Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notation List
Uploaded by
Emrah ozkanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notation List
Uploaded by
Emrah ozkanCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendices
Notation list
There are various systems of notation in use, and the IB has chosen to adopt a system based on the
recommendations of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This notation is used in the
examination papers for this course without explanation. If forms of notation other than those listed in this
guide are used on a particular examination paper, they are defined within the question in which they
appear.
Because students are required to recognize, though not necessarily use, IB notation in examinations, it is
recommended that teachers introduce students to this notation at the earliest opportunity. Students are
not allowed access to information about this notation in the examinations.
Students must always use correct mathematical notation, not calculator notation.
SL and HL
ℕ the set of positive integers and zero, {0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
ℤ the set of integers, {0, ± 1, ± 2, ± 3, ...}
ℤ+ the set of positive integers, {1, 2, 3, ...}
ℚ the set of rational numbers
ℚ+ the set of positive rational numbers, {x | x ∈ ℚ, x > 0}
ℝ the set of real numbers
ℝ+ the set of positive real numbers, {x | x ∈ ℝ, x > 0}
{x1, x2, . . .} the set with elements x1, x2, ...
n(A) the number of elements in the finite set A
{x | } the set of all x such that
∈ is an element of
∉ is not an element of
∅ the empty (null) set
U the universal set
∪ union
∩ intersection
A′ the complement of the set A
1
a 2, a 1
a to the power , square root of a (if a ≥ 0 then a ≥ 0)
2
1
a n, n a 1
a to the power of , nth root of a (if a ≥ 0 then n a ≥ 0)
n
1 a to the power of −n, reciprocal of an
a−n =
an
x x for x ≥ 0, x ∈ ℝ
the modulus or absolute value of x, that is {
−x for x < 0, x ∈ ℝ
Mathematics: analysis and approaches guide 89
Notation list
≡ identity
≈ is approximately equal to
> is greater than
≥ is greater than or equal to
< is less than
≤ is less than or equal to
≯ is not greater than
≮ is not less than
⇒ implies
⇔ implies and is implied by
un the nth term of a sequence or series
d the common difference of an arithmetic sequence
r the common ratio of a geometric sequence
Sn the sum of the first n terms of a sequence, u1 + u2 + ... + un
S∞ the sum to infinity of a sequence, u1 + u2 + ...
n u1 + u2 + . . . + un
∑ ui
i=1
n! n(n − 1)(n − 2) . . . 3 × 2 × 1
nCr n!
r!(n − r)!
∆ the discriminant of a quadratic equation, Δ = b2 − 4ac
f (x) the image of x under the function f
f −1 the inverse function of the function f
f ∘g the composite function of f and g
dy the derivative of y with respect to x
dx
f ′(x) the derivative of f (x) with respect to x
d2y the second derivative of y with respect to x
dx2
f ′′(x) the second derivative of f (x) with respect to x
∫ ydx the indefinite integral of y with respect to x
∫
b the definite integral of y with respect to x between the limits
ydx
a x = a and x = b
ex the exponential function of x
loga x the logarithm to the base a of x
lnx the natural logarithm of x, loge x
sin, cos, tan the circular functions
A(x, y) the point A in the plane with Cartesian coordinates x and y
90 Mathematics: analysis and approaches guide
Notation list
[AB] the line segment with end points A and B
AB the length of [AB]
(AB) the line containing points A and B
^ the angle at A
A
^ the angle between [CA] and [AB]
CAB
∆ ABC the triangle whose vertices are A, B and C
P(A) probability of event A
P(A′) probability of the event “not A”
P(A | B) probability of the event A given B
x1, x2, ... observations
f 1, f 2, ... frequencies with which the observations x1, x2, ... occur
E(X) the expected value of the random variable X
μ population mean
σ2 population variance
σ population standard deviation
x̄ the sample mean of a set {x1, x2, ..., xn} of observations
P(X = x) the probability that the random variable X takes the value x
B(n, p) binomial distribution with parameters n and p
N(μ, σ 2) normal distribution with mean μ and variance σ 2
X~B(n, p) the random variable X has a binomial distribution with
parameters n and p
X~N(μ, σ 2) the random variable X has a normal distribution with mean μ
and variance σ 2
r Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient
AHL only
ℂ the set of complex numbers, {a + bi | a , b ∈ ℝ}
i −1 where i2 = − 1
z a complex number
z* the complex conjugate of z
z the modulus of z
argz the argument of z
Rez the real part of z
Imz the imaginary part of z
cisθ cosθ + isinθ
eiθ Euler/exponential form of a complex number
Mathematics: analysis and approaches guide 91
Notation list
n
Pr n!
(n − r)!
⇐ is implied by
[a, b] the closed interval a ≤ x ≤ b
]a, b[ the open interval a < x < b
f :A → B f is a function under which each element of a set A has an
image in set B.
lim f (x) the limit of f (x) as x tends to a
x→a
dny the nth derivative of y with respect to x
dxn
f (n)(x) the nth derivative of f (x) with respect to x
arcsin, sin−1 the inverse circular functions
−1
arccos, cos
arctan, tan−1
cosec, sec, cot the reciprocal circular functions
v the vector v
→
AB
the vector represented in magnitude and direction by the
directed line segment from A to B
a →
the position vector OA
i, j, k unit vectors in the directions of the Cartesian coordinate axes
a the magnitude of a
→ →
AB the magnitude of AB
v·w the scalar product of v and w
v×w the vector product of v and w
f (x) the probability density function of the continuous random
variable X
Var(X) the variance of the random variable X
92 Mathematics: analysis and approaches guide
You might also like
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970From EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SL Notation List PDFDocument5 pagesMathematics SL Notation List PDFFerdinand AguilaNo ratings yet
- Solving ODE Using SeriesDocument44 pagesSolving ODE Using SeriesMaulana ArifNo ratings yet
- Maths NotationDocument5 pagesMaths Notationang_chang_1No ratings yet
- Maths DictionaryDocument25 pagesMaths DictionaryManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument10 pagesPolynomialsAli Al-HamadiNo ratings yet
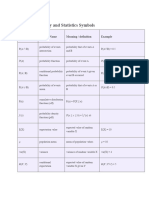
- Statistics SymbolsDocument7 pagesStatistics Symbolsapi-3857574100% (4)
- NotationDocument4 pagesNotationDavid Tersoo IorngurumNo ratings yet
- Solution of Differential EquationsDocument34 pagesSolution of Differential Equationspja752No ratings yet
- StatsymbolsDocument8 pagesStatsymbolsNiranjan KaushikNo ratings yet
- Solution of Differential EquationsDocument34 pagesSolution of Differential EquationsSaddie SoulaNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument11 pagesFormulae Sheetthyanh.vuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1ching chauNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Mathematical BackgroundDocument132 pagesAppendix: Mathematical BackgroundDominik SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FormsDocument5 pagesQuadratic FormsMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument34 pagesUnit IIIapi-352822682No ratings yet
- Metode Deret PDFDocument80 pagesMetode Deret PDFDio D SaputraNo ratings yet
- cs530 12 Notes PDFDocument188 pagescs530 12 Notes PDFyohanes sinagaNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 Module1 Anova 1Document10 pagesLecture3 Module1 Anova 1Deep DmNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 PolyomialsDocument2 pagesChapter2 PolyomialsveereshNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesQuiz 2 Formula SheetdawnNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Formulas and ConceptDocument33 pagesMaths Class X Formulas and ConceptgehygyhyNo ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics Formulas and TablesDocument10 pagesIntroductory Statistics Formulas and TablesP KaurNo ratings yet
- Math PDFDocument65 pagesMath PDFadfm680No ratings yet
- Reverse Order Triangular, Trapezoidal and Pentagonal Fuzzy NumbersDocument11 pagesReverse Order Triangular, Trapezoidal and Pentagonal Fuzzy NumbersShaymaa YasNo ratings yet
- 408 NoteDocument57 pages408 Notevaibhavsingh4594No ratings yet
- The 77th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2016Document1 pageThe 77th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2016Ramneek SinghNo ratings yet
- The 77th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2016Document1 pageThe 77th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2016Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Symbols TableDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Symbols TableChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghNo ratings yet
- Calculus III: Practice Problems: Some Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument2 pagesCalculus III: Practice Problems: Some Trigonometric IdentitiesRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Notes On P-Adic NumberDocument13 pagesNotes On P-Adic NumberdmtriNo ratings yet
- DF FormulaeDocument7 pagesDF FormulaeBentojaNo ratings yet
- Curve FittingDocument17 pagesCurve FittingGunawan RisdiyantoNo ratings yet
- s08 Basic AdvcalcDocument2 pagess08 Basic AdvcalcshottyslingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 - Miscellaneous Preliminaries: EE 520: Topics - Compressed Sensing Linear Algebra ReviewDocument18 pagesChapter 0 - Miscellaneous Preliminaries: EE 520: Topics - Compressed Sensing Linear Algebra ReviewmohanNo ratings yet
- ExpectationDocument19 pagesExpectationShah FahadNo ratings yet
- Taylor SeriesDocument6 pagesTaylor SeriesJunior Briones VelizNo ratings yet
- 5 Prob - OverviewDocument10 pages5 Prob - OverviewRinnapat LertsakkongkulNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 Revision Notes On Statistics and Probability - Free PDFDocument7 pagesJEE Main 2023 Revision Notes On Statistics and Probability - Free PDFBfjncfNo ratings yet
- Formula PDFDocument7 pagesFormula PDFPramit BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-2857Document8 pagesChapter 3-2857Kevin FontynNo ratings yet
- Steepest Descent Is An Iterative Method For Solving Sparse Systems of Linear EquaDocument5 pagesSteepest Descent Is An Iterative Method For Solving Sparse Systems of Linear Equakushal bosuNo ratings yet
- EN530.678 Nonlinear Control and Planning in Robotics Lecture 1: Matrix Algebra Basics January 27, 2020Document4 pagesEN530.678 Nonlinear Control and Planning in Robotics Lecture 1: Matrix Algebra Basics January 27, 2020SAYED JAVED ALI SHAHNo ratings yet
- Statistical symbols & probability symbols (μ,σ,..Document2 pagesStatistical symbols & probability symbols (μ,σ,..John Bond100% (1)
- List of Probability and Statistics SymbolsDocument6 pagesList of Probability and Statistics SymbolsDave VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Ma207 TSCDocument38 pagesMa207 TSCAnonymous SomeoneNo ratings yet
- Qm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dDocument13 pagesQm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dJan BorowskiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linear Algebra V: 1 Eigenvalue and EigenvectorDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Linear Algebra V: 1 Eigenvalue and EigenvectorRoghieh Mahdavi HajiNo ratings yet
- SAT Math To Know in One Page PDFDocument3 pagesSAT Math To Know in One Page PDFhaya khaledNo ratings yet
- 4 - Power Series - Practice ProblemDocument9 pages4 - Power Series - Practice Problemzxeexz zxcecxzNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Test SeriesDocument48 pagesReal Analysis Test Series21mma019 Anmol PatialNo ratings yet
- Mathematic NotationDocument9 pagesMathematic NotationmdeziderioNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Formula BookletDocument24 pagesClass 10 Formula Bookletmayukhsarkar100No ratings yet
- Quiz 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 SolutionTumpa MitraNo ratings yet
- Random Variable Modified PDFDocument19 pagesRandom Variable Modified PDFIMdad HaqueNo ratings yet
- Series Solutions of Second Order Linear EquationsDocument22 pagesSeries Solutions of Second Order Linear EquationsMohNajiNo ratings yet
- Lagrange IntepolationDocument10 pagesLagrange IntepolationceanilNo ratings yet
- Ma2aPracLectures 10-12Document16 pagesMa2aPracLectures 10-12Muhammed YagciogluNo ratings yet
- Category 2 Paper 1Document11 pagesCategory 2 Paper 1Emrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Category Topics 1 Online Math ChallengeDocument1 pageCategory Topics 1 Online Math ChallengeEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Prior Learning TopicsDocument2 pagesPrior Learning TopicsHorstNo ratings yet
- Algebra Refresher 1Document2 pagesAlgebra Refresher 1Emrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Command TermsDocument2 pagesCommand TermsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 9709 Y20-22 SW ProbStats1 v1Document17 pages9709 Y20-22 SW ProbStats1 v1Emrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 07 Logarithmic and Exponential FunctionsDocument13 pages07 Logarithmic and Exponential FunctionsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 04 Indices and SurdsDocument19 pages04 Indices and SurdsCandleNo ratings yet
- 04 Indices and SurdsDocument19 pages04 Indices and SurdsCandleNo ratings yet
- 02 FunctionsDocument21 pages02 Functionsben0706No ratings yet
- 10 TrigonometryDocument35 pages10 TrigonometryWeteachNo ratings yet
- 03 Quadratic FunctionsDocument18 pages03 Quadratic FunctionsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 06 Simultaneous EquationsDocument6 pages06 Simultaneous EquationsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 05 Factors of PolynomialsDocument13 pages05 Factors of PolynomialsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- A Discipline-Specific Approach To The History of US Science EducationDocument7 pagesA Discipline-Specific Approach To The History of US Science EducationEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Indices: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsDocument1 pageIndices: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
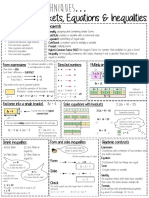
- Brackets, Equations & Inequalities: Substitute To Check Your Answer. This Could Be Negative or A Fraction or DecimalDocument1 pageBrackets, Equations & Inequalities: Substitute To Check Your Answer. This Could Be Negative or A Fraction or DecimalEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
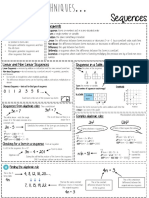
- Sequences: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsDocument1 pageSequences: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- A Discipline-Specific Approach To The History of US Science EducationDocument7 pagesA Discipline-Specific Approach To The History of US Science EducationEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Fractions & Percentages: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsDocument1 pageFractions & Percentages: Keywords What Do I Need To Be Able To Do? @whisto - MathsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
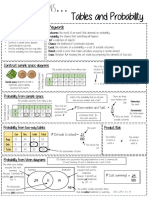
- 06 Tables and ProbabilityDocument1 page06 Tables and ProbabilityEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 02 Multiplicative ChangeDocument1 page02 Multiplicative ChangeEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Working in The Cartesian Plane: KeywordsDocument1 pageWorking in The Cartesian Plane: KeywordsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 03 Multiplying and Dividing FractionsDocument1 page03 Multiplying and Dividing FractionsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Representing Data: Keywords @whisto - MathsDocument1 pageRepresenting Data: Keywords @whisto - MathsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 01 RatioDocument1 page01 RatioEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 0580 m18 Ms 42Document7 pages0580 m18 Ms 42Resti Siti SalehaNo ratings yet
- SM-G900F Esquematico Completo Anibal Garcia IrepairDocument2 pagesSM-G900F Esquematico Completo Anibal Garcia Irepairfix marketNo ratings yet
- Rotc Reviewer FinalsDocument11 pagesRotc Reviewer FinalsAngel Atienza100% (1)
- DRUGPDocument371 pagesDRUGPPolarogramaNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson MF7600 Technician Workshop ManualDocument798 pagesMassey Ferguson MF7600 Technician Workshop Manualgavcin100% (5)
- Hazop Close Out ReportDocument6 pagesHazop Close Out ReportKailash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Market Challengers StrategiesDocument19 pagesMarket Challengers Strategiestobbob007100% (20)
- Helical Coil FlowDocument4 pagesHelical Coil FlowAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- NCP81205Document1 pageNCP81205Tom TomNo ratings yet
- 064 DIR - Launching Whipping Creme & Skimmed Milk Di Channel Horeka (Subdist Masuya)Document3 pages064 DIR - Launching Whipping Creme & Skimmed Milk Di Channel Horeka (Subdist Masuya)indra sapta PrahardikaNo ratings yet
- José Guadalupe PosadaDocument19 pagesJosé Guadalupe PosadaJudy Baca100% (1)
- Trend in Agricultural ProductivityDocument1 pageTrend in Agricultural ProductivityGiaNo ratings yet
- 3S Why SandhyavandanDocument49 pages3S Why SandhyavandanvivektonapiNo ratings yet
- Maven MCQDocument55 pagesMaven MCQANNAPUREDDY ANIL KUMAR REDDY CSENo ratings yet
- Classical School of Thought: Ms. Salma ShaheenDocument62 pagesClassical School of Thought: Ms. Salma ShaheenQasim Ali100% (1)
- KPI's Troubleshooting GuideDocument27 pagesKPI's Troubleshooting GuideMohamed SayedNo ratings yet
- GCG Damri SurabayaDocument11 pagesGCG Damri SurabayaEndang SusilawatiNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash Flows AnswerDocument3 pagesStatement of Cash Flows Answeranber mohammadNo ratings yet
- Components of Vectors Prepared By: Victor Rea OribeDocument17 pagesComponents of Vectors Prepared By: Victor Rea OribeGerone Tolentino AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal DraftDocument1 pageProject Proposal DraftCarl Axel M. FajardoNo ratings yet
- APS PresentationDocument32 pagesAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackNo ratings yet
- m07srt Lesson KmarlinkDocument3 pagesm07srt Lesson Kmarlinkapi-515106812No ratings yet
- Permutation, Combination & ProbabilityDocument9 pagesPermutation, Combination & ProbabilityVicky RatheeNo ratings yet
- Esp Kelompok 2Document19 pagesEsp Kelompok 2Taufiq DiNo ratings yet
- Shaft DeflectionDocument15 pagesShaft Deflectionfreek_jamesNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaDocument15 pagesThe Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaAasvogel Felodese Carnivora64% (14)
- H I Ôn Thi Aptis & Vstep - Tài Liệu - Anna MaiDocument4 pagesH I Ôn Thi Aptis & Vstep - Tài Liệu - Anna Maihanh.mt2022No ratings yet
- Part 1. Question 1-7. Complete The Notes Below. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER For Each AnswerDocument13 pagesPart 1. Question 1-7. Complete The Notes Below. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER For Each Answerahmad amdaNo ratings yet
- Exam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)Document10 pagesExam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)SadishNo ratings yet
- Construction of Perimeter Fence of BFP NHQ PDFDocument133 pagesConstruction of Perimeter Fence of BFP NHQ PDFYalla ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- (IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630Document43 pages(IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630VictoriaNo ratings yet