Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus Engg Chemistry
Uploaded by
broadbazaar3819845Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus Engg Chemistry
Uploaded by
broadbazaar3819845Copyright:
Available Formats
ANJUMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
MANGALWARI BAZAAR ROAD, SADAR, NAGPUR - 440001.
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
SYLLABUS – SEMESTER I (CBS)
Engineering Chemistry (BESI-3T)
(Total Credits: 03)
Scheme Lectures: 2 Hours/ Week Theory Tutorial: 1 Hours / Week
Scheme Examination
T (U) : 40 Marks T (I) : 10 Marks Duration of University Exam. : 02 Hrs
Unit – I: Water Technology (12 Hrs)
Hardness of water and types of hardness Domestic water treatment: Brief discussion of coagulation and
sterilization using UV. Ozone, chlorine, Break point chlorination. Softening of water-principle, reactions,
advantages, limitations and Comparison of – Lime-Soda process, Zeolite process, and de-mineralization
process. Boiler Troubles-(causes, effect on boiler operation and methods of prevention) – Carry over-
priming and foaming; Scales and sludges, caustic embrittlement, boiler corrosion; internal conditioning
phosphate, carbonate, calgon conditioning. Numericals based on lime-soda and Zeolite process.
Desalination-using electro dialysis and reverse osmosis processes. Waste water treatment (introduction
and importance) – Brief idea about tertiary treatment methods.
Unit – II: Corrosion Science (10 Hrs)
Introduction, Causes and Consequence of corrosion, brief idea about electrochemical & galvanic series,
Factors influencing corrosion) Nature of metal b) Nature of environment, Chemical and electrochemical
corrosion, Mechanisms of electrochemical corrosion; Pilling Bed worth rule; Differential aeration theory
of corrosion. Types of Corrosion – Pitting, inter granular, stress, waterline and galvanic corrosion.
Corrosion Prevention – a) Design and material selection b) Cathodic and anodic protection, c) Protective
surface coatings- tinning, galvanizing and powder coating, metal cladding and electroplating.
Unit – III: Construction Materials (08 Hrs)
Cement: Portland cement – Raw material, Dry and wet process of manufacture, Proportion and role of
microscopic constituents, Additives of cement ,Setting and hardening of cement; heat of hydration,
soundness; Types of cement ( characteristics & applications ) – White, High alumina, Low heat ,Rapid
hardening cement, Ready Mix Concrete, fly ash as cementing material( properties, advantages,
limitations & application)
Unit – IV: Green Chemistry and Battery Technology (10 Hrs)
Green Chemistry: Introduction, Principles and significance, industrial application (supercritical fluids as
Solvents, Example-super critical CO2 ), Biocatalysis and concept of carbon credits. Battery Technology:
Types of batteries, primary, secondary and reverse batteries, important definition-energy density, power
density. a) Secondary Battery: Lithium ion, Nickel-Cadmium b) Fuel cell application, advantages and
limitation (Example: Alkaline fuel Cell).
Books Recommended:
Text Books:
1. Text Book of Engineering Chemistry: S.S. Dara, S. Chand and Company Ltd. New Delhi.
2. Engineering Chemistry: Arty Dixit Dr. Kirtiwardhan Dixit, Harivansh Prakashan, Chandrapur.
3. Textbook of Engineering Chemistry: P.C. Jain and Monica Jain, Dhanpat Rai and Sons, New Delhi.
4. Textbook of Engineering Chemistry: S.N. Narkhede, R.T. Jadhav, AB. Bhake, A.U. Zadgaonkar, Das
Ganu Prakashan, Nagpur
Reference Books:
1. A Text book of Engineering Chemistry : Shashi Chawla; Dhanpat Rai & Sons, New Delhi.
2. A textbook of Polymer Science : Fred, Billmeyer Jr. ,Wiley India Third edition.
3. Applied Chemistry by N. Krishnamurthy:P. Vallinavagam. And K. Jeysubramanian TMH
4. Applied Chemistry for Engineers : T.S. Gyngell.
5. Chemistry of Advanced Materials : CNR Rao, Rsc Publication
PROF TASNEEM K. KHAN Page 1
You might also like
- Sylabus ChemistryDocument8 pagesSylabus ChemistryAvinash AwasthiNo ratings yet
- CHY1701 - ENGINEERING-CHEMISTRY - ETH - 1.0 - 46 - CHY1701 - Engineering ChemistryDocument3 pagesCHY1701 - ENGINEERING-CHEMISTRY - ETH - 1.0 - 46 - CHY1701 - Engineering ChemistryLikhita NarraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Document4 pagesEngineering Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21cat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry: Water Treatment, Corrosion, and PolymersDocument3 pagesEngineering Chemistry: Water Treatment, Corrosion, and PolymersdfdffNo ratings yet
- NBA Course Plan Chemistry 22-23 ODDDocument17 pagesNBA Course Plan Chemistry 22-23 ODDAldrin D CruzNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For B.E First Semester in Nagpur UniversityDocument25 pagesSyllabus For B.E First Semester in Nagpur UniversityAdibaTabassumNo ratings yet
- Echmsyll PDFDocument8 pagesEchmsyll PDFashishNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Course FileDocument32 pagesCHEMISTRY Course FileRangothri Sreenivasa SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- CY1001+CY1002 Chemistry+LabDocument4 pagesCY1001+CY1002 Chemistry+LabMayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Uvce 2nd Sem B.e-Mech Syl Copy 2k11Document12 pagesUvce 2nd Sem B.e-Mech Syl Copy 2k11hemanth kumar s gNo ratings yet
- CY 110 COURSE EVALUATION PLAN Jan 2024Document2 pagesCY 110 COURSE EVALUATION PLAN Jan 2024Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemsitry Syllabus - 2022 - Chemistry Curiculum-1Document4 pagesEngineering Chemsitry Syllabus - 2022 - Chemistry Curiculum-1Sachin NaikNo ratings yet
- IT1T3Document2 pagesIT1T3Vyshnavi ThottempudiNo ratings yet
- COURSE EVALUATION PLAN For Theory-CY110 - Revised1Document2 pagesCOURSE EVALUATION PLAN For Theory-CY110 - Revised1itsmekrishna2006No ratings yet
- Engg. Chemistry IDocument4 pagesEngg. Chemistry IHimanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry (Non IT)Document5 pagesApplied Chemistry (Non IT)himanshuchawla654No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes VtuDocument160 pagesChemistry Notes VtuNarayan S. Burbure67% (3)
- Chemistry NotesDocument115 pagesChemistry NotesGaddam RangaNo ratings yet
- Green ChemistryDocument2 pagesGreen ChemistryANUNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II Partial Differentiation 12 Hrs PDFDocument350 pagesUNIT - II Partial Differentiation 12 Hrs PDFbarbara_ropeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry 1ST YEAR LMDocument111 pagesEngineering Chemistry 1ST YEAR LMSANJEEV100% (1)
- Graphic Era (Deemed To Be University), DehradunDocument7 pagesGraphic Era (Deemed To Be University), DehradunMansi NegiNo ratings yet
- 2666first Year B.tech Syllabus For Admission Batch 2016-17Document19 pages2666first Year B.tech Syllabus For Admission Batch 2016-17rajmohapatraNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive VivaDocument9 pagesComprehensive VivaSAURABH KUMAR PANDEY Research Scholar, Chemical Engg. & Technology , IIT(BHU)No ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology (Common For All Branches) Credit-Based (2014-15 Onwards in Phased Manner)Document47 pagesBachelor of Technology (Common For All Branches) Credit-Based (2014-15 Onwards in Phased Manner)Mohit GanwaalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Theory 2020-21Document168 pagesEngineering Chemistry Theory 2020-21architabarmanroyNo ratings yet
- Materials and Manufacturing Processes CurriculumDocument41 pagesMaterials and Manufacturing Processes CurriculumAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BE MergedDocument95 pagesSyllabus BE MergedSANGITA CHIRANJIBI POKHRELNo ratings yet
- EngineeringChemistry by Jain and JainDocument11 pagesEngineeringChemistry by Jain and Jainateet100% (2)
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengal 1 Year Curriculum Structure For B.Tech Courses in Engineering & TechnologyDocument2 pagesMaulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West Bengal 1 Year Curriculum Structure For B.Tech Courses in Engineering & Technologyanushaghosh2003No ratings yet
- JUT Syllabus Chemistry-I Bit SindriDocument4 pagesJUT Syllabus Chemistry-I Bit SindriPalNo ratings yet
- GANPAT UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS COURSEDocument13 pagesGANPAT UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS COURSEMalith MadushanNo ratings yet
- Vignan University B.Tech I Year Engineering Chemistry SyllabusDocument2 pagesVignan University B.Tech I Year Engineering Chemistry SyllabusMohammd SaliqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 18CHE12 (All. Websites)Document94 pagesChemistry Notes 18CHE12 (All. Websites)arpitaNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument3 pagesEngineering ChemistrydivNo ratings yet
- Appliec ChemistryDocument3 pagesAppliec ChemistryQueen Ann NavalloNo ratings yet
- IT All Sem Syllabus-Converted - 2Document243 pagesIT All Sem Syllabus-Converted - 2MadhavNo ratings yet
- 14.materials Science and Engineering PDFDocument18 pages14.materials Science and Engineering PDFs_manikandanNo ratings yet
- Engineering chemistry notes pdf free downloadDocument3 pagesEngineering chemistry notes pdf free downloadGohan SayanNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument3 pagesContinueGohan SayanNo ratings yet
- M.Phil Applied Chemistry Program DetailsDocument5 pagesM.Phil Applied Chemistry Program DetailsAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- PhD Admission Syllabus Metallurgical EngineeringDocument2 pagesPhD Admission Syllabus Metallurgical Engineeringchauhan100% (1)
- Engineering Chemistry - I SyllabusDocument5 pagesEngineering Chemistry - I Syllabussenthil kumaran mNo ratings yet
- Eng Common Chm102 2014Document4 pagesEng Common Chm102 2014Ihjaz VarikkodanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus GtuDocument3 pagesSyllabus GtuManvendra RaiNo ratings yet
- Ece SyllabusDocument68 pagesEce SyllabusKRISHNA SAI.VASAMSETTYNo ratings yet
- Engg Chem SyllabusDocument4 pagesEngg Chem Syllabusaravelli abhinavNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistrySk KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For EEE StreamDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank For EEE Streamsindhu sindhuNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument4 pagesEngineering ChemistrySaha naNo ratings yet
- App - Chem New MaterialDocument117 pagesApp - Chem New MaterialMadhavarao MaddisettyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry 2019-20 Study MaterialDocument125 pagesEngineering Chemistry 2019-20 Study MaterialG23 nagaleekar nikithaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics SyllabusDocument25 pagesEngineering Physics SyllabusPrerna BhendarkarNo ratings yet
- North Maharashtra University Jalgaon (Common To All Branches of Engineering) W. E. F.2005 - 2006Document19 pagesNorth Maharashtra University Jalgaon (Common To All Branches of Engineering) W. E. F.2005 - 2006satish173No ratings yet
- Course Sec Course Name: Instructor Day Start Time End Time BLD Room Corrosion Science and Engineering 1830 1945 149Document3 pagesCourse Sec Course Name: Instructor Day Start Time End Time BLD Room Corrosion Science and Engineering 1830 1945 149Anonymous NxpnI6jCNo ratings yet
- Small Angle X-Ray and Neutron Scattering with Applications to GeomaterialsFrom EverandSmall Angle X-Ray and Neutron Scattering with Applications to GeomaterialsNo ratings yet
- IK Ratings For Enclosures (IEC62262) : Degree of Protection Against External Mechanical Impacts (IK Code)Document1 pageIK Ratings For Enclosures (IEC62262) : Degree of Protection Against External Mechanical Impacts (IK Code)fajar agungNo ratings yet
- Sop TurbineDocument4 pagesSop TurbinesambhuNo ratings yet
- AirslideConveyingTechnology PDFDocument6 pagesAirslideConveyingTechnology PDFGarfang RattanapunNo ratings yet
- 01 Factsheet TT TESTEX EN V02Document3 pages01 Factsheet TT TESTEX EN V02Fathi MustafaNo ratings yet
- Extrusion Second EditionDocument604 pagesExtrusion Second EditionMartin Marroquin100% (2)
- Increasing Profits in Jet Fighter Manufacturing - BCG CaseDocument3 pagesIncreasing Profits in Jet Fighter Manufacturing - BCG CaseAkhilGovindNo ratings yet
- Universal IV™ Series Pro and Lite Models: DrexelbrookDocument10 pagesUniversal IV™ Series Pro and Lite Models: DrexelbrookHECTOR ENRIQUE DE PAZ CRUZNo ratings yet
- The Vlasov Foundation Model: Summary-AnDocument7 pagesThe Vlasov Foundation Model: Summary-AnPartho MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Pt. Estu Artha LancarDocument9 pagesPt. Estu Artha Lancarhelmi_69No ratings yet
- HV Machines WEBDocument16 pagesHV Machines WEBVassilis DanakasNo ratings yet
- How To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2 PDFDocument83 pagesHow To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2 PDFbarbiesmilez100% (1)
- EML3100 Exam2ReviewDocument3 pagesEML3100 Exam2ReviewMax MichaudNo ratings yet
- MR Aviation Turbine Fuel (Def Stan 91 91 Issue 6)Document4 pagesMR Aviation Turbine Fuel (Def Stan 91 91 Issue 6)Karthik BalajiNo ratings yet
- Guide to Requalifying Gas CylindersDocument13 pagesGuide to Requalifying Gas CylindersEmran UmerNo ratings yet
- Yield Line Theory: Prepared byDocument22 pagesYield Line Theory: Prepared byKartikMandaniNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping ScheduleDocument3 pagesHousekeeping ScheduleJohn Dominic AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Peracetic Acid SDSDocument3 pagesPeracetic Acid SDSEsteban MurilloNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification - ChillerDocument15 pagesTechnical Specification - Chillerrkpatel40No ratings yet
- Inspection Checklist Overhead Crane PDFDocument2 pagesInspection Checklist Overhead Crane PDFMOST PASONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document4 pagesChapter 18Marco LuigiNo ratings yet
- 1995 ManualDocument33 pages1995 ManualAntonis BafatakisNo ratings yet
- GES-CA-TST-01 - GradationDocument16 pagesGES-CA-TST-01 - GradationSantosh ZunjarNo ratings yet
- Plastics Machinery Manufacturers Association of India (PMMAI)Document105 pagesPlastics Machinery Manufacturers Association of India (PMMAI)deepahireNo ratings yet
- Montana State Electrical Code BookletDocument35 pagesMontana State Electrical Code BookletMetis2011No ratings yet
- Catalog 2008 SM6 24kvDocument100 pagesCatalog 2008 SM6 24kvari_aristaNo ratings yet
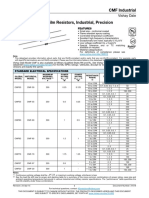
- Data Sheet Res PDFDocument5 pagesData Sheet Res PDFToufani Rizal AlfarisiNo ratings yet
- MSS-SP-112 (1999)Document9 pagesMSS-SP-112 (1999)mubs997100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument1 pageNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equationscaptain6233No ratings yet
- 18) The Study of Possibilities of Selective Recovery of Palladium (II) From Chlorides Solutions by Ion Exchange Resin Lewatit TP-214Document7 pages18) The Study of Possibilities of Selective Recovery of Palladium (II) From Chlorides Solutions by Ion Exchange Resin Lewatit TP-214SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Technologies of Wood CombustionDocument16 pagesTechnologies of Wood Combustionclucian2000No ratings yet