Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Parasitology
Uploaded by
Joyce LeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Parasitology
Uploaded by
Joyce LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Notes in Introduction to Parasitology Francis Cedrick J.
Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
PARASITOLOGY • Examples:
• The study of parasites o Sarcoptes scabeii
o Pulex irritans
HOST-PARASITE RELATIONSHIP o Pediculus humanus capitis
• Symbiosis - the association of two different o Pediculus humanus corporis
organisms.
C. ERRATIC
1. Mutualism • parasites that invade a part of the body where
2. Commensalism it is ____________________.
3. Parasitism • Examples:
o Entamoeba histolytica
TYPES OF HOSTS o Ascaris lumbricoides
A. DEFINITIVE HOST
• AKA _____________________ D. PATHOGENIC
• harbors the ___________________ stage of • ____________ of producing disease
the parasite • Examples:
• Example: ___________________ o Plasmodium spp.,
o Entamoeba histolytica,
B. INTERMEDIATE HOST o Trichomonas vaginalis
• harbors the ______________________ stage
of the parasite E. NON-PATHOGENIC
• Example: ___________________ • ________________ of producing disease
• AKA _________________
C. RESERVOIR • Examples:
• harbors the parasite and serve as an important o __________________________
source of nutrients for parasite to continue its o __________________________
life cycle. o __________________________
• also serve as o __________________________
_________________________ for the
susceptible host F. FACULTATIVE
• Example: • parasites that are capable of
o Pigs ______________
o Dogs _______________________.
• Example:
D. PARATENIC HOST o __________________________
• host the parasite but o __________________________
____________________ o __________________________
• only serve as ________ or __________
host G. OBLIGATORY
• Example: • parasites that cannot live without a ______
• Freshwater prawns • Example: ____________________
• Freshwater fishes
• Big suitable fishes H. INTERMITTENT
• parasites that only visit the host during
__________________.
TYPES OF PARASITES • Example:
A. ENDOPARASITE o ___________________ (Anopheles
• parasites that live _______ the host spp, Aedes spp, Culex spp)
(_________) o ________________ (Phlebotomus
• Examples: spp.)
o _________________________ o _____________________ (Glossina
o _________________________ spp)
B. ECTOPARASITE I. INCIDENTAL
• parasites that live __________ the body of • parasites that infect __________________.
the host (_____________) • Example: _________________________
Original Intellectual Resource Material of Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
2 Notes in Introduction to Parasitology Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
J. ZOONOTIC R. COELOZOIC
• _____________ parasite that are also • parasites found in the ________________
capable of infecting human • Examples:
• Example: o ______________________
o Ancylostoma caninum o ______________________
o Ancylostoma braziliense
o Toxocara canis S. PSEUDOPARASITES
o Toxocara cati • non-living things mistaken as parasites in the
o Ascaris suum laboratory
• Examples:
K. ABERRANT o pollen grains - ___________________
• infects host where they ________________ o plant hairs - _____________________
______________
• aka _____________________________
• Example: ___________________. MODE OF TRANSMISSION
A. INGESTION
L. PERMANENT • Pork
• parasites that are found within the host from o _______________________
______________________________. o _______________________
• Example: • Beef
o ____________________________ o _______________________
• Crabs
M. __________________ o _______________________
• parasites wherein the larval stage develops o _______________________
inside the host but the adult is free-living • Fishes
• Example: Strongyloides stercoralis o _______________________
o Larva - _____________ o _______________________
o Adult - _____________ • Snail
o _______________________
N. __________________
• parasite wherein the larval stage develops in a B. ORAL CONTACT
host different from that of the adult • ______________________
• Example: Schistosoma japonicum • ______________________
o Larva - __________________
o Adult - __________________ C. TRANSPLACENTAL
• ______________________
O. CYTOZOIC • ______________________
• parasites that are found • ______________________
__________________
• Examples: D. SEXUAL
o _______________________ • ______________________
o _______________________ • Annilingus
o _______________________ o ______________________
o ______________________
P. HEMATOZOIC o ______________________
• parasites that are found inside ___________
________. E. SKIN PENETRATION
• Examples: • ______________________
o _______________________ • ______________________
o _______________________ • ______________________
Q. ENTEROZOIC F. BLOOD TRANSFUSION
• parasites that are found in the __________ • ______________________
• Examples: • ______________________
o Ascaris lumbricoides • ______________________
o Entamoeba histolytica • ______________________
o Giardia lamblia
Original Intellectual Resource Material of Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
3 Notes in Introduction to Parasitology Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
• Examples:
G. AUTOINFECTION o A–S-H
• Enterobius vermicularis o _____________________
• Strongyloides stercoralis, Hymenolepis nana, o _____________________
Taenia solium, Cryptosporidium parvum
B. SPACE-OCCUPYING LESION
• Some parasites may produce cysts that may
SOURCES OF INFECTION compress surrounding tissues/organ.
A. MAN - ___________________________ • Examples:
B. ANIMALS o Echinococcus granulosus
• _____________________________ o Taenia solium
• _____________________________
• _____________________________ C. INFLAMMATORY REACTION
C. RAW/UNCOOKED MEAT • Examples:
• Food transmitted parasites o Entamoeba histolytica
D. CONTAMINATED SOIL AND WATER o Wuchereria bancrofti
• Soil-transmitted parasites o Trematode eggs
o _________________________
o _________________________ D. ENZYME PRODUCTION & LYTIC NECROSIS
o _________________________ • Examples:
o _________________________ o Plasmodium spp., Leishmania spp.,
E. VECTOR Trypanosoma
• _______________ o Entamoeba histolytica
• Transmits infection from one organism to
another E. TOXINS - ____________________________
• Types of Vectors:
o Biologic vector – transmits the F. ALLERGIC REACTION
parasite only after it ________ • Examples:
______________________. • Schistosomes:
o Example: Mosquito (Anopheles spp) • Ruptures hydatid cyst:
• Occult filariasis:
o Mechanical vector
o Only transports the parasite G. NEOPLASIA
o Example: Cockroach, Fly • Examples:
• Schistosoma haematobium:
• Clonorchis spp, Opistorchis spp.:
PATHOGENESIS OF PARASITIC INFECTIONS
A. MECHANICAL DAMAGE H. SECONDARY BACTERIAL INFECTION
• EGGS • Examples:
• large parasitic egg may be deposited in organs o Schistosoma spp.
or tissues which may cause irritation o Strongyloides stercoralis
• Examples:
o Schistosoma japonicum LIFE CYCLE OF PARASITES
o Schistosoma haematobium IMPORTANT TERMS
o Paragonimus westermani • Infective stage
o Fasciola hepatica o the stage in the life cycle of parasite
that is _______________________
• LARVA ________________.
• migratory helminths may cause trauma • Diagnostic stage
• Examples: o the stage in the life cycle of parasite
o Ascaris lumbricoides that can be ___________________
o Strongyloides stercoralis, ________________.
o Hookworms o the stage wherein the parasite can be
_____________.
• ADULT
• may cause trauma of intestinal wall
Original Intellectual Resource Material of Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
4 Notes in Introduction to Parasitology Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
TWO TYPES
I. DIRECT LIFE CYCLE
• aka __________________________
• Involves only __________________
II. INDIRECT LIFE CYCLE
• aka __________________________
• Involves ______________________ to
complete its life cycle
Original Intellectual Resource Material of Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
5 Notes in Introduction to Parasitology Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
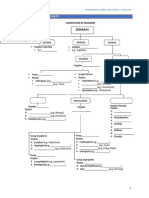
Kingdom Animalia
Subkingdom Metazoa
Phylum Nemahelminthes Phylum Platyhelminthes
Class Adenophorea Class Rhabditea Class Cestoidea Class Trematoda
Order Trichurida Subclass Secernentia Subclass Cestoda Subclass Digenea
Order Ascaridida,
Order Plagiochiformes
Order Oxyurida,
Order Pseudophyllidea, Order Echinostomatifermes
Order Strongylida,
Order Cyclophyllidea Order Opistorchiformes
Order Rhabditida, Order
Order Strigeiformes
Spirurida
Original Intellectual Resource Material of Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
6 Notes in Introduction to Parasitology Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
Kingdom Protista
Subkingdom Protozoa
Phylum Sarcomastigophora Phylum Ciliophora Phylum Apicomplexa Phylum Microscopa
Subphylum Sarcodina Subphylym Mastigophora Class Ciliatea Class Sporozea
Class Lobosea Class Zoomastigophora Order Trichostomatida Subclass Coccidia Subclass Piroplasmia
Order Trichomonadida
Order Diplomonadida
Order Amoebida Suborder Haemosporina
Order Retortomonadida Order Piroplasmidora
Order Schizopyrenida Suborder Eimeriina
Order Enteromonadida
Order Kinetoplastida
Original Intellectual Resource Material of Francis Cedrick J. Victorino, RMT, MSMT(c)
You might also like
- Practice with Prepositions in Everyday English, Advanced LevelFrom EverandPractice with Prepositions in Everyday English, Advanced LevelRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Parasitology NematodesDocument28 pagesParasitology NematodesJoshua Richard Jr Tubiano PayopaninNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument8 pagesParasitologyJoshua Richard Jr Tubiano PayopaninNo ratings yet
- Para Lab Module 1 NotesDocument4 pagesPara Lab Module 1 NotesJoyce LeeNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus, HACEK, Anaerobes HANDOUTSDocument57 pagesHaemophilus, HACEK, Anaerobes HANDOUTSEkhizz VicenteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document5 pagesLecture 1Cherold RoldanNo ratings yet
- New - Micro-2023-Part-1Document15 pagesNew - Micro-2023-Part-1Trisha RomeoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in ParasitologyDocument15 pagesLecture Notes in ParasitologyNicollo DadiavelliNo ratings yet
- Review in Microbiology Part 1Document30 pagesReview in Microbiology Part 1sini gangNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.16 Classification AssignmentDocument5 pagesUnit 1.16 Classification AssignmentEric ChiangNo ratings yet
- Bacte Part 1-ActsDocument12 pagesBacte Part 1-ActsAngela De LeonNo ratings yet
- Lab Practice For Prac EXAMDocument3 pagesLab Practice For Prac EXAM4cmkrvvfcyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in ParasitologyDocument15 pagesLecture Notes in Parasitologyjiday23100% (5)
- Imported FileDocument3 pagesImported FilemaotianjiamattymNo ratings yet
- 2+ +unit+1+ +Introduction+to+Biology+and+Characteristics+of+LifeDocument5 pages2+ +unit+1+ +Introduction+to+Biology+and+Characteristics+of+LifeKarthikgayan (Karthik) VicneswaranNo ratings yet
- Protist WorksheetDocument4 pagesProtist WorksheetRozuwan ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Diseases Parasites NotesDocument4 pagesDiseases Parasites NotesRayge HarbskyNo ratings yet
- NMAT ReviewerDocument36 pagesNMAT ReviewerchayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Module 11 NotesDocument5 pagesModule 11 NotespatatasituuNo ratings yet
- Grade-3 - Level-E - Science - Revision Sheets - Sec.1.3, 2.1 and 2.2 (Used To Be 2.3-4.1-4.2)Document3 pagesGrade-3 - Level-E - Science - Revision Sheets - Sec.1.3, 2.1 and 2.2 (Used To Be 2.3-4.1-4.2)Mona EL-SherifNo ratings yet
- Finding The Mystery Pathogen: Bacteria Virus FungusDocument3 pagesFinding The Mystery Pathogen: Bacteria Virus Fungusapi-350126589No ratings yet
- Animal Report: Name: Class: Day/DateDocument16 pagesAnimal Report: Name: Class: Day/DateFierissya YuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Microbe-Human Interactions: Infection & DiseaseDocument23 pagesMicrobe-Human Interactions: Infection & DiseaseUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SOL Review - New One Answer KeyDocument30 pagesEarth Science SOL Review - New One Answer KeyXiandan AyjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BionotesDocument13 pagesChapter 1 BionotesAIRA SYAFIQAH BINTI MOHD KHAIRANI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Avaliação Bimestral 9º Ano 2º BimestreDocument5 pagesAvaliação Bimestral 9º Ano 2º BimestreJuliane GuedesNo ratings yet
- Bio - Unit - 10 - Animal - Notes - 2020 - SC RIGHT ONEDocument3 pagesBio - Unit - 10 - Animal - Notes - 2020 - SC RIGHT ONENatalie KuNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes - The Process of EvolutionDocument6 pagesGuided Notes - The Process of Evolutiondiamond25% (4)
- Pharmacognosy: Mocule 1tDocument78 pagesPharmacognosy: Mocule 1tIrene CerisseNo ratings yet
- Classification Cladogram Notes Day FourDocument2 pagesClassification Cladogram Notes Day FourElora Rogers100% (1)
- History of The Earth Evolution Fill-In NotesDocument20 pagesHistory of The Earth Evolution Fill-In Notesapi-622033028No ratings yet
- Genbio Part 1 of 2Document6 pagesGenbio Part 1 of 2Gerrel Lloyd DistrajoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Community InteractionsDocument12 pagesWorksheet Community InteractionsrkvNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology (Prokaryotes) : Two Prokaryotic Domains: Archaea, BacteriaDocument9 pagesBacteriology (Prokaryotes) : Two Prokaryotic Domains: Archaea, BacteriaCatalinaCardenasNo ratings yet
- 1) Introduction To Microbiology - Cell StructureDocument34 pages1) Introduction To Microbiology - Cell StructureJustin Dave ManantanNo ratings yet
- Science 6 1 Fib HandoutDocument4 pagesScience 6 1 Fib Handoutapi-210074080No ratings yet
- Animals Vertebrates-And-InvertebratesDocument2 pagesAnimals Vertebrates-And-InvertebratesPilarnarNo ratings yet
- VariationDocument30 pagesVariationFarhan RosleeNo ratings yet
- Review Teori Bahasa Inggris ANKESDocument4 pagesReview Teori Bahasa Inggris ANKESdepaNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide CHP 3Document9 pagesLearning Guide CHP 3wworldwide7No ratings yet
- Invertebrates (Insects, Crustaceans and Arachnids) : Fill in The Blanks With The Words From The BoxDocument2 pagesInvertebrates (Insects, Crustaceans and Arachnids) : Fill in The Blanks With The Words From The BoxKlaus MerschbacherNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Student (Answer Sheet) Microbes and Infectious DiseaseDocument6 pagesKami Export - Student (Answer Sheet) Microbes and Infectious DiseaseAylin Oropeza (578AylOrop)No ratings yet
- Bryan Doucette - Simpsons Scientific MethodDocument2 pagesBryan Doucette - Simpsons Scientific MethodBryanNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Q2 LP4Document14 pagesBiotechnology Q2 LP4コミKomiNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Kingdoms and Domains, 1.4 Classifying Types of Biodiversity-Student SheetDocument4 pages1.3 Kingdoms and Domains, 1.4 Classifying Types of Biodiversity-Student Sheeteshaaljamal27No ratings yet
- 14 - Six Kingdoms and Three Domains of Life - PowerPoint Worksheet - Answer KeyDocument3 pages14 - Six Kingdoms and Three Domains of Life - PowerPoint Worksheet - Answer KeyChloe HallNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology, Growth & Reproduction - Free NotesDocument4 pagesBacterial Morphology, Growth & Reproduction - Free NotesMika De VeraNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument6 pagesAssessmentKimberlyn Male100% (1)
- Pathogens and Disease Worksheets Science HouseDocument4 pagesPathogens and Disease Worksheets Science HouserileysandersjakeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 BlankedDocument4 pagesWeek 3 BlankedAbraham WalkthewokNo ratings yet
- Microbio 12Document5 pagesMicrobio 12Chicken AdoboNo ratings yet
- HANDS OUT Specimen Collection and The AmeobaDocument114 pagesHANDS OUT Specimen Collection and The AmeobaClaudine DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Boy Boy Girl Girl: Radio RadioDocument8 pagesBoy Boy Girl Girl: Radio RadioRocío ChioNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecology Notes PPT Worksheet: NAME: - DATE: - PERIODDocument6 pagesBasic Ecology Notes PPT Worksheet: NAME: - DATE: - PERIODPeng MacNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument1 pageClassificationcharlotte.jamesNo ratings yet
- Diversity Animals (Primary 3 Syllabus)Document12 pagesDiversity Animals (Primary 3 Syllabus)krtcMP100% (5)
- KEY Sci10 Biology WorkbookDocument74 pagesKEY Sci10 Biology Workbooklevi letetaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lecture 2024 M1 Introduction To ParasitologyDocument4 pagesParasitology Lecture 2024 M1 Introduction To Parasitologyeumhir7No ratings yet
- Internal Medicine HISTORYDocument4 pagesInternal Medicine HISTORYClaire FNo ratings yet
- Mites and Ticks (Acari) : BioriskDocument44 pagesMites and Ticks (Acari) : BioriskSesi AgustinNo ratings yet
- Las Sci6 Q2 Week6Document9 pagesLas Sci6 Q2 Week6Gianna BaldoradoNo ratings yet
- Crop ProtectionDocument14 pagesCrop ProtectionWala Lang100% (2)
- Test 1 Question Banks Part 1 (Mich Kel L As2ila Lal Fahes)Document19 pagesTest 1 Question Banks Part 1 (Mich Kel L As2ila Lal Fahes)Anthony Al LakissNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Reviewer Grade 8 3rd QuarterDocument12 pagesMAPEH Reviewer Grade 8 3rd QuarterAmelia Ria Canlas92% (13)
- Definitions of Parasitism Considering Its Potentially Opposing Effects at Different Levels of Hierarchical OrganizationDocument8 pagesDefinitions of Parasitism Considering Its Potentially Opposing Effects at Different Levels of Hierarchical OrganizationwellingtonlimaNo ratings yet
- 12-1 Community InteractionsDocument11 pages12-1 Community Interactionsapi-265907602No ratings yet
- Concept of Epidemiology - VRBDocument49 pagesConcept of Epidemiology - VRBAnand gowdaNo ratings yet
- Sheep Goat 3Document174 pagesSheep Goat 3Ch Abdul Bari100% (1)
- Cot 1-Science 4-02-22-21Document36 pagesCot 1-Science 4-02-22-21Michelle JapayNo ratings yet
- Emerging Microbial Biocontrol Strategies For Plant PathogensDocument10 pagesEmerging Microbial Biocontrol Strategies For Plant PathogensAlex PradoNo ratings yet
- Animal RelationshipsDocument7 pagesAnimal RelationshipsnidhiNo ratings yet
- CNs InfectionDocument6 pagesCNs InfectionChefera AgaNo ratings yet
- Medtech ReviewerDocument4 pagesMedtech ReviewerLyudmyla Gillego100% (4)
- 9700 s12 QP 23Document16 pages9700 s12 QP 23Farhad AliNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: Sample Discussion QuestionsDocument24 pagesAgriculture: Sample Discussion QuestionsMutungi FelixNo ratings yet
- Types of Animal Adaptations: by Vyoma Patel, Nandini Soni and Parthvi PatelDocument44 pagesTypes of Animal Adaptations: by Vyoma Patel, Nandini Soni and Parthvi Patelvyoma patelNo ratings yet
- STPM Biology Chapter 6 NotesDocument8 pagesSTPM Biology Chapter 6 NotesVentus Tan100% (1)
- Fish Parasite Heavy Mental and Gene ExpressionDocument22 pagesFish Parasite Heavy Mental and Gene ExpressionJackyLeeNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Chicken Production: Why Should You Keep Indigenous Chickens?Document12 pagesIndigenous Chicken Production: Why Should You Keep Indigenous Chickens?IdrisNo ratings yet
- Practice Test in Crop Protection: DIRECTION: Encircle The Letter of The Best Answer From The Choices Given. 1Document25 pagesPractice Test in Crop Protection: DIRECTION: Encircle The Letter of The Best Answer From The Choices Given. 1Loida Manluctao Gacusan100% (2)
- June 2012 (v3) QP - Paper 2 CIE Biology A-LevelDocument16 pagesJune 2012 (v3) QP - Paper 2 CIE Biology A-LevelSalman Farsi TaharatNo ratings yet
- SERRES Parasites As Agents of ChangeDocument2 pagesSERRES Parasites As Agents of ChangekellycigmanNo ratings yet
- Elp Health 3Document9 pagesElp Health 3Charito Vargas CordialNo ratings yet
- 13 Tips For Pigeon RacersDocument4 pages13 Tips For Pigeon RacersAljames Gaerlan RullodaNo ratings yet
- SS1 Biology For Third TermDocument55 pagesSS1 Biology For Third TermBenedicta AnyaNo ratings yet
- (Bruce Hannon, Matthias Ruth) Dynamic Modeling of (BookFi) PDFDocument284 pages(Bruce Hannon, Matthias Ruth) Dynamic Modeling of (BookFi) PDFmyra umar100% (1)
- A1 Micro AssignDocument3 pagesA1 Micro AssignMichelle PanlilioNo ratings yet
- 2021 1 Introduction To Parasitologi - April 2021Document31 pages2021 1 Introduction To Parasitologi - April 2021Aiko Anisah FarellaNo ratings yet
- Parasite Control in Zoo Animals 2015Document38 pagesParasite Control in Zoo Animals 2015Ellana Sue HetheringtonNo ratings yet