Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure
Uploaded by
Shean LimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure
Uploaded by
Shean LimCopyright:
Available Formats
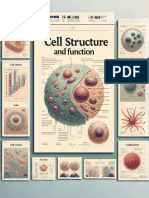
Cell structure
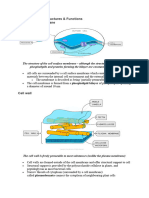
Cell surface membrane
- The cell surface membrane is extremely thin (about
7 nm). The membrane is partially permeable and controls
the exchange between the cell and its environment.
Microvilli
- microvilli (singular: microvillus): small, finger-like
extensions of a cell which increase the surface
area of the cell for more efficient absorption
or secretion
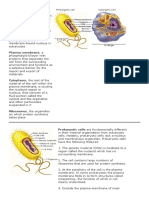
Nuclear envelope
- the two membranes, situated
close together, that surround the nucleus;
the envelope is perforated with nuclear pores
Nuclear pores
- pores found in the nuclear envelope
which control the exchange of materials, e.g.
mRNA, between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
-a network of flattened sacs running through the cytoplasm of
eukaryotic cells; molecules, particularly proteins,
can be transported through the cell inside the
sacs separate from the rest of the cytoplasm; ER
is continuous with the outer membrane of the
nuclear envelope.
- ER membranes form cisternae
Ribosome
- a tiny organelle found in large numbers in all cells; prokaryotic ribosomes are
about 20 nm in diameter while eukaryotic ribosomes are about 25 nm in
diameter
- not visible under a light microscope
- eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S
- prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S
- made of rRNA and protein
- allows all molecules involved in protein synthesis to grather tgt(mRNA, rRNA,
amino acids and regulatory proteins)
Golgi apparatus (Golgi body, Golgi complex)
- an organelle found in eukaryotic cells; the Golgi apparatus consists of a stack of
flattened sacs, constantly forming at one end and breaking up into Golgi vesicles
at the other end
Golgi vesicles
- carry their contents to other parts of the cell, often to the cell surface
membrane for secretion; the Golgi apparatus chemically modifies the molecules
it transports, e.g. sugars may be added to proteins to make glycoproteins
control of the genetical information of the cell and thus the heredity
characteristics of an organism,
control of the protein and enzyme synthesis.
control of cell division and cell growth.
storage of DNA, RNA and ribosome.
regulation of the transcription of the mRNA to protein.
production of ribosomes.
You might also like
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- H2 BIO Cell Structure NotesDocument15 pagesH2 BIO Cell Structure NotesEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesLecture Cross Section of Plant and Animal CellTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesBasic Cell Structure & FunctionJawaad AsifNo ratings yet
- 6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Document7 pages6.1-How Are Cells Studied?: Magnification Resolution Contrast Electron Microscope (EM)Sadasivarao GaddeNo ratings yet
- AP Cell Structure and Function Copy IpadDocument25 pagesAP Cell Structure and Function Copy IpadEbtisam AlmenhaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarNo ratings yet
- 04 Structure To FunctionDocument5 pages04 Structure To Function897291868100% (1)
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellssalahuddin_md5935100% (1)
- Cytology OrganellesDocument33 pagesCytology OrganellesMitzel SapaloNo ratings yet
- Morphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDocument52 pagesMorphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDoc HamsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport MechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport Mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument44 pagesCell Structure and FunctionPedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- Cell Intro InfoDocument12 pagesCell Intro Infoapi-237058097No ratings yet
- Topic 1.1 OrganellesDocument2 pagesTopic 1.1 OrganellesShean LimNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles NotesDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Notesoriel blountNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture 1Document17 pagesCell Biology Lecture 1NIMRAHNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Last-Cell Organelles.Document3 pagesLecture Last-Cell Organelles.OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures: The BasicsDocument4 pagesCell Structures: The BasicsParama CinthyaNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForShakera ReidNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForAlix AliNo ratings yet
- Cell & Intercellular JunctionsDocument35 pagesCell & Intercellular JunctionsDikpal BikramNo ratings yet
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument22 pagesCell Structure and FunctionKarren MakamureNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument6 pagesBiology ProjectBemnet TayeNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesComparison of Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsmalathyNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Document8 pagesStructure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Ishita KumariNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument30 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumMuhammad Junaid Iqbal100% (1)
- Cell OrganellesDocument4 pagesCell OrganellesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument8 pagesPlant CellIrish Nicole PacionNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- The Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell TermsDocument5 pagesThe Following Is A Glossary of Animal Cell Termsnelah roswatiNo ratings yet
- Er, Structure & Its FunctionsDocument20 pagesEr, Structure & Its FunctionsTalha AfzalNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument8 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumShahab Saqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Organelles FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Structures & Organelles Functionsnasimzand78100% (1)
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- Gen BioCell TheoryDocument18 pagesGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 pagesPlant Cell - LayoutMahiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell StructureDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell Structureteee100% (1)
- Plant Cell StructureDocument13 pagesPlant Cell Structureshamosa85.saNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure2Document6 pagesCell Structure2CRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Cell Structure and MitosisDocument10 pagesTopic 3 Cell Structure and MitosisdaniaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingDocument24 pagesCell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingWina MaeNo ratings yet
- Nature of CellsDocument7 pagesNature of CellsAdrian Lee VannorsdallNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter6 AnswersSammy AhmedNo ratings yet
- Upload It 1Document5 pagesUpload It 1John Rey Bandong100% (1)
- عرض تقديمي تركيب الخلية المحاضرة الثانية لتخديرDocument28 pagesعرض تقديمي تركيب الخلية المحاضرة الثانية لتخديرzaidemad05No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Crop PhysiologyDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Crop PhysiologyRsNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellWhyL NificentNo ratings yet
- Biology ObjectivesDocument12 pagesBiology ObjectivesNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- SJDFSJHDocument3 pagesSJDFSJHapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellKu Ya ÇhrisNo ratings yet
- 4.4, 4.5 Exam QuestionsDocument17 pages4.4, 4.5 Exam Questionsmegaman31080% (1)
- Commerce Notes Abt TransportationDocument5 pagesCommerce Notes Abt TransportationShean Lim100% (1)
- Chapter 13 - LightDocument2 pagesChapter 13 - LightShean LimNo ratings yet
- Organelles in The CellsDocument4 pagesOrganelles in The CellsShean LimNo ratings yet
- Movement of MoleculesDocument1 pageMovement of MoleculesShean LimNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Replication and Division of Nuclei and Cells-MinDocument3 pages5.1 Replication and Division of Nuclei and Cells-MinShean LimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9701 Paper 1 - Atomic StructureDocument15 pagesChemistry 9701 Paper 1 - Atomic StructureShean LimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Presentation:: Covalent BondingDocument9 pagesChemistry Presentation:: Covalent BondingShean LimNo ratings yet
- Seri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickDocument24 pagesSeri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickShean LimNo ratings yet
- Seri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickDocument26 pagesSeri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickShean LimNo ratings yet
- Seri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickDocument18 pagesSeri Omega Private & International School: To View The Video For This Worksheet, ClickShean LimNo ratings yet