Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Current & Its Effect HO
Uploaded by
chrisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Current & Its Effect HO
Uploaded by
chrisCopyright:
Available Formats
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
HANDOUT
NAME: _______________________ REF: 2022-23/ Science/STD 7/ HO
CLASS: VII SUBJECT: SCIENCE
DATE: TOPIC: ELECTRIC CURRENT & ITS EFFECT
ELECTRIC CURRENT AND ITS EFFECTS
Electricity: Electricity is a form of energy which is produced by the tiny charged particles
such as electrons.
Electrical energy is the most useful form of energy as it can easily be converted into
various other forms of energy such as heat energy, light energy, mechanical energy
and chemical energy.
Electric current:
The flow of electric charges in a circuit (through conductor) is called electric current.
• The SI unit of electric current is ampere and denoted by A.
• An electric current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the cell.
Electric circuit:
The closed path along which the electric current flows from one terminal to another is
called as an electric circuit.
A circuit consists of an electric cell, devices which use the electrical energy, a switch
and connecting wires. These all are called components of the circuit or circuit
elements.
• If any part of a circuit is broken, electric current does not flow through it and
such a circuit is called an open circuit.
• If there are no breaks in a circuit, it provides a closed and continuous path for
the flow of electric current and such a circuit is called a closed circuit.
• Electric current can flow only through closed circuit
Page 1 of 7 Copyright © Global Indian International School
Components of an electric circuit:
Cell or battery:
• A cell is a source of current.
• It has a positive and a negative terminal.
• When two or more cells are connected such that the positive terminal of one
cell touches the negative terminal of the other, it forms a battery.
• They can be connected in series or in parallel.
Switch:
• A switch is used to close or open a circuit.
• When the switch is off, the circuit is open and no current flows through it.
• When the switch is on, the circuit is closed allowing current to flow.
Electrical appliance:
• An electrical appliance is a device that uses the current flowing through it to
function.
• Electric bulbs, electric iron, fans, electric motors are some commonly used
electrical appliances in our daily life.
Wires:
• Wires connect the components of the electric circuit. They are made up of
materials that are good conductors of electricity such as copper.
•
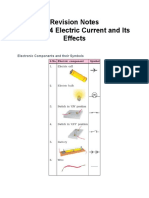
Electrical Symbol
component
1. Cell
2. Battery
3. Open Switch
4. Close Switch
5. Wire
6. Bulb
7. Fuse
Circuit diagram:
A schematic diagram that represents an electric circuit using the standard symbols
of the components used in the circuit is called a circuit diagram.
Page 2 of 7 Copyright © Global Indian International School
Effects of electric Current
• Heating effect - Heating of Electric iron
• Magnetic effect - Working of electric bell
• Mechanical effect - Working of Vacuum cleaner
• Chemical effect - Polishing of artificial jewellery
Heating effect of electric current:
• Production of heat in an electric device due to the flow of electric current is called the
heating effect of electric current.
• When electric current pass through a high resistance wire, the electric energy gets
converted into heat energy and this heat energy heats up the wire.
• The degree to which a material opposes the passage of current through itself is known
as its resistance.
• All the heating devices have a coil of wire called an element. The heating element is
made up of metal alloy called nichrome (alloy of nickel, chromium and often iron).
Factors on Which the Heating Effect of Current Depends:
(i) Resistance of wire: Greater the resistance of a wire, greater will be the heat produced
in it by a given current. The resistance and thus the heat that is produced in the wire
depends upon-
a. The material of the wire- Resistance of nichrome wire is more than that of the copper wire.
b. The length of the wire- Resistance increase with increase in the length of wire.
c. The thickness of the wire- Resistance and the heat produced decreases if thickness of the
wire increases.
(ii) Magnitude of current passed through a given wire: If the magnitude of current passed
through a given wire is greater, then the heat produced in it will also be greater.
Applications of the Heating Effect of Current
1. For the working of electrical heating appliances.
• The appliances such as water heater, electric room heater, electric iron, etc.
work on the heating effect of the electric current.
Page 3 of 7 Copyright © Global Indian International School
• All the devices have a coil of nichrome wire (element) that have high
resistance to electric current and can withstand high temperatures.
• When the appliance is switched on, the element becomes red hot and give out
heat.
2. The heating effect of electric current is utilised in the electric bulbs.
• A bulb has a thin filament of tungsten metal. Tungsten has a very high
resistance and very high melting point.
• When an electric current pass through the filament, its heat up quickly to about
2500 degree Celsius and begins to glow and emits light.
• Disadvantage- In Incandescent light bulb large amount of electricity consumed
by the filament is converted into heat and only small part of electricity is
converted to light. This results in the wastage of electricity. So, this wastage
can be decreased by using compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) or Light emitting
diodes (LEDs).
Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs) - Fluorescent light do not have filament. It
contains mercury vapour which emits ultra violet radiation when current passes
through it. The inside of glass tube is coated with an opaque white material called
‘phosphor’. Phosphor absorb the UV radiations emitted by mercury and glow to emit
white light. It uses 70% less electricity.
3. Electric fuse
Electric fuse works on the principle of the heating effect of electric current.
• A fuse is a safety device that breaks a circuit in times of overloading. Thus it
prevent electric fire or damage to electrical appliances due to excessive flow of
current.
A fuse is a thin wire of short length that melts easily when heated. The fuse wire is
made from an alloy of tin and lead and has high resistance and low melting point.
• We should not use a thick wire as a fuse wire as it will have low resistance and
will not get heated.
Page 4 of 7 Copyright © Global Indian International School
• In Fuse wire a copper wire cannot be used because it has a high melting point
and will not break when a high electric current passes through it.
• Cartridge fuses are provided in appliances like refrigerators, television sets,
geysers etc. to prevent damage from excessive current flow and during short
circuit.
Cause of Large Current Flow in Household Electric Wiring
1. Overloading- It is a situation when too many electrical appliances are
connected to a single socket, they draw an extremely large amount of current from
the household circuit. As a result, the load on the circuit increases and it can lead to a
short circuit or fire.
2. Short Circuit- When the insulation of wires (the live wire and the neutral wire)
gets torn away, the wires can come in contact with each other, large current flows
through the household wiring which cause a spark or may lead to a fire. This touching
of live wire and neutral wire directly is known as a short circuit.
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)-
• MCB does not work on the heating effect of current. It works on the magnetic
effect of current.
• These switches automatically turn OFF when the current in a circuit exceeds
the safe limit. We turn them ON and the circuit is once again completed.
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
When an electric current is passed through a wire it behaves like a magnet. This is
called the magnetic effect of the electric current.
• Scientist Hans Christian Oersted found that when an electric current is passed
in a wire, then the compass needle placed near it got deflected from its usual
position.
• The magnetic effect is increased if we use a long coil of wire instead of straight
wire.
Page 5 of 7 Copyright © Global Indian International School
Electromagnet-
An Electromagnet is a material that act as a magnet when a current flows through its
coil.
• Electromagnet is a temporary magnet which behaves like a magnet only when
electric current flows through it. When the electric current is switched off it
loses its magnetism.
• It consists of a magnetic material such a soft iron piece and the coil of
insulated copper wire tightly wound around it.
• Core- The material on which the insulated wire is wound is called its core
The factors through which an electromagnet can be made stronger are-
1. By increasing the amount of current flowing through the coil.
2. By increasing the number of turns forming the coil.
Applications of electromagnet:
• These magnets are used in electrical appliances such as an electric bell,
electric fan, electric motor, telephone instruments, TV, etc.
• Used in electric cranes to lift iron and other magnetic materials.
• For the magnetic separation of iron ores from the earthly substances,
electromagnets are used.
• For preparing strong permanent magnets.
• In CT/ MRI scanning for medical diagnosis.
• Eye doctors use electromagnets to remove tiny particles of magnetic material
that have accidentally fallen in the eye.
Electric Bell
• An electric bell is a device in which to and fro movement of a smaller hammer
(or clapper) on a gong produces the sound of a bell.
• It works on the principle of magnetic effect of current, i.e. electromagnetism.
Page 6 of 7 Copyright © Global Indian International School
Construction and Working of an Electric Bell-
Contact
P
Screw
screscrew
Construction:
• The electric bell has a U-shaped electromagnet.
• There is a small iron bar called armature which is held in front of the poles of
the electromagnet.
• The lower end of the iron bar is attached to a flat spring which is fixed to a
metal bracket.
• The upper end of the iron bar has a clapper/hammer attach to it.
• A metal gong is fixed near the clapper.
Working-
• When the bell is pressed, the contact screw touches the iron strip and the
circuit is completed.
• The current starts flowing through the coil.
• The electromagnet becomes magnetised and the soft iron armature is
attracted towards the electromagnet. The movement of the iron causes the
hammer to hit the gong.
• This movement breaks the circuit at contact point P of contact screw, so that
the current stops flowing and switches off the electromagnet.
• The spring pulls the armature back to its original position, the circuit is remade
and the process starts over again. This is how the bell rings.
Page 7 of 7 Copyright © Global Indian International School
You might also like
- Electronics by Sir JoelDocument47 pagesElectronics by Sir JoelDann SarteNo ratings yet
- E201 - Elec Inspection Test Plan Template Rev 00 11.11Document15 pagesE201 - Elec Inspection Test Plan Template Rev 00 11.11Arbaaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Pre Commissioning Tests ChecklistDocument9 pagesPre Commissioning Tests ChecklistFeroz Hakkim80% (5)
- Electric Current and Its Effects - NotesDocument9 pagesElectric Current and Its Effects - Notessmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- PPPPPPDocument3 pagesPPPPPPGOD OF GLITCH.No ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its EffectDocument21 pagesElectric Current and Its EffectPrisha SwamNo ratings yet
- Csir NML Training Deepak PDFDocument26 pagesCsir NML Training Deepak PDFAnabiya NoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Student S BookDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Student S BookIre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 Electric Current and Its Effects: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument1 pageChapter - 14 Electric Current and Its Effects: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksSufi SoulNo ratings yet
- UIIS W Revision Notes Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument5 pagesUIIS W Revision Notes Electric Current and Its Effectsjonathanshiroj10No ratings yet
- G7 CBSE - Electric Current and Its Effects - ANAND KUMARDocument2 pagesG7 CBSE - Electric Current and Its Effects - ANAND KUMARAnandNo ratings yet
- Q1L7 ElectricityDocument61 pagesQ1L7 ElectricityCarmella Raguindin100% (1)
- Chapter - 14: Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument10 pagesChapter - 14: Electric Current and Its EffectsDhruv GuptaNo ratings yet
- 14 Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument10 pages14 Electric Current and Its EffectsSnehil VargheseNo ratings yet
- Class 7TH Electric Current and Effects NotesDocument22 pagesClass 7TH Electric Current and Effects NotesSaurabh Gupta100% (1)
- Unit 4 ElectricityDocument34 pagesUnit 4 ElectricityCesca DalisayNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument3 pagesClass 7 Electric Current and Its EffectsNitesh KohliNo ratings yet
- Notes Electric Current and Its Effects GR 7Document9 pagesNotes Electric Current and Its Effects GR 7minecraftpriyansh232No ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument4 pagesElectric Current and Its EffectsKunal SumukNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Prepared By: Puan Farizah Binti AriffinDocument49 pagesElectricity: Prepared By: Puan Farizah Binti AriffinAzyyati Azahari0% (1)
- Electrical and Machine SafetyDocument49 pagesElectrical and Machine SafetyJely Taburnal Bermundo100% (1)
- PRELIMDocument23 pagesPRELIMJames SelibioNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument96 pagesLab ManualASWANI RAJAN50% (2)
- Electric Power and Household CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectric Power and Household Circuitsshubham kumar ramNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Machine SafetyDocument49 pagesElectrical and Machine SafetyJely Taburnal BermundoNo ratings yet
- Electic Current NotesDocument6 pagesElectic Current Notesnaikkt24No ratings yet
- Ch-14 Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument5 pagesCh-14 Electric Current and Its Effectstanshikha dharNo ratings yet
- Grade-Vi Science - Worksheet Term-2 Ch-12-Electricity and CircuitsDocument4 pagesGrade-Vi Science - Worksheet Term-2 Ch-12-Electricity and CircuitsmohinderNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Electricityjustin christopher antonioNo ratings yet
- Notes PHYSICSDocument6 pagesNotes PHYSICSAryaan LaskarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ElectricityDocument20 pagesUnit 4 ElectricityManan Goyal.No ratings yet
- Group 6 - Electrical SafetyDocument14 pagesGroup 6 - Electrical SafetyNiña Marie RoblesNo ratings yet
- CE115 Electrical Part ADocument45 pagesCE115 Electrical Part AMrSamspartNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its Effects - NoteDocument6 pagesElectric Current and Its Effects - NoteToshit Kumar NaikNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter-14 Electric Current and Its Effects: Electronic Components and Their SymbolsDocument11 pagesRevision Notes Chapter-14 Electric Current and Its Effects: Electronic Components and Their SymbolsRaman -No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ElectricityDocument33 pagesBasic Concepts of ElectricitykpchakralaNo ratings yet
- Electric PowerDocument36 pagesElectric PowerfruqaiyahamzaNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Grade 9Document9 pagesElectricity - Grade 9nidda beeNo ratings yet
- Beee PPT LN 5Document25 pagesBeee PPT LN 5Omprakash GNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Electrical InstallatiosDocument34 pagesUnit-V Electrical Installatiosnaveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Electrical InstallatiosDocument32 pagesUnit-V Electrical Installatiosltsreeram12No ratings yet
- Lightning ProtectionDocument15 pagesLightning ProtectionEnglish words BY Utkarsh johriNo ratings yet
- Amta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical SafetyDocument67 pagesAmta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical Safetydunlut pelemNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10th NotesDocument3 pagesElectricity Class 10th Notesyo yeNo ratings yet
- Notes - Electricity (Mick)Document10 pagesNotes - Electricity (Mick)SoniaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument5 pagesPhysics ProjectAgnivo SahaNo ratings yet
- House Wiring MCB MAVDocument7 pagesHouse Wiring MCB MAVP. ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- English Group 4Document26 pagesEnglish Group 4Erine Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Notes:: Electric Current & Its EffectsDocument2 pagesNotes:: Electric Current & Its EffectsJaynarayan HalderNo ratings yet
- Simple House Wiring With MCB or Fuse Project: Wire (Or Positive), and AnotherDocument6 pagesSimple House Wiring With MCB or Fuse Project: Wire (Or Positive), and AnotherP. ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Electric CircuitDocument30 pagesLesson 8 Electric CircuitRonnie AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument11 pagesElectric Current and Its EffectsRajeevSangam100% (1)
- Unit 4: Electricity: IHM Notes Site - Hotel EngineeringDocument25 pagesUnit 4: Electricity: IHM Notes Site - Hotel EngineeringEr Navaraj ParajuliNo ratings yet
- Electricity Lesson 1: Electron TheoryDocument11 pagesElectricity Lesson 1: Electron TheoryMarie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Conductors - Report in ScienceDocument16 pagesConductors - Report in ScienceRose JumagdaoNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument13 pagesBuilding Constructionaakash purohitNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Fire Fighting ServicesDocument106 pagesElectrical and Fire Fighting ServicesBUNTI MNNo ratings yet
- Circuits in Electrical System-MatshikaDocument17 pagesCircuits in Electrical System-Matshikawillard sitholeNo ratings yet
- Aditya College of Allied Health ScienceDocument23 pagesAditya College of Allied Health ScienceApurv RajNo ratings yet
- ESC IV: Introduction To Electronics and Electrical EngineeringDocument43 pagesESC IV: Introduction To Electronics and Electrical EngineeringChirag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Children's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Cavotec Connectors - A Manufacturing Company of The Cavotec GroupDocument1 pageCavotec Connectors - A Manufacturing Company of The Cavotec GroupAshok AeroNo ratings yet
- 6V6GT-STR DATASHEET TubeAmpDoctorDocument1 page6V6GT-STR DATASHEET TubeAmpDoctorRafael SantanaNo ratings yet
- Price List Connector: Connector Type Colore Color Fase Phase Code PR 1-5pcs PR 6-50 Pcs PR 50 PcsDocument1 pagePrice List Connector: Connector Type Colore Color Fase Phase Code PR 1-5pcs PR 6-50 Pcs PR 50 PcsscacchiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 Induction Motors IDocument2 pagesTutorial 9 Induction Motors IAkshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- UC22/UC27: Aftermarket Parts ListDocument14 pagesUC22/UC27: Aftermarket Parts ListAmmar BaigNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Mosfet PDFDocument21 pagesShort Notes Mosfet PDFAnant GoyalNo ratings yet
- 500-kHz Half-Bridge DC-DC ConverterDocument17 pages500-kHz Half-Bridge DC-DC Converteratkxyz777100% (1)
- Influence of Third Harmonic Circulating Currents in Selecting Neutral Grounding DevicesDocument8 pagesInfluence of Third Harmonic Circulating Currents in Selecting Neutral Grounding DevicesAnonymous BBX2E87aHNo ratings yet
- Impedance Neutral Grounding Assembly Installation and Maintenance InstructionsDocument10 pagesImpedance Neutral Grounding Assembly Installation and Maintenance InstructionsRodNo ratings yet
- EXB19027 - Brochure - Galion Low ResDocument24 pagesEXB19027 - Brochure - Galion Low ResHwei Hwa LimNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Mesin ABBDocument10 pagesJurnal Mesin ABBAndi Adriani AdiwijayaNo ratings yet
- sjzl20094551-ZXDL01 T110 T010 S105 & ZXDL02 T804 (V1.0R01M01) Power Supply LightDocument55 pagessjzl20094551-ZXDL01 T110 T010 S105 & ZXDL02 T804 (V1.0R01M01) Power Supply Lightgonshui gonshuiNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Cogging and CrawlingDocument2 pagesInduction Motor Cogging and CrawlingChandaKundaNo ratings yet
- RZE2M114Document56 pagesRZE2M114zainahmedscribdNo ratings yet
- Fusology PDFDocument34 pagesFusology PDFharshv3No ratings yet
- 1 Tle5206 2 - 1Document23 pages1 Tle5206 2 - 1Fran CastanoNo ratings yet
- Application of AC Motors and Drives in Steel Industries: A K Paul, I Banerjee, B K Santra and N NeogiDocument5 pagesApplication of AC Motors and Drives in Steel Industries: A K Paul, I Banerjee, B K Santra and N NeogiMohamed Elsaid El ShallNo ratings yet
- ANSI CodesDocument12 pagesANSI CodesmgkvprNo ratings yet
- Contactor Ac3 9aDocument3 pagesContactor Ac3 9aRicardo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document14 pagesExperiment 1rohit kumar rajNo ratings yet
- Circuit BreakerDocument14 pagesCircuit BreakerAviral OjhaNo ratings yet
- RMU TestSheetDocument4 pagesRMU TestSheetTihomir BotevNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 DC Series MotorDocument5 pagesExp 5 DC Series MotorKlydeJoseNo ratings yet
- 1Mhz 1A Synchronous Step-Down Regulator: Features General DescriptionDocument2 pages1Mhz 1A Synchronous Step-Down Regulator: Features General DescriptionM. M.No ratings yet
- An66f PDFDocument104 pagesAn66f PDFMarco PerezNo ratings yet
- Transformer Stability Test: ProjectDocument3 pagesTransformer Stability Test: ProjectsanjayNo ratings yet
- Regulador de Voltaje AVR/UVRDocument6 pagesRegulador de Voltaje AVR/UVRJuan MoraNo ratings yet
- NC1D-LR Catalog Telemecanique LC1 Contactor LR2 Overload Relay Cross-RefDocument9 pagesNC1D-LR Catalog Telemecanique LC1 Contactor LR2 Overload Relay Cross-RefGuillaume CODRONNo ratings yet