Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pressure - QP
Uploaded by
PhysicsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pressure - QP
Uploaded by
PhysicsCopyright:
Available Formats
5
3 Fig. 3.1 shows a spring with no load attached. Fig. 3.2 shows the same spring with a load attached.
stand
spring
load
Fig. 3.1 Fig. 3.2
(a) Describe how a student can determine the extension of the spring. You may draw on Fig. 3.1
and Fig. 3.2 as part of your answer.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [3]
© UCLES 2019 0625/31/O/N/19 [Turn over
6
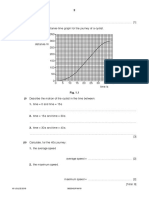
(b) The student plots a graph of load against extension, as shown in Fig. 3.3.
10.0
load / N
9.0
8.0
7.0
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0.0
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40
extension / cm
Fig. 3.3
(i) Determine the extension produced by a load of 7.5 N.
extension = ................................................... cm [1]
(ii) Determine the load that would produce an extension of 10.0 cm.
load = ..................................................... N [1]
(c) Calculate the mass that has a weight of 6.0 N.
mass = .................................................... kg [3]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2019 0625/31/O/N/19
7
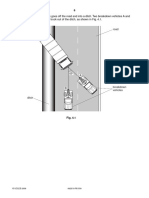
4 Fig. 4.1 shows a tractor fitted with a device for breaking up soil in a field.
device tractor
heavy weight
pivot point soil
Fig. 4.1
(a) (i) The tractor has a heavy weight at the front. Explain why the heavy weight is needed.
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
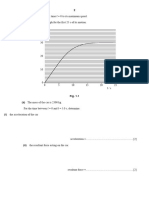
(ii) Fig. 4.2 represents the weight of the device and its distance from the pivot.
pivot
2.1 m
6000 N
Fig. 4.2
Calculate the moment of the weight of the device about the pivot. State the unit.
moment = ........................................................ [4]
© UCLES 2019 0625/31/O/N/19 [Turn over
8
(b) Fig. 4.3 shows a tractor fitted with narrow tyres and the same tractor fitted with wide tyres.
narrow tyre wide tyre
tractor fitted with same tractor fitted with
narrow tyres wide tyres
Fig. 4.3 (view from the front)
Explain why wide tyres are more suitable for the tractor on soft soil.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [3]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2019 0625/31/O/N/19
You might also like
- 2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A CarDocument5 pages2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A CarYakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Safari PDFDocument13 pagesSafari PDFHussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic Questions ForcesDocument9 pagesTopic Questions ForcesJoe Y. MathewNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law QPDocument10 pagesHooke's Law QPgambixo3005No ratings yet
- Hooke's Law QPDocument10 pagesHooke's Law QPbhumika mehtaNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law QPDocument10 pagesHooke's Law QPGiraffe thingNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law QPDocument10 pagesHooke's Law QPNurulAinMatAronNo ratings yet
- Length & Time 2 QPDocument9 pagesLength & Time 2 QPTan Chen WuiNo ratings yet
- Forces Theory QuestionsDocument10 pagesForces Theory Questionsvictor bettNo ratings yet
- Forces 1 QPDocument11 pagesForces 1 QPNam Khanh Peter VuNo ratings yet
- 2023 Specimen Paper 4Document16 pages2023 Specimen Paper 4Olanibi GratitudeNo ratings yet
- 12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023Document3 pages12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- FORM 3 Phy PAPER 4Document22 pagesFORM 3 Phy PAPER 4Sabbath the sign of GodNo ratings yet
- Forces 1 QPDocument11 pagesForces 1 QPAden FatimaNo ratings yet
- Forces 1 QPDocument11 pagesForces 1 QPkhalil rehman100% (1)
- 0625-3jun03 s46413Document2 pages0625-3jun03 s46413shiphrahdon145No ratings yet
- Physics P2 9Document14 pagesPhysics P2 9sara khanNo ratings yet
- Set 61 - Chapter 1Document25 pagesSet 61 - Chapter 1lelon81No ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Ved P4h PratapNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/02Document20 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/02Arslan SarwarNo ratings yet
- Forces 6 QPDocument9 pagesForces 6 QPGiorgioNo ratings yet
- Q2,3Document3 pagesQ2,3PC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Igcse - Physics Density ProblemsDocument7 pagesIgcse - Physics Density Problemsvictor bettNo ratings yet
- Mass & Weight 3 QPDocument11 pagesMass & Weight 3 QPTinevimbo ChimusuwoNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power P2Document69 pagesWork, Energy and Power P2carbohemoglobinNo ratings yet
- 2 Moments Hydraulics CM Self Study QuestionsDocument48 pages2 Moments Hydraulics CM Self Study QuestionsRiyan PurewalNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Maram MohanNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For A Vehicle Accelerating From RestDocument3 pages2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For A Vehicle Accelerating From RestYakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- P 1Document10 pagesP 1ayeshaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Mechanics Part 1Document4 pagesAssessment 1 Mechanics Part 1Nirmani RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Krisha ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-03 at 9.41.01 PMDocument100 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-03 at 9.41.01 PM8f7cbjgh6vNo ratings yet
- 17.1-Energy Work Power-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpDocument10 pages17.1-Energy Work Power-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpsaNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration QnsDocument29 pagesSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration Qnsimaanzuberi123No ratings yet
- Phy Worksheet IG 3 Phase 2Document6 pagesPhy Worksheet IG 3 Phase 2Umair RazaNo ratings yet
- Phys p2Document16 pagesPhys p2Kalana GamageNo ratings yet
- CH 8 3Document9 pagesCH 8 3Muhammad ZainNo ratings yet
- 1Document7 pages1zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Phys p2Document16 pagesPhys p2Kalana GamageNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter KinematicDocument3 pagesPages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter Kinematiclelon81No ratings yet
- Forces 3 QPDocument7 pagesForces 3 QPItz MeNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and MeasurementDocument8 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Measurementmanya mustafaNo ratings yet
- Work & EnergyDocument13 pagesWork & EnergySelina LINo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QP-Samra-No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPmexicohunt6No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPRahat RizwanNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPItz MeNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Dynamics)Document6 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Dynamics)Syed Jawwad JD JamaliNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42...No ratings yet
- Assessment April 18Document7 pagesAssessment April 18wajeehmohsin96No ratings yet
- Forces & Braking 3 QPDocument15 pagesForces & Braking 3 QPdeepheat_008No ratings yet
- Physics Paper 3 SLDocument33 pagesPhysics Paper 3 SLSaniya DautovaNo ratings yet
- Pressure in Fluids QPDocument9 pagesPressure in Fluids QPIbrahim MehmoodNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicswabumundupallaso076No ratings yet
- Fa Wa600-3 - Gen00090-00Document37 pagesFa Wa600-3 - Gen00090-00Robet carlesNo ratings yet
- Physics Year 10 Assessment TestDocument16 pagesPhysics Year 10 Assessment TestJoyceNo ratings yet
- 11C Specified CTDocument6 pages11C Specified CTadilNo ratings yet
- Vectors UpdatedDocument16 pagesVectors UpdatedppsppcyhbsNo ratings yet
- Q1. The Diagram Shows A Fork-Lift Truck With A Load of 2.4 Kn. The Clockwise MomentDocument9 pagesQ1. The Diagram Shows A Fork-Lift Truck With A Load of 2.4 Kn. The Clockwise Momentdeepheat_008No ratings yet
- Solid State PhysicsDocument5 pagesSolid State PhysicsPhysicsNo ratings yet
- IGCSE PHYSICS Revision 2 - MomentsDocument9 pagesIGCSE PHYSICS Revision 2 - MomentsPhysicsNo ratings yet
- M1 Kinematics - 1D Vectors & Calculus 2 QPDocument3 pagesM1 Kinematics - 1D Vectors & Calculus 2 QPPhysicsNo ratings yet
- M1 Kinematics - 1D Vectors & Calculus 1 QPDocument4 pagesM1 Kinematics - 1D Vectors & Calculus 1 QPPhysicsNo ratings yet
- 2022 Grade 10 Study GuideDocument85 pages2022 Grade 10 Study Guideeskaykhan11No ratings yet
- Final Edit Na Talaga ToDocument82 pagesFinal Edit Na Talaga ToExequel DionisioNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Lecture 04Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics - Lecture 04Danny SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Lego RoboticsDocument6 pagesLego RoboticsMohd Asri TaipNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions Set 2 Introduction To AccountingDocument3 pagesMCQ Questions Set 2 Introduction To AccountingHsiu PingNo ratings yet
- CV Achmad AgusDocument11 pagesCV Achmad AgusWoori ConsultingNo ratings yet
- BED SyallabusDocument32 pagesBED Syallabushp4cool9660No ratings yet
- Special Theory of RelativityDocument16 pagesSpecial Theory of RelativityBrigita SteffyNo ratings yet
- Code For VirtualboxDocument1 pageCode For VirtualboxAnonymous 4m8ueTNo ratings yet
- TOC - Building in TimeDocument3 pagesTOC - Building in Timemillerka2No ratings yet
- Scribd Sap SD Pricing in Depth Configuration GuideDocument136 pagesScribd Sap SD Pricing in Depth Configuration GuideRavi SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Strength of Materials 5691845f3ea8eDocument13 pagesDokumen - Tips Strength of Materials 5691845f3ea8eJay GeeNo ratings yet
- Put An ACE in The Hole: Vam Top Vam Top HC Vam Top HT Vam Top Fe New VamDocument8 pagesPut An ACE in The Hole: Vam Top Vam Top HC Vam Top HT Vam Top Fe New VamjoseNo ratings yet
- Deed of Sale SampleDocument3 pagesDeed of Sale Samplebarbiegirl9497No ratings yet
- Did Tucson City Attorney Mike Rankin Commit A Half Million Dollar Fraud On Tucson Taxpayers?Document4 pagesDid Tucson City Attorney Mike Rankin Commit A Half Million Dollar Fraud On Tucson Taxpayers?Roy Warden50% (2)
- Mechanisms of Nutrient Uptake of Plant Root Cells From SoilDocument47 pagesMechanisms of Nutrient Uptake of Plant Root Cells From SoilMaha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cut Pieces: From Flat Plates, Strips and Coil Stock. A. Shearing B. Bend Allowance C. Forming Dies D. Spring BackDocument100 pagesCut Pieces: From Flat Plates, Strips and Coil Stock. A. Shearing B. Bend Allowance C. Forming Dies D. Spring BackJade DigNo ratings yet
- ISTH v50 Porto Rico 2006 Trabalho Filme Morango OFSDocument169 pagesISTH v50 Porto Rico 2006 Trabalho Filme Morango OFSAlexandra MamedeNo ratings yet
- IBP1941 14 Fatigue of Pipelines Subjecte PDFDocument10 pagesIBP1941 14 Fatigue of Pipelines Subjecte PDFAnjani PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Inviscid, Incompressible FlowDocument57 pagesFundamentals of Inviscid, Incompressible FlowpaariNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesPeriodic Trends Lesson PlanWadé AzuréNo ratings yet
- On Campus BA - Consultant JDDocument2 pagesOn Campus BA - Consultant JDSivaramakrishna SobhaNo ratings yet
- How Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherDocument9 pagesHow Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherjohnteecubeNo ratings yet
- NEB Syllabus For Class 12 Science PhysicsDocument4 pagesNEB Syllabus For Class 12 Science Physicskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Peh 12 Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument12 pagesPeh 12 Reviewer 3RD QuarterRalph Louis RosarioNo ratings yet
- Zulfia Karimova - ENGLISHDocument13 pagesZulfia Karimova - ENGLISHtncj664sp6No ratings yet
- Induction Motor NotesDocument20 pagesInduction Motor NotesMani SaiNo ratings yet
- Study of Steam Generation Units With Their Accessories and MountingsDocument64 pagesStudy of Steam Generation Units With Their Accessories and MountingsMasudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Customized ListDocument6,024 pagesCustomized ListItiNo ratings yet
- Oslo Mihai Neacsu, IcpeDocument12 pagesOslo Mihai Neacsu, IcpeMihaiNeacsuNo ratings yet