Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AO1 Quiz Transport Across Membranes
Uploaded by
Faiza Hamid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesOriginal Title
AO1 Quiz transport across membranes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesAO1 Quiz Transport Across Membranes
Uploaded by
Faiza HamidCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
AO1 Quiz- Transport across membranes
1) What is the difference between a plasma membrane and a cell surface
membrane? (1)
2) What is the role of cholesterol in cell surface membranes? (3)
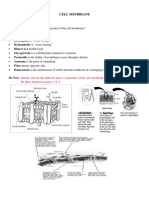
3) Describe the basic structure of cell surface membranes, and of membrane
bound organelles in eukaryotes e.g. chloroplast and mitochondria (3)
4) Describe the fluid mosaic model of the cell surface membrane (6)
5) Why is this model known as the fluid mosaic model? (2)
6) What is the difference between an extrinsic and intrinsic protein? (1)
7) What is the role of a glycoprotein? (1)
8) What is the role of a glycolipid? (1)
9) Define simple diffusion (1)
10)Define facilitated diffusion (1)
11)Define osmosis (1)
12)Define active transport (1)
13)How is the simple diffusion of many molecules restricted across the
phospholipid bilayer? (1)
14)Explain the process of co-transport of amino acids/glucose in the ileum (5)
15)How are mitochondria adapted for carrying out a fast rate of respiration? (2)
16)Name 3 factors that can affect the rate of facilitated diffusion (3)
Answers
1) All membranes are ‘plasma membranes’ and are all made up of a
phospholipid bilayer. The term ‘cell-surface membrane’ is only used to
describe the plasma membrane that makes up the cell membrane
2) Regulates fluidity, increases stability and has a role in preventing loss of water
as it is hydrophobic
3)
a. Phospholipids are arranged as bilayer in membrane
b. The phosphate head is hydrophilic/polar and the fatty acid tail is
hydrophobic/non-polar
c. The heads are located on the outside and the tails are attracted to
each other on the inside
4)
a. The cell surface membrane is a phospholipid bilayer
b. Which is made up of phospholipids and proteins
c. Phospholipid molecules are arranged ‘Tails to tails’
d. With ‘floating’ protein molecules that are able to move in the
membrane
e. Intrinsic proteins extend through bilayer
f. Extrinsic proteins in one single outer layer only;
g. Channel proteins are embedded into the cell surface membrane
which have a role in transport of molecules (e.g. water, ions)
h. Glycoproteins are embedded into the cell surface membrane
which have a role as receptors of hormones/neurotransmitters
i. Presence of cholesterol in the cell surface membrane
j. which regulates fluidity, increases stability and has a role in
preventing loss of water as it is hydrophobic
5)
a. Molecules within the membrane are able to move
b. due to the mixture of phospholipid and protein / arrangement of
protein
6) Intrinsic proteins extend through the bilayer whereas extrinsic proteins are in a
single outer layer
7) Are embedded into the cell surface membrane which have a role as receptors
of hormones/neurotransmitters
8) Used in cell recognition and for stability of cell membrane
9) Movement of non-polar/lipid soluble molecules from an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration, down the concentration
gradient. Doesn’t use carrier or channel proteins or ATP
10)Movement of polar/water soluble molecules from an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration, down the concentration
gradient. Uses a carrier or channel proteins but doesn’t use ATP
11)Movement of water molecules from a high water potential to a low water
potential through, down the water potential gradient. Uses channel proteins
but doesn’t use ATP
12)Movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high
concentration, against the concentration gradient. Uses a carrier protein and
energy from the hydrolysis of ATP
13)Only lipid soluble molecules (not water soluble) can diffuse across due to the
hydrophobic nature of the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids
14)
a. Sodium ions are actively transported from the epithelial cell to the
blood
b. This maintains/forms a concentration gradient for sodium ions to enter
the epithelial cells from the ileum by diffusion
c. Glucose/amino acid moves into the epithelial cell from the ileum with
the sodium ion
d. Via (carrier / channel) protein
e. Glucose/amino acid then moves into blood by facilitated diffusion
15)
a. They have a folded inner membrane that provides a large surface area
b. to have an increased number of protein channels and carrier proteins
that are involved in the respiratory reactions
16)
a. Having a large surface area with more channel proteins embedded into
it
b. Having a steep concentration gradient
c. Having a higher temperature
You might also like
- Cooling System, Service MP7 EPA2004, EPA2007Document150 pagesCooling System, Service MP7 EPA2004, EPA2007Hamilton MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes and Transport As BiologyDocument41 pagesCell Membranes and Transport As BiologyADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- UNIT I (Cell - Transport Mechanisms)Document20 pagesUNIT I (Cell - Transport Mechanisms)Rex Daniel Tingson100% (1)
- Cell MebraneDocument10 pagesCell MebraneChandra SihombingNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyDocument51 pagesCell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyChester WengerNo ratings yet
- 2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDocument6 pages2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDuong TongNo ratings yet
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Functionapi-455371000No ratings yet
- IB HL Biology Notes Cell MembranesDocument12 pagesIB HL Biology Notes Cell MembranesayushfmNo ratings yet
- 0000001743-Calculation Report Conveyor Structure T-1022Document29 pages0000001743-Calculation Report Conveyor Structure T-1022Shada Mohammed96% (27)
- How To Build An Afghan Box Camera A5 2013 PDFDocument30 pagesHow To Build An Afghan Box Camera A5 2013 PDFs fNo ratings yet
- UNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument16 pagesUNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated MotionSahat Rein Jeremay PardedeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - Questions中华雅思王No ratings yet
- ECE 2416 JKUAT 2021 - Lecture NotesDocument52 pagesECE 2416 JKUAT 2021 - Lecture NotesThomasNo ratings yet
- C9e Answers Active Reading 07Document7 pagesC9e Answers Active Reading 07Daniel DHizzy Hizgilov83% (18)
- BEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument201 pagesBEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFMax DurendNo ratings yet
- 008 - The Cell Surface MembraneDocument2 pages008 - The Cell Surface MembraneSanah KhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 MembranesDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 5 MembranesNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3Document8 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3MSKNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review ANSWERSDocument7 pagesCell Transport Review ANSWERSAnonymous pUJNdQNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument30 pagesTransport MechanismsApril VeraNo ratings yet
- Cells: DetailsDocument109 pagesCells: DetailsAishwarya SivakumarNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Document6 pagesAP Biology Outline - Chapter 5Omar LopezNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Pre-ReadingDocument7 pagesCh. 5 Pre-ReadingDJ ISAACS50% (2)
- Biology Module 2: Section 2.5Document20 pagesBiology Module 2: Section 2.5Nasteexo CaliNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Membranes (Main)Document53 pages1.3 Cell Membranes (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- BioPhysics New MCQDocument95 pagesBioPhysics New MCQAchraf RabadiNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane The Big PictureDocument4 pagesPlasma Membrane The Big PictureNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Q2Document20 pagesGen Bio - Q2Mary Angel DimasacatNo ratings yet
- KANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument6 pagesKANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneKaness MathzNo ratings yet
- Biol Worksheet 2013 Grade 11thDocument5 pagesBiol Worksheet 2013 Grade 11thendalew damtieNo ratings yet
- PhysioDocument81 pagesPhysioDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - DissertationDocument7 pagesCell Biology - Dissertationprerana chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Biology 110 (Section 152) - Intro To Biology & Society (Fall 2019)Document3 pagesBiology 110 (Section 152) - Intro To Biology & Society (Fall 2019)John MixerNo ratings yet
- 5. Cấu Trúc Màng Tế Bào - HằngDocument7 pages5. Cấu Trúc Màng Tế Bào - Hằngngoccanh10493No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study Guide AK - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Study Guide AK - Cell Structure and Functionweijun wuNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.3: Membrane Structures: Key FactsDocument3 pagesTopic 1.3: Membrane Structures: Key FactsArvinNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Exam in General Biology IDocument5 pagesSecond Quarter Exam in General Biology IAubrey SalidoNo ratings yet
- DLaboratory Actiivty 3 - Cellular Basis of LifeDocument5 pagesDLaboratory Actiivty 3 - Cellular Basis of LifeSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Document7 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Astrii LyNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectDocument53 pagesSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoNo ratings yet
- The Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument7 pagesThe Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneAlya HusnaNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Membrane StructureDocument3 pagesAssignment For Membrane Structurejane austin lynn rebancosNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes - Role and Structure 1Document6 pagesCell Membranes - Role and Structure 1ariko471No ratings yet
- C2022 Topic 1.3 and 1.4 QuizDocument5 pagesC2022 Topic 1.3 and 1.4 Quizlprinsloo75No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesCell BiologyNoelia MaizaNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesDocument11 pagesThe Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesSyeda Kaneez Mohammadi MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationFaheymNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Bio 110 - Chapter 5Document32 pagesBio 110 - Chapter 5moayadNo ratings yet
- 1 3+1 4+1 6Document2 pages1 3+1 4+1 6Thalia VladimirouNo ratings yet
- ClaseDocument7 pagesClasef.tellelopezNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 4 CIE Biology A-Level PDFDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 4 CIE Biology A-Level PDFoqypooNo ratings yet
- The Working Cell: Chapter ObjectivesDocument12 pagesThe Working Cell: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellDocument94 pagesChapter 3 Cellmohamedshilleh7No ratings yet
- Pertanyaan SGDDocument6 pagesPertanyaan SGDMartinoKhanzaniaNo ratings yet
- 2a-Membranes and Transport 2Document67 pages2a-Membranes and Transport 2kfy8vr7wtwNo ratings yet
- Simple Notes - Paper I PhysiologyDocument147 pagesSimple Notes - Paper I PhysiologyArrya DSNo ratings yet
- Physio 1 Day MainDocument302 pagesPhysio 1 Day Mainanup raoNo ratings yet
- Transport of Substances Through Cell MembranesDocument34 pagesTransport of Substances Through Cell MembranesSanchezNo ratings yet
- Biology Essay QuestionsDocument117 pagesBiology Essay QuestionsRemas HarthyNo ratings yet
- Bimenyimana Bio ExercisesDocument119 pagesBimenyimana Bio Exercisesmunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Nelson Biology Answers 1Document2 pagesNelson Biology Answers 1ritaNo ratings yet
- NSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer KeyDocument43 pagesNSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer Keygian leepsuNo ratings yet
- Spare Part List - LJ 320P - 20110316Document54 pagesSpare Part List - LJ 320P - 20110316Henrique J. AntunesNo ratings yet
- A Refinery Pan BatchDocument5 pagesA Refinery Pan Batchmuhammad alaik nailal HudaNo ratings yet
- Flexural Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam SectionsDocument15 pagesFlexural Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam SectionsAamir HaideriNo ratings yet
- 2013 Influence of Gel Content On The Physical Properties of Unfilled and Carbon Black Filled PDFDocument32 pages2013 Influence of Gel Content On The Physical Properties of Unfilled and Carbon Black Filled PDFPilar MayaNo ratings yet
- Jayden Almeida - Investigating Projectile Motion Lab Marble LauncherDocument2 pagesJayden Almeida - Investigating Projectile Motion Lab Marble Launcherapi-537729628No ratings yet
- Science Speed of Sound WorksheetsDocument1 pageScience Speed of Sound Worksheetsbart PorcadillaNo ratings yet
- Cyclotron Safety Manual 1981Document24 pagesCyclotron Safety Manual 1981Eskadmas BelayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Association of Vanadium Compounds in Heavy Oil and Bitumen, and Implications For Their Selective RemovalDocument14 pagesChemistry and Association of Vanadium Compounds in Heavy Oil and Bitumen, and Implications For Their Selective RemovalMelNo ratings yet
- MET 52 3 337 340 RudolfDocument4 pagesMET 52 3 337 340 RudolfEduardo FlorianoNo ratings yet
- 01-Mi-Dti Cut Sheet 0715Document2 pages01-Mi-Dti Cut Sheet 0715Marvin EstradaNo ratings yet
- Climate ZonesDocument2 pagesClimate Zonesapi-308047560No ratings yet
- SG Test3MCQ 64ac8bc86f1720.64ac8bcaa19898.54250131Document34 pagesSG Test3MCQ 64ac8bc86f1720.64ac8bcaa19898.54250131390108263No ratings yet
- Adiabatic Ideal GasDocument4 pagesAdiabatic Ideal GasMaria AngelinNo ratings yet
- Gas-Vapor Mixtures and Air-Conditioning: Çengel BolesDocument37 pagesGas-Vapor Mixtures and Air-Conditioning: Çengel Boleskebaman1986No ratings yet
- Worksheet Phy 11Document10 pagesWorksheet Phy 11kcricketer75No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells AbstractDocument3 pagesHydrogen Fuel Cells AbstractAKNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Characteriation of P-N Junction DiodeDocument11 pagesFabrication and Characteriation of P-N Junction Diode12343567890No ratings yet
- Nptel - Ac.in Courses IIT-MADRAS Applied Thermodynamics Module 4 6 AsdcDocument4 pagesNptel - Ac.in Courses IIT-MADRAS Applied Thermodynamics Module 4 6 AsdcSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Bell-Type Inequalities On The IBM's Open-Access Quantum ComputerDocument5 pagesAnalysis of The Bell-Type Inequalities On The IBM's Open-Access Quantum ComputerYulied Porras RamírezNo ratings yet
- Quantum Numbers and Electron Configuration: Group 8 11-St. Camill Us de LellisDocument10 pagesQuantum Numbers and Electron Configuration: Group 8 11-St. Camill Us de LellisRyzellNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometers Coupled To Thermal AnalysisDocument24 pagesFourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrometers Coupled To Thermal Analysisc_passerino6572No ratings yet
- Beam 189Document1 pageBeam 189Vinay RaiNo ratings yet
- 3 CH 6Document149 pages3 CH 6eeesolomon2124No ratings yet
- DX Evaporator Eng00013632 PDFDocument10 pagesDX Evaporator Eng00013632 PDFYaretiNo ratings yet