Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EPAs Biology B A - Level Ch4
Uploaded by
Moha Saad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document provides sample exam questions and answers for the Edexcel A-level Biology B exam on the topics of exchange and transport, gas exchange, transport in plants, and the cardiovascular system. Key points covered include:
- The structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer and protein channels in facilitating the passage of molecules and ions.
- Mechanisms of diffusion down concentration gradients and facilitated diffusion through carrier proteins.
- Identification of blood vessels and description of circulatory system components like the heart and blood vessels.
- Processes of transpiration and translocation of sugars in plants.
- Gas exchange mechanisms in the lungs and calculations related to diffusion gradients.
- Cardiovascular system
Original Description:
Original Title
854859 EPAs Biology B A_level Ch4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides sample exam questions and answers for the Edexcel A-level Biology B exam on the topics of exchange and transport, gas exchange, transport in plants, and the cardiovascular system. Key points covered include:
- The structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer and protein channels in facilitating the passage of molecules and ions.
- Mechanisms of diffusion down concentration gradients and facilitated diffusion through carrier proteins.
- Identification of blood vessels and description of circulatory system components like the heart and blood vessels.
- Processes of transpiration and translocation of sugars in plants.
- Gas exchange mechanisms in the lungs and calculations related to diffusion gradients.
- Cardiovascular system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesEPAs Biology B A - Level Ch4
Uploaded by
Moha SaadThis document provides sample exam questions and answers for the Edexcel A-level Biology B exam on the topics of exchange and transport, gas exchange, transport in plants, and the cardiovascular system. Key points covered include:
- The structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer and protein channels in facilitating the passage of molecules and ions.
- Mechanisms of diffusion down concentration gradients and facilitated diffusion through carrier proteins.
- Identification of blood vessels and description of circulatory system components like the heart and blood vessels.
- Processes of transpiration and translocation of sugars in plants.
- Gas exchange mechanisms in the lungs and calculations related to diffusion gradients.
- Cardiovascular system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Edexcel A-level Biology B exam practice answers
4 Exchange and transport
1 (a) The continuous (bi)layer restricts the entry of large molecules; the phospholipid bilayer
restricts the entry of water-soluble molecules/ions; protein channels allow the entry of
ions/charged particles; protein carriers the allow entry of larger
molecules/glucose/amino acids. [4]
(b) (i) The steeper the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion. [1]
(ii) Facilitated diffusion takes place through channel proteins; the rate of diffusion
levels as the number of carrier proteins becomes limiting. [2]
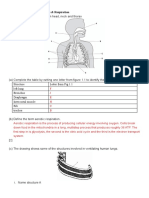
2 (a) A = (anterior/posterior) vena cava; B = hepatic portal vein; C = renal artery. [3]
(b) The thick layer of elastic tissue allows for expansion as blood flows into the artery from
the heart/it allows recoil after the heart contracts that evens out the flow; squamous
epithelium provides a friction-free inner surface. [2]
(c) To prevent the backflow of blood; to fill with blood, closing the lumen of the vein. [2]
(d) (i) The insect has an open system whereas mammals have a closed system. [1]
(ii) A fish has a single system whereas mammals have a double system. [1]
3 (a) By osmosis; from a solution with a high/less negative water potential to one with a
lower/more negative water potential. [2]
(b) Water evaporates from the mesophyll cells and diffuses out of the leaves; water lost
from the mesophyll cells is replaced by water from the xylem in leaves; cohesion
between the water molecules pulls more water from the xylem; tension in the xylem
pulls the water from root. [4]
14
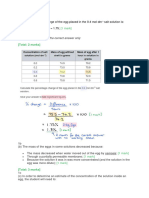
(c) CO2 is used to make sucrose, which is transported in the phloem; the radioactivity
level is high/2.34 units in the leaf where sugar is made; radioactivity is 3.46 units in the
bud and 0.92 in the roots, which shows these regions are sinks; so the movement (of
sugars) must be both up and down the plant, but mass-flow hypothesis accounts for
movement in one direction. [4]
4 (a) In both, the diaphragm muscle relaxes; at rest, the internal and external intercostals
relax; when blowing up a balloon, the external intercostals relax and the internal
intercostals contract. [3]
(b) (i) Nitrogen does not diffuse between blood and alveolar air. [1]
(ii) Alveolar air mixes with atmospheric air in the trachea and bronchi; (This air) has
a lower carbon dioxide concentration and higher oxygen concentration. [2]
(iii) Gas exchange is (relatively) inefficient; as only 34.4% of oxygen is removed from
the air; but the concentration of carbon dioxide increases over 100-fold/by 132
times. [3]
5 (a) A potometer. [1]
Hodder Education © 2016 1
(b) Cut the end of the plant stem under water/assemble the apparatus under water/cover all
joints with petroleum jelly. [1]
(c) It allows the bubble to be moved back to the starting position. [1]
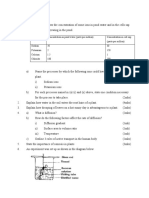
(d) Measure the diameter of the capillary tube and halve it to get the radius; multiply the
distance moved (d) by pi (π) and by the square of the radius/find dπr2; divide by the
time over which the bubble moved. [3]
(e) The increase in speed of the fan increases the rate of transpiration; because the faster
fan/air speed creates a steeper diffusion gradient from the leaf; the rate increases rapidly
at first but becomes less rapid after setting 1/from setting 2; because air humidity
changes less as air/fan speed increases. [4]
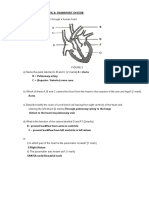
6 (a) 80 beats per minute. (If answer is incorrect, allow 1 mark if the working shows the time
of one heart beat as 0.8 s.) [2]
(b) The pressure in the atrium became greater than the pressure in the ventricle; blood flow
down the pressure gradient pushed the valve open. [2]
(c) 0.34 s. [1]
(d) The wave of impulses passes quickly across atria/over in 0.04 s; so the atria contract
together; there is a delay of 0.12 s at the AV node; this allows the atria to empty before
the ventricles contract. [4]
Hodder Education © 2016 2
You might also like
- Consonant Blends: BL PR DR FR CR BR GL CL GRDocument26 pagesConsonant Blends: BL PR DR FR CR BR GL CL GRBenedict Affleck100% (4)
- The Nexian - Issue 1Document56 pagesThe Nexian - Issue 1Thijs Bierman100% (2)
- F3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticeDocument10 pagesF3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticePianna IeongNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)Document4 pagesRespiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)lee67% (3)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Biodiversity As Tourism Attraction: The Perspective of TouristDocument10 pagesMangrove Biodiversity As Tourism Attraction: The Perspective of TouristInternational Network For Natural Sciences100% (1)
- Jack From The Forest: Simple Present, Story 1Document6 pagesJack From The Forest: Simple Present, Story 1Kurnia AjwaNo ratings yet
- Ga ExchangeDocument9 pagesGa ExchangeKev TangNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - MsDocument11 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - MsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- S4 Suggested Solution: 2015 - 2016 Secondary 4 Final ExaminationDocument5 pagesS4 Suggested Solution: 2015 - 2016 Secondary 4 Final ExaminationMa Hau YiNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 2 - MSDocument9 pages3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 2 - MSMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Transport ADocument4 pagesTransport AKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesLungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- June 2003 U2bDocument3 pagesJune 2003 U2bapi-3726022No ratings yet
- A2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2014 13644Document7 pagesA2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2014 13644Mariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Lungs MSDocument3 pagesUnit 1 The Lungs MSHassanIsmailNo ratings yet
- Core CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument6 pagesCore CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansommpNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2 - Mark Scheme - Updated 131022Document14 pages2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2 - Mark Scheme - Updated 131022anya de silvaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants MSDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants MSOtniel Dita NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants 1 MS PDFDocument6 pagesTransport in Plants 1 MS PDFImran MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 - MSDocument3 pagesPaper 3 - MSSaneliso TsabedzeNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 1 - MSDocument24 pages3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 1 - MSMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- 5126 w09 Ms 4Document5 pages5126 w09 Ms 4mstudy123456No ratings yet
- 2A Exam PracticeDocument3 pages2A Exam PracticeMuhammad BinyameenNo ratings yet
- Revision For SA1 (Students' Copy)Document7 pagesRevision For SA1 (Students' Copy)SUNDARI SIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- Bio 01 Life ProcessDocument5 pagesBio 01 Life Processsamarth mishraNo ratings yet
- 5125 w09 Ms 4Document5 pages5125 w09 Ms 4mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Paper 4 - MSDocument3 pagesPaper 4 - MSSaneliso TsabedzeNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances - M - AnsDocument8 pagesMovement of Substances - M - Answs2t41m4d1No ratings yet
- 0653 Combined Science: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument6 pages0653 Combined Science: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SerieskeyzainbNo ratings yet
- Solution 633529Document5 pagesSolution 633529sujinNo ratings yet
- 8.1-Transport - in - Plants - Igcse-Cie-Biology - Solved OLIDocument13 pages8.1-Transport - in - Plants - Igcse-Cie-Biology - Solved OLIAmber TeacherNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 MsDocument23 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 MsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Transport in Cells 1 QP PDFDocument18 pagesTransport in Cells 1 QP PDFAlexia Micallef GattNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCell PhysiologywallyNo ratings yet
- A2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2012 10459Document8 pagesA2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2012 10459Abby TinNo ratings yet
- IX HalfYearly Dec21Document5 pagesIX HalfYearly Dec21Hasna Hena SarkerNo ratings yet
- Skema Kertas 2Document9 pagesSkema Kertas 2Sitinorsyahidah Jantan100% (1)
- Topic 11 Gas Exchange in HumanDocument23 pagesTopic 11 Gas Exchange in HumanPianna IeongNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Gas Exchange MSDocument8 pages3.2 Gas Exchange MSeissafitaihiNo ratings yet
- HKCEE Paper I Running Answer Text 2001 BiologyDocument7 pagesHKCEE Paper I Running Answer Text 2001 BiologyKathy WongNo ratings yet
- Term 3 & 4 MEMODocument16 pagesTerm 3 & 4 MEMOsavagep948No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- 10th (ICSE) - (BIOLOGY) - Absorption by Roots+Circulatory SystemDocument2 pages10th (ICSE) - (BIOLOGY) - Absorption by Roots+Circulatory SystemDhun100% (2)
- Exam G 12QDocument10 pagesExam G 12Qpatrick.justsalesmarketingNo ratings yet
- Life Processes-Question BankDocument9 pagesLife Processes-Question Bankkfjg47zq26No ratings yet
- November 2007 Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesNovember 2007 Paper 2 Mark Schemenehemiahedwards100% (1)
- Pure Bio ANSWERDocument17 pagesPure Bio ANSWERlohbernard168No ratings yet
- Transport System Question and AnswersDocument12 pagesTransport System Question and Answerskumara guruparanNo ratings yet
- Test With Answers of Unit 07 (B-Ii)Document4 pagesTest With Answers of Unit 07 (B-Ii)Arnav BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 0653 w16 Ms 33Document6 pages0653 w16 Ms 33yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument23 pagesGaseous ExchangeSsaku BoscoNo ratings yet
- Bio Papers AnswersDocument10 pagesBio Papers AnswersCarl Agape Davis75% (4)
- CBSE G+10 Life+Processes EIQDocument3 pagesCBSE G+10 Life+Processes EIQyeahmevaibhaviNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderNo ratings yet
- HKCEE Paper I Running Answer Text 2000 BiologyDocument6 pagesHKCEE Paper I Running Answer Text 2000 BiologyKathy WongNo ratings yet
- F4Bio (C8) NotesDocument11 pagesF4Bio (C8) NotesGrace LeeNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology RevisionDocument2 pagesGCSE Biology RevisionsannnnnNo ratings yet
- Cells, Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesCells, Matter in Our SurroundingsAPS Apoorv prakash singhNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheeet 2Document4 pagesRevision Worksheeet 2SpablaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument7 pagesStates of MatterabhayNo ratings yet
- 7 3 104 192Document4 pages7 3 104 192Sonia BalintNo ratings yet
- Lejeuneaceae (Marchantiophyta) of Sicike-Cike Natural Park, North Sumatra IndonesiaDocument7 pagesLejeuneaceae (Marchantiophyta) of Sicike-Cike Natural Park, North Sumatra IndonesiaRaisa AzhariNo ratings yet
- API Valves: A. API Gate Valves B. Mud Gate Valves C. API Plug ValvesDocument15 pagesAPI Valves: A. API Gate Valves B. Mud Gate Valves C. API Plug Valveskaveh-bahiraeeNo ratings yet
- The Giving TreeDocument33 pagesThe Giving TreeKiên Nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Community EcologyDocument90 pagesCommunity Ecologytanmay_envsNo ratings yet
- Base Job: Ragnarok X SEA APKDocument23 pagesBase Job: Ragnarok X SEA APKInnocentius Paul AldiNo ratings yet
- Ekspor Impor Asam Asetat (Acetic Acid)Document10 pagesEkspor Impor Asam Asetat (Acetic Acid)Fathur Deka ApriandaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition NuggetDocument2 pagesNutrition Nuggetapi-341491567No ratings yet
- 19.A1.0062 - Yemima Putri K, A - JurnalDocument11 pages19.A1.0062 - Yemima Putri K, A - JurnalYEMIMA PUTRI KRISTYANA A.No ratings yet
- Particle BoardDocument1 pageParticle BoardNamrata RamahNo ratings yet
- Guia Ingles QuantifiersDocument3 pagesGuia Ingles QuantifiersHEIDY LORENA LEON RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document41 pagesChapter 1Jodi SorianoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Bio Paper 4 Worksheet Chapter 1to10, 15Document12 pagesIGCSE Bio Paper 4 Worksheet Chapter 1to10, 15Anand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ians Pizza Madison MenuDocument4 pagesIans Pizza Madison Menusupport_local_flavorNo ratings yet
- Black Pepper: Food and Agriculture Organization of The United NationsDocument5 pagesBlack Pepper: Food and Agriculture Organization of The United NationslouisaNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification in 1GEN BIO 1STDocument3 pagesTable of Specification in 1GEN BIO 1STLouie DenostaNo ratings yet
- ElectropathyDocument51 pagesElectropathyKarolay Bolaño Durango100% (1)
- Science 8 Week 3 Quarter 4Document9 pagesScience 8 Week 3 Quarter 4Juliana ChuaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Synthetic Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles (HIPV's) On Okra Fruit and Shoot Borer (Earias Vittella Fab.) PopulationDocument4 pagesEffect of Synthetic Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles (HIPV's) On Okra Fruit and Shoot Borer (Earias Vittella Fab.) PopulationRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CBCS Scheme: Seventh Semester B.E. Degree Examination, December2018/January2019Document2 pagesCBCS Scheme: Seventh Semester B.E. Degree Examination, December2018/January2019ChiduNo ratings yet
- UNITV11Document12 pagesUNITV11api-3758209No ratings yet
- FarmingDocument3 pagesFarmingMerida BravoNo ratings yet
- Stocktake Template Trinity End of December 2017Document89 pagesStocktake Template Trinity End of December 2017fendi hermantoooNo ratings yet
- Aiats Neet - Aiims 2020 (Xii Studying)Document1 pageAiats Neet - Aiims 2020 (Xii Studying)Abhishek DograNo ratings yet
- Part 4 Transport in Plants Lesson 4Document10 pagesPart 4 Transport in Plants Lesson 4Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal Us Bahasa Inggris Tahun 2021Document6 pagesKumpulan Soal Us Bahasa Inggris Tahun 2021harisunNo ratings yet