Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STS Final Brochure 2
STS Final Brochure 2
Uploaded by
Virgelio Sayson AbesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STS Final Brochure 2
STS Final Brochure 2
Uploaded by
Virgelio Sayson AbesCopyright:
Available Formats
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living species on Earth,
including plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. While Earth’s
biodiversity is so rich that many species have yet to be C Climate is sometimes mistaken for weather. But climate
is different from weather because it is measured over a
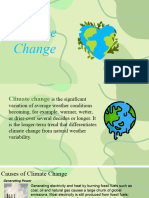
Causes of Climate Change
discovered, many species are being threatened with long period of time, whereas weather can change from
extinction due to human activities, putting the Earth’s L day to day, or from year to year. The climate of an area
includes seasonal temperature and rainfall averages, and
magnificent biodiversity at risk.
wind patterns. Different places have different climates.
I A desert, for example, is referred to as an arid climate
because little water falls, as rain or snow, during the 1. Generating power -Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels
causes a large chunk of global emissions.
M year. Other types of climate include tropical climates,
which are hot and humid, and temperate climates,
2. Manufacturing goods- Manufacturing and industry produce emissions,
mostly from burning fossil fuels to produce energy for making things like
cement, iron, steel, electronics, plastics, clothes, and other goods.
which have warm summers and cooler winters.
A
3. Cutting down forests -Cutting down forests to create farms or pastures, or
B Biodiversity refers to the variety of living species on
Climate change is the long-term alteration of
temperature and typical weather patterns in a 4.
for other reasons, causes emissions, since trees, when they are cut, release
the carbon they have been storing.
Using transportation- Most cars, trucks, ships, and planes run on fossil
T place. Climate change could refer to a particular fuels. That makes transportation a major contributor of greenhouse gases,
I Earth, including plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi.
While Earth’s biodiversity is so rich that many species
have yet to be discovered, many species are being
location or the planet as a whole. Climate change may
cause weather patterns to be less predictable. These
5.
especially carbon-dioxide emissions.
Producing food-Producing food causes emissions of carbon dioxide,
methane, and other greenhouse gases in various ways, including through
O threatened with extinction due to human activities, E unexpected weather patterns can make it difficult to
maintain and grow crops in regions that rely on farming
deforestation and clearing of land for agriculture and grazing, digestion by
cows and sheep, the production and use of fertilizers and manure for
growing crops, and the use of energy to run farm equipment or fishing
putting the Earth’s magnificent biodiversity at risk. because expected temperature and rainfall levels can no boats, usually with fossil fuels.
6. Powering buildings-Globally, residential and commercial buildings
longer be relied on. Climate change has also been
D
consume over half of all electricity. As they continue to draw on coal, oil,
connected with other damaging weather events such as and natural gas for heating and cooling, they emit significant quantities of
Biodiversity is a term used to describe the enormous greenhouse gas emissions
more frequent and more intense hurricanes, floods,
variety of life on Earth. It can be used more specifically
C downpours, and winter storms.
7. Consuming too much- Your home and use of power, how you move
I to refer to all of the species in one region around, what you eat and how much you throw away all contribute to
greenhouse gas emissions. So does the consumption of goods such as
or ecosystem. Biodiversity refers to every living thing,
H
clothing, electronics, and plastics.
including plants, bacteria, animals, and humans.
V Scientists have estimated that there are around 8.7
million species of plants and animals in existence.
However, only around 1.2 million species have been A
E identified and described so far, most of which are
insects. This means that millions of
N Effects of Climate Change
other organisms remain a complete mystery.
R Biodiversity is essentially everywhere, ubiquitous on
earth’s surface. G
All of the Earth’s species work together to survive and 1. Hotter temperatures- As greenhouse gas concentrations rise, so does
S maintain their ecosystems. For example, the grass in
pastures feeds cattle. Cattle then produce manure that
E 2.
the global surface temperature.
More severe storms- Destructive storms have become more intense
and more frequent in many regions.
3. Increased drought- Climate change is changing water availability,
I
returns nutrients to the soil, which helps to grow more
making it scarcer in more regions.
grass. This manure can also be used to fertilize cropland. 4. A warming, rising ocean- The ocean soaks up most of the heat from
Many species provide important benefits to humans, global warming. The rate at which the ocean is warming strongly
increased over the past two decades, across all depths of the ocean.
T including food, clothing, and medicine. 5.
6.
Loss of species -Climate change poses risks to the survival of species
on land and in the ocean.
Not enough food- Changes in the climate and increases in extreme
Y
weather events are among the reasons behind a global rise in hunger
and poor nutrition.
"Human cannot exist 7. More health risks- Climate change is the single biggest health threat
facing humanity.
without Biodiversity” 8. Poverty and displacement- Climate change increases the factors that
put and keep people in poverty.
You might also like
- Sherry B. Ortner - Is Female To Male As Nature Is Tu Culture (Rosaldo & Lamphere, 1974)Document21 pagesSherry B. Ortner - Is Female To Male As Nature Is Tu Culture (Rosaldo & Lamphere, 1974)P. A. F. JiménezNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources Notes PDFDocument34 pagesRenewable and Nonrenewable Resources Notes PDFMr. PoGoNo ratings yet
- Ebook-Learn Thermal Analysis With Altair OptiStructDocument114 pagesEbook-Learn Thermal Analysis With Altair OptiStructRAHUL K SEC 2020No ratings yet
- Help Your Kids With Science - Carol Vorderman PDFDocument258 pagesHelp Your Kids With Science - Carol Vorderman PDFcharu67% (6)
- 111 Environmental LawDocument116 pages111 Environmental Lawbhatt.net.inNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Power Calculation PDFDocument5 pagesWind Turbine Power Calculation PDFsmartman35No ratings yet
- Essentials of Radiologic ScienceDocument392 pagesEssentials of Radiologic ScienceKhalil Issaad50% (2)
- CpSci 101 - MODULE 4 - Lesson 1 Factors Affecting Crop ProductionDocument14 pagesCpSci 101 - MODULE 4 - Lesson 1 Factors Affecting Crop ProductionRegan Roldan RolaNo ratings yet
- Giraldo 2019 Political - Ecology - of - AgricultureDocument161 pagesGiraldo 2019 Political - Ecology - of - AgriculturecatalinaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Daily Lesson Plan Grade 10 ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Daily Lesson Plan Grade 10 ScienceYhan Brotamonte Boneo100% (3)
- Management Theories and ModelsDocument41 pagesManagement Theories and ModelsVirgelio Sayson Abes0% (1)
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate ChangeMary Francesca CobradoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesEnvironmental Science 14th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1yvonnesmithpfidmgwzek100% (29)
- Biology ScrapbookDocument12 pagesBiology ScrapbookNuraina ZafirahNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument8 pagesDeforestationgabrieleyannNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Act of 2009Document6 pagesClimate Change Act of 20092023201040No ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument20 pagesClimate ChangeSangguniang Bayan DamulogNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Science 15th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadBrett Bunch100% (20)
- Project Global Warming TimmyDocument4 pagesProject Global Warming TimmyRuthNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate ChangeAji Love SuropiaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change BrochureDocument2 pagesClimate Change BrochureNicole Natcher Gallego100% (1)
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1Sangishetti Ravi kumarNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Climate ChangeDocument13 pagesImpacts of Climate ChangetanangelsyvilleNo ratings yet
- Evs 4Document12 pagesEvs 4varunigoyal333No ratings yet
- Gee 302 - NotesDocument1 pageGee 302 - NotesJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Local Media6961030938989118801Document5 pagesLocal Media6961030938989118801Flordelyn CagadasNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Report G3Document11 pagesClimate Change Report G3Camille CaguinguinNo ratings yet
- Brochure DRRR Global WarmingDocument3 pagesBrochure DRRR Global Warmingalsisto.myreneNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledQUINTOS, JOVINCE U. G-12 HUMSS A GROUP 8No ratings yet
- Exploring The Climate ChangeDocument13 pagesExploring The Climate Changeananonymousgirl947No ratings yet
- Unit I EnvironmentDocument10 pagesUnit I Environmentatharvnetke9No ratings yet
- NSTP LawDocument5 pagesNSTP LawVee Jay LiquidoNo ratings yet
- E.S FinalsDocument17 pagesE.S FinalsPLATON GLADYS B.No ratings yet
- Worksheet Biosphere (KEY)Document7 pagesWorksheet Biosphere (KEY)rkvNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesWhat Is Climate ChangeArthur Medellin IINo ratings yet
- Lesson 19Document8 pagesLesson 19maureensolano63No ratings yet
- TRENDS AND ISSUES Part II - 3Document5 pagesTRENDS AND ISSUES Part II - 3ebrahim.jeanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Reading Questions Chapters 25-26Document2 pagesAP Biology Reading Questions Chapters 25-26Kamal AndrawisNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Easter RevisionDocument3 pagesWeek 7 Easter RevisionJenny ChalmersNo ratings yet
- Theory EnviornmentDocument132 pagesTheory EnviornmentAnu Sandeep AggrawalNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Human Activities That Endanger An EcosystemDocument7 pages9.1 Human Activities That Endanger An EcosystemMuhamad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Causes of Global Warming-1Document9 pagesCauses of Global Warming-1Salim Mohammed0% (1)
- Em Unit-1Document10 pagesEm Unit-1Hemant Kumar AhirwarNo ratings yet
- TYPES:1.solar Energy 2.wind e 3hydropower e 5.biomass:: Economic Value Oil Natural GasDocument6 pagesTYPES:1.solar Energy 2.wind e 3hydropower e 5.biomass:: Economic Value Oil Natural GasswatiNo ratings yet
- Your Paragraph TextDocument10 pagesYour Paragraph Textgji6299No ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate Change: - Kritika FY Sanskrit HonoursDocument16 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate Change: - Kritika FY Sanskrit Honourskritika kashyapNo ratings yet
- Environment and DevelopmentDocument84 pagesEnvironment and DevelopmentSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Votar FmsDocument79 pagesVotar Fmssebastian francoNo ratings yet
- Raport EU 2019-Poluare SolDocument60 pagesRaport EU 2019-Poluare SolIulian Adrian SorcaruNo ratings yet
- Faces of Poverty Effects of ErosionDocument5 pagesFaces of Poverty Effects of ErosionKeeven MacapanasNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: Allig, Raisa Binalay, Raizel Magno, Aileen Piocos, AlexisDocument13 pagesClimate Change: Allig, Raisa Binalay, Raizel Magno, Aileen Piocos, AlexisAlexis PiocosNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesLiving in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manualkhuongdiamond6h5100% (24)
- Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesLiving in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFFredMurphybgzr100% (15)
- NotesDocument5 pagesNotesRuqayya AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate Change BrochureDocument1 pageWhat Is Climate Change BrochureLadyArwen Sasota VentilacionNo ratings yet
- Hydro Assign 1Document8 pagesHydro Assign 1AHR NICOLE PANGILINANNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledJeralyn MacarealNo ratings yet
- Soils, Land: and WaterDocument16 pagesSoils, Land: and WaterChristian Eduardo Valencia AlbitresNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Is A Change in The Statistical Distribution What Makes The Climate Change?Document4 pagesClimate Change Is A Change in The Statistical Distribution What Makes The Climate Change?Khriestal BalatbatNo ratings yet
- How To Change It?: What Is Climate Change?Document1 pageHow To Change It?: What Is Climate Change?Zoja WeisováNo ratings yet
- Fires, Ecological Effects Of: William BondDocument9 pagesFires, Ecological Effects Of: William BondAzido Laurentino Salimo CoteNo ratings yet
- A-Biotic FactorsDocument24 pagesA-Biotic Factorsإخلاص الغامديNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual DownloadTina Morgan100% (19)
- FinalDocument2 pagesFinalNayeema khanNo ratings yet
- 1940 - F23 - L20 - Climate Change - 2Document35 pages1940 - F23 - L20 - Climate Change - 2ashwingupta88077No ratings yet
- Hi 2docxDocument2 pagesHi 2docxkaustubh guptaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument5 pagesGlobal WarmingTulika RajeshNo ratings yet
- TareaDocument7 pagesTareaCarlos Alberto Ramírez RestrepoNo ratings yet
- 1.-PrinciplesofManagement 01 IntroductiontoManagementDocument33 pages1.-PrinciplesofManagement 01 IntroductiontoManagementVirgelio Sayson AbesNo ratings yet
- Employment, Labor, Inflation, and PovertyDocument35 pagesEmployment, Labor, Inflation, and PovertyVirgelio Sayson AbesNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Reporting HBODocument37 pagesGroup 1 Reporting HBOVirgelio Sayson AbesNo ratings yet
- Planning: Principles of Organization and ManagementDocument35 pagesPlanning: Principles of Organization and ManagementVirgelio Sayson AbesNo ratings yet
- Organizing: Principles of Management and OrganizationDocument27 pagesOrganizing: Principles of Management and OrganizationVirgelio Sayson AbesNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Stones and RocksDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Stones and RocksfelipeNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Activities DLPDocument24 pagesReinforcement Activities DLPaidarahim0205No ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction Explained by The Wave and Particle Nature of LightDocument3 pagesReflection and Refraction Explained by The Wave and Particle Nature of LightRubin RubinNo ratings yet
- 2a-18 Phase Change MaterialDocument14 pages2a-18 Phase Change MaterialMaheshNo ratings yet
- Design of An Automatic Transfer Switch For Households Solar PV SystemDocument13 pagesDesign of An Automatic Transfer Switch For Households Solar PV Systemoguche emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Page of Paper Trick-4-ScienceDocument2 pagesPage of Paper Trick-4-ScienceKirti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Soil MechanicsDocument38 pagesSoil MechanicsAnsh Kushwaha50% (2)
- June 2010 (v3) QP - Paper 2 CIE Physics IGCSEDocument24 pagesJune 2010 (v3) QP - Paper 2 CIE Physics IGCSEύπατίαNo ratings yet
- Geography Past PapersDocument9 pagesGeography Past PapersTaimur KhanNo ratings yet
- Dictionary ScienceDocument19 pagesDictionary ScienceVALERIE RODRÍGUEZNo ratings yet
- Begun and Held in Metro Manila, On Monday, The Twenty-Fourth Day of July, Two Thousand SeventeenDocument12 pagesBegun and Held in Metro Manila, On Monday, The Twenty-Fourth Day of July, Two Thousand SeventeenCZARINA ANN CASTRONo ratings yet
- Question 966541Document4 pagesQuestion 966541gauravgambhirsonowalNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Word Basics ModelDocument4 pagesExercise 1 Word Basics ModelBRAIS HIDALGO RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics 3.3 SeasonsDocument11 pagesGCSE Physics 3.3 Seasonsameerul_hazeeqNo ratings yet
- Global Environmental Change (Perubahan Persekitaran Global) AID2003Document36 pagesGlobal Environmental Change (Perubahan Persekitaran Global) AID2003Almiezero GraschiazngNo ratings yet
- Global Warming (Word Formation)Document2 pagesGlobal Warming (Word Formation)EvaNo ratings yet
- Cogeneration in IndiaDocument22 pagesCogeneration in Indiaashwini_kumar19840% (1)
- Yes-O Calendar of Annual Proposed Activities (Capa) S.Y. 2022-2023Document1 pageYes-O Calendar of Annual Proposed Activities (Capa) S.Y. 2022-2023Dhenniz FlorezNo ratings yet
- Blackbody RadiationDocument23 pagesBlackbody RadiationkowletNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Quarter 4 - Module 6 Lunar EclipseDocument5 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 4 - Module 6 Lunar Eclipsevincent baltazarNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: Utilization As A Heat Pump: Mr. A. M. Vibhute, Prof. S.M.Shaikh, Prof. A. M. PatilDocument5 pagesGeothermal Energy: Utilization As A Heat Pump: Mr. A. M. Vibhute, Prof. S.M.Shaikh, Prof. A. M. PatilSongül BayındırNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic SustentationDocument6 pagesSymbiotic SustentationMj ShobanaNo ratings yet