Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanical Drawing and Design N6 QP
Uploaded by
murendeni phuluwaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanical Drawing and Design N6 QP
Uploaded by
murendeni phuluwaCopyright:
Available Formats
T1150(E)(N14)T
NOVEMBER 2012
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE
MECHANICAL DRAWING AND DESIGN N6
(8090086)
14 November (X-Paper)
09:00 – 13:00
OPEN-BOOK EXAMINATION.
This question paper consists of 5 pages.
Copyright reserved NOV 2012 Please turn over
(8090086) -2- T1150(E)(N14)T
DEPARTMENT OF HIGHER EDUCATION AND TRAINING
REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE
MECHANICAL DRAWING AND DESIGN N6
TIME: 4 HOURS
MARKS: 100
________________________________________________________________________
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Number the answers according to the numbering system used in this question
paper.
3. ALL work you do NOT want to be marked must be clearly crossed out.
4. A correct answer is worth only ONE mark. Show ALL the steps to obtain as
many marks as possible. (An incorrect answer which must be carried
forward will receive fair consideration.)
5. One mark = 1%.
6. Write neatly and legibly.
Copyright reserved NOV 2012 Please turn over
(8090086) -3- T1150(E)(N14)T
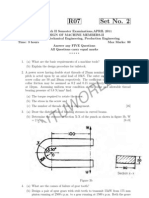
QUESTION 1
The diagram shows a part of a gear reduction unit. The pinion has 25 teeth with a
tooth module of 8 mm, rotates at 1 000 r/min and delivers 150 kW. The transmission
ratio is 5:1. The spur gear has a mass of 40 kg and is mounted on a hollow shaft with
an inside diameter four-tenths of the outside diameter (d = 0,4 D).
Consider a temporary overload of 10% when determining the hollow shaft torque.
Calculate the following:
1.1 The hollow shaft diameters for combined stresses. Use the following
stresses:
Tensile stress : 60 MPa
Shear stress : 50 MPa (24)
1.2 The tooth width for the gear pair. Use the Lewis formula for the gear width
calculations. Check the answers.
The spur gear has a basic stress of 250 MPa and the pinion has a basic
stress of 320 MPa. (12)
1.3 ALL the required gear wheel dimensions including the boss, key, outside
diameter and spoke sizes.
Gear wheel spokes : 4
Ratio of axis of elliptical spokes : 2:1
Allowable bending stress in arms : 16 MPa (12)
[48]
Copyright reserved NOV 2012 Please turn over
(8090086) -4- T1150(E)(N14)T
QUESTION 2
Collar bearings are used to support a shaft with an axial load of 150 kN. The shaft
rotates at 400 r/min. The outside diameter of the collar bearings is 250 mm and the
inside diameter is 80 mm. The average permissible intensity of normal pressure on the
collars is 250 kPa and the coefficient of friction is 0,03.
Determine the following:
2.1 The number of collars required (2)
2.2 The actual intensity of normal pressure on the collars (2)
2.3 The torque required to overcome friction in the bearings (4)
2.4 The heat generated in J/s at the bearings (3)
2.5 The amount of cooling oil which must be circulated through the bearings in
litres per minute to absorb the heat generated if the specific heat capacity of
the oil is 1,8 kJ/kg oC. The density of the oil is 800 kg/m3. The difference in
oil temperature between exit and entrance is 30 oC. (4)
[15]
QUESTION 3
A single-plate clutch has inside and outside diameters of 160 mm and 300 mm
respectively. The friction material provides a coefficient of friction of 0,4 when in
contact with the flywheel. The maximum engine torque is 245 Nm. A clamping force
of 1 200 N is provided by each of the EIGHT springs when the springs are compressed
to 6 mm.
Calculate the following:
3.1 The factor of safety with respect to slippage when the clutch is new (uniform
pressure) (6)
3.2 The factor of safety with respect to slippage after initial wear has taken place
(uniform wear) (4)
3.3 How much can the friction material wear before the clutch will slip? (4)
3.4 The power transmitted at 900 r/min (uniform wear) (1)
[15]
Copyright reserved NOV 2012 Please turn over
(8090086) -5- T1150(E)(N14)T
QUESTION 4
The diagram shows a mild steel compression member.
The 50 mm diameter pins each has a bearing surface length of 40 mm and when the
member is in compression the bearing pressure in the eye portion is 8 MPa.
Regard the member as a column with the end fixation conditions as follows:
4.1 Relative to the X-X axis the ends may be regarded as pivoted (hinged)
4.2 Relative to the Y-Y axis the ends may be regarded as fixed.
Use the Rankine formula with appropriate constants and determine the stresses
induced in the material for the above conditions in 4.1 and 4.2.
[13]
QUESTION 5
A 350 mm pulley rotating at 900 r/min has to transmit 42 kW by means of a flat belt to
a second pulley 750 mm in diameter, the pulley centres being 1,5 m apart. The belt,
18 mm thick, has a mass of 0,8 kg/m and may be loaded to a maximum value of
30 N/mm belt width. Assume the friction coefficient as 0,4 and calculate the following:
5.1 Belt width (8)
5.2 Belt length (1)
[9]
TOTAL: 100
Copyright reserved NOV 2012 Please turn over
You might also like
- r05321403 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pagesr05321403 Principles of Machine DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- rr321401 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pagesrr321401 Principles of Machine DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Strength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesFrom EverandStrength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- B.Tech Degree S8 (S, FE) / S6 (PT) (S, FE) Examination June 2023 (2015 Scheme)Document3 pagesB.Tech Degree S8 (S, FE) / S6 (PT) (S, FE) Examination June 2023 (2015 Scheme)Venkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- T1080 - Mechanical Drawing and Design N5 QP Apr 2018Document6 pagesT1080 - Mechanical Drawing and Design N5 QP Apr 2018pearlmayongoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- t1120 Mechanotechnics n4 QP April 2017Document9 pagest1120 Mechanotechnics n4 QP April 2017bistopooe3No ratings yet
- Mech Design N6 Q&A CombinedDocument406 pagesMech Design N6 Q&A CombinedNyiko DaveNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine ElementsDocument3 pagesDesign of Machine ElementsHariharanAutoNo ratings yet
- MD-III - TUT - 5 and 6Document5 pagesMD-III - TUT - 5 and 6Sushil ThakkarNo ratings yet
- rr320305 Design of Machine Members IIDocument8 pagesrr320305 Design of Machine Members IISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- r05320305 Design of Machine Members IIDocument11 pagesr05320305 Design of Machine Members IISrinivasa Rao G100% (4)
- rr321401 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pagesrr321401 Principles of Machine DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 08 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IDocument9 pages08 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IKrupanandareddyYarragudiNo ratings yet
- Me1302 DmeDocument4 pagesMe1302 DmesumikannuNo ratings yet
- nr321401 Principles of Machine DesignDocument2 pagesnr321401 Principles of Machine DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- r05320305 Design of Machine Members IIDocument9 pagesr05320305 Design of Machine Members IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- ECP210 11 ECP210Dec2010Document4 pagesECP210 11 ECP210Dec2010Priviledge MuzotaNo ratings yet
- rr312404 Design of Machine ElementsDocument8 pagesrr312404 Design of Machine ElementsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Machine Design-II EME602 2012-13Document4 pagesMachine Design-II EME602 2012-13nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- SOM Ques KeyDocument15 pagesSOM Ques KeySiva RamanNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ame, Me)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ame, Me)Vikranth DeepakNo ratings yet
- TE 2008 Mechanical Qp2013Document56 pagesTE 2008 Mechanical Qp2013avinash119870% (1)
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.lavanya babuNo ratings yet
- Free Mechanotechnics N4 Question Memo DownloadDocument18 pagesFree Mechanotechnics N4 Question Memo Downloadck.cathykayNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Mechanical Engineering)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Mechanical Engineering)Mohammed SohailNo ratings yet
- R5310305-Design of Machine Members - IDocument4 pagesR5310305-Design of Machine Members - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Supp Nov 2009Document10 pagesSupp Nov 2009prk74No ratings yet
- B.S.A.C.E.T., Mathura Machine Design/MD-II (KME602/RME603) B.Tech., 6 SEMESTER, CT-2, 2021-22Document1 pageB.S.A.C.E.T., Mathura Machine Design/MD-II (KME602/RME603) B.Tech., 6 SEMESTER, CT-2, 2021-22ROHIT SRIVASTAVNo ratings yet
- S7 Previous Year QPDocument31 pagesS7 Previous Year QPbjt2k1No ratings yet
- N5 Strength of Materials and Structures November 2020Document7 pagesN5 Strength of Materials and Structures November 2020lechutnmNo ratings yet
- rr320305 Design of Machine Members IIDocument8 pagesrr320305 Design of Machine Members IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- N5 Mechanotechnics August 2022 Question PaperDocument9 pagesN5 Mechanotechnics August 2022 Question PaperBlessing ChumaNo ratings yet
- Me8593 - Dme - Model QPDocument3 pagesMe8593 - Dme - Model QPChandrasekhar PrabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Mechanotechnology Question Memo N3 DownloadDocument22 pagesMechanotechnology Question Memo N3 DownloadMonaheng DimoNo ratings yet
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocument6 pages4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Design of Machine Members: Part-ADocument4 pagesDesign of Machine Members: Part-ARkrishna ANo ratings yet
- Dmm2 Mar2006Document8 pagesDmm2 Mar2006Abdul Saleem MohammedNo ratings yet
- 3-1 DMM1 (Nov 2009 Regular)Document9 pages3-1 DMM1 (Nov 2009 Regular)micmechNo ratings yet
- 15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIDocument2 pages15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIJagannath CherkuNo ratings yet
- AECD QuestionsDocument7 pagesAECD QuestionssbkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1QS8ME Winter2020Document2 pagesAssignment 1QS8ME Winter2020VinayakNo ratings yet
- t1000 Mechanical Drawing and Design n5 QP Aug 2014Document6 pagest1000 Mechanical Drawing and Design n5 QP Aug 2014Mokgadi KupaNo ratings yet
- 2 Design of Machine Elements MechDocument2 pages2 Design of Machine Elements MechSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- R8 Nov-Dec-2015Document3 pagesR8 Nov-Dec-2015Hari VenkitNo ratings yet
- Machine Design - LDocument2 pagesMachine Design - LNilesh Mistry (Nilesh Sharma)No ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument6 pagesMachine DesignRishi SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Paper For MeDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper For MeVishal JhaNo ratings yet
- Makalah GTWDocument8 pagesMakalah GTWfaisalNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological Universityrajushamla9927No ratings yet
- 15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIDocument2 pages15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIJagannath CherkuNo ratings yet
- DME4THDocument17 pagesDME4THManivannanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1Document2 pagesAssignment-1Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- 9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pages9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIDocument11 pages07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIzahid_polyNo ratings yet
- Snist Dom Previous PaperDocument9 pagesSnist Dom Previous PaperKapil Siddhant DevulapalliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Academy: Mechanical Engineering Ese Conventional Test - 5Document8 pagesEngineering Academy: Mechanical Engineering Ese Conventional Test - 5vidya chakitwarNo ratings yet
- Barangay Budget ExecutionDocument6 pagesBarangay Budget Executionlinden_07100% (1)
- Re Assignment MarriageDocument2 pagesRe Assignment MarriageSamNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction: Raeesa VakilDocument18 pagesJurisdiction: Raeesa VakilAadhitya NarayananNo ratings yet
- Ang Vs American Steamship DigestDocument2 pagesAng Vs American Steamship DigestsaraNo ratings yet
- CAPE Accounting Unit 1 2009 P2Document8 pagesCAPE Accounting Unit 1 2009 P2Sachin BahadoorsinghNo ratings yet
- John Oda v. Transcon Lines Corporation, 650 F.2d 231, 10th Cir. (1981)Document4 pagesJohn Oda v. Transcon Lines Corporation, 650 F.2d 231, 10th Cir. (1981)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument10 pagesMomentumBatisane Kantsu MathumoNo ratings yet
- GAAPDocument2 pagesGAAPMunaf KhanNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Social Security Benefit Payments 2019: Socialsecurity - GovDocument1 pageSchedule of Social Security Benefit Payments 2019: Socialsecurity - GovBejan OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Reading OrganizerDocument3 pagesChapter 18 Reading OrganizerAnna SongNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledPhillips West News OutletNo ratings yet
- Beaches and Resorts TariffsDocument31 pagesBeaches and Resorts TariffskudaNo ratings yet
- Ia 2Document2 pagesIa 2Nadine SofiaNo ratings yet
- Mack The Knife (Arr. Rick Stitzel) - Tenor Sax 1 Sheet Music Bobby Darin Jazz EnsembleDocument1 pageMack The Knife (Arr. Rick Stitzel) - Tenor Sax 1 Sheet Music Bobby Darin Jazz EnsembleAlan MackieNo ratings yet
- SIP Report Atharva SableDocument68 pagesSIP Report Atharva Sable7s72p3nswtNo ratings yet
- #1. Register: Steps in Becoming A Lazada SellerDocument5 pages#1. Register: Steps in Becoming A Lazada SellerblessingNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Warranty Expired:NDocument3 pagesTax Invoice: Warranty Expired:NSanjay PatelNo ratings yet
- SHFC Applicant Data SheetDocument2 pagesSHFC Applicant Data SheetAlvy Faith Pel-eyNo ratings yet
- Rationale As1099C Has Been Reaffirmed To Comply With The Sae Five-Year Review PolicyDocument3 pagesRationale As1099C Has Been Reaffirmed To Comply With The Sae Five-Year Review PolicyLarry HareNo ratings yet
- KSA ODN ConfigurationDocument7 pagesKSA ODN ConfigurationAhmed Hamouda NasrNo ratings yet
- PelicanStores QMDocument26 pagesPelicanStores QMPhuntru PhiNo ratings yet
- Important!: Flights Hotel CAR Rentals Manage MY BookingDocument3 pagesImportant!: Flights Hotel CAR Rentals Manage MY BookingAlena FediakinaNo ratings yet
- 1980 Convention On Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) : Advisory ServiceDocument2 pages1980 Convention On Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) : Advisory ServicePrincess Rosshien HortalNo ratings yet
- Drafting Project SynopsisDocument5 pagesDrafting Project SynopsisbhanwatiNo ratings yet
- Did Pharoah Drown in The Red SeaDocument4 pagesDid Pharoah Drown in The Red SeaAnonymous d8N4gqNo ratings yet
- Jackson V AEG Live July 17th 2013 Transcripts of Arthur Erk (Entertainment Industry Certified Public Accountant)Document125 pagesJackson V AEG Live July 17th 2013 Transcripts of Arthur Erk (Entertainment Industry Certified Public Accountant)TeamMichaelNo ratings yet
- All SitesDocument21 pagesAll SitesFurqon MahdiNo ratings yet
- What Holds Japan BackDocument6 pagesWhat Holds Japan BackMaryamNo ratings yet
- BD 041222 ICC Update Bank ListDocument18 pagesBD 041222 ICC Update Bank ListArdian MantowNo ratings yet
- Procurment Management Plan TemplateDocument15 pagesProcurment Management Plan TemplateMonil PatelNo ratings yet