Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO Lab 6
Uploaded by
Antonio WilloughbyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO Lab 6
Uploaded by
Antonio WilloughbyCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME: Antonio Willoughby
DATE: January 15, 2023
LAB #: 6
TITLE: PLANT TISSUES
AIM: To draw, label and annotate low power plan drawing and high-power detailed drawing of
Dicot Root using light microscope
APPARATUS/MATERIALS: Light Microscope, prepared slides of dicotyledonous root, pencil,
ruler, plain paper.
METHOD:
1. Prepared slides of a dicotyledonous root were obtained.
2. A light microscope was set up.
3. The objective was made sure to be at the lowest magnification.
4. A slide was positioned on the stage and focused at low power.
5. A plan-drawing was made showing the distribution of tissues.
6. The objective was switched to high power (x40) and the slide was focused.
7. Different tissue types were observed and identified.
8. A high-power drawing of a section across the organ, 3 to 4 cells in width, was made to show
representative cells of each tissue type.
BACKGROUND INFORMATION:
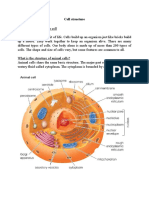
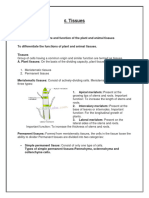
A tissue encompasses a group of similar cells that have a defined function within an organism. The four
main types of tissues found in both plants and animals include epithelial, connective, muscular, and
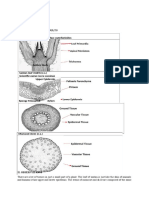
nervous.The dicotyledonous root is composed of the epidermis, cortex, endodermis, and xylem
tissues.The cells that make up these tissues have specialized functions. For example, the cells in the
epidermis are tightly packed to provide a protective barrier, while the cells in the cortex are loosely
packed to store food. The tightly packed cells in the endodermis regulate the flow of water and minerals,
and the cells in the xylem transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.The dicotyledonous root is
considered an organ because it is composed of various tissues that work together to fulfill a specific
function. In this instance, the function is to absorb water and nutrients from the soil and convey it to the
rest of the plant.
OBSERVATION/RESULTS:
You might also like
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- General Biology 1 As v1.0Document19 pagesGeneral Biology 1 As v1.0John Rex100% (4)
- Lab 6 Tissue Answers PDFDocument9 pagesLab 6 Tissue Answers PDFJameson Ephisson Ferguson Forson100% (3)
- Group1 Week11 LaboratoryActivity TissuesDocument9 pagesGroup1 Week11 LaboratoryActivity TissuesErika Mae CastroNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Life Sciences Workbook 2021 3Document49 pagesGrade 10 Life Sciences Workbook 2021 3mpilwentlephiwokuhleNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Histology Bios E1b 2016cDocument13 pagesLab1 Histology Bios E1b 2016cwekrjbhweiuNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument6 pagesGeneral BiologykazuchiNo ratings yet
- Observation of Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue: Unit 3Document5 pagesObservation of Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue: Unit 3Wiyah AlbannaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pengamatan Mikroskopis, 210109512012 Muh Irgi Bahqiawan P.Document18 pagesLaporan Pengamatan Mikroskopis, 210109512012 Muh Irgi Bahqiawan P.Mhmd IrgiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Cells and Tissues: Exercise: Short & Long QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Cells and Tissues: Exercise: Short & Long QuestionsSardar Mohsin Bin NazirNo ratings yet
- Complete Report of Basic Biology "Microscopic Observation": Ratification PageDocument30 pagesComplete Report of Basic Biology "Microscopic Observation": Ratification PageNisa AndiniNo ratings yet
- Microscope UseDocument7 pagesMicroscope UsebegNo ratings yet
- Science FinalDocument96 pagesScience FinalChitransh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1-2.4.3 Cell DiversityDocument8 pages2.4.1-2.4.3 Cell Diversity13593678No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Animal Tissues & CellsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Animal Tissues & CellsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Histo CompilationDocument217 pagesHisto CompilationNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Annissa Pacaldo - Experiment On Cell TissuesDocument7 pagesAnnissa Pacaldo - Experiment On Cell TissuesAnnissa PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TissuesDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Tissuesh8631259No ratings yet
- Class9, Plant and Animal TissuesDocument4 pagesClass9, Plant and Animal Tissuessachdevashaurya08No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 1 Plant and Animal CellsDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Cellseasylearning83No ratings yet
- Andrea BioDocument4 pagesAndrea BioAlexander Fabros SolivenNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesPia CincoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Activity Sheets Answers KeyDocument6 pagesGroup 4 Activity Sheets Answers KeyClaire Angelie RuayaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab 1Document2 pagesBiology Lab 1shylaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Cell Tissues - Catli, Justin LorenzDocument7 pagesExperiment Cell Tissues - Catli, Justin LorenzAnnissa PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document5 pagesExperiment 5Gavrielle DelacruzNo ratings yet
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocument11 pages642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueL Sri Madhi100% (1)
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocument16 pages3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellAllyson CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Philoid-In)Document8 pagesChapter 10 (Philoid-In)Shrey BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Drawing of A Root Dicot Under A Light MicroscopeDocument3 pagesLab 6 Drawing of A Root Dicot Under A Light MicroscopeAshley LewisNo ratings yet
- Bio Presentation Week 2.1Document53 pagesBio Presentation Week 2.1NormanNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Lesson PlanDocument4 pages9.2 Lesson PlanG Krishna VamsiNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemDocument5 pagesLab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemPaulNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Plant Tissues: Biology Sb015 Lab E-ReportDocument5 pagesExperiment 2: Plant Tissues: Biology Sb015 Lab E-ReportRANIA TEONI BINTI TEO KO SIONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Organization in Living ThingsDocument29 pagesOrganization in Living ThingsAvni PuriNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Lesson PlanDocument4 pages9.2 Lesson PlanG Krishna VamsiNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument6 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocument7 pagesActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cell Possible ActivitiesDocument21 pagesCell Possible ActivitiesPrincess JacintoNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument6 pagesTissues NotesYashvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCell Structure & Function ObjectivesNathan NkNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument12 pagesTissueschandankrdumkaNo ratings yet
- Biology Special Notes (Question & Answer Format) - 2Document180 pagesBiology Special Notes (Question & Answer Format) - 2Agola SimonNo ratings yet
- Tissue Notes 9Document7 pagesTissue Notes 9Priyad MundadaNo ratings yet
- Biology Essays 5Document67 pagesBiology Essays 5maingialex03No ratings yet
- Loquire Labsheet ACTIVITY NO.4Document3 pagesLoquire Labsheet ACTIVITY NO.4Mary Criscebel Kyla LoquireNo ratings yet
- Introduction EpitheliumDocument75 pagesIntroduction EpitheliumzaryyshahidNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument45 pagesAnatomyMB Loterte100% (1)
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- MODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsDocument94 pagesMODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsZenaNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument11 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument31 pagesZoologymatinaj974No ratings yet
- Activity No. 6: Tissues, Glands and MembranesDocument3 pagesActivity No. 6: Tissues, Glands and MembranesAlexander DacumosNo ratings yet
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- PDF 20221214 190246 0000Document11 pagesPDF 20221214 190246 0000Hiba ZiziNo ratings yet
- Cell Lesson NotesDocument8 pagesCell Lesson NotesNikshita KNo ratings yet
- Lec 1-2Document7 pagesLec 1-2Monenus KedirNo ratings yet
- WBS Med Club ProposalDocument3 pagesWBS Med Club ProposalAntonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- BIO Lab 5Document10 pagesBIO Lab 5Antonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- Papers 1 and 2Document20 pagesPapers 1 and 2Antonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- WBS Stakeholders' Bulletin - 9 Jan 2023 - 230108 - 184832Document3 pagesWBS Stakeholders' Bulletin - 9 Jan 2023 - 230108 - 184832Antonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- High School Rankings 2023Document12 pagesHigh School Rankings 2023Antonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Part 1Document90 pagesPhotosynthesis - Part 1Antonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet