Professional Documents
Culture Documents
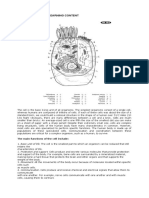
Cell-Cell Communication
Cell-Cell Communication
Uploaded by
reynaldo banaria jrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell-Cell Communication
Cell-Cell Communication
Uploaded by
reynaldo banaria jrCopyright:
Available Formats
REYNALDO M. BAÑARIA, JR.
MS BIO 220
Cell to Cell Communication in Development
1. Explain the principle of induction during embryonic development and cite 1 specific example
to elaborate the process leading to development or formation of a part/structure.
2. What will happen if there is cell to cell communication breakdown? Give 1 specific example.
3. What are cell adhesion molecules? Give its roles in morphogenesis and development.
4. Explain the role of Hippo pathway during development.
Discussion:
1. The principle of induction plays a vital role in embryonic development of all living organisms,
especially of animals. As its definition implies, this interaction (at close range) between two or
more cells or tissues will promote embryonic development, evident in the formation of our
organs, each with specific structures and functions uniquely to each other. Through the
interaction of the two components, the inducer and the responder, the formation of organs
become possible that is essential in an organism’s embryonic development.
An example of which can be seen in the induction of the mouse lens. The optic vesicle extends
toward the surface ectoderm from the forebrain during embryonic day 9. The lens placode
appears as a local thickening of the surface ectoderm near the optic vesicle. At the middle of
day 9, the lens placode has enlarged and the two optic vesicles has formed an optic cup and at
the middle of day 10, the central portion of the lens-forming ectoderm invaginates, while the
two layers of the retina become distinguished. By the middle of day 11, the lens vesicle has
formed and at day 13, the lens consists of anterior cuboidal epithelial cells and elongating
posterior fiber cells. Then the cornea develops in front of the lens.
2. Breakdown or miscommunication in cells poses adverse and imbalance results in organisms’
state of being. One example is the retinal homeostasis by changing gene expression of connexin
and gap junction intercellular communication, leading to cell apoptosis and breakdown of the
blood-retinal barrier.
3. Cell adhesion molecules are proteins found at the cell’s surface that are involved in binding
cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix. For example, is the adhesion between
leukocytes and endothelial cells, a hallmark of the inflammatory process. Leukocytes leave the
circulation at sites of tissue inflammation by interacting with the endothelial cells of capillary
walls.
4. Hippo pathway is a signaling pathway that controls organ size in animals through the regulation
of cell proliferation and apoptosis. This pathway is necessary in limiting tissue and organ
growth. It also plays critical roles in early embryonic development such as in trophoblast
differentiation and inner cell mass formation. To sum up, hippo pathway serves as the controller
and regulator in tissue and organ formation that when affected may lead to diseases such as
tumor growth and cancers.
You might also like
- Cell Biology Illustrated ReportDocument21 pagesCell Biology Illustrated ReportIlze Krauze100% (11)
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 11 SummaryDocument7 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 11 SummaryDana PorterNo ratings yet
- MorphogenesisDocument25 pagesMorphogenesisDrAbhilasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Teacher: DR Gouri Course: Zoology Hons. 6 Sem Paper: Developmental BiologyDocument17 pagesTeacher: DR Gouri Course: Zoology Hons. 6 Sem Paper: Developmental BiologyApratim SinghNo ratings yet
- Wolpert, L. - 1994 - Do We Understand DevelopmentDocument2 pagesWolpert, L. - 1994 - Do We Understand DevelopmentcontulmmivNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: DR QurbanDocument8 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: DR QurbansaranNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualGregoryStricklandgtak100% (58)
- Chapter 2 How Development Works AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 2 How Development Works Answersbiblioteca10.uni.patxiNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of Oral Physiology and Oral BiologyDocument87 pagesA Handbook of Oral Physiology and Oral Biologyamirmaafi100% (1)
- Teoría Celular 01Document5 pagesTeoría Celular 01Mildred Yaniret Guillermo ChávezNo ratings yet
- All Sexual Organisms Begin As A Single CellDocument12 pagesAll Sexual Organisms Begin As A Single CellAFRIADMA AULIA PERDANANo ratings yet
- Principles of Development. Cap 1Document32 pagesPrinciples of Development. Cap 1Gre Vega ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Arranged By: Hasmi Syahputra Harahap Meti Agustina Butarbutar Sukmawati Sundari Siregar Winny Sunfriska LDocument31 pagesArranged By: Hasmi Syahputra Harahap Meti Agustina Butarbutar Sukmawati Sundari Siregar Winny Sunfriska LAyesha NuraisyiahNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio Cell Election Project Cell MembraneDocument9 pagesAp Bio Cell Election Project Cell Membraneapi-553676905No ratings yet
- Seatwork in Oral HistologyDocument3 pagesSeatwork in Oral Histologyjindaprankster28No ratings yet
- Activity 1 (Physiology)Document4 pagesActivity 1 (Physiology)dianarosedejorasNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology: Sengamala Thayaar Educational Trust Women's CollegeDocument35 pagesDevelopmental Biology: Sengamala Thayaar Educational Trust Women's CollegeApratim SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes Hand Out '21Document3 pagesCell Processes Hand Out '21Amazing GreenNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument9 pagesCell Biologyrubab azizNo ratings yet
- 1st, 2nd & 3rdweeksDocument9 pages1st, 2nd & 3rdweeksPristine KrNo ratings yet
- Intercellular Communication in The Cumulus - Oocyte Complex During Folliculogenesis: A ReviewDocument13 pagesIntercellular Communication in The Cumulus - Oocyte Complex During Folliculogenesis: A ReviewJohn XIENo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions Manual PDFjonathanwelchjrcizmsdty100% (11)
- Veta 60. Module 6Document9 pagesVeta 60. Module 6Adrianne Joy De Castro100% (1)
- Understanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesUnderstanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFslypesecularjgi77100% (5)
- Underwood: Chapter 3: Disorders of Growth, Differentiation and MorphogenesisDocument27 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 3: Disorders of Growth, Differentiation and MorphogenesisSANo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- Biotech Session 1Document18 pagesBiotech Session 1j_ngetich_k7375No ratings yet
- Weeks 1-3 Module: Learning Content: Basic Unit of Life. Protection and SupportDocument8 pagesWeeks 1-3 Module: Learning Content: Basic Unit of Life. Protection and SupportShana AquinoNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- The Histology and Biology of The LensDocument8 pagesThe Histology and Biology of The LensIdham BaharudinNo ratings yet
- MB501-Practical Exam Notes VU by Muhammad KashifDocument22 pagesMB501-Practical Exam Notes VU by Muhammad KashifSagheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0022202X15447736 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0022202X15447736 MainKhan FatemaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocument19 pagesCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- Biology Investigatory Project Ageing: Submitted By:-Jayashri CBSE Roll No.Document35 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Ageing: Submitted By:-Jayashri CBSE Roll No.Anonymous ImSMU2BqNSNo ratings yet
- Genetic Basis of Cell-Cell Fusion MechanismsDocument11 pagesGenetic Basis of Cell-Cell Fusion MechanismsDaniela AvilaNo ratings yet
- LESSON TITLE: Cell DivisionDocument25 pagesLESSON TITLE: Cell DivisionAlthea nicole CrespoNo ratings yet
- Learning Module in General Biology 1: First Semester, S.Y. 2020 - 2021Document6 pagesLearning Module in General Biology 1: First Semester, S.Y. 2020 - 2021Arlene MenaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Development-For NotesDocument19 pagesPlant Growth and Development-For NotesMARIA ISABILLE DUALLO MUSONGNo ratings yet
- B2.3 Biology NotesDocument2 pagesB2.3 Biology Noteskounis2011No ratings yet
- Xüsusi Histologiya Dərslik 2015-1Document14 pagesXüsusi Histologiya Dərslik 2015-1aydinmemmedov9009No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument10 pagesCell BiologySaadNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Document27 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Ashay Kumar0% (1)
- Trager 1963Document6 pagesTrager 1963IñigoGaitanSalvatellaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Embryonic AppendixADocument21 pagesThe Science of Embryonic AppendixAPeggy W SatterfieldNo ratings yet
- Describe Microbial GrowthDocument8 pagesDescribe Microbial GrowthDonita CL Nobong PinatNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesDocument21 pagesAP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesjanaNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument104 pagesCell BiologyADARSH RNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestDocument8 pagesCHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestLyka Abdullah TayuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Gene DevelopmentDocument3 pagesChapter 7. Gene Developmentvimbee alipoonNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch08 Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument8 pages11 Biology Notes Ch08 Cell Structure and FunctionsVansh Mehta100% (1)
- Module 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesModule 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionBalolot RalphNo ratings yet
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Document11 pagesInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- CellDocument61 pagesCellAbdul Rehman100% (1)
- Development Q&ADocument6 pagesDevelopment Q&AKathleen AraújoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Renewal and Repair RegenerationDocument13 pagesTissue Renewal and Repair Regenerationمحسن حدوان عليخانNo ratings yet
- CellMol Thesis StatementsDocument7 pagesCellMol Thesis Statementsmirandajealyn28No ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue CulturesDocument5 pagesCell and Tissue CulturesJessa Nicole ReteracionNo ratings yet
- Developmental GeneticsDocument20 pagesDevelopmental GeneticsabhishekNo ratings yet
- Embryology of Inner Ear Recent TrendsDocument22 pagesEmbryology of Inner Ear Recent TrendsDr. T. BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Updated Data On VAWCDocument5 pagesUpdated Data On VAWCreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Program Prom 2024Document2 pagesProgram Prom 2024reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Teenage PregnancyDocument19 pagesTeenage Pregnancyreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Reading Material Grades 3 5Document5 pagesProperties of Matter Reading Material Grades 3 5reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- District Completion ReportDocument2 pagesDistrict Completion Reportreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- 8th Bañaria Clan ReunionDocument2 pages8th Bañaria Clan Reunionreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log TemplateDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Log Templatereynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Lecture Guide in Science 10Document5 pagesLecture Guide in Science 10reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- CH 19 The Reproductive System (GC)Document73 pagesCH 19 The Reproductive System (GC)reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic ClassificationDocument3 pagesTaxonomic Classificationreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Infrared Group5Document20 pagesInfrared Group5reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Lac 2024Document5 pagesLac 2024reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- AP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab FA23Document14 pagesAP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab FA23reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument3 pagesMatterreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate BoundariesDocument3 pagesTypes of Plate Boundariesreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Taco Casserole: Main CoursesDocument1 pageTaco Casserole: Main CoursesJennyNo ratings yet
- Fire DynamicsDocument11 pagesFire DynamicsSelvakumar BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 00381 v2Document11 pagesBiology 11 00381 v2paolaNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance.Q2.Module 6Document3 pagesHomeroom Guidance.Q2.Module 6Marjorie TigoyNo ratings yet
- IEEE PES Aug 18 - Corrosion - TDGDocument66 pagesIEEE PES Aug 18 - Corrosion - TDGtekno foniNo ratings yet
- Physics Assessment 1Document8 pagesPhysics Assessment 1Nayyir Mumtasir Rahman 2323059047No ratings yet
- Software Development ProcessDocument16 pagesSoftware Development ProcessSri WulanNo ratings yet
- Sous Vide Time and Temperature Guide - ChefStepsDocument9 pagesSous Vide Time and Temperature Guide - ChefStepssalzedofranciscoNo ratings yet
- 10october2020 FriendsNewsDocument4 pages10october2020 FriendsNewspatloubarNo ratings yet
- Classification of Machinery and EquipmentDocument2 pagesClassification of Machinery and EquipmentAamir BasheerNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Thermodynamical RelationsDocument19 pagesMaxwell's Thermodynamical RelationssNo ratings yet
- Organizational Resilience Cranfieldresearch ExecutivesummaryDocument12 pagesOrganizational Resilience Cranfieldresearch ExecutivesummaryAhmar HayatNo ratings yet
- Designing A Lactose Crystallization Process Based On Dynamic Metastable LimitDocument13 pagesDesigning A Lactose Crystallization Process Based On Dynamic Metastable LimitGian VillafverteNo ratings yet
- Schooling and Aggregation of FishDocument12 pagesSchooling and Aggregation of FishMUHAMMAD HAIKAL0% (1)
- Steam Iron: MM 433: Manufacturing Processes SeminarDocument35 pagesSteam Iron: MM 433: Manufacturing Processes SeminarPrasoon MeenaNo ratings yet
- Cranfield University: Attempt All QuestionsDocument6 pagesCranfield University: Attempt All QuestionsFabio BosioNo ratings yet
- GAS FLOW MEASUREMENT - PPSXDocument47 pagesGAS FLOW MEASUREMENT - PPSXMasood Alam Farooqui100% (2)
- Front Elevation: 760 M.M Above Roof SurfaceDocument1 pageFront Elevation: 760 M.M Above Roof SurfaceAbid AyubNo ratings yet
- AS - CBSE - X - Math - Practise - Standard 2Document11 pagesAS - CBSE - X - Math - Practise - Standard 2Kattirsitti Jeet Govind100% (1)
- Order of Elements and Primitive RootsDocument27 pagesOrder of Elements and Primitive RootsGlenn Michael PascuaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Tax PlanningDocument18 pagesCorporate Tax PlanningSANDEEP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Monthly Remittance Form: For Creditable Income Taxes Withheld (Expanded)Document1 pageMonthly Remittance Form: For Creditable Income Taxes Withheld (Expanded)Jonalyn BalerosNo ratings yet
- Red Hat EX294 Real Questions: This Study Resource Was Shared ViaDocument9 pagesRed Hat EX294 Real Questions: This Study Resource Was Shared ViaHammed Majouri100% (1)
- Financial Statement Analysis of Exide IndustriesDocument11 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Exide IndustriesSrihari KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document77 pagesChapter 15Jocelyn LuiNo ratings yet
- Ultrafiltration of Aqueous Solutions Containing DextranDocument11 pagesUltrafiltration of Aqueous Solutions Containing DextranJulio TovarNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Writing A DiaryDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Writing A DiaryJohn christopher Baria100% (2)
- Test Physics Chapter# 12,13,14 (2 Year) NameDocument1 pageTest Physics Chapter# 12,13,14 (2 Year) NameStay FocusedNo ratings yet
- GSRTC 24novDocument1 pageGSRTC 24novJitin NairNo ratings yet
- Art History Research PosterDocument10 pagesArt History Research Posterapi-259714129No ratings yet