Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histopath Pre Exam
Uploaded by
Marie Llanes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesHistopath Pre Exam
Uploaded by
Marie LlanesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
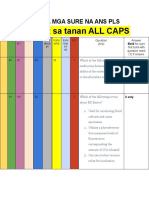
HISTOPATH PRE-EXAM HONING
15) Temp for water bath?
1) It refers to the rotting or decomposition 45 deg C
of the body due to bacterial action? 16) Common staining procedure in
PUTREFACTION Histopath?
2) The process by which the tissue is HEMATOXYLIN AND EOSIN
arranged in precise position in the mold 17) Natural dye from Mexican tree?
during embedding, on the microtome HEMATOXYLIN
before cutting, and on the slide before 18) Anionic dyes?
staining? ACID DYES
ORIENTATION 19) Purpose of descending concentrations
3) Paraffin wax substitute made up of of alcohol?
highly purified paraffin and synthetic REHYDRATION
plastic polymers? 20) Staining method that involves
PARAPLAST overstaining the tissue and then
4) Embedding mold consists of 2 differentiating the tissue details through
adjustable L-shaped strips of heavy decolorization?
brass or metal arranged on a flat metal REGRESSIVE STAINING
plate? 21) Staining method in which reaction
LEUCKHART’S EMBEDDING MOLD proceeds forward and is stopped once
5) The microtome used for EM is called? intensity of color is achieved?
ULTRATHIN MICROTOME PROGRESSIVE STAINING
6) A frozen section apparatus is called? 22) Staining method where tissue is
CRYOSTAT overstained and then differentiated or
7) Used for cutting celloidin sections? decolorized until only the desired
SLIDING MICROTOME elements remained stained?
8) Most dangerous type of microtome? REGRESSIVE STAINING
SLIDING 23) Staining method with the use of agents
9) Microtome invented by Paldwell Trefall such as mordants and accentuators?
designed to cut small and large blocks INDIRECT STAINING
of paraffin tissues? 24) Stain for neurofibril, axons, and
ROCKING MICROTOME dendrites?
10) Who introduced frozen sectioning? BIELSCHOWSKY’S
JULIUS CONHEIM 25) Stain for glycogen?
11) Designed by Adams for cutting PAS
celloidin-embedded tissues, considered 26) Stain for DNA?
the most dangerous microtome FEULGEN REACTION
because the exposed knife moves back 27) Special stain for glycogen?
and forth while the block holder remains PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF STAIN
stationary? 28) Stain for histones?
STANDARD SLIDING MICROTOME ALKALINE FAST GREEN
12) Type pf knife used only for celloidin 29) Stain for lipids?
work? SUDAN BLACK B
PLANO-CONCAVE 30) Mucicarmine stain is for?
13) Which of the ff is incorrectly matched? MUCIN
NONE OF THE ABOVE
31) Eosin stains?
14) The removal of gross nicks or ERYTHROCYTES, COLLAGEN, CYTOPLASM
irregularities on the knife edge and 32) Stain for copper?
grinding to restore sharpness? LINDQUIST’S MODIFIED RHODAMINE
33) Dye that is synthetic in nature? 49) Ideal time to perform fixation after
EOSIN interruption of blood supply?
34) Stain for melanin? 20 – 30 MINS
MASSON-FONTANA 50) Volume of fixative for museum
35) Method for calcium staining? specimens?
MODIFIED VON-KOSSA’S 50 – 100 times
36) Cationic dyes are those having a ___ 51) Order of tissue processing?
charge, and commonly known as ____? FIX-DEHYDRATE-CLEAR-IMPREGNATE
POSITIVE, BASIC 52) All are criteria for specimen rejection
37) Sudan III stains? except?
FATS ABSENT PATIENT’S MEDICATION
38) Carmine is produced from? 53) These are observable manifestations of
BUGS a disease?
39) Process of sealing the margins of the SIGNS
coverslip? 54) Failure of an organ to appear?
RINGING AGENESIA
40) Microscopic study of cells that have 55) Blockage or complete absence of an
been desquamated from epithelial opening or passage in an organ?
surfaces? ATRESIA
EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY 56) Excision and examination of solid tissues
41) Color of superficial cells when stained from living subjects?
with Papanicolaou stain? BIOPSY
ORANGE TO PINK 57) Most reliable feature of malignancy?
42) Dye in Papanicolaou that stains nothing ABILITY TO METASTASIZE
and is often omitted? 58) For specimen with tumors, all of these
BISMARCK BROWN Y must be identified except?
43) Absence of these in sputum means NONE OF THE CHOICES
saliva was collected rather than 59) Most important component of all tumor
sputum? resections?
ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES LYMPH NODES
44) Technique in autopsy where all organs 60) A tumor made up of nerve cells?
in thoracic, abdominal and pelvic are NEUROMA
removed at the same time? 61) Malignant tumor of epithelial cell origin?
EN MASSE CARCINOMA
45) Death of an organism as a whole, 62) Increase in size of tissues?
marked by cessation of functional HYPERTROPHY
activities of the different organs? 63) Clearing time of benzene?
SOMATIC DEATH 15 TO 60 MINS
46) Characterized by the cooling of the 64) Most rapid hardening and commonly
body, also known as “The Chill of used clearing agent?
Death”? XYLENE
ALGOR MORTIS 65) Becomes milky when dehydration is
incomplete?
47) Refers to the purplish discoloration of the XYLENE
skin due to pooling of blood in 66) Also known as dealcoholization?
capillaries? CLEARING
LIVOR MORTIS 67) Not a clearing agent?
48) Autopsy technique where organs were ALCOHOL
removed one by one? 68) Cytoplasmic fixatives: pH>4.6; Nuclear
VIRCHOW’S fixatives: pHN<4.6?
BOTH ARE CORRECT DOLOR
69) Not an additive fixative? 88) The body’s response to an injury,
ACETIC ACID involving vasculature, chemotactic
70) Not a non-coagulant fixative? factors and immune cells?
ZINC SALT INFLAMMATION
71) Smallest aldehyde? 89) Stain for reticulin?
GLYCOXAL GOMORI’S
72) Fixatives that create a network that 90) Used for honing badly nicked knives?
allows solution to readily penetrate the FINE CARBORUNDUM
interior of the tissue? 91) Ideal fixative to tissue ratio?
COAGULANT 15-20:1
73) Most rapid fixative? 92) Normal hydrogen ion concentration of
CARNOY’S fixatives?
74) Not a non-coagulant fixative? pH 6-8
ALCOHOL 93) Primary goal of fixation?
75) Fixative for urgent biopsies? PRESERVE MORPHOLOGIC AND
CARNOY’S INTEGRITY OF THE CELL
76) Both a nuclear and histochemical 94) Fixatives that act on tissue without
fixative? chemically combining with it?
NEWCOMER’S NON-ADDITIVE FIXATIVES
77) Osmolality: Slightly hypotonic; pH: 95) Cytoplasmic fixatives contain glacial
neutral/6-8? acetic acid; Glacial acetic acid
I IS INCORRECT WHILE II IS CORRECT destroys mitolchondria and golgi
78) Highly explosive when dry? bodies?
PICRIC ACID I IS INCORRECT AND II IS CORRECT
79) Black precipitate of mercury can be 96) First and most crucial step in tissue
removed by? processing?
ALCOHOLIC IODINE SOLUTION FIXATION
80) Characteristic of an ideal dehydrating 97) All are functions of fixation except?
agent? NONE OF THE ABOVE
MUST BE ABLE TO DEHYDRATE WITHOUT 98) All of these factors are affecting fixation
PRODUCING CONSIDERABLE SHRINKAGE except?
OR DISTORION NONE OF THE CHOICES
81) Process of placing tissue in ascending
grades of alcohol?
DEHYDRATION
82) Deals with preparation of tissues for
microscopic examination?
HISTOPATH TECHNIQUES
83) Epithelia found in urinary tract lining?
TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM
84) Transitional epithelial cells are seen in?
URINARY BLADDER
85) Epithelial cells that form the lining of the
mouth, throat, and esophagus?
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS
86) Father of modern pathology?
VIRCHOW
87) Cardinal sign which means pain?
You might also like
- Colloidal Gold: Principles, Methods, and ApplicationsFrom EverandColloidal Gold: Principles, Methods, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- WORKING WITH MIGMATITES Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series Volume 38Document168 pagesWORKING WITH MIGMATITES Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series Volume 38Walter Cruz MermaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Zoological Micropalaeontology: International Series of Monographs on Earth Sciences, Vol. 1From EverandPrinciples of Zoological Micropalaeontology: International Series of Monographs on Earth Sciences, Vol. 1No ratings yet
- Ophtho SolvedDocument26 pagesOphtho SolvedDr Afzal HussainNo ratings yet
- Untitled15 PDFDocument22 pagesUntitled15 PDFElizabeth LeonNo ratings yet
- Human Actinomycosis: What the General Practitioner Ought to Know AboutFrom EverandHuman Actinomycosis: What the General Practitioner Ought to Know AboutNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument113 pagesManualJose PototskiNo ratings yet
- Manual de HistotecnologíaDocument113 pagesManual de Histotecnologíaderyan mirandaNo ratings yet
- Sans TitreDocument6 pagesSans TitrerollinpeguyNo ratings yet
- Specialized Techniques in DermatopathologyDocument23 pagesSpecialized Techniques in Dermatopathologyadriana PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Quiz IntegumentaryDocument44 pagesQuiz IntegumentaryMedShare100% (5)
- RAU's IAS - Science & Technology - BookDocument249 pagesRAU's IAS - Science & Technology - Booksanyam jainNo ratings yet
- Untitled5 PDFDocument16 pagesUntitled5 PDFElizabeth LeonNo ratings yet
- HTMLE SEMINAR NOTES DOC. ORTEGA - CompressedDocument35 pagesHTMLE SEMINAR NOTES DOC. ORTEGA - CompressedNISSI JUNE T. UNGABNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spatial Mapping of Biomolecules by Imaging Mass Spectrometry Bindesh Shrestha Full ChapterDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Spatial Mapping of Biomolecules by Imaging Mass Spectrometry Bindesh Shrestha Full Chaptercathy.johnson159100% (4)
- PPSC Past Paper Lecturer Papaer Biology 15!06!2015Document6 pagesPPSC Past Paper Lecturer Papaer Biology 15!06!2015Kashmala Zia khanNo ratings yet
- Cmai PG Diploma in Histopathological Techniques Final Examination 2014Document6 pagesCmai PG Diploma in Histopathological Techniques Final Examination 2014Reuben VijaysekarNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Introduction To Spatial Mapping of Biomolecules by Imaging Mass Spectrometry PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Introduction To Spatial Mapping of Biomolecules by Imaging Mass Spectrometry PDFwillie.carr901100% (15)
- UntitledDocument339 pagesUntitledJOS� FRANCISCO G�MEZ RODR�GUEZNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Sample BTXLDocument16 pagesMicrobiology Sample BTXLaditya paulNo ratings yet
- Htmle Diagnostic Exam RatioDocument18 pagesHtmle Diagnostic Exam RatioAlliah Jessa PascuaNo ratings yet
- Final 1 (12TH June) - 230530 - 115919Document26 pagesFinal 1 (12TH June) - 230530 - 115919Arda DumanNo ratings yet
- A Picture of Gwenyth Paltros Vagina Candle 1Document45 pagesA Picture of Gwenyth Paltros Vagina Candle 1Trisha ArtosNo ratings yet
- Raus PRE COMPASS 2024 SCIENCE TECHNOLOGYDocument165 pagesRaus PRE COMPASS 2024 SCIENCE TECHNOLOGYjeshwanth2305No ratings yet
- Sodium Hypochlorite, Bleaching Agents, and The Stratum CorneumDocument4 pagesSodium Hypochlorite, Bleaching Agents, and The Stratum CorneumMuhammad Jawad Ul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Study Question Chp3Document10 pagesAnatomy Study Question Chp3Hema JothyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 4 - Biological Classifiation - Answer KeyDocument1 pageWorksheet - 4 - Biological Classifiation - Answer KeyVishalNo ratings yet
- Hema Lab Quiz CompilationDocument6 pagesHema Lab Quiz CompilationFrancis Zaccheau ValdezNo ratings yet
- Histology Prelim Review Notes Leclab 1Document16 pagesHistology Prelim Review Notes Leclab 1Justin BellosaNo ratings yet
- J Clin Pathol 1972 Marks 799 803Document6 pagesJ Clin Pathol 1972 Marks 799 803Arif RahmadiNo ratings yet
- The Operative's DossierDocument100 pagesThe Operative's DossierReinner Vasconcelos100% (3)
- Integumentary SystemDocument13 pagesIntegumentary SystemRayyanNo ratings yet
- LiposomesDocument71 pagesLiposomesDr. Aliha AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Asti Ghar Maa Hudaa Test Ko SolnDocument12 pagesAsti Ghar Maa Hudaa Test Ko SolnManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Document68 pagesCutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Marl EstradaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Nanotechnology: Lecture 19: in Vitro Methods To Study Antibacterial and Anticancer Properties of NanomaterialsDocument46 pagesBiomedical Nanotechnology: Lecture 19: in Vitro Methods To Study Antibacterial and Anticancer Properties of NanomaterialsDURGA DEVI T 037 BMENo ratings yet
- Staining and Micros PDFDocument51 pagesStaining and Micros PDFIshaanNo ratings yet
- XII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyDocument1 pageXII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyKishor KumarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology A Systems Approach 6th Edition Marjorie Kelly Cowan Heidi SmithDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology A Systems Approach 6th Edition Marjorie Kelly Cowan Heidi SmithAmandaReynoldsagfcy100% (24)
- DermatologyDocument44 pagesDermatologyakufahaba100% (2)
- Microbiology PDFDocument40 pagesMicrobiology PDFputri tyas100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions Subject: Microbiology: Question Bank: Mcqs Department of Biotechnology, SacDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Subject: Microbiology: Question Bank: Mcqs Department of Biotechnology, SacDulay, Shennah S.No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY - Assignment: Chapter: Biotechnology: Principles and Processes & Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY - Assignment: Chapter: Biotechnology: Principles and Processes & Biotechnology and Its Applicationsyogesh ahireNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Easy GuideDocument38 pagesDermatology Easy GuideGina Ramirez RosaNo ratings yet
- Scene Examination For BombingDocument28 pagesScene Examination For BombingNasraRealino100% (1)
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 2nd Edition Bauman Test BankDocument14 pagesMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 2nd Edition Bauman Test BankDonna Browning100% (30)
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (Antibiogram) : DR Alia Abdel MonaemDocument51 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (Antibiogram) : DR Alia Abdel MonaemAlia Abdelmonem100% (1)
- Giovanni Fogazzi. The Urinary SedimentDocument269 pagesGiovanni Fogazzi. The Urinary SedimentAlexis Martín Pérez LozanoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive For MBDocument26 pagesComprehensive For MBAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Exfoliative Cytology: NAME-Saniya Kulkarni Class-3 Year Roll No-22Document27 pagesExfoliative Cytology: NAME-Saniya Kulkarni Class-3 Year Roll No-22bhushanNo ratings yet
- CH 4take Home Test - Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesCH 4take Home Test - Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemKatieNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 13th Edition MadiganDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Brock Biology of Microorganisms 13th Edition MadiganjendengrawrNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1 Final TermDocument1 pageQuiz No. 1 Final TermジェスNo ratings yet
- FulltextDocument10 pagesFulltextakshadaranalkar27No ratings yet
- 12 - Zoology - Second Revision Test - 2022Document4 pages12 - Zoology - Second Revision Test - 2022Rangaraj RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Endotoxin - Group 2Document2 pagesEffect of Endotoxin - Group 2Polu ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Decalcification: By: Riman Mustafa IbrahimDocument21 pagesDecalcification: By: Riman Mustafa IbrahimdaliaNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Reproduction of ALgaeDocument810 pagesThe Structure and Reproduction of ALgaeManudev MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Micro ExamDocument7 pagesMicro ExamMarie Llanes100% (1)
- Med Tech LawsDocument78 pagesMed Tech LawsMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Blood BankDocument10 pagesBlood BankMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Immunosero Review Notes 1Document41 pagesImmunosero Review Notes 1Marie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1 Laboratory ModuleDocument1 pageHematology 1 Laboratory ModuleMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- BB Aytona Aug 2021Document43 pagesBB Aytona Aug 2021Marie LlanesNo ratings yet
- CC ChekDocument105 pagesCC ChekMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review NotesDocument27 pagesParasitology Review NotesMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Deed of Undertaking Limited F2F InternshipDocument2 pagesDeed of Undertaking Limited F2F InternshipMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- 1 Immunology Serology NotesDocument13 pages1 Immunology Serology NotesMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Histopathology Review BookletDocument21 pagesHistopathology Review BookletMarie Llanes100% (1)
- Histopathology Chapter 1 11Document38 pagesHistopathology Chapter 1 11Marie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1:: Capillary Fragility TestDocument1 pageLaboratory Activity 1:: Capillary Fragility TestMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Takehome MCQ Questions Hema1Document5 pagesTakehome MCQ Questions Hema1Marie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Local Media5318352258259372198Document23 pagesLocal Media5318352258259372198Marie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes 2Document69 pagesMicrobiology Notes 2Marie Llanes100% (1)
- Name: Gotoh, Aaron Tzergio C. DATE: 05/12/20 Erythrocyte Indices WorksheetDocument3 pagesName: Gotoh, Aaron Tzergio C. DATE: 05/12/20 Erythrocyte Indices WorksheetMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Give The Tests Done Using The Different Timed SpecimenDocument1 pageGive The Tests Done Using The Different Timed SpecimenMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Anurbf - 222508387Document2 pagesCase Study - Anurbf - 222508387Marie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Aaron Tzergio C. Gotoh: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesAaron Tzergio C. Gotoh: Personal InformationMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Disc & Motivators Report For: Aaron Tzergio GotohDocument10 pagesDisc & Motivators Report For: Aaron Tzergio GotohMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Activity 14 Gotoh Aaron TzergioDocument3 pagesActivity 14 Gotoh Aaron TzergioMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2Document89 pagesHematology 2Marie Llanes100% (1)
- X FilesDocument47 pagesX FilespopNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: The MeningesDocument5 pagesMeningitis: The MeningesGiane DavidNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy ThesisDocument4 pagesBrain Anatomy Thesisbrittanyjonescolumbia100% (2)
- Termin SarafDocument26 pagesTermin SarafSyifa KaniaNo ratings yet
- A Case of DNSDocument14 pagesA Case of DNSAviNo ratings yet
- Ocular Examination and Imaging TechniqueDocument33 pagesOcular Examination and Imaging TechniqueluckyNo ratings yet
- Speech and Communication DisordersDocument3 pagesSpeech and Communication Disordersalessandra padulaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral NeuropathyDocument30 pagesPeripheral NeuropathyLyn LynNo ratings yet
- The TUR Syndrome REVDocument19 pagesThe TUR Syndrome REVTitus RheinhardoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Lumbar PunctureDocument19 pagesLesson Plan Lumbar PunctureLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)No ratings yet
- G9 - Lesson 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesG9 - Lesson 1 Cardiovascular SystemKhrean Kae SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Long TestDocument2 pagesLymphatic System Long TestSucceed ReviewNo ratings yet
- Autopsy Report For Wade WelchDocument8 pagesAutopsy Report For Wade WelchKOLD News 13No ratings yet
- 2018 CONTINUUM Multimodality Monitoring in The Neurocritical Care UnitDocument13 pages2018 CONTINUUM Multimodality Monitoring in The Neurocritical Care UnitKarl Jimenez SeparaNo ratings yet
- Cocaine-mediated circadian reprogramming in the striatum through dopamine D2R and Ppar γ activationDocument14 pagesCocaine-mediated circadian reprogramming in the striatum through dopamine D2R and Ppar γ activationGabriele SantosNo ratings yet
- Embryo Development (Embryogenesis)Document31 pagesEmbryo Development (Embryogenesis)SHEMAR STEWARTNo ratings yet
- Cellular Communication POGILDocument5 pagesCellular Communication POGILJiwon Shin60% (5)
- Spindle Cell TumorsDocument138 pagesSpindle Cell TumorsMadhura ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- Head Injuries Adelina NorvaisyteDocument14 pagesHead Injuries Adelina Norvaisyteadelina.norvaisyteNo ratings yet
- Mild Fetal VentriculomegalyDocument8 pagesMild Fetal VentriculomegalyFeli FelNo ratings yet
- Classification of Intervertebral Disc Disease - 2020Document17 pagesClassification of Intervertebral Disc Disease - 2020Alice PaimNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 13th Edition Shier Test BankDocument31 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 13th Edition Shier Test BankKatherineBowenfojib100% (15)
- Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Spinal CordGargi MPNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy Narayani FinderDocument50 pagesHomeopathy Narayani FinderNicky Chhajwani100% (1)
- Vertiginous EpilepsyDocument5 pagesVertiginous Epilepsyzudan2013No ratings yet
- 03 Retinal Vascular Occlution - Dr. Darwan Triyono, SP.MDocument28 pages03 Retinal Vascular Occlution - Dr. Darwan Triyono, SP.MDissa Yulianita SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Hyt Patho MmeDocument3 pagesHyt Patho MmeSagnik BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Performance Freediving Medical Form: Name: Date of BirthDocument1 pagePerformance Freediving Medical Form: Name: Date of BirthAnonymous I5hdhuCxNo ratings yet
- CNS Tumor Map 2020 FullDocument1 pageCNS Tumor Map 2020 FullAlves de MeloNo ratings yet
- პანკრეასიDocument24 pagesპანკრეასიSASIDHARNo ratings yet