Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Chem Semis Reviewer
Uploaded by
HakdogOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Chem Semis Reviewer
Uploaded by
HakdogCopyright:
Available Formats
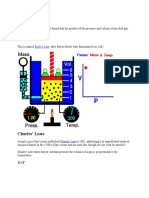
Jacques Charles (1746-1823)
- Was a French inventor, scientist,
mathematician, and balloonist. Charles
wrote almost nothing about mathematics,
and most of what has been credited to him
was due to mistaking him with another
Jacques Charles, also a member of the Paris
Academy of Sciences, entering on May
12,1785.
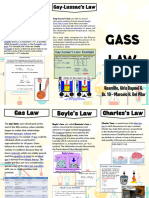
Charles Law
- Is an experimental gas law that describes
how gases tent to expand when heated. A
modern statement of Charles’s law is:
When the pressure on sample of a dry gas
is held constant, the Kelvin temperature
and the volume will be in direct proportion.
Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856)
- Was an Italian scientist, most noted for his
contribution to molecular theory now
known as Avogadro’s law, which states that
equal volumes of gases under the same
conditions of temperature and pressure will
contain equal numbers of molecules.
Avogadro’s Law
- Or Avogadro-Ampere’s hypothesis is an
experimental gas law relating the volume of
gas present. The law is a specific case of the
ideal gas law.
GAS LAWS
GAS
- Is a state of matter that has no fixed shape
and fixed volume.
- Also has a lower density compared to other
states of matter, such as solid and liquid.
Gases behave differently from solids and liquids due
to differences in their molecule behavior.
1. Gases are readily compressible
2. Volume of a gas refers to the free space
available for compression or molecular
motion. Therefore, volume of a gas is taken
to be equal to that of the container, not the
actual space that the molecules occupy.
3. Change in temperature changes gas volume
even when pressure is unchanged.
4. Densities of gases are much lower than
densities of the same substance n the solid
and liquid state under the same conditions
of temperature and pressure.
5. Gases are miscible, or can be mixed in all
proportions.
6. Gases are less viscous than liquids.
Pressure of a Gas
- Is the force that the gas exerts on the walls
of its container.
Pressure
- Is defined as the force exerted by colliding
molecules per unit area of container walls.
COMMON UNITS OF PRESSURE
THE IDEAL GAS LAWS
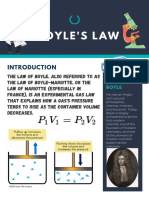
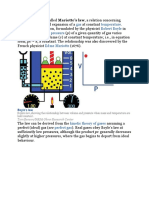
Robert Boyle (1627-1691)
- Was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher,
chemist, physicist, and inventor. Boyle
is largely regarded today as the first
modern chemist, and therefore one of
the founders of modern chemistry, and
one of the pioneers of modern
experimental scientific method.
Boyle’s Law
- Also referred to as the Boyle-Mariotte
Law, or Mariotte’s law(especially in
France), is an experimental gas law that
describes how the pressure of s gas
tends to decrease as the volume of the
container increases.
You might also like
- PVE Piping Layout Presentation - Part 2Document117 pagesPVE Piping Layout Presentation - Part 2Nguyen Quang NghiaNo ratings yet
- Vacuum DistillationDocument8 pagesVacuum DistillationPrashanth Chidambaram100% (1)
- Gpa 2145Document15 pagesGpa 2145Sergio David Ruiz100% (1)
- Predict Gas Hydrate FormationDocument4 pagesPredict Gas Hydrate Formationkronaf100% (1)
- GAS LAWS: Boyle's Law, Charles's Law and Gay-Lussac's Law: Waste-Face-Masks-Ppe-CovidDocument9 pagesGAS LAWS: Boyle's Law, Charles's Law and Gay-Lussac's Law: Waste-Face-Masks-Ppe-CovidMichiiee BatallaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: 1 MatterDocument8 pagesLearning Module: 1 MatterErika Magat CustodioNo ratings yet
- CE8403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringDocument15 pagesCE8403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringHussain Deen100% (1)
- Info GraphicsDocument3 pagesInfo Graphicsqt patootieNo ratings yet
- A Closer Look at Gases English Test N°4 Name: Date:: I. Answer The QuestionsDocument2 pagesA Closer Look at Gases English Test N°4 Name: Date:: I. Answer The QuestionsPocho RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chemitry ProjectDocument14 pagesChemitry Projectcharul sahuNo ratings yet
- Compilation OF Different Gas LawsDocument7 pagesCompilation OF Different Gas LawsJean Angelove SantosNo ratings yet
- Behavior of GasesDocument27 pagesBehavior of GasesIvan BobeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10Document8 pagesChemistry 10nowahernandez007No ratings yet
- Notes in Science 10Document2 pagesNotes in Science 10Sasha MaeNo ratings yet
- AbccDocument4 pagesAbccSushanta Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Solids LiquidsDocument2 pagesGas Laws: Solids LiquidsRaymond CabanillaNo ratings yet
- CITATION HTT /L 1033Document2 pagesCITATION HTT /L 1033Ahmad NajibNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law, Also Referred To As TheDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law, Also Referred To As TheMaria Lana Grace DiazNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Science IV: 1.) Boyle's LawDocument6 pagesAssignment: Science IV: 1.) Boyle's LawIrish WahidNo ratings yet
- SciDocument12 pagesSciYannyNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Mas1Document2 pagesConservation of Mas1PRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry ReviewerAlthea ElaineNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentGlady TagtagonNo ratings yet
- GasDocument12 pagesGasEgbebessemenow oben ashuNo ratings yet
- Lemuel Jay A. Segovia Science Q3M2Document3 pagesLemuel Jay A. Segovia Science Q3M2Zarah Joyce SegoviaNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 7Document1 pageAP Chemistry 7yudhis cieloNo ratings yet
- Gas Law Brochure SampleDocument2 pagesGas Law Brochure SampleVincentt Store100% (1)
- UP2 - Ch2. The Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument42 pagesUP2 - Ch2. The Kinetic Theory of Gasesdarnit2703No ratings yet
- Ley Ded Robert Boyle MariotteDocument2 pagesLey Ded Robert Boyle MariotteGianpierre de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument80 pagesGas LawsChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Law of DiffusionDocument2 pagesLaw of DiffusionDaniel CorcinoNo ratings yet
- Avgardos LawDocument3 pagesAvgardos LawSumesh ThekkepatNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: CE 314 - Engineering Utilities 2: Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument9 pagesGas Laws: CE 314 - Engineering Utilities 2: Basic Mechanical EngineeringMelanie Love Pjr AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Gay Lussac's LawDocument3 pagesGay Lussac's LawEn CsakNo ratings yet
- Quiz - 1Document6 pagesQuiz - 1rodgieoptionalNo ratings yet
- Amedeo AvogadroDocument8 pagesAmedeo AvogadroSameh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Boyle's Law (Sometimes Referred To As The Boyle-Mariotte Law) Is One of ManyDocument19 pagesBoyle's Law: Boyle's Law (Sometimes Referred To As The Boyle-Mariotte Law) Is One of ManyAngelie Peredo ArranzNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document6 pagesScience 10Andy ValdezNo ratings yet
- The Empirical Gas LawsDocument32 pagesThe Empirical Gas LawsMirabel SikaNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Navigation SearchDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law: Navigation SearchAdhoniyha Prospero Plinius-SuNealNo ratings yet
- Abstract and Compact Documentation of Hooke's Law and Boyle's LawDocument3 pagesAbstract and Compact Documentation of Hooke's Law and Boyle's LawAlexiaNo ratings yet
- كيمياء رابع علمي متميزينDocument132 pagesكيمياء رابع علمي متميزينalmuhndsNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Gas LawsDocument12 pagesModule 3 Gas Lawsmarcarvielloydperla3No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic ConceptDocument2 pagesThermodynamic ConceptMateo, Dale Vincent A.No ratings yet
- GASES SendingDocument2 pagesGASES Sendingyoow.youthNo ratings yet
- Ch5 ChemDocument21 pagesCh5 ChemNishwa NiaziNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument20 pagesGas LawsDavidNo ratings yet
- 5 GasesDocument6 pages5 GasesAnnie GraceNo ratings yet
- Austin, Vinny, Steven - Combined Gas Law PresentationDocument24 pagesAustin, Vinny, Steven - Combined Gas Law PresentationAustin MaNo ratings yet
- Avogadro's LawDocument3 pagesAvogadro's LawEn CsakNo ratings yet
- Q1-M1-KMT and Gas Laws (BL)Document34 pagesQ1-M1-KMT and Gas Laws (BL)Jim AñonuevoNo ratings yet
- Handouts in StoichDocument6 pagesHandouts in StoichAila Jane Olano VestidasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7Rochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Jerico June C. Gazil ScienceDocument4 pagesJerico June C. Gazil ScienceVirgie Cabuyao GazilNo ratings yet
- History: Thomas Graham EffusionDocument6 pagesHistory: Thomas Graham Effusionemmanuel_gwapoNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: ConstantDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law: ConstantChristian CabacunganNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: ConstantDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law: ConstantChristian CabacunganNo ratings yet
- S3-1 - AuditorioDocument54 pagesS3-1 - AuditorioPedro ArtetaNo ratings yet
- History of ChemistryDocument9 pagesHistory of ChemistryLyrielle DagsaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument17 pagesIntroduction To ChemistryLeovihilda BalalangNo ratings yet
- GASES and The Kinetic ThoeryDocument5 pagesGASES and The Kinetic ThoeryEnkhbayasgalan SodbayarNo ratings yet
- Empirical: Compression Gas Temperature Robert Boyle Pressure Edme MariotteDocument2 pagesEmpirical: Compression Gas Temperature Robert Boyle Pressure Edme MariotteSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Avogadro's LawDocument1 pageAvogadro's LawDestrofan GamingNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument2 pagesGas Lawfranklin.yin2020No ratings yet
- Noviembre 15 11 ENGDocument21 pagesNoviembre 15 11 ENGjmaldonado07No ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration by Kern and Bland Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesSolid Mensuration by Kern and Bland Solutions ManualJem Donan0% (2)
- 3 Properties of Refrigerants On P-H DiagramDocument7 pages3 Properties of Refrigerants On P-H DiagramJustin MercadoNo ratings yet
- DesalinationDocument21 pagesDesalinationberanosh100% (1)
- Lab Report 28 Molar Volume of Hydrogen GasDocument4 pagesLab Report 28 Molar Volume of Hydrogen GasShree samvunatNo ratings yet
- Fet Ci Projects Project-GM 3Document74 pagesFet Ci Projects Project-GM 3Gurpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Table of Specs - Long Test GAS LAWDocument2 pagesTable of Specs - Long Test GAS LAWMarlon Joseph ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems L1Document22 pagesChapter 3 Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems L1Toke BekeleNo ratings yet
- Manometer Instructions PortfolioDocument5 pagesManometer Instructions Portfolioapi-594255167No ratings yet
- NSPR Ipp Ac 001Document1 pageNSPR Ipp Ac 001rutujaNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle SEDocument3 pagesWater Cycle SEAlexNo ratings yet
- Name:Michael Max Rey C. Arnoza Date:21/07/2021 Check Your UnderstandingDocument4 pagesName:Michael Max Rey C. Arnoza Date:21/07/2021 Check Your UnderstandingMichaelmr ArnozaNo ratings yet
- Biomaterial AssignmentDocument4 pagesBiomaterial AssignmentAhmad DboukNo ratings yet
- Open Quiz When Told at 7:00 PM: Quiz 2 THURSDAY, November 18, 2004, 7:00-9:00 P.MDocument4 pagesOpen Quiz When Told at 7:00 PM: Quiz 2 THURSDAY, November 18, 2004, 7:00-9:00 P.MManu K VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Video - 18ME43 - Module 2 - Velocity Problems - YoganandaDocument11 pagesLecture Video - 18ME43 - Module 2 - Velocity Problems - YoganandaYogananda Bangalore ShanthamurthyNo ratings yet
- Brayton CycleDocument18 pagesBrayton CycleHassan SheikhNo ratings yet
- FM OrientationDocument32 pagesFM OrientationJoshua SaladiNo ratings yet
- Spillways and Energy DissipatorsDocument55 pagesSpillways and Energy Dissipatorsmustafa elrasheedNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)annamalai_s873323No ratings yet
- Presentation of DR A Gunasekar WHO Country Office For IndiaDocument23 pagesPresentation of DR A Gunasekar WHO Country Office For Indiajona phie MonteroNo ratings yet
- Dgttech Fchprod Compact Togb2 Rev2 11-V3Document2 pagesDgttech Fchprod Compact Togb2 Rev2 11-V3ctartzaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report in Atmosphere SandDocument3 pagesNarrative Report in Atmosphere SandJonathanNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument59 pagesFinal ProjectMariari KelvinNo ratings yet
- PHY02 - Course Outcome 1Document50 pagesPHY02 - Course Outcome 1k marcusNo ratings yet