Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
Shantejah Mitchell0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesUntitled Document
Uploaded by
Shantejah MitchellCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Living Organism and Cells
All living organisms are made of cells. Cells are so small that they can
only be seen with a microscope and not with the naked eye. From the
simplest unicellular organisms to the most complex multicellular
organisms, living organisms all share certain characteristics.
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
● Nutrition (feeding): the process by which living organisms
obtain or make food. Animals take in ready-made food and are
called heterotrophs. Plants make their own food by the
process of photosynthesis and are called autotrophs.
• Respiration: the process by which energy is released from food by
all living cells. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and takes place
in most cells. Anaerobic respiration takes place without oxygen in
certain cells.
● Excretion: the process by which waste and harmful
substances, produced by the body’s metabolism,
are removed from the body.
● Growth: a permanent increase in the size and complexity of
an organism.
● Irritability (sensitivity): the ability of organisms to detect
and respond to changes in their environment or within
themselves.
● Movement: a change in the position of a whole organism or of
parts of an organism. Most animals can move their whole
bodies from place to place, known as locomotion. Plants and
Some animals can only move parts of their bodies.
● Reproduction: is the process by which living organisms
generate new individuals of the same kind as
themselves. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of
gametes (sex cells) produced by two parents. Asexual
reproduction does not involve the fusion of gametes and
requires only one parent. Cells.
CELLS
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living
organisms. A single cell possesses all of the seven
characteristics of living organisms.
Some organisms are unicellular, being composed of a
single cell; others are multicellular, being composed of many
cells.
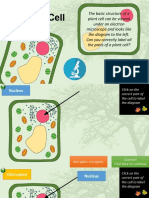
Plant and animal cells
All plant and animal cells contain structures called organelles
that are specialised to carry out one or more vital functions, for
example the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum,
ribosomes, chloroplasts and vacuoles. Organelles are found
within the cytoplasm of the cells and most are
surrounded by one or two membranes. The following structures
are found in all plant and animal cells:
• Cell membrane or plasma membrane
• Cytoplasm
• Nucleus
• Mitochondria (singular mitochondrion)
• Endoplasmic reticulum
In addition to the above, plant cells also possess:
• Cell wall
• Chloroplasts
• Large vacuole
Cell Structure Functions
Cell Membrane Controls what substances enter and leave
the cell.
Cytoplasm
You might also like
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Unit 0 - The CellDocument5 pagesUnit 0 - The CellDavid ToledanoNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument51 pagesMicroorganismsAchira DeemanthaNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeMohamad Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Cells: Cell TheoryDocument17 pages1.1 Introduction To Cells: Cell Theoryarcman17No ratings yet
- Living OrganismsDocument9 pagesLiving OrganismsMeharNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells NotesDocument21 pagesBiology Cells NotesashwanthraNo ratings yet
- What A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About ProtistsDocument3 pagesWhat A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About Protistsapi-300685908No ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Cells: Cell TheoryDocument17 pages1.1 Introduction To Cells: Cell TheoryTulika RajeshNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Topic 1 CellsDocument16 pagesIB Biology Topic 1 CellsIfa Zawarin HussainNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document53 pagesWa0000.Bunny SuvvariNo ratings yet
- 01 Living ThingsDocument32 pages01 Living Thingsapi-632307358No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Page 1 NotesDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science Page 1 Notessrossor6No ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology Study GuideDocument14 pagesHuman and Social Biology Study GuideThompson Ta Ta Jevon80% (10)
- The Cell Theory: Presented By: Rickyla Vien A. VienteDocument25 pagesThe Cell Theory: Presented By: Rickyla Vien A. VienteRickyla VienteNo ratings yet
- Cell as the Basic Unit of LifeDocument9 pagesCell as the Basic Unit of LifeOWEN LEONG WUN THYE MoeNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Cell StructureDocument58 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Cell StructureAya GasparNo ratings yet
- Newly Edited G Biology 10-12Document197 pagesNewly Edited G Biology 10-12Kennedy BwalyaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisHeterotrophicnutrition Animals and fungiOrganiccompoundsDocument110 pagesPhotosynthesisHeterotrophicnutrition Animals and fungiOrganiccompoundsPika PiNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio w1 SummaryDocument5 pagesGen Bio w1 Summaryyxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- CellDocument44 pagesCellIngridNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument18 pagesCell Biology NotesZara100% (2)
- Cells: Building Blocks of LifeDocument28 pagesCells: Building Blocks of LifeScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1, Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesChapter-1, Cell Biologyguptanirmal996No ratings yet
- lower secondary BIOLOGY NOTESDocument19 pageslower secondary BIOLOGY NOTESmamboian01No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science UNIT 1: Cells and Living Organisms: Shaista, 2020Document13 pagesGrade 7 Science UNIT 1: Cells and Living Organisms: Shaista, 2020Shaista ecdcNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture:: Questioning The Cell Theory - Atypical CellsDocument6 pagesThe Big Picture:: Questioning The Cell Theory - Atypical CellsNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Life Chapter 3 From A Cell To An OrganismDocument39 pagesLife Chapter 3 From A Cell To An OrganismvaleNo ratings yet
- CAP 1Document14 pagesCAP 1Francesca PrevitaliNo ratings yet
- Bio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesBio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesMuhammad Mahi Nurul IslamNo ratings yet
- 1 Bridge OverviewOfBiologyDocument46 pages1 Bridge OverviewOfBiologyJOCELYN JOSE IMS22136No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyRizzuya UrakuwaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 16.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 16.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeWinsear VardeNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes Chapter 1-8Document36 pagesBio Notes Chapter 1-8Zhi En LeeNo ratings yet
- Bio g7Document66 pagesBio g744mnx692cbNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Cells & Cell Organelles PDFDocument19 pagesLesson 5 - Cells & Cell Organelles PDFLjasmine MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument16 pagesCharacteristics of Living OrganismsSayeef MahdiNo ratings yet
- Concept of LifeDocument78 pagesConcept of LifeazaNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesLevels of OrganizationSwayangdipta TalapatraNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Topic 1: The Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Biology: Topic 1: The Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsNoor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- BIO 103 Lecture 1Document25 pagesBIO 103 Lecture 1Samiul Hasan Pranto100% (1)
- Lesson - 2 - Cell TheoryDocument28 pagesLesson - 2 - Cell Theoryafif kaziNo ratings yet
- PRPLLLDocument19 pagesPRPLLLPraveen KolaganiNo ratings yet
- Cell History Structure ComparisonDocument25 pagesCell History Structure ComparisonQasimNo ratings yet
- science revisionDocument38 pagesscience revisiongamerboy1234567890000No ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life Cell TheoryDocument87 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Cell TheoryAryan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Life Science FinalDocument50 pagesIntro To Life Science FinalMary Kristine Silerio-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Part 1Document21 pagesCell Biology Part 1SAMIM ANSARINo ratings yet
- Parts of The Cell and Its FunctionDocument24 pagesParts of The Cell and Its FunctionErnest De Mesa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Biology Study GuideDocument35 pagesBiology Study GuideJuliana Gortaire EspinosaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument27 pagesBIOLOGYElijah AtudilloNo ratings yet
- Extended Only: CHP 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms: BasicsDocument21 pagesExtended Only: CHP 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms: BasicsX GamerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Living OrganismsSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Intro To Cells 2017Document38 pagesIntro To Cells 2017YHTAK1792No ratings yet
- Name: Anisyah Ayu Suryaningsih Class: Biology B Group: 8 ResumeDocument2 pagesName: Anisyah Ayu Suryaningsih Class: Biology B Group: 8 ResumeJaya PonselNo ratings yet
- 1 Cytology CelllDocument48 pages1 Cytology CelllSamNo ratings yet
- Bio 103-L1Document24 pagesBio 103-L1Nahid Sagar 1812889042No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument20 pagesCell Structure and FunctionAPS UpdatesNo ratings yet
- Biology: By: Melis Doğu BAYAZITDocument39 pagesBiology: By: Melis Doğu BAYAZITMelis Doğu BayazıtNo ratings yet
- PT. Andaru Persada MandiriDocument18 pagesPT. Andaru Persada Mandiriferdy firmansyahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral InfectionDocument85 pagesLecture 3 Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral InfectionNedhal Mahmoud KaleefahNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Polarizing Microscope TechniquesDocument14 pagesIntroduction to Polarizing Microscope TechniquesAli MohammadNo ratings yet
- Genbio ReviewerDocument7 pagesGenbio ReviewerMary Jean BoNo ratings yet
- Rapid Preparation of Polymersomes by A Water Addition - Solvent Evaporation MethodDocument20 pagesRapid Preparation of Polymersomes by A Water Addition - Solvent Evaporation MethodMuhammad FitrianorNo ratings yet
- A6. Karring T, Lang N, Löe H. The Role of Gingival Connective Tissue in Determining Epithelial Differentiation. J Perio Res 1975Document12 pagesA6. Karring T, Lang N, Löe H. The Role of Gingival Connective Tissue in Determining Epithelial Differentiation. J Perio Res 1975Daniel CubasNo ratings yet
- Micro MeriticsDocument42 pagesMicro MeriticsZeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Laboratory (Faculty of Pharmacy UST)Document9 pagesMicrobiology Laboratory (Faculty of Pharmacy UST)Bianca OcampoNo ratings yet
- Science Notebook Biology The Science of LifeDocument394 pagesScience Notebook Biology The Science of LifeJanice ReadNo ratings yet
- Zaber Catalog2012Document86 pagesZaber Catalog2012Tee Bun PinNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Manongol National High School 7 Ivy Joy O. Balawag Science August 19-23, 2019 2 QuarterDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log Manongol National High School 7 Ivy Joy O. Balawag Science August 19-23, 2019 2 QuarterIvy Joy BalawagNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews-1994-Robinow-211.fullDocument22 pagesMicrobiology and Molecular Biology Reviews-1994-Robinow-211.fullBruno RivoiraNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument10 pagesPlant CellRHEY ANNE TEHENGNo ratings yet
- Leica FS C Leica FS CB Leica FS4000: Living Up To LifeDocument22 pagesLeica FS C Leica FS CB Leica FS4000: Living Up To Lifejuk expertNo ratings yet
- Zaluzec 1 InstrumentationDocument97 pagesZaluzec 1 InstrumentationSimona TocanieNo ratings yet
- Pump Probe TechniqueDocument10 pagesPump Probe TechniqueRaisul A. MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Biomedical imaging techniques and applicationsDocument63 pagesBiomedical imaging techniques and applicationsYlrebmik ArrabiNo ratings yet
- Ugsemstersyllabus Physics 6sem 61802 Physics English PhysicsofnanomaterialsDocument204 pagesUgsemstersyllabus Physics 6sem 61802 Physics English Physicsofnanomaterialsmallikamandapati93No ratings yet
- Exercise 2 Microscopy Part III (Viewing)Document9 pagesExercise 2 Microscopy Part III (Viewing)Cresostomo NogasNo ratings yet
- BacteriaWorksheet1 AKDocument4 pagesBacteriaWorksheet1 AKAgnese NNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooters in Light Micros PDFDocument9 pagesTroubleshooters in Light Micros PDFsponge 2512No ratings yet
- B.Sc. Biotechnology Syllabus Provides Course Details and Assessment SchemeDocument13 pagesB.Sc. Biotechnology Syllabus Provides Course Details and Assessment SchemeNISHANTHNo ratings yet
- 9 - Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots With A Surface State Controlled Luminescence MechanismDocument8 pages9 - Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots With A Surface State Controlled Luminescence MechanismAndy HermanNo ratings yet
- Histological TechniquesDocument61 pagesHistological TechniquesTeddy ChilalaNo ratings yet
- (Transes) Human Histology - 12 Peripheral BloodDocument5 pages(Transes) Human Histology - 12 Peripheral BloodReina CastronuevoNo ratings yet
- Microscope Skills ReviewDocument5 pagesMicroscope Skills Reviewapi-329085879No ratings yet
- 2013 TemeDocument310 pages2013 Temedana.trifanNo ratings yet
- Brock Cell Structures - Uploaded Nov 10, 2020 PDFDocument162 pagesBrock Cell Structures - Uploaded Nov 10, 2020 PDFJBNo ratings yet
- Course Content - SCI 8008SEF Medical Microbiology Virology II - OLEDocument5 pagesCourse Content - SCI 8008SEF Medical Microbiology Virology II - OLEYY CheungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology: Dr.B.Reena RajkumariDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Dr.B.Reena RajkumariSubhi Mishra100% (1)