Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Quality
Food Quality
Uploaded by
Yến Nhi Lê0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesThe document discusses food quality management and the agri-food production chain. It notes that agri-food production transforms agricultural products into food and involves living organisms, restricted shelf-life, seasonality, and safety risks. Food quality management considers both the physical quality of food and quality management. It is complex due to the interactions between food and people and high quality requirements. Food quality is affected by multiple internal and external factors relating to consumers, production systems, supply chains, and business environments. Achieving food quality involves understanding these complex and dynamic systems.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses food quality management and the agri-food production chain. It notes that agri-food production transforms agricultural products into food and involves living organisms, restricted shelf-life, seasonality, and safety risks. Food quality management considers both the physical quality of food and quality management. It is complex due to the interactions between food and people and high quality requirements. Food quality is affected by multiple internal and external factors relating to consumers, production systems, supply chains, and business environments. Achieving food quality involves understanding these complex and dynamic systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesFood Quality
Food Quality
Uploaded by
Yến Nhi LêThe document discusses food quality management and the agri-food production chain. It notes that agri-food production transforms agricultural products into food and involves living organisms, restricted shelf-life, seasonality, and safety risks. Food quality management considers both the physical quality of food and quality management. It is complex due to the interactions between food and people and high quality requirements. Food quality is affected by multiple internal and external factors relating to consumers, production systems, supply chains, and business environments. Achieving food quality involves understanding these complex and dynamic systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Course contents: - living systems => differ from other product manufacturing chains
Main characteristics of agri-food production chain
- Introduction of Food quality management (FQM)
- Have restricted shelf-life, harvested seasonally
- Food quality
- Heterogeneous and large variability (10% is common)
- Quality management - Contain hidden safety risks (chemical contaminants or pathogens)
- Food quality management Other characteristics
- Complicated production chains
- Networks with many suppliers and customers
Lesson 1: Introduction of Food Quality Management - Unintentional and unwanted by-products
Date: 31/08/2023 - High turnover volumes but low-values products
1. Food quality management - Substantial environmental impact (packaging material, used product)
Food quality management = Food quality (physical aspects of quality) + Quality - Public interests and concerns (for ex, each country has different interests of
management (Managing people who realise FQ and apply FQ) eating habit because their work-life are different to each other, so a suitable food
Main challenges: that fit their schedule and interest will be more purchased. Banana is not a widely
- Complexity: because food is living things, not also contain nutrition value for consumed product in Vietnam but not in Korean)
human live but also contain living organism Importance of food quality
- Food – people interactions: people need food to live and food trend will People have had faced too many serious food scandal with major impact on human
change based on the demand of people, how people choose food will affect and animal health so the food quality is important. Some famous cases can be
the trend of food quality and environment mentioned: The Belgian dioxin affair in 1999; food fraud scandals; or baby milk powder
- High quality requirements: people always require the high quality of food contaminated with melamine in China.
products and food should be better and better Quality requirements:
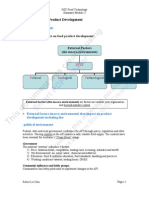
Characterisation of the agri-food production chain - Specific product-related aspects (safety, shelf-life and authenticity – where
The agri-food production chain: the food came from)
- the chain transforming agricultural products into food products for use, - Packaging issues (how convenience it is)
consumptions and emotional purposes.
- Broader societal concerns (social and ethical interest and sustainable Internal factors: those within the control of the business, such as:
constrains) - the products
- Modifications in demographic situations (ageing populations) - pricing
- Shifting social situations (more double incomes) - marketing and advertising
- Changing consumer behaviour and lifestyles (increased outdoor - level of food and service
consumption, changes in food preparation habits). Like the food can encourage people - financial resources of business.
to consume more plant-based food to save the environment External factors: those outside the control of business, such as
- Globalization of markets - climate
- politics
- social trends
- technological advances
- raw materials
- competition from other businesses.
Complexity of food quality management
Factors affecting the management of food quality
- Consumer characteristics
- Properties of food production system
- Features of agri-food supply chain
- The internal and external food business environment:
~~0~~
NOTE - Cannot infer the response of a combination of factors from the response of
Food quality and food safety issues are due to the combination of multiple causes each factor
embedding in different systems => So we cannot approach FQM issues from one disciplines, whereas the dynamic
and complex characteristics of both food production systems and the people
Ambiguity and Uncertainty inherent to the dynamic and complex character of food involved in this
and human systems involved in producing food quality.
Ambiguity is a situation in which the meaning of something is unclear or open
to multiple interpretations. This could occur, for example, when there are unclear or
conflicting regulations, or when there is a lack of scientific consensus on a particular
food safety issue.
Uncertainty is a situation in which there is incomplete or imperfect
information. This could occur, for example, when there is limited data on the
prevalence of a foodborne pathogen, or when the effectiveness of a particular food
safety control measure is not fully known.
The outcome of food quality management is not fully predictable, so food business
- do not achieve the intended results
- must reach predictive and guaranteed quality levels
- reduce a simpler system
- consider food quality a rather controllable processes
Complex system: systems that are part of continuously changing, self-organising,
interdependent and adaptive systems
- Multiple factors determine their behaviour and they are in a continuous state
of flux
You might also like
- 02 Concepts of Quality Control Quality Assurance and Food SafetyDocument18 pages02 Concepts of Quality Control Quality Assurance and Food SafetyGIRMA SELALE GELETANo ratings yet
- Incident Report and InvestigationDocument2 pagesIncident Report and InvestigationHerwin Syaid Ibramin HaminataNo ratings yet
- Food Product DevelopmentDocument21 pagesFood Product Developmentapi-409521281No ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Entrepreneurship Quarter 1Document14 pagesMODULE 2 Entrepreneurship Quarter 1Justine Teasacam78% (9)
- Qualitative and Quantitative Loss Assessment of Selected High Value Food Crops (Mango, Banana, Calamansi, Carrots, Cabbage, Onion)Document15 pagesQualitative and Quantitative Loss Assessment of Selected High Value Food Crops (Mango, Banana, Calamansi, Carrots, Cabbage, Onion)UPLB Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research and ExtensionNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Food Product DevelopmentDocument16 pagesModule 3 - Food Product Developmentrbtlch1n88% (8)
- Food Handler's Manual: InstructorFrom EverandFood Handler's Manual: InstructorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Food Traceability PPT 01Document25 pagesFood Traceability PPT 01Muddasir Ahmad Akhoon100% (2)
- Abme 103 LectureDocument12 pagesAbme 103 LectureAlexa CuevasNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Implement Good Manufacturing Practice ProcedureDocument7 pagesModule 5: Implement Good Manufacturing Practice ProcedureStevenNo ratings yet
- Thinking about the Future of Food Safety: A Foresight ReportFrom EverandThinking about the Future of Food Safety: A Foresight ReportNo ratings yet
- Food AgribusinessDocument20 pagesFood Agribusiness21B1308 Khairunnisa NoorhayatiNo ratings yet
- Food Plant Sanitation SylabusDocument4 pagesFood Plant Sanitation SylabusAnh TúNo ratings yet
- Food Tech NotesDocument37 pagesFood Tech NotesAxqen kmorjNo ratings yet
- Full Syllabus Notes Food Technology 61a9835cd9361Document26 pagesFull Syllabus Notes Food Technology 61a9835cd9361Sia GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5B Mr. Chan Seng Kit The Next Strategy in The Adaptation of GAP - APO PDFDocument23 pages5B Mr. Chan Seng Kit The Next Strategy in The Adaptation of GAP - APO PDFDavaatseren NarmandakhNo ratings yet
- Scope and Need of Modern Food Processing TechniquesDocument5 pagesScope and Need of Modern Food Processing TechniquesShivaniNo ratings yet
- Identifying Scientific Problems or QuestionsDocument13 pagesIdentifying Scientific Problems or QuestionsRyan Christian JacintoNo ratings yet
- Sectors of Australian Food IndustryDocument3 pagesSectors of Australian Food IndustryPrayas TamangNo ratings yet
- RT40402 Kuliah 3 - Food Safety Issues (Sem. 1 Sesi 2020-21) (05nov2020 19R.awal1442HThu)Document23 pagesRT40402 Kuliah 3 - Food Safety Issues (Sem. 1 Sesi 2020-21) (05nov2020 19R.awal1442HThu)bella TorresNo ratings yet
- Food Tec HSC SummaryDocument33 pagesFood Tec HSC SummarySia GuptaNo ratings yet
- Food Safety and QMDocument9 pagesFood Safety and QMmohanpbisNo ratings yet
- PGS in Lebanon - MSC ProjectDocument15 pagesPGS in Lebanon - MSC ProjectRania Touma WannaNo ratings yet
- IFBC-Module HandbookDocument24 pagesIFBC-Module HandbookVanya RagulNo ratings yet
- Agri Fresh Produce Supply Chain Management A State of The Art Literature Review PDFDocument46 pagesAgri Fresh Produce Supply Chain Management A State of The Art Literature Review PDFvonimeisthersonNo ratings yet
- Global Standards Local Realities Private Agrifood GovernanceDocument26 pagesGlobal Standards Local Realities Private Agrifood GovernancePablo Perez AkakiNo ratings yet
- Concept of Quality: Dr. Anil PanghalDocument90 pagesConcept of Quality: Dr. Anil PanghalSimple sharmaNo ratings yet
- DC-5 - Lesson 1Document12 pagesDC-5 - Lesson 1Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Sab1401 Lect1Document22 pagesSab1401 Lect1noreenasyikinNo ratings yet
- TVET Agrecology Curriculum CambodiaDocument32 pagesTVET Agrecology Curriculum CambodiaGuillaume JumelNo ratings yet
- Present and Future Challenges in Food Analysis: Foodomics: Supporting InformationDocument10 pagesPresent and Future Challenges in Food Analysis: Foodomics: Supporting InformationAna RebeloNo ratings yet
- Fqa 362-1Document437 pagesFqa 362-1amay attriNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Food Safety: Sunil AdsuleDocument3 pagesEmerging Trends in Food Safety: Sunil AdsuleSunil AdsuleNo ratings yet
- MRP Research Proposal: GuidelinesDocument16 pagesMRP Research Proposal: GuidelinesvamsibuNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation - Patrizia Fracassi - Webinar 28.04.2020Document19 pagesPowerPoint Presentation - Patrizia Fracassi - Webinar 28.04.2020Yogi SaputraNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id996762Document23 pagesSSRN Id996762Tania KovalNo ratings yet
- SEARCA Seminar Jose Falck Zepeda July 2011Document39 pagesSEARCA Seminar Jose Falck Zepeda July 2011Jose Benjamin Falck ZepedaNo ratings yet
- NICOLAE Paper 18-05-2009 Tane N Buletin 09Document6 pagesNICOLAE Paper 18-05-2009 Tane N Buletin 09mihaela_neacsuNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Extrinsic Key Quality Characteristics of FoodDocument64 pagesIntrinsic Extrinsic Key Quality Characteristics of FoodAnanda LathifaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Chapter 2Document26 pagesMODULE 1 Chapter 2Claire GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Food Science: Job Duties and Tasks For: "Food Scientists and Technologist"Document3 pagesFood Science: Job Duties and Tasks For: "Food Scientists and Technologist"Francisco Sann RoseNo ratings yet
- GuideDocument10 pagesGuidedevsantosNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentNoah Ras LobitañaNo ratings yet
- Food Quality and Safety Standards at A Glance PDFDocument8 pagesFood Quality and Safety Standards at A Glance PDFLeshnoj PansoyNo ratings yet
- Food Systems Glossary Final - 1675951149Document4 pagesFood Systems Glossary Final - 1675951149DianaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food Analysis: By: DR Nor Raihana Mohamed ZamDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Food Analysis: By: DR Nor Raihana Mohamed ZamDaniel IsmailNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S092552730700312X MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S092552730700312X MainmanishniceNo ratings yet
- Syllabus IntroductionDocument7 pagesSyllabus IntroductionmaingcduNo ratings yet
- FRESCA ISO-14000,22000 & Sơ đồ nước cấp-thải-Tiếng AnhDocument16 pagesFRESCA ISO-14000,22000 & Sơ đồ nước cấp-thải-Tiếng AnhHoang Minh HungNo ratings yet
- 0P 2013 Modul 1 Introduction CorrDocument12 pages0P 2013 Modul 1 Introduction CorrWilliam F. De GraciaNo ratings yet
- COURSE DESCRIPTION - AFAE I and IIDocument3 pagesCOURSE DESCRIPTION - AFAE I and IIrosavilla mandagdagNo ratings yet
- Food Tech Full Summary HSCDocument46 pagesFood Tech Full Summary HSCAxqen kmorjNo ratings yet
- Statistical Process Control in The FoodDocument15 pagesStatistical Process Control in The FoodJOSE RINCONNo ratings yet
- Pps Arable Vegetable Crops 2009Document17 pagesPps Arable Vegetable Crops 2009YanoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Nanotechnology: Draft OnlyDocument23 pagesBiotechnology and Nanotechnology: Draft OnlyPrabhu GandiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Food AnalysysDocument40 pagesWeek 1 Food AnalysysTombiruo JbNo ratings yet
- 40522L22 Article-Rotaru Rev IV PDFDocument9 pages40522L22 Article-Rotaru Rev IV PDFMariana VictoriaNo ratings yet
- 40522L22 Article-Rotaru Rev IVDocument9 pages40522L22 Article-Rotaru Rev IVMariana VictoriaNo ratings yet
- 10 - 7 Group WorkDocument3 pages10 - 7 Group WorkDương Khanh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationWisnu SAmuel GantengNo ratings yet
- tmp49F TMPDocument5 pagestmp49F TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Post-Harvest Loss Management : Reducing Food Waste in DistributionFrom EverandPost-Harvest Loss Management : Reducing Food Waste in DistributionNo ratings yet
- Propec® 5S Audit Checklist: Work Area Completed by DateDocument1 pagePropec® 5S Audit Checklist: Work Area Completed by DatePratik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Support Materials For GR09 GHSD-GOV-PPT-014Document25 pagesSupport Materials For GR09 GHSD-GOV-PPT-014svalenzpNo ratings yet
- TourismDocument10 pagesTourismgargi yadavNo ratings yet
- Major ProjectDocument16 pagesMajor ProjectKate Marielle M. EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Unmsm/Fqiq/Epiq/Daadp/Inglés TÉCNICO/EF5/2020-I: Section V: The Impact of Chemical Engineering Design On SocietyDocument3 pagesUnmsm/Fqiq/Epiq/Daadp/Inglés TÉCNICO/EF5/2020-I: Section V: The Impact of Chemical Engineering Design On SocietyJuanLopezTrujilloNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Impact of COVID-19 On The Sports IndustryDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The Impact of COVID-19 On The Sports IndustrySimona CuciureanuNo ratings yet
- Adani PDFDocument21 pagesAdani PDFSaleem MohammedNo ratings yet
- CBT in Rural Malaysia Is It A SuccessDocument8 pagesCBT in Rural Malaysia Is It A SuccessyudiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Parafrase FinalDocument6 pagesTugas Parafrase FinalDota skuyyNo ratings yet
- External EnvironmentDocument5 pagesExternal Environmentkaye cadizNo ratings yet
- 5-3 Case Study - New Belgium BrewingDocument4 pages5-3 Case Study - New Belgium BrewingTonya Irby- Langley100% (1)
- Persuasive Messages - Radical RewriteDocument3 pagesPersuasive Messages - Radical RewriteFarrahNo ratings yet
- Culture and Its Effect On Business:: Key Elements in Showing How Business Activities Will Be Conducted". DiscussDocument2 pagesCulture and Its Effect On Business:: Key Elements in Showing How Business Activities Will Be Conducted". Discussrichard jarabeNo ratings yet
- Buku Jawaban Tugas Mata Kuliah Tugas 3: Nama Mahasiswa: Desmaria SilalahiDocument3 pagesBuku Jawaban Tugas Mata Kuliah Tugas 3: Nama Mahasiswa: Desmaria Silalahieli sintauliNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document5 pagesActivity 1Meine ShcwächeNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Rural DevelopmentDocument29 pagesDeterminants of Rural DevelopmentShafie ElmiNo ratings yet
- Green Marketing: Research Methodlogy Project PDocument31 pagesGreen Marketing: Research Methodlogy Project PManar AdelNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Factors On Stock Prices and Corporate PerformanceDocument5 pagesThe Impact of Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Factors On Stock Prices and Corporate Performancesrivastavakarishma18No ratings yet
- EIA - For - NH 707 POUNTA - GUMMA - Annexures PDFDocument330 pagesEIA - For - NH 707 POUNTA - GUMMA - Annexures PDFVARUNNo ratings yet
- Five Dimensions of Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesFive Dimensions of Corporate Social Responsibility2K20DMBA158 Prabhakar MallikNo ratings yet
- Increasing Efficiency and Cost Effectiveness of Business Transport ServicesDocument5 pagesIncreasing Efficiency and Cost Effectiveness of Business Transport Servicesaliraza.prime1984No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 ANSWERS Ecosystem Goods and ServicesDocument9 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 ANSWERS Ecosystem Goods and ServiceskalebNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Impact of Covid19 On Sustainable Fashion Consumption With A Model Based On Consumer Value Perceptions 2023 Emerald PublishingDocument25 pagesAnalyzing The Impact of Covid19 On Sustainable Fashion Consumption With A Model Based On Consumer Value Perceptions 2023 Emerald PublishingASMITA MAHAPATRANo ratings yet
- PPL Internship Report Abdullah Haider AliDocument15 pagesPPL Internship Report Abdullah Haider AliAbdullah Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Green Finance in India and ChinaDocument6 pagesComparative Study of Green Finance in India and ChinasushmasreedaranNo ratings yet
- RFP MahagamaDocument67 pagesRFP MahagamaMahabodhi NGONo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Impact Assessment of Pesticides: Current Issues and PerspectivesDocument19 pagesLife Cycle Impact Assessment of Pesticides: Current Issues and PerspectivesTrieuLuongHaiNo ratings yet
- Brambles GRI Disclosure 2022Document88 pagesBrambles GRI Disclosure 2022sushantNo ratings yet