Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra Tasks and Answers
Algebra Tasks and Answers
Uploaded by
Ludmila DorojanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Tasks and Answers
Algebra Tasks and Answers
Uploaded by
Ludmila DorojanCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Accounting For Decision Making
Nescol
Task 1
Calculate mathematically what the optimum mix is using the following
information:
Product A requires 4 kgs of material
Product B requires 2 kgs of material
Limiting factor 14,750 kgs of material.
Product A requires 3 hours of labour
Product B requires 8 hours of labour
Limiting factor 20,000 hours of labour.
Task 2
Calculate mathematically what the optimum mix is using the following
information:
Product A requires 3 kgs of material
Product B requires 4 kgs of material
Limiting factor 50,000 kgs of material.
Product A requires 6 hours of labour
Product B requires 2 hours of labour
Limiting factor 40,000 hours of labour.
Task 3
Calculate mathematically what the optimum mix is using the following
information:
Product A requires 6 kgs of material
Product B requires 8 kgs of material
Limiting factor 35,000 kgs of material.
Product A requires 2 hours of labour
Product B requires 7 hours of labour
Limiting factor 25,000 hours of labour
Task 4
Calculate mathematically what the optimum mix is using the following
information:
Product A requires 12 kgs of material
Product B requires 4 kgs of material
Limiting factor 59,950 kgs of material.
Product A requires 4 hours of labour
Product B requires 5 hours of labour
Limiting factor 22,000 hours of labour
Management Accounting For Decision Making
Nescol
Task 1
4A + 2B = 40,000 (Line 1)
3A + 8B = 20,000 (Line 2)
Multiply line 1 by 4 gives;
16A + 8B = 160,000
Less Line 2 3A + 8B = 20,000
13A = 140,000
A= 140,000/13
A = 10,769
Substitute this into line 1, 4A + 2B = 40,000
gives
(4 x 10769) + 2B = 40,000
43076 + 2B = 40,000
2B = 40,000 – 43076
2B= -3076
B = -3076/2
B = -1538
Optimum mix is to produce 10,769 units of A and -1,538 units of B
Task 2
3A + 4B = 50,000 (Line 1)
6A + 2B = 40,000 (Line 2)
Multiply line 1 by 2 gives;
6A + 8B = 100,000
Less Line 2 6A + 2B = 40,000
6B = 60,000
B = 60,000/6
B = 10,000
Substitute this into line 1, 3A + 4B = 50,000
gives
3A + (4 x 10000) = 50,000
3A + 40,000 = 50,000
3A = 50,000 - 40000
3A = 10,000
A= 10,000/3
A = 3333
Optimum mix is to produce 3333 units of A and 10,000 units of B
Management Accounting For Decision Making
Nescol
Task 3
6A + 8B = 35,000 (Line 1)
2A + 7B = 25,000 (Line 2)
Multiply line 2 by 3 gives;
6A + 21B = 75,000
Less Line 1 6A + 8B = 35,000
13B = 40,000
B = 40000/13
B = 3076 (remember to round down here)
Substitute this into line 1, 6A + 8B = 35,000
gives
6A + (8 x 3076) = 35,000
6A + 24,608 = 35,000
6A = 35,000 – 24,608
6A = 10,392
A= 10,392/6
A = 1,732
Optimum mix is to produce 1,732 units of A and 3076 units of B
Task 4
12A + 4B = 59,950 (Line 1)
4A + 5B = 22,000 (Line 2)
Multiply line 2 by 3 gives;
12A + 15B = 66,000
Less Line 1 12A + 4B = 59,950
11B = 6050
B = 6050/11
B = 550
Substitute this into line 2, 4A + 5B = 22,000
gives
4A + (5 x 550) = 22,000
4A + 2750 = 22,000
4A = 22,000 - 2750
4A = 19,250
A= 19,250/4
A = 4812
Optimum mix is to produce 4812 units of A and 550 units of B
You might also like
- Balgownie LTD Solution 2021 - V2Document12 pagesBalgownie LTD Solution 2021 - V2Ludmila DorojanNo ratings yet
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Using R Introductory STDocument33 pagesSolutions Manual Using R Introductory STGeorgiana RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Jannes Klaas - Machine Learning For Finance - The Practical Guide To Using Data-Driven Algorithms in Banking, Insurance, and Investments-Packt Publishing (2019)Document456 pagesJannes Klaas - Machine Learning For Finance - The Practical Guide To Using Data-Driven Algorithms in Banking, Insurance, and Investments-Packt Publishing (2019)Dipen Pandya100% (1)
- Statics AnDocument13 pagesStatics AnIsaac Davy100% (1)
- Dependent MotionDocument6 pagesDependent MotionAmeya1823No ratings yet
- SBEC-NMEC Unit1Document26 pagesSBEC-NMEC Unit1Austin RebbyNo ratings yet
- Estática 1Document22 pagesEstática 1Eduardo FloresNo ratings yet
- Clase Semana 03BDocument11 pagesClase Semana 03BNicolas RojasNo ratings yet
- Stranalysis SD METHODDocument78 pagesStranalysis SD METHODNaveen RevannaNo ratings yet
- 10 19Document11 pages10 19AlcyrNo ratings yet
- Lecture Four Quadratic and Cubic Functions Lecture Outline: C BX Ax yDocument8 pagesLecture Four Quadratic and Cubic Functions Lecture Outline: C BX Ax yVincent OmondiNo ratings yet
- Cube of A Sum or Difference of TwoDocument24 pagesCube of A Sum or Difference of TwoAngela CatainaNo ratings yet
- West Bengal CL 10 Exam QN Paper Solutions March 2016Document30 pagesWest Bengal CL 10 Exam QN Paper Solutions March 2016nutandas525No ratings yet
- New ProjDocument30 pagesNew ProjHueyNo ratings yet
- Array Operations: Deleting Row or ColumnDocument7 pagesArray Operations: Deleting Row or ColumnabasNo ratings yet
- CE Maths 2009 Paper1 (ANS)Document5 pagesCE Maths 2009 Paper1 (ANS)Mok Sze Nga100% (1)
- Latihan 4sa 22/10/2008Document8 pagesLatihan 4sa 22/10/2008Khairul Risor LegacyNo ratings yet
- Kerala SSLC 2023 Maths Answer Key by GIGI SirDocument7 pagesKerala SSLC 2023 Maths Answer Key by GIGI SirD R VoyageNo ratings yet
- Caltech in Engg Mechanics FinalDocument153 pagesCaltech in Engg Mechanics FinalblehNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 SignalDocument5 pagesLab 1 SignaljavedshamzaNo ratings yet
- Statics: SolutionDocument32 pagesStatics: SolutionNecille Garcia SalinasNo ratings yet
- SSC CHSL 4 March 2018 Evening Shift by CrackuDocument37 pagesSSC CHSL 4 March 2018 Evening Shift by CrackuucivbhchccihoblNo ratings yet
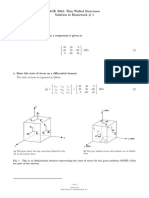
- AOE 3024: Thin Walled Structures Solution To Homework # 1: XX Xy XZ Yx Yy Yz ZX Zy ZZDocument7 pagesAOE 3024: Thin Walled Structures Solution To Homework # 1: XX Xy XZ Yx Yy Yz ZX Zy ZZsydavali.shaikNo ratings yet
- Arrays and MatricesDocument34 pagesArrays and Matrices87vr772j64No ratings yet
- Semana4 RM CpuDocument8 pagesSemana4 RM CpuJENRRY JAMER RODRIGO VITONNo ratings yet
- Selected Solutions - 13Document5 pagesSelected Solutions - 13moonisqNo ratings yet
- Matrices and DeterminantsDocument14 pagesMatrices and Determinantsgautam9699No ratings yet
- Matlab CH 1 SolutionDocument24 pagesMatlab CH 1 SolutionHammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Sadler-Specialist Mathematics-Unit 3A-Chapter 2-SolutionsDocument17 pagesSadler-Specialist Mathematics-Unit 3A-Chapter 2-SolutionsRolou15100% (1)
- Problem 2Document5 pagesProblem 2Andres Mauricio Moreno LunaNo ratings yet
- Calculation S, R Lab 3Document19 pagesCalculation S, R Lab 3nnurulhassanNo ratings yet
- AME 204 HW Answers Not in The ListDocument3 pagesAME 204 HW Answers Not in The ListnjkianNo ratings yet
- PHP BK Fu BNDocument24 pagesPHP BK Fu BNkripaelizabethofficialNo ratings yet
- Procedure For AnalysisDocument19 pagesProcedure For AnalysisGLENN BRYAN FELIXNo ratings yet
- Y4 Topic1Document8 pagesY4 Topic1danu07No ratings yet
- Zero GDocument4 pagesZero Gapi-244386271No ratings yet
- 00 Calculator Techniques 01Document2 pages00 Calculator Techniques 01vincelord92% (12)
- PROBLEM 2.38: SolutionDocument6 pagesPROBLEM 2.38: SolutionGonçalo CruzeiroNo ratings yet
- 28 36Document10 pages28 36Carlos Moran CepedaNo ratings yet
- Tugas MK Persamaan Diferensial, Semester 2 Jts FT UnnesDocument1 pageTugas MK Persamaan Diferensial, Semester 2 Jts FT UnnesDhini Nur LestariNo ratings yet
- Section 6 - Combined Stresses PDFDocument133 pagesSection 6 - Combined Stresses PDFGlënnLibönTäbiölö100% (1)
- PlymouthUniversity MathsandStats Matrix MultiplicationDocument37 pagesPlymouthUniversity MathsandStats Matrix MultiplicationGood DeedsNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan - 2: Operasi MatriksDocument14 pagesPertemuan - 2: Operasi Matrikswww_ikhsan_nulkhairNo ratings yet
- 114 119Document9 pages114 119Carlos Moran CepedaNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument57 pagesSlope Deflection MethodpratyushaNo ratings yet
- Kxu Chap02 SolutionDocument6 pagesKxu Chap02 SolutionAkmal GondalNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures Solving Indeterminates Members (Civil Engineering)Document10 pagesTheory of Structures Solving Indeterminates Members (Civil Engineering)Louisgospel EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SolutionsDocument7 pagesChapter 5 SolutionsUsaidMandviaNo ratings yet
- Alternatif Trase I Dan II GDJRDocument6 pagesAlternatif Trase I Dan II GDJRDYAH WAHYU ARIANING TYASNo ratings yet
- Solved SSC CHSL 4 March 2018 Evening Shift Paper With Solutions PDFDocument40 pagesSolved SSC CHSL 4 March 2018 Evening Shift Paper With Solutions PDFSumit VermaNo ratings yet
- 4038CEM Engineering Mathematics I 4010CEM Mathematics For Physics and EngineeringDocument20 pages4038CEM Engineering Mathematics I 4010CEM Mathematics For Physics and EngineeringMicah TamunoNo ratings yet
- Metodo de CrossDocument20 pagesMetodo de CrossJoseph Hensy Sierra YayaNo ratings yet
- Field of SpecializationDocument240 pagesField of SpecializationMildred Ewag50% (2)
- Resolução Do Capítulo 4 - Equilíbrio de Corpos Rígidos PDFDocument231 pagesResolução Do Capítulo 4 - Equilíbrio de Corpos Rígidos PDFMalik PassosNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Answer KeyDocument2 pagesMathematics Answer KeyMadhav PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Ce1013 09Document42 pagesCe1013 09Durga SharmaNo ratings yet
- Arrays & MaticesDocument16 pagesArrays & MaticesazlanNo ratings yet
- Two Steel Bars AbDocument10 pagesTwo Steel Bars AbextianlangNo ratings yet
- HW3 SolutionDocument5 pagesHW3 SolutiondcasaliNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Math Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandMath Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Short CoursesDocument1 pageShort CoursesLudmila DorojanNo ratings yet
- Careers ExhibitionDocument1 pageCareers ExhibitionLudmila DorojanNo ratings yet
- Essay 1Document6 pagesEssay 1Ludmila DorojanNo ratings yet
- Assessment ReportDocument7 pagesAssessment ReportLudmila DorojanNo ratings yet
- MEMODocument6 pagesMEMOLudmila DorojanNo ratings yet
- Report On Analysis of Financial Statement and Recommendations For Lexicon LTDDocument1 pageReport On Analysis of Financial Statement and Recommendations For Lexicon LTDLudmila DorojanNo ratings yet
- 11 Cbse Practical FileDocument22 pages11 Cbse Practical FilePriyanshNo ratings yet
- Simplex MethodDocument3 pagesSimplex MethodShreyNo ratings yet
- CG FileDocument41 pagesCG FileRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Package Mlogit': R Topics DocumentedDocument41 pagesPackage Mlogit': R Topics DocumentedNoureddineLahouelNo ratings yet
- DAA - QuestionBank - CSITDocument6 pagesDAA - QuestionBank - CSITMamata swainNo ratings yet
- Syed Ammal Engineering College: Department of Computer Science and EngineeringDocument34 pagesSyed Ammal Engineering College: Department of Computer Science and EngineeringGuru BalanNo ratings yet
- Dspa 17ec751 M2Document27 pagesDspa 17ec751 M2digital loveNo ratings yet
- Unit - V &VI Graph TheoryDocument55 pagesUnit - V &VI Graph Theorynaman jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Slide 2 - Computer Number SystemDocument104 pagesSlide 2 - Computer Number SystemSanskriti LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Radix SortDocument10 pagesRadix SortC-1962 Anwesha BaruaNo ratings yet
- REQPA1Document8 pagesREQPA1nimra sohailNo ratings yet
- Arduino Cheat SheetDocument1 pageArduino Cheat SheetHarshad MalikNo ratings yet
- Frmed2 IEC61850ConfigurationDocument624 pagesFrmed2 IEC61850ConfigurationsaurabhNo ratings yet
- Dr. Faris LlwaahDocument25 pagesDr. Faris LlwaahHussein ShakirNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument3 pagesData StructuresHarshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Important QuestionsDocument14 pagesChapter 9 Important QuestionsBolt FFNo ratings yet
- INT404 Artificial Intelligence: Lecture ZeroDocument28 pagesINT404 Artificial Intelligence: Lecture ZeroAmit SevenNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On AES 128 BIT AND AES 256 BITDocument5 pagesA Comparative Study On AES 128 BIT AND AES 256 BITAlexander Hurtado CubillosNo ratings yet
- Ma Chan Myae Thu (For Third Seminar)Document47 pagesMa Chan Myae Thu (For Third Seminar)Dr. Myat Mon KyawNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Functions and Methods in C# For UnityDocument34 pages2.4 Functions and Methods in C# For Unitythìn đinh xuânNo ratings yet
- BCA245 - Web Technology LaboratoryDocument46 pagesBCA245 - Web Technology LaboratoryPradnya KambleNo ratings yet
- Programming in C++Document20 pagesProgramming in C++Shabad KaurNo ratings yet
- Intro To Artificial Intelligence Assignment 1: Search AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesIntro To Artificial Intelligence Assignment 1: Search AlgorithmsJay SinghNo ratings yet
- Indices Challenge CardsDocument2 pagesIndices Challenge CardsGielyn NuqueNo ratings yet
- BookDocument352 pagesBookCon Sói BaNo ratings yet
- U4 JavaDocument16 pagesU4 Javavenkat mNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION PSUC End Term ExamDocument9 pagesSOLUTION PSUC End Term ExamL PircyNo ratings yet
- MSC ParameterDocument4 pagesMSC Parametershuvankartns100% (1)