Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculus - Calc 1000
Uploaded by
fun dipOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculus - Calc 1000
Uploaded by
fun dipCopyright:
Available Formats
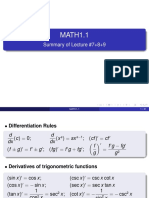
● Related Rates
(1) Quantities: express quantity as function “V(x)” and it’s rate (dv/dt)
(2) Relate: Formula with both quantities: (e.g. geometric: V(x) = π * r * h(x)
(3) Derive: Derivative of both sides (e.g Turns “V(x) =” into “dv/dx =”
(4) Plug, solve: Plug given information, and isolate for unknown rate
● L'hospital's Rule
(1) Attempt to plug in limit
(2) Indeterminate form: limit = 0/0 or inf/inf
(3) Derivative of top+bottom: (f’(x) = 0, top = 0, bottom = 0)
(4) Re-evaluate limit: if not, try again
- Might not go anywhere or gets more complicated
- Try to recognize a pattern. Usually can lead to constant/infinity which is 0
● Maximum And Minimum
(1) 1st derivative: (if not given)
(2) Critical points: (f’(x) = 0, top = 0, bottom = 0)
(3) Evaluate at f(x): plug crit. Points into f(x)
(4) Sign: = positive: incr, negative: decr.
● Concavity, Inflection Points, 2nd Derivative Test
(1) 2nd derivative: (if not given)
(2) Inflection points: (when f’’(x) = 0)
(3) Evaluate in intervals: [x<2]: (+): conc. up, min. - (-): conc. down, max
- Can be counted by seeing how many times the sign changes
● Optimization
(1) Formulas: for box: surface area, and volume
(2) Solve for variable: (when f’’(x) = 0)
(3) Plug back into main formula: for single-variable expression
(4) Derive: take 1st derivative
(5) Optimize: finding absolute max/min, or solving for missing values
● Indefinite Integrals Or Antiderivatives
(1) Simplify: check if anything can be expanded or simplified
(2) Separate: terms +/- other terms can be separated
(3) Try to substitute: choose a function that will cause [udu]
(4) Try to partial: recognize a function that can be derived, and integrated
● Area Between Curves, Volume
(1) Determine top function: comparing result by plugging value on the interval
(2) Subtract definite integrals: ∫[b,a] f(x)dx - ∫[b,a] g(x)dx
(3) Finding volume: ∫[b,a] π([f(x)]2 - [g(x)]2) dx
You might also like
- Calculus Tutorial 1 - Differential CalculusDocument25 pagesCalculus Tutorial 1 - Differential CalculusDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -K100% (9)
- General Mathematics Reviewer!Document4 pagesGeneral Mathematics Reviewer!Jane Anonas100% (8)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Limits and Continuity PDFDocument107 pagesLimits and Continuity PDFAnonymous 0MTQ0BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Extrema and Double Integrals: Section 4.1: Extrema, Second Derivative TestDocument6 pagesChapter 4. Extrema and Double Integrals: Section 4.1: Extrema, Second Derivative TestStelios KondosNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On DifferentiationDocument12 pagesLecture Notes On DifferentiationMd Arif Ul Islam-KowshikNo ratings yet
- Maple: Derivatives and Critical Points: F F: X 3 (X 2-1)Document6 pagesMaple: Derivatives and Critical Points: F F: X 3 (X 2-1)rahayu rizki putriNo ratings yet
- Group 6: By: Mirador, Vien Quidez, Jessa Mae Rebota, Rene Joy Rebultan, Diane Rose Reyes, Lesly Ann Rivera, GracielDocument15 pagesGroup 6: By: Mirador, Vien Quidez, Jessa Mae Rebota, Rene Joy Rebultan, Diane Rose Reyes, Lesly Ann Rivera, GracielRene joy rebotaNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus Differentiation Increment Method BDocument14 pagesBasic Calculus Differentiation Increment Method Bsijeysanchez56No ratings yet
- Math CalculusDocument60 pagesMath Calculuserffan yusofNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2Document20 pagesCalculus 2Germain TrugnanNo ratings yet
- MTH308 and MTH308B Lab Assignment 6Document2 pagesMTH308 and MTH308B Lab Assignment 6SAURABH VISHWAKARMANo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument22 pagesIntegral CalculusARGHYA MANDALNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Function and Limits With Derivatives: Module OutlineDocument10 pagesIntroduction, Function and Limits With Derivatives: Module OutlineErn NievaNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus Differentiation Increment Method 4Document11 pagesBasic Calculus Differentiation Increment Method 4sijeysanchez56No ratings yet
- Heavy Duty Math Writing: 1 Utilizing Large DelimitersDocument9 pagesHeavy Duty Math Writing: 1 Utilizing Large DelimitersCurtis HelmsNo ratings yet
- Solve, Differential/Quadratic Differential, Integration, Maximum/Minimum Value, and CalculationsDocument16 pagesSolve, Differential/Quadratic Differential, Integration, Maximum/Minimum Value, and Calculationsathembo georgeNo ratings yet
- Homework5 Solution PDFDocument4 pagesHomework5 Solution PDFKensleyTsangNo ratings yet
- 1 Linearisation & DifferentialsDocument6 pages1 Linearisation & DifferentialsmrtfkhangNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear OptimizationDocument6 pagesNonlinear OptimizationKibria PrangonNo ratings yet
- Review MaterialsDocument33 pagesReview MaterialsLeonor Ines OberaNo ratings yet
- AddMathLesson (5th Form Term 1, Lesson 24 - The Derivative)Document6 pagesAddMathLesson (5th Form Term 1, Lesson 24 - The Derivative)The MathematicianNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Differentiation MATH161 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture Notes On Differentiation MATH161 PDFalchemistNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument7 pagesTutorialSelwyn Elijah RodelasNo ratings yet
- Numerical DifferentiationDocument2 pagesNumerical DifferentiationChang Jae LeeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document15 pagesPresentation 2Kushal BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Calculus For Business and EconomicsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Calculus For Business and EconomicsFaheem AslamNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 SpringstudyguideDocument5 pagesCalc 2 SpringstudyguideDefault AccountNo ratings yet
- Notes Day 18-22Document12 pagesNotes Day 18-22api-272815616No ratings yet
- MATH 115: Lecture XIV NotesDocument3 pagesMATH 115: Lecture XIV NotesDylan C. BeckNo ratings yet
- Lecture #1Document37 pagesLecture #1Mohamed ElsafanyNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONSDocument7 pagesFUNCTIONSLia Riobelle ParkNo ratings yet
- Derivative Tests SummaryDocument5 pagesDerivative Tests Summarydalmikhaila9No ratings yet
- June 29Document22 pagesJune 29charlotawalaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Theorem of CalculusDocument5 pagesThe Fundamental Theorem of CalculusDaiszyBarakaNo ratings yet
- Maxima and MinimaDocument3 pagesMaxima and Minimadellrubion011No ratings yet
- A) Graphs of Functions NotesDocument10 pagesA) Graphs of Functions NotesHaoyu WangNo ratings yet
- Global (Absolute) Extrema Point: Report TitleDocument14 pagesGlobal (Absolute) Extrema Point: Report TitleDaneal SofiNo ratings yet
- Limit RepoartDocument11 pagesLimit Repoartabdulsamadshwani67No ratings yet
- PortfolioDocument18 pagesPortfoliocharlotawalaNo ratings yet
- Best Method For Solving Quadratic InequalitiesDocument7 pagesBest Method For Solving Quadratic InequalitiesGoodmobo 123No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Maxima and Minima of Function of Two VariablesDocument29 pagesLecture 4 Maxima and Minima of Function of Two VariablesAlfez tintoiyaNo ratings yet
- Finite Differences: Aim of This SectionDocument10 pagesFinite Differences: Aim of This SectionMuhammad FatkhurroziNo ratings yet
- Discovering Derivative RulesDocument5 pagesDiscovering Derivative RulesRobert Talbert100% (1)
- Square Root Functions Domain, RangeDocument13 pagesSquare Root Functions Domain, Rangepaolo furioNo ratings yet
- Octav Dragoi - Lagrange MultipliersDocument5 pagesOctav Dragoi - Lagrange MultipliersOctav DragoiNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 8 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.1 To 4.4Document11 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 8 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.1 To 4.4Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome 4 - Ac 2 (Analytical Methods)Document4 pagesLearning Outcome 4 - Ac 2 (Analytical Methods)Chan Siew ChongNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB - Ultimate Guide Notes - KnowtDocument29 pagesAP Calculus AB - Ultimate Guide Notes - Knowtcondyerhaze1No ratings yet
- EdrawDocument6 pagesEdrawNedjlah PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Functions PDFDocument38 pagesFunctions PDFAathith SaiprasadNo ratings yet
- Differentiation of Algebraic and TranscendentalDocument7 pagesDifferentiation of Algebraic and TranscendentalCM AvenidoNo ratings yet
- Calculus, Probability, and Statistics Primers: Dave GoldsmanDocument104 pagesCalculus, Probability, and Statistics Primers: Dave Goldsmanbanned minerNo ratings yet
- Modified Section 01Document7 pagesModified Section 01Eric ShiNo ratings yet
- Onion AjsdkflajDocument11 pagesOnion AjsdkflajadelelelNo ratings yet
- Math (P) Refresher Lecture 1: FunctionsDocument9 pagesMath (P) Refresher Lecture 1: FunctionsKazaaeratoNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument9 pagesDifferentiationsalviano81No ratings yet
- Lecture 30Document13 pagesLecture 30The tricksterNo ratings yet
- Review of Calculus 1Document2 pagesReview of Calculus 1HT KangNo ratings yet