 pagesMC9S12C Family MC9S12GC Family Reference Manual: HCS12 MicrocontrollerssimocriciNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of A Separation Process For Higher Alcohols Made Bycatalytic Condensation of Ethanol 2090 4568 1000134Document9 pagesConceptual Design of A Separation Process For Higher Alcohols Made Bycatalytic Condensation of Ethanol 2090 4568 1000134shridharNo ratings yet
- Hons - NBSXCDocument1 pageHons - NBSXCAachal SinghNo ratings yet