Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment2 Open Book examPDF
Uploaded by
Abdul Hanan Sheikh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesopen book exam on numerical computing
Original Title
Assignment2_open_book_examPDF
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentopen book exam on numerical computing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesAssignment2 Open Book examPDF
Uploaded by
Abdul Hanan Sheikhopen book exam on numerical computing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
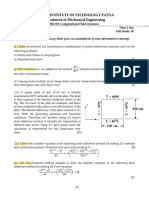
Assignment 2( Open Book Examination)
Submit solution before 12:00 Noon, March 21, 2021.
All questions are in context of linear system 𝐴𝑢 = 𝑏. Iterative methods means
basic iterative methods for linear systems, which are Gauss Jacobi, Gauss Seidel
and Successive Over Relaxation methods.
1. Show that the iteration given by
𝑢𝑘+1 = 𝑢𝑘 + 𝑒 𝑘 , for 𝑘 = 0,1,2, … Eq. (1)
can be written in the form
𝑢𝑘+1 = 𝑇𝑢𝑘 + 𝑐, Eq. (2)
−1 𝑘 −1 𝑘 𝑘 𝑘
where 𝑇 = 𝐼 − 𝑃 𝐴, 𝑒 = 𝑃 𝑟 and 𝑟 = 𝑏 − 𝐴𝑢 .
2. Write Gauss Jacobi and Gauss Seidel iterations in form given in Eq. (2).
Identify 𝑃 in each method.
3. Consider the iterative method given in Eq. (2) for solving any linear system
𝐴𝑢 = 𝑏. Choosing initial guess 𝑢0 = 𝟎, prove that solution after 𝑘 𝑡ℎ
iterations will be 𝑢𝑘 = (𝐼 − 𝑇 𝑘 )𝐴−1 𝑏.
4. Use four iterations of Gauss Jacobi and Gauss Seidel on problem
10𝑥 + 𝑦 = 1
𝑥 + 10𝑦 = 10,
while choosing (0,0) as initial guess. Write results in format given under
Table (1). Exact answer is (0,1).
5. Repeat Q. 4 for problem
𝑥+𝑦 =2
4𝑥 + 5𝑦 = 9.
Write results in a separate table of same format. Exact answer is (1,1).
6. Compare convergence speed of Gauss Jacobi for two problem given in Q. 4
and Q. 5.
7. Compare convergence speed of Gauss Seidel for two problem given in Q. 4
and Q. 5.
8. Identify 𝑇 of Eq. (2) from Q. 4 and Q. 5 for each Gauss Jacobi and Gauss
Seidel method. Then find eigenvalues of such matrices 𝑇.
Jacobi Sol Jacobi Seidel Sol Seidel
𝒖𝒌 Convergence 𝒖𝒌 Convergence
Q. 4
Rate Rate
𝒆 /𝒆𝒌−𝟏
𝒌
𝒆 /𝒆𝒌−𝟏
𝒌
k=0 (0,0) N.A (0,0) N.A
k=1
k=2
k=3
k=4
Jacobi Sol Jacobi Seidel Sol Seidel
𝒖𝒌 Convergence 𝒖𝒌 Convergence
Q. 5
Rate Rate
𝒆 /𝒆𝒌−𝟏
𝒌
𝒆 /𝒆𝒌−𝟏
𝒌
k=0 (0,0) N.A (0,0) N.A
k=1
k=2
k=3
k=4
You might also like
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsFrom EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNo ratings yet
- Iterative Techniques in Matrix Algebra Jacobi & Gauss-Seidel Iterative Techniques IIDocument107 pagesIterative Techniques in Matrix Algebra Jacobi & Gauss-Seidel Iterative Techniques IIsofianina05No ratings yet
- Iterative Techniques in Matrix AlgebraDocument107 pagesIterative Techniques in Matrix AlgebraJuan JuanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods PPT AYUSH MISHRADocument11 pagesNumerical Methods PPT AYUSH MISHRAsubscribe.us100No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document1 pageAssignment 3DarshanPandeNo ratings yet
- Ma214 S23 Part06Document30 pagesMa214 S23 Part06Vishal PuriNo ratings yet
- Iterative Techniques in Matrix Algebra PDFDocument57 pagesIterative Techniques in Matrix Algebra PDFWezda KingstonNo ratings yet
- Jacobi Method PDFDocument57 pagesJacobi Method PDFRajinder Sanwal100% (1)
- More On Iterative Solution Of: Successive Over-RelaxationDocument2 pagesMore On Iterative Solution Of: Successive Over-RelaxationSerkan SancakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Saransh DixitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 03Document2 pagesTutorial 03Anne Shanone Chloe LIM KINNo ratings yet
- First Semester B. SC Degree Examination Calculus and Linear AlgebraDocument4 pagesFirst Semester B. SC Degree Examination Calculus and Linear Algebragoutami SunthankarNo ratings yet
- Vjekoslav Kovač - Past Proposals For High School and College Studentmath Competitions PDFDocument41 pagesVjekoslav Kovač - Past Proposals For High School and College Studentmath Competitions PDFMohammadNo ratings yet
- Yu Kuzmina 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1847 012031Document6 pagesYu Kuzmina 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1847 012031louis donyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Vector Spaces - Part 2Document31 pagesChapter 4 Vector Spaces - Part 2Aqeel AbqariNo ratings yet
- EE101A Engineering Electromagnetics Fall 2017Document4 pagesEE101A Engineering Electromagnetics Fall 2017krazykrnxboyNo ratings yet
- Jacobi and Gauss SeidelDocument9 pagesJacobi and Gauss SeidelJero CaliguiranNo ratings yet
- VL2023240501285 Da02Document1 pageVL2023240501285 Da02devvijay635No ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations: JacobiDocument25 pagesPartial Differential Equations: Jacobiđại phạmNo ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations: JacobiDocument25 pagesPartial Differential Equations: Jacobiđại phạmNo ratings yet
- Tut Sheets Unit-1Document4 pagesTut Sheets Unit-1akashNo ratings yet
- ME 261 Numerical Analysis: System of Linear EquationsDocument15 pagesME 261 Numerical Analysis: System of Linear EquationsTahmeed HossainNo ratings yet
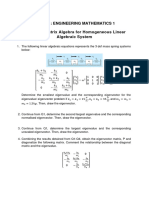
- Tutorial 7 Matrix Algebra For Homogeneous Linear Algebraic SystemDocument3 pagesTutorial 7 Matrix Algebra For Homogeneous Linear Algebraic System徐子裕No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS TUTORIAL S1 P1 & P2-QpZ9UADocument2 pagesMATHEMATICS TUTORIAL S1 P1 & P2-QpZ9UAshashankshekharkashyap1No ratings yet
- 2 MATS11 Set 1Document3 pages2 MATS11 Set 1PRABHANJANNo ratings yet
- UE23MA141A - Unit 3 and 4 CWDocument9 pagesUE23MA141A - Unit 3 and 4 CWiammusharraf11No ratings yet
- 22MATS11 MQP SolvedDocument70 pages22MATS11 MQP SolvedADITYA BhedasurNo ratings yet
- 2 MATS11 Set 1Document3 pages2 MATS11 Set 1Rajathos OsNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2Document11 pagesCircuits 2kyle reyesNo ratings yet
- InteractivosDocument13 pagesInteractivosdiegoferro90No ratings yet
- 7.14.13 Kepler's Problem: 7.14 Problems 395Document5 pages7.14.13 Kepler's Problem: 7.14 Problems 395sergio lopezNo ratings yet
- MATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 6 Vector Calculus L2/L3 (Fall 2019)Document40 pagesMATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 6 Vector Calculus L2/L3 (Fall 2019)物理系小薯No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Solving Ordinary Differential Equations System: Profa. Liliane - em RevisãoDocument30 pagesChapter 6 - Solving Ordinary Differential Equations System: Profa. Liliane - em RevisãoMônica CarneiroNo ratings yet
- CE 27 11617 Practice Problems For Second LEDocument2 pagesCE 27 11617 Practice Problems For Second LECJNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Random NumbersDocument19 pagesLaplace and Random NumbersJohnson LiuNo ratings yet
- Matlab Software For Iterative Methods and Algorithms To Solve A Linear SystemDocument6 pagesMatlab Software For Iterative Methods and Algorithms To Solve A Linear SystemerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Some Asymptotic Properties of The Spectrum of The Jacobi EnsembleDocument20 pagesSome Asymptotic Properties of The Spectrum of The Jacobi Ensemblemassoud_pNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Solved PDFDocument6 pagesHomework 2 Solved PDFFrancisco QuingaNo ratings yet
- 11 Ec Uuuuuu UuuuuuDocument5 pages11 Ec Uuuuuu UuuuuuvaleriaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Stokes Flow Problem Using Biharmonic Equation Formulation and Multiquadrics MethodDocument6 pagesSolution of Stokes Flow Problem Using Biharmonic Equation Formulation and Multiquadrics MethodSalimNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Iterative Methods: C 2006 Gilbert StrangDocument7 pages6.2 Iterative Methods: C 2006 Gilbert StrangEfstathios SiampisNo ratings yet
- 09-25 Problem SetDocument2 pages09-25 Problem SetsonjabottlelawNo ratings yet
- DDP - Questions - JEE ADVANCED - Matrices & DeterminantsDocument4 pagesDDP - Questions - JEE ADVANCED - Matrices & DeterminantsBhoomika Singh SirohiNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 BDocument40 pagesSheet 4 BAbdulRahmanNo ratings yet
- Model Question Pape 2 M3Document4 pagesModel Question Pape 2 M3chaitra malipatilNo ratings yet
- 22MA21A - Cluster A - Model PaperDocument3 pages22MA21A - Cluster A - Model PaperSunay B SNo ratings yet
- Ma 2264 NM Eee Q.BDocument26 pagesMa 2264 NM Eee Q.BpmagrawalNo ratings yet
- Solution Key Comprehensive Question PaperDocument8 pagesSolution Key Comprehensive Question PaperADITYA K RNo ratings yet
- 2024 TEST1 MemoDocument6 pages2024 TEST1 Memochidochashe monalisaNo ratings yet
- Tut Sheets - Unit-1 - 21MA11ADocument4 pagesTut Sheets - Unit-1 - 21MA11AhitheshNo ratings yet
- Principles of Least SquaresDocument44 pagesPrinciples of Least SquaresdrdahmanNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Patna Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Patna Department of Mechanical EngineeringPranav BajajNo ratings yet
- Numerical Algebra, Control and Optimization Volume 1, Number 1, March 2011Document20 pagesNumerical Algebra, Control and Optimization Volume 1, Number 1, March 2011Costica PetreNo ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizDocument58 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson QuizMuneerNo ratings yet
- II PUC Board APR - 2022 (Mathematics) - Answer KeyDocument19 pagesII PUC Board APR - 2022 (Mathematics) - Answer KeyJhenkarNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics RevisionDocument58 pagesApplied Mathematics Revisionshamma0721No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledmuhammad adnielNo ratings yet
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)From EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)No ratings yet
- Fog Computing in Internet of ThingsDocument7 pagesFog Computing in Internet of ThingsAbdul Hanan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Current Govt Sector Jobs (13!12!2021)Document21 pagesCurrent Govt Sector Jobs (13!12!2021)Abdul Hanan SheikhNo ratings yet
- An Impact of The Small and Large Grid Sizes On Differential EquationsDocument6 pagesAn Impact of The Small and Large Grid Sizes On Differential EquationsAbdul Hanan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Assignment Applications Two Variable FunctionsDocument1 pageAssignment Applications Two Variable FunctionsAbdul Hanan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Inequalities ListDocument4 pagesInequalities ListjoshuabaleteNo ratings yet
- Rational Algebraic ExpressionsDocument6 pagesRational Algebraic ExpressionsAnnie DosmanosNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computing For Computer Scientists (PDFDrive - Com) (092-120)Document29 pagesQuantum Computing For Computer Scientists (PDFDrive - Com) (092-120)Johann Steven BogotàNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 3Document5 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 3John Nino DoligolNo ratings yet
- Math 202 HW 8 AsolsDocument4 pagesMath 202 HW 8 AsolsMorvaridYiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Universal Set and Complement of A SetDocument42 pages1.2 Universal Set and Complement of A SetNE RONo ratings yet
- Workbook Unit 4 1º ESODocument30 pagesWorkbook Unit 4 1º ESOFrancisco Botella JuanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometric IdentitiesEye ShieldNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics-ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Mathematics-ReviewerElla Benedictine C. EboNo ratings yet
- Transformation: 2.kinematicsDocument79 pagesTransformation: 2.kinematicsHayleysus ShmelashNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Matrix AlgebraDocument20 pages1.introduction To Matrix AlgebraRiko Chy MakNo ratings yet
- Mathematics II-matricesDocument52 pagesMathematics II-matricesBagus RizalNo ratings yet
- Limits of FunctionDocument20 pagesLimits of FunctionRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- IFP - Mathematics and Statistics PDFDocument346 pagesIFP - Mathematics and Statistics PDFNguyen Châu AnhNo ratings yet
- GRE - Basic Algebra RefresherDocument4 pagesGRE - Basic Algebra RefresherRakesh_Ranjan_3304100% (2)
- Badawi F 2 PDFDocument160 pagesBadawi F 2 PDFMuhammad SadnoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 9: One-to-One Functions: Learning Outcome (S) : Lesson OutlineDocument6 pagesLESSON 9: One-to-One Functions: Learning Outcome (S) : Lesson OutlineCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Ch-2, Class-11 Mathematics - Relations & Functions (Ver-1) PPT - OpenClassDocument63 pagesCh-2, Class-11 Mathematics - Relations & Functions (Ver-1) PPT - OpenClassBimlendu Jha100% (1)
- Assignment 12 AnsDocument10 pagesAssignment 12 AnsAnuska DeyNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 5) LimitsDocument20 pages(Chapter 5) LimitsdenixngNo ratings yet
- 4037 s20 QP 21 PDFDocument16 pages4037 s20 QP 21 PDFJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- NP Bali Unit 1Document87 pagesNP Bali Unit 1Aman Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Little Flower School: GorakhpurDocument4 pagesLittle Flower School: GorakhpurMritunjayNo ratings yet
- Florida End-Of-Course Assessments Algebra 1, Geometry, Biology 1 AND U.S. HistoryDocument81 pagesFlorida End-Of-Course Assessments Algebra 1, Geometry, Biology 1 AND U.S. HistoryChris JosephNo ratings yet
- Curve Fitting For Gtu AmeeDocument20 pagesCurve Fitting For Gtu AmeeMohsin AnsariNo ratings yet
- Model Q Paper - V Cbse PatternDocument6 pagesModel Q Paper - V Cbse PatternMUKESH DHALNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus 11 Textbook CH 4Document65 pagesPre-Calculus 11 Textbook CH 4iamparam31No ratings yet
- Simultaneous (Linear) Equations - Summary Notes: X y X y y X y X y X y X yDocument3 pagesSimultaneous (Linear) Equations - Summary Notes: X y X y y X y X y X y X yklkhguNo ratings yet
- SIM Quadratic Equation by SquareDocument40 pagesSIM Quadratic Equation by SquareRochelle AdlaoNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document5 pagesHW 4dzs6w3No ratings yet