0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views7 pagesUnderstanding English Conjunctions
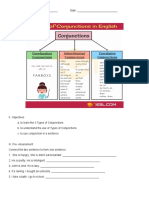
1) Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses. There are three main types of conjunctions in English: coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions.
2) Coordinating conjunctions like and, but, or, and so join elements of equal grammatical rank. Subordinating conjunctions like after, because, and when introduce dependent clauses. Correlative conjunctions like either...or, neither...nor, and both...and work in pairs to connect two items.
3) Conjunctions are an important part of speech that allow for the combination of language elements and the creation of complex sentences. Understanding
Uploaded by
Zehnouni AbderezakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views7 pagesUnderstanding English Conjunctions
1) Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses. There are three main types of conjunctions in English: coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions.
2) Coordinating conjunctions like and, but, or, and so join elements of equal grammatical rank. Subordinating conjunctions like after, because, and when introduce dependent clauses. Correlative conjunctions like either...or, neither...nor, and both...and work in pairs to connect two items.
3) Conjunctions are an important part of speech that allow for the combination of language elements and the creation of complex sentences. Understanding
Uploaded by
Zehnouni AbderezakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd