Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metabolic Bone Disease
Uploaded by
Sean KeenanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metabolic Bone Disease
Uploaded by
Sean KeenanCopyright:
Available Formats
Metabolic Bone Disease
Differential Lab Results in Metabolic Bone Disease
Disease Calcium Phosphate ALP PTH VitD
Osteoporosis ↔ ↔ ↔ ↔ ↔
Osteomalacia ↓ ↓ ↑ ↔ ↓
Renal Osteodystrophy ↔/ ↑ ↑ ↑ v ↔
Paget's Disease of Bone ↔ ↔ ↑ ↔ ↔
Description
Osteoporosis is a reduction in overall bone mass and may be 1 o (age related) or 2o to other conditions or drugs. 18 %
of females (80 % of hip fractures are in women >50 YO) and 6 % of males >50 YO are affected. Trabeculae are lost in
women’s bones over time but in men it is mostly conserved.
In Osteomalacia, bone mass is conserved but mineral content is low (reverse of osteoporosis). This leads to rickets
when it occurs during bone growth while osteoporosis occurs after the fusion of the epiphyses.
Paget’s disease of the bone occurs when there is increased bone turnover associated with increased numbers of
osteoblasts and osteoclasts. This results in remodelling, bone enlargement and deformities. Rare <40 YO with 3 % of
>55 YO affected. It is more common in temperate climates and Anglo-Saxons.
Osteoporosis
Presentation Management
- Trabecular: Vertebral crush injury; Dowager’s hump - Lifestyle modifications
- Cortical: Long bone fractures; Femoral neck common o ↓Risks: Smoking cessation; Alcohol reduction
- NB: Femoral neck is biggest risk of death o Diet: ↑ Calcium + VitD; ↑ BMI
Causes o Home Aids: ↓ Fall risks
- Important: RA; Corticosteroids; ↑↑ Levothyroxine o Exercises: Weigh bearing; Balance
- Age: Bone mineral density decreases with age - Pharmacological
- Lifestyle: Alcohol >4 units daily; BMI <19 o Key: If Fragility fracture skip DEXA scan to treat
- Systemic: Menopause; CKD; DM o Supplements: Calcium + VitD
- Activity: Prolonged immobility; Falls o Bisphosphonate: Alendronate (CI: GFR<35;
- Drugs: SSRIs; Antiepileptics; PPIs; Thiazolinediones PUD)
Investigations o Denosumab: RANKLi; Preferred if GFR <30
- Bloods: Ca2+; PO43-; ALP normal o Strontium Ranelate: Last line (CI: CVD)
- Bone densitometry: Bone mineral density (BMD) o Raloxifene: Selective oestrogen receptor mod.
- DEXA: <2.5 SD below young adult mean density o HRT: Post-menopause (CI: Breast Ca; CVD)
- NB: See table below for DEXA scoring
o Teriparatide: Recombinant PTH (SE: Renal Ca)
- T-Score: Based on bone mass of young population
o Calcitonin: ↓ Pain after vertebral fracture
- Z-Score: Age; Gender; Ethnic adjusted score
- Steroid Therapy
- X-Ray: Low sensitivity and specificity
o Risk: Significant if ≥75 mg for 3 months
- FRAX: 10 yr risk of fragility fracture
o Key: Start bone protection immediately
- NB: Assess all women ≥65 YO and ≥75 males
Osteoporosis Risk Factors DEXA Bone Densiometruy WHO Criteria
Description T-Score Description
S Steroid use of >5 mg/d of Prednisolone >0 BMD is better than the reference
H Hyperthyroidism; Hyperparathyroidism; Hypercalciuria 0 → -1 BMD is in top 84 % (No evidence of osteoporosis)
A Alcohol + Tobacco use -1 → -2.5 Osteopenia (risk of later osteoporotic fracture)
T Thin (BMI <18.5) <-2.5 Osteoporosis (Repaet DEXA every 2 yrs)
T Testosterone deficient
E Early menopause
R Renal or Liver failure
E Erosive / Inflammatory bone disease
D Dietary Calcium deficiency/malabsorption; T1DM
Osteomalacia
Presentation Investigations
- Features: Bone pain; Fractures; Proximal myopathy - Plasma: ↓ Ca2+; ↓ PO43-; ↑ ALP; ↑ PTH; ↓VitD
Causes - X-Ray: Translucent bands (Looser’s zones)
- VitD deficiency: Malabsorption; Poor diet; ↓ Sun Management
- Renal osteodystrophy: Calciferol deficiency - Diet: Calcium + VitD3 supplements (Adcal)
- Drug-induced: Anticonvulsants ↑ VitD breakdown - Liver disease: VitD2 (ergocalciferol); IM Calcitriol
- VitD resistance: Inherited conditions (X-linked) - Renal disease: Alfacalcidol; Calcitriol
- Liver disease: ↓ Conversion of VitD Calciferol - NB: Risk of dangerous hypocalcaemia
- Tumour: Hypophosphatemia + Hyperphosphaturia - Inherited: Phosphate and Calcitriol supplements
- Inherited: X-Linked Hypophosphataemic rickets - Monitor: Ca2+ weekly initially; Check during N&V
Paget’s Disease of the Bone
Presentation Management
- ASx: Asymptomatic in 95 % - Basic: Analgesia
- Key: Older male; Bone pain; ↑ ALP - Bisphosphonate: PO Risedronate; IV Zoledronate
- Features: Deep bone pain in bones Complications
- Bones: Pelvis; Skull; Spine; Femur; Tibia - Bone: OA; Skull thickening; Hypercalcaemia
- Untreated: Skull bossing; Tibia bowing - SNHL: Nerve compression by bones (deafness)
Causes - Cardiac: High-output CCF
- Risks: ↑ Age; Male; Northern latitude; FHx - Onco: Osteosarcoma (<1 % cases >10 yrs post-Δ)
Investigations
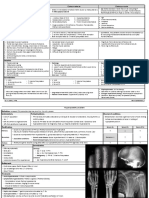
- XR: Bow-Saber tibia; Bony enlargement; Hot-spots
- Bloods: ↔ Ca2+; ↔PO43-; ↑ ALP
- Other: P1NP; Serum CTx; Urine NTx; Urinalysis
Above: Bow-Saber
Tibia (classical)
Left: Skull thickening
Right: Hot-spots
shown on isotope
bone scan
You might also like
- Gold Standard For NclexDocument113 pagesGold Standard For NclexMaria Margarita86% (29)
- Pharmacology Viva QuestionsDocument24 pagesPharmacology Viva QuestionsMinhaz Islam100% (1)
- Community Health NursingDocument8 pagesCommunity Health NursingLloyd rafael100% (2)
- SCI Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSCI Cheat SheetJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Hyperparathyrodism Hypoparathyrodism: Dr. A. Wahyudi Pababbari, SPPD, FinasimDocument48 pagesHyperparathyrodism Hypoparathyrodism: Dr. A. Wahyudi Pababbari, SPPD, FinasimKahfiyahNo ratings yet
- Paratiroid and OsteoporosisDocument48 pagesParatiroid and OsteoporosisMuhammad Nur DelaphanEnamNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument5 pagesOsteoporosisjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Inroduction & MetabolicDocument49 pagesInroduction & MetabolicFamous manNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone Disease & Bone Markers - SlidesDocument46 pagesMetabolic Bone Disease & Bone Markers - Slidesmonday125100% (1)
- Secondary Osteoporosis AssessmentDocument12 pagesSecondary Osteoporosis AssessmentBibiana Prada de Camargo ColenciNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Metabolik Dan Endokrin Oleh Dr. RonaldDocument48 pagesKelainan Metabolik Dan Endokrin Oleh Dr. RonaldOdilia Maria RahalusNo ratings yet
- Osteoprosis, Osteomalacia and Pagets DiseaseDocument31 pagesOsteoprosis, Osteomalacia and Pagets DiseaseayeshasadiqamukhtarNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone DiseaseDocument41 pagesMetabolic Bone DiseaseVenerandaNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument2 pagesOsteoporosistjelongNo ratings yet
- Bone DiseaseDocument1 pageBone DiseaseLe RobertNo ratings yet
- Muh. Ismail Pratama A. Tenri Luwu MutmainnahDocument34 pagesMuh. Ismail Pratama A. Tenri Luwu MutmainnahNurul Qalby AmiluddinNo ratings yet
- IKD3 - Uraemic Leontiassis OsseaDocument41 pagesIKD3 - Uraemic Leontiassis OsseaRenal Association MauritiusNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis by DR MehmoodDocument66 pagesOsteoporosis by DR Mehmoodorthopaedic huraymilaNo ratings yet
- Slides by Dan Mandel, MD UC Irvine School of MedicineDocument45 pagesSlides by Dan Mandel, MD UC Irvine School of Medicineaddison wood100% (4)
- Endo 5 MDDocument80 pagesEndo 5 MDIulia IuliaNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: by Ali Naqvi, Jeff Hughes, and Shuktika NandkekolyarDocument19 pagesOsteoporosis: by Ali Naqvi, Jeff Hughes, and Shuktika NandkekolyarAdelaide SharfinaNo ratings yet
- Pathology IcsmDocument84 pagesPathology IcsmAlice TangNo ratings yet
- Penyakit DegeneratifDocument108 pagesPenyakit DegeneratifYauffa Hanna Elt MisykahNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis - 2022 CanvasDocument61 pagesOsteoporosis - 2022 CanvasSHEILA HADIDNo ratings yet
- Pseudogout Case PresentationDocument16 pagesPseudogout Case PresentationSamantha SykesNo ratings yet
- Hematology NotesDocument5 pagesHematology NotesAngela TiqueNo ratings yet
- Board Review Endocrinology A. ApiradeeDocument47 pagesBoard Review Endocrinology A. ApiradeePiyasak NaumnaNo ratings yet
- Peds HemeImmune OUTLINEDocument10 pagesPeds HemeImmune OUTLINEAshleyNo ratings yet
- 1-19 Diagnosis and Risk Factors of Osteoporosis 2004Document53 pages1-19 Diagnosis and Risk Factors of Osteoporosis 2004tarikeopsNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes, Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument15 pagesFluids and Electrolytes, Acid-Base ImbalancesJherome FernandoNo ratings yet
- Total Knee Replacement: Done By: Sajeda Moha'dDocument27 pagesTotal Knee Replacement: Done By: Sajeda Moha'dlolo223No ratings yet
- Ch. 39 40 MusculoskeletalDocument21 pagesCh. 39 40 MusculoskeletalNurseNancy93100% (1)
- Applied Aspect of CA Metabolism and Bone PhysiologyDocument16 pagesApplied Aspect of CA Metabolism and Bone Physiologykehigeh812No ratings yet
- Bone Markers Univ West APC Feb 2013Document82 pagesBone Markers Univ West APC Feb 2013monday125No ratings yet
- Osteomalacia: - Disorder of Mature Bone in Which Mineralisation of New Osteoid Bone Is Inadequate or DelayedDocument48 pagesOsteomalacia: - Disorder of Mature Bone in Which Mineralisation of New Osteoid Bone Is Inadequate or DelayedHimanshu NarangNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Bone: Growth Hormone: Sex Hormones (Estrogen/testosterone) Thyroid Hormones (PTH & Calcitonin)Document7 pagesPhysiology of Bone: Growth Hormone: Sex Hormones (Estrogen/testosterone) Thyroid Hormones (PTH & Calcitonin)Ayuub AbdirizakNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Document2 pagesDr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Herato MenaNo ratings yet
- Case of Back PainDocument55 pagesCase of Back PainaayceeNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis (Osteoporoza)Document44 pagesOsteoporosis (Osteoporoza)VedadNo ratings yet
- Hyper Parathyroid IsmDocument20 pagesHyper Parathyroid IsmPartha SarathyNo ratings yet
- Metabolic and Endocrine DisordersDocument76 pagesMetabolic and Endocrine DisordersMika Kresna100% (1)
- حل اسئلة العملي-1Document91 pagesحل اسئلة العملي-1حسام الوجيهNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument20 pagesCase PresentationkaleeswariNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 ReviewDocument2 pagesExam 1 Reviewtschreiber29No ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy Handbook 7th Edition-1-31-43Document13 pagesPharmacotherapy Handbook 7th Edition-1-31-43Erfin NingoNo ratings yet
- Lec13 Gout and PseudogoutDocument55 pagesLec13 Gout and PseudogouttentenNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument93 pagesOsteoporosisprotikNo ratings yet
- Skeletal DysplasiasDocument64 pagesSkeletal DysplasiasSam0% (1)
- Osteoprosis Presentation 2Document38 pagesOsteoprosis Presentation 2Shaz RizwanNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis PEDocument51 pagesOsteoporosis PENitin BansalNo ratings yet
- Secondary OsteoporosisDocument22 pagesSecondary OsteoporosisBenny Chris TantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9Zaky DavidiaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal ProblemsDocument22 pagesMusculoskeletal ProblemsShauki AliNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation of IHD-1Document48 pagesCase Presentation of IHD-122 Prem PatelNo ratings yet
- Pagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Document28 pagesPagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Lolo TotoNo ratings yet
- RicketsDocument7 pagesRicketsGhadeer EbraheemNo ratings yet
- Adult 1 - Week 4 (Chapters 45 & 46)Document5 pagesAdult 1 - Week 4 (Chapters 45 & 46)Sydney SmallNo ratings yet
- Concept Maps Test 3 410Document12 pagesConcept Maps Test 3 410Ashley BurnsNo ratings yet
- RICKETSDocument52 pagesRICKETSDoc On CallNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument71 pagesOsteoporosisGuna NikhilNo ratings yet
- T Score - 1Document8 pagesT Score - 1muhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Paget's Disease in Service TrainingDocument4 pagesPaget's Disease in Service TrainingrinninNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument7 pagesOsteoporosisLorebell100% (2)
- Concordant Materia Medica Frans Vermeulen.00266 - 3hippozaenium PDFDocument5 pagesConcordant Materia Medica Frans Vermeulen.00266 - 3hippozaenium PDFDipankar Ganguly0% (1)
- DR Lal Pathlabs: LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini Delhi 110085Document2 pagesDR Lal Pathlabs: LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini Delhi 110085Yousra ZeidanNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrlytes 1Document14 pagesFluids and Electrlytes 1Pau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- 2.lecture-2, Physical Aspects of AgeingDocument49 pages2.lecture-2, Physical Aspects of AgeinglujainNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument6 pagesNursing Informatics: Bachelor of Science in NursingMichelle MallareNo ratings yet
- BST NotesDocument6 pagesBST NotesshanggariNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry: Surface Markers and Beyond: Methods of Allergy and ImmunologyDocument10 pagesFlow Cytometry: Surface Markers and Beyond: Methods of Allergy and ImmunologyMunir AliNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument5 pagesThesis - Iron Deficiency Anemiaafaybiikh100% (2)
- Diagnostic Laboratoric To Anemia: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH) - Dr. Malayana Nasution Mked. Clin - Path. SPPKDocument41 pagesDiagnostic Laboratoric To Anemia: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH) - Dr. Malayana Nasution Mked. Clin - Path. SPPKrubyniNo ratings yet
- Satya Prakash Gupta - Cancer-Causing Viruses and Their Inhibitors (2014, Taylor & Francis - CRC Press, CRC Press)Document501 pagesSatya Prakash Gupta - Cancer-Causing Viruses and Their Inhibitors (2014, Taylor & Francis - CRC Press, CRC Press)rfmihaiNo ratings yet
- Wawa - Sistem Saraf PusatDocument38 pagesWawa - Sistem Saraf PusatnuhaNo ratings yet
- Drugs That May Unmask or Worsen Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesDrugs That May Unmask or Worsen Myasthenia GravisnuriajiNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFDocument8 pages5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFVince Alvin DaquizNo ratings yet
- Lithiumtherapybenefits PDFDocument3 pagesLithiumtherapybenefits PDFArhip CojocNo ratings yet
- Psychoses: CNS Dopamine Levels Perception, Thought, Consciousness, Social, Affective DisordersDocument3 pagesPsychoses: CNS Dopamine Levels Perception, Thought, Consciousness, Social, Affective DisordersJustin Hulin100% (1)
- Antepartum Notes Maternal and Child NursingDocument12 pagesAntepartum Notes Maternal and Child NursingJoana Rose FantonialNo ratings yet
- Pediatric RehabDocument32 pagesPediatric RehabRainy DaysNo ratings yet
- Essential Components of Primary Eye Care: EditorialDocument3 pagesEssential Components of Primary Eye Care: EditorialAreenaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B Deficiency in Children With Infantile Spasms: A Case-Control StudyDocument5 pagesVitamin B Deficiency in Children With Infantile Spasms: A Case-Control StudyireneaureliaNo ratings yet
- طفيليات وحشرات PDFDocument261 pagesطفيليات وحشرات PDFمحمد الفراصيNo ratings yet
- 6d52cb67c16c45b194398c6189999984Document196 pages6d52cb67c16c45b194398c6189999984SasiRekhaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Steroid TherapyDocument10 pagesPulse Steroid Therapyselvie87No ratings yet
- Electrolyte DisturbanceDocument21 pagesElectrolyte DisturbanceLuke TosingaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Shock: By: DR Ismah, Ortho DepartmentDocument16 pagesSpinal Shock: By: DR Ismah, Ortho Departmentbosnia agusNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRICS NursingDocument5 pagesPEDIATRICS NursingAndrea Franchesca DelaCruz DescalzoNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoDocument15 pagesNCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet