Professional Documents
Culture Documents
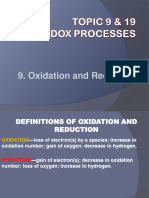
Oxidising and Reducing Agents
Uploaded by
KOVLEEN SAHNIOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oxidising and Reducing Agents
Uploaded by
KOVLEEN SAHNICopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 9 Study of the first element-Hydrogen Dr.
Kovleen Sahni
Oxidation Reduction
Electronic concept: Electronic concept:
Process in which an atom or ion loses electrons: Process in which an atom or ion gains electrons:
Zn -2e- Zn2+ Cu2+ + 2e- Cu
Addition of oxygen Removal of oxygen
2Mg + O2 2MgO CuO + H2 Cu + H2O
C + O2 CO2 ZnO + C Zn + CO
Addition of electronegative atom Addition of electropositive atom/ion
2FeCl2 + Cl2 2FeCl3 2HgCl2 + SnCl2 Hg2Cl2 + SnCl4
Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2
Removal of Hydrogen Addition of Hydrogen
H2S + Cl2 2HCl + S H2S + Cl2 2HCl + S
2NH3 + 3Cl2 2FeCl2 + 2HCl + S
Removal of electropositive ion Removal of electropositive ion
2KI + H2O2 2KOH + I2 2KI + H2O2 2KOH + I2
Oxidising agent: Oxidises other substance by: Oxidising agent: Oxidises other substance by:
a. Accepting electrons a. Providing electrons
b. providing oxygen b. providing hydrogen
c. providing electronegative ion c. providing electropositive ion
d. removing hydrogen d. removing oxygen
e. removing electro positive ion e. removing electro negative ion
Examples: Examples:
Solids : MnO2, red lead, KMnO4, K2Cr2O7 Solids : C, Zn, Al, Cu, Stannous chloride, glucose
Liquid: Bleaching powder, conc. HNO3, conc. H2SO4, Liquid: H2O2, HI, HBr
Br2
Gaseous : H2S, CO, SO2, NH3
Gaseous : O2, O3, Cl2, SO2
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HydrogenDocument25 pagesChemistry HydrogenHarshwardhan UndeNo ratings yet
- Std.8 Module.7 Semester.2Document56 pagesStd.8 Module.7 Semester.2Md ZayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document11 pagesChapter 4J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Note For G12 DBSDocument19 pagesElectrochemistry Note For G12 DBSlenlucy13frNo ratings yet
- Post-Lab 6 Copper Cycle-ProblemsDocument4 pagesPost-Lab 6 Copper Cycle-ProblemsUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsDocument2 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis of Molten SaltsSunnyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualDocument8 pagesChemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualCindyCurrydwqzr100% (74)
- Electrochemistry NoteDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry NoteNaguib Zakaria100% (3)
- Lab 2 - 555Document9 pagesLab 2 - 555Nurzawanah AkmarNo ratings yet
- 6A Electrochemistry - AnswerDocument6 pages6A Electrochemistry - AnswerWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- HydrogenDocument22 pagesHydrogenKeerthana MNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis O LevelDocument17 pagesElectrolysis O LevelInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- Redox Dan Electrochemistry (Kimia)Document65 pagesRedox Dan Electrochemistry (Kimia)Rocky Simon HiaNo ratings yet
- Redox Practice Test 2Document22 pagesRedox Practice Test 2Sam KothuriNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationTharmendran MaganteranNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument41 pagesElectrochemistry Notesthomaspodo76No ratings yet
- 1 ElectrochemistryTheoryDocument29 pages1 ElectrochemistryTheoryEdon Bedi100% (1)
- RedoxDocument14 pagesRedoxsaraNo ratings yet
- New Electrolysis 1Document18 pagesNew Electrolysis 1Rethabile LekgethoNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis in SolutionsDocument13 pagesElectrolysis in SolutionsTeandraNo ratings yet
- Test4 Ch19 Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsDocument13 pagesTest4 Ch19 Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsPhysiochemo Chemical100% (1)
- Introductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Document26 pagesIntroductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Ayanthi ShashikalaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry II Jasperse Electrochemistry. Extra Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry II Jasperse Electrochemistry. Extra Practice ProblemsYash BhattNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument32 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationsAple RigorNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: Redox EquationsDocument3 pagesChemguide - Answers: Redox EquationsKokuro MurozakiNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSISDocument12 pagesELECTROLYSISKatlo KgosiyangNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction - Chemical Reactions in Which Both Oxidation and Reduction Occur SimultaneouslyDocument17 pagesRedox Reaction - Chemical Reactions in Which Both Oxidation and Reduction Occur SimultaneouslyJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument92 pagesRedoxMollel TajiriNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument67 pagesREDOXLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration KDBDocument45 pagesRedox Titration KDBKiranNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- Chemrxntypesf07 PDFDocument1 pageChemrxntypesf07 PDFSuneel kumarNo ratings yet
- C12 Electrochemistry IgcseDocument33 pagesC12 Electrochemistry IgcseAnna DixonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision Notes PDFDocument22 pagesChemistry Revision Notes PDFtanish gehlotNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen in 1 Shot - Class Notes - JEEDocument22 pagesHydrogen in 1 Shot - Class Notes - JEESaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations: Preparation For College Chemistry Columbia University Department of ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equations: Preparation For College Chemistry Columbia University Department of ChemistryLakshmi SinghNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- OxidationreductionDocument40 pagesOxidationreductionMohamad HanifNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanDocument22 pagesRedox Reaction Shobhit NirwanBhavya Goyal XI Non med100% (7)
- Ch5 Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanDocument22 pagesCh5 Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanPROFESSOR0% (1)
- Ch-18 Electrochemistry CaabilDocument50 pagesCh-18 Electrochemistry CaabilAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument74 pagesChapter 4 - Electrochemistryhoboslayer97No ratings yet
- HYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE MindmapDocument15 pagesHYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE Mindmapadsaditya24No ratings yet
- Oxidation Is The Process in Which Oxygen or An Electronegative Element Is AddedDocument2 pagesOxidation Is The Process in Which Oxygen or An Electronegative Element Is Addedveeresh punjaniNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesCh. 6 ElectrochemistryOhshshssjNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesDocument13 pagesElectrolysis of Solutions: Earning UtcomesNicaliaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesDocument20 pagesElectricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesKim SewoonNo ratings yet
- Redox Practice Test 1Document21 pagesRedox Practice Test 1Edon BediNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeDocument12 pagesChemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeSooryaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document18 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- ICSE Board Class X ChemistryDocument10 pagesICSE Board Class X ChemistryMaria Kanwal Maria KanwalNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Ck OoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionKavitha ThayagarajanNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 Chem Summer NoteDocument22 pagesYr 10 Chem Summer NoteTokoni DanielNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2024Document62 pagesElectrochemistry 2024shellodkomaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions II2023Document92 pagesRedox Reactions II2023nadeemyakubu47No ratings yet
- Redox & Equivalent Concepts Chemistry Zenith 2022 A01 & A021591183372Document53 pagesRedox & Equivalent Concepts Chemistry Zenith 2022 A01 & A021591183372SonalNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisapi-381901275% (4)