Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trematodes General Characteristics
Uploaded by
eseyesmontecalvosabanalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trematodes General Characteristics
Uploaded by
eseyesmontecalvosabanalCopyright:
Available Formats
TREMATODES
TREMATODES / FLUKES BLOOD FLUKES - Schistosoma spp.
leaf-shaped, unsegmented, flat, & broad Lives in: vascular system / venous plexuses
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Cause Schistosomiasis (2nd most devastating tropical parasitic disease)
Class: Trematoda Order: Strigeida
Superfamily: Schistosomatoides
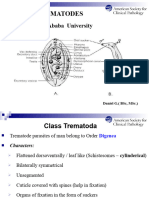
Adult worm: Family: Schistosomatidae
Unsegmented & flattened dorsoventrally but have thick fleshy bodies
(schistosomes) Adult worms:
Sucker: Live in venous plexuses of the definitve host
Aids in movement and enable the flukes to maintain their position Body: cylindrical, covered w/ thick tuberculated & syncytial tegument
inside the veins No muscular pharynx; intestinal caeca reunite behind ventral sucker to
Oral sucker - anterior form canal
Ventral sucker - acetabulum Suckers: armed w/ delicate spines
Genital sucker / gonotyl - heterophyids Sexes are diecious (separate)
Oral & ventral sucker - muscular cup-shaped (hence called Male worm gas sex canal (gynecophoric canal) on ventral side on
distomata) which the female worm reposes
Digestive system: Eggs:
Incomplete Non-operculated w/ spine-like projection
Caeca - pair of blind intestinal pouches Fully embryonated when excreted in urine & feces
most trematodes are hermaphrodites (monoecious) but schistosomes are Hatch out immediately to form miracidia
diecious (sexes are separate)
Excretory system - bilaterally symmetrical; consists of flame cells & collecting Larva:
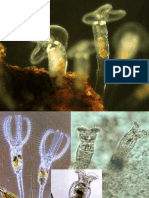
tubules Miracidium → Sporocyst → Cercaria
Nervous system - paired ganglia Cercaria:
Oviparous (lay eggs) Infective form to man (penetration)
Forked tail but no pharynx
Larva: miracidium, sporocyst, redia, cercaria, metacercaria No rediae & metacercariae stages
Host: Host:
One definitive, 2 intermediate Definitive: Humans
Definitive: human Intermediate: Snail - Oncomelania
1st intermediate: freshwater snail / mollusc
2nd intermediate: aquatic plant, fish / crab
MOT:
Ingestion of metacercariae through aquatic plants, fish / crabs
Penetration of free living cercariae (schistosomes)
All schistosomes live in venous plexuses
Bedrijo
You might also like
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- RMTnotes PARASITOLOGYDocument68 pagesRMTnotes PARASITOLOGYArvin O-CaféNo ratings yet
- Helminthes: / Medical Laboratory TechnologyDocument17 pagesHelminthes: / Medical Laboratory Technologyصفا رياض محمد /مسائيNo ratings yet
- Meet the Invertebrates: Anemones, Octopuses, Spiders, Ants, and OthersFrom EverandMeet the Invertebrates: Anemones, Octopuses, Spiders, Ants, and OthersNo ratings yet
- Trichuris Trichura: Enterobius VermicularisDocument38 pagesTrichuris Trichura: Enterobius VermicularisArvin DiNozzoNo ratings yet
- Helminths and Protozoa: Parasitic Worms and Single-Celled ParasitesDocument6 pagesHelminths and Protozoa: Parasitic Worms and Single-Celled ParasitesSuzanne RibsskogNo ratings yet
- Trematodes - PreFinalDocument13 pagesTrematodes - PreFinalAndriaNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument30 pagesTrematodesJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Helminths 12Document34 pagesHelminths 12malakaiad212No ratings yet
- Helminth Introduction 160619043259Document12 pagesHelminth Introduction 160619043259JaneYlNo ratings yet
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- Helminths (Parasitic worms) Kingdom Animalia Phylum PlatyhelminthsDocument11 pagesHelminths (Parasitic worms) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Platyhelminthsemil diogoNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- ParasiteDocument16 pagesParasiteFlorence Lynn BaisacNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFDocument23 pagesPlatyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFAbdulla Hil KafiNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: An Introduction to Nematodes, Cestodes, Trematodes and ProtozoaDocument8 pagesParasitology: An Introduction to Nematodes, Cestodes, Trematodes and ProtozoaRuthenie RedobleNo ratings yet
- Flatworms 1Document31 pagesFlatworms 1GuteNo ratings yet
- ParasiteDocument27 pagesParasiteAbdullah AlkharsNo ratings yet
- Trematodes LECDocument2 pagesTrematodes LECAki SuzumeNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Lec 5 TrematodesDocument5 pagesParasitology-Lec 5 Trematodesapi-3743217100% (2)
- 7 - Nematodes (Aphasmids and Phasmids)Document9 pages7 - Nematodes (Aphasmids and Phasmids)Scarlet WitchNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical ParasitologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Medical ParasitologySidra DollNo ratings yet
- Trematodes LectureDocument7 pagesTrematodes LectureCherie QuintoNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes (Flatworms, Tapeworms) : Diversity of Life - AnimalsDocument21 pagesPlatyhelminthes (Flatworms, Tapeworms) : Diversity of Life - AnimalskingNo ratings yet
- Review Vet - Parasitology 1-1Document58 pagesReview Vet - Parasitology 1-1AttiqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cestodes and Minor CestodesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Cestodes and Minor CestodesJustin TayabanNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument75 pagesTrematodesHann SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Trematode 2021Document46 pagesTrematode 2021ShanmathiNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Dr Amal Helminthology Lec 1Document8 pagesParasitology Dr Amal Helminthology Lec 1Cosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia by DR - SHAHID IQBALDocument9 pagesKingdom Animalia by DR - SHAHID IQBALTaimoor Qadeer100% (1)
- Nematodes Cestodes, Trematodes NoteDocument3 pagesNematodes Cestodes, Trematodes NoteJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Clinpara Lec M2Document11 pagesClinpara Lec M2eumhir7No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - Platyhelminthes & NematodaDocument14 pagesAnimal Kingdom - Platyhelminthes & NematodaJoanna Susan JojiNo ratings yet
- Flatworms, Segmented and Round WormsDocument45 pagesFlatworms, Segmented and Round Wormsmathew mawien dengNo ratings yet
- Parasitology OspeDocument166 pagesParasitology OspePuvana PuvanaNo ratings yet
- Trematodes: Intestinal SpeciesDocument7 pagesTrematodes: Intestinal SpeciesMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument20 pagesTrematodesmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument9 pagesTrematodesLewis P. SanchezNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument2 pagesNematodesRheila DuyaNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Prelim Introduction To ParasitologyDocument27 pages1 2 Prelim Introduction To ParasitologyHersey MiayoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Metazoa: ProtozoaDocument7 pagesParasitology Metazoa: ProtozoaTrishaNo ratings yet
- 9.parasit Filariasis-Amoeba (Rev 03.17)Document36 pages9.parasit Filariasis-Amoeba (Rev 03.17)maya dwiNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Mind MapDocument4 pagesAnimal Kingdom Mind MapVedanti Naik100% (1)
- Introduction To The Endoparasites: NematodesDocument24 pagesIntroduction To The Endoparasites: NematodesdanielaNo ratings yet
- ChinilinDocument37 pagesChinilinyepNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument7 pagesNotesVermillion ZedNo ratings yet
- Trematodes: 2. MiracidiaDocument3 pagesTrematodes: 2. MiracidiaBikram ChohanNo ratings yet
- Trematodes and NemahelminthesDocument6 pagesTrematodes and NemahelminthesEvelyn TingNo ratings yet
- Standard XI ppt (invert)Document45 pagesStandard XI ppt (invert)kiran kombeNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument12 pagesTrematodesur.yared21No ratings yet
- 7-Introduction To Medical ParasitologyDocument32 pages7-Introduction To Medical Parasitologytruch 2022No ratings yet
- Classification, General Characteristics of Parasites and Medically Important ParasitesDocument30 pagesClassification, General Characteristics of Parasites and Medically Important ParasitesSteph AsideNo ratings yet
- Para-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Document11 pagesPara-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Aysha AishaNo ratings yet
- Schistosoma Lecture OutlineDocument2 pagesSchistosoma Lecture OutlineMershen GaniaNo ratings yet
- Cestodes 2020Document10 pagesCestodes 2020CDNo ratings yet
- 1A Finals Notes (04-04-2022)Document35 pages1A Finals Notes (04-04-2022)Aoun Sial60No ratings yet
- 4 Pseudocoelomated RoundwormsDocument26 pages4 Pseudocoelomated Roundwormsbulucgheorghe25No ratings yet
- l7 Rotifera 07Document17 pagesl7 Rotifera 07Femil adellaNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument7 pagesCestodesENRIKA ROSE B. ALBIS100% (1)
- ISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 01 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5Document5 pagesISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 01 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5HemantNo ratings yet
- Love of Lab 1: Spontaneous Generation vs. BiogenesisDocument5 pagesLove of Lab 1: Spontaneous Generation vs. Biogenesisi believe in dabdab and bambamNo ratings yet
- Adachi and Shimamura - Anime Special Novel 1Document23 pagesAdachi and Shimamura - Anime Special Novel 1SHUM JING FUN MoeNo ratings yet
- Invisible ItchesDocument4 pagesInvisible ItchesGrace Saria MadridNo ratings yet
- Practicas Microbiologicas EstandarDocument2 pagesPracticas Microbiologicas EstandarWendy JNo ratings yet
- ShirinDocument2 pagesShirinKhadiza ShirinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 RRL of PiggeryDocument8 pagesChapter 2 RRL of PiggerySha TomasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Community Health NursingDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Community Health NursingAlmasNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood Pressure Disorders in Diabetes MellitusDocument467 pages1 Blood Pressure Disorders in Diabetes MellitusPaola alvarezNo ratings yet
- DR Tam-Climate Change and BeekeepingDocument11 pagesDR Tam-Climate Change and BeekeepingIvana ArsovskaNo ratings yet
- From Best Practices To Breakthrough Impacts-3Document52 pagesFrom Best Practices To Breakthrough Impacts-3Jorge BoschNo ratings yet
- Six Kingdoms of LifeDocument48 pagesSix Kingdoms of LifesagiNo ratings yet
- Reptiles & Amphibians of The Hajar MountainsDocument24 pagesReptiles & Amphibians of The Hajar Mountainsluca.b.pacioli8708No ratings yet
- Journal A. Arviani Desianti NurDocument9 pagesJournal A. Arviani Desianti NurPengetikan ARVNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument6 pagesPaper ChromatographyMuslimah Anggun100% (1)
- Ssc-Biology Text Book Must StudyDocument212 pagesSsc-Biology Text Book Must StudyShaik BajiNo ratings yet
- Board of Intermediate & Secondary Education Saidu Sharif SwatDocument2 pagesBoard of Intermediate & Secondary Education Saidu Sharif SwatMUSHTAQ AHMADNo ratings yet
- 10th Science II SemiENG QueBank MSCERTDocument48 pages10th Science II SemiENG QueBank MSCERTuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument708 pagesCourseedson santos86% (7)
- Adenocarcinoma PulmonarDocument75 pagesAdenocarcinoma PulmonarLigia Micaela García XitamulNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Vocational NursingDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Vocational NursingTram NgocNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Molecules Their Interaction Relevant To Biology CSIR UGC NET Life SciencesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Molecules Their Interaction Relevant To Biology CSIR UGC NET Life SciencesKishan KoyaniNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Chart Types and UsesDocument18 pagesPedigree Chart Types and UsesDrMohd IQbal SoFiNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesPavani ReddyNo ratings yet
- RMP ContractDocument181 pagesRMP ContractHillary AmistosoNo ratings yet
- DPP - Daily Practice Problems - BIOLOGYDocument6 pagesDPP - Daily Practice Problems - BIOLOGYmansoorbariNo ratings yet
- Lloyd Rice - Distribution - of - Heartwater - in - Cattle - in - Gokwe North District ZimbabweDocument32 pagesLloyd Rice - Distribution - of - Heartwater - in - Cattle - in - Gokwe North District ZimbabweLloyd RiceNo ratings yet
- Curso Online Fermentación 1-Modulo-1-FermentedDocument13 pagesCurso Online Fermentación 1-Modulo-1-FermentedHu LaNo ratings yet
- Patient TSH test reportDocument1 pagePatient TSH test reportVeenu SehrawatNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument6 pagesActivity No. 4 Amino Acids and ProteinsAngel EspanolNo ratings yet