Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A600 - Engine Controls
Uploaded by
mazizOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A600 - Engine Controls
Uploaded by
mazizCopyright:
Available Formats
Operation and maintenance manual Control instruments
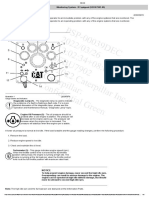
Engine control panel Cummins QSB
1 2 3 4 6
5 7
1. Idle speed adjust switch
Push up the switch in order to increase (+) the idle speed,
push down the in order to decrease (-) the idle speed.
2. Maximum engine rpm limit switch
Selecting this switch the maximum engine rpm will be limited at
2000.
Note: it is recommended to use this control in the yard to
improve hydraulic system efficiency and to decrease machine
noise level
3. Diagnostic switch
To be used to check for active engine electronic fuel system and
engine protection system fault codes.
4. Stop light
The STOP lamp is red and indicates the need to stop the engine as
soon as it can be safely done. The engine should remain shut down
until the fault can be repaired.
5. Warning light
The WARNING lamp is yellow and indicates the need to repair the
fault at the first available opportunity.
6. Water-in-fuel separator light.
The WATER-IN-FUEL (WIF) lamp is green and indicates that the
engine’s water-in-fuel separator needs to have the water drained out
of it. This task should be performed as soon as possible whenever
this lamp is illuminated.
7. Wait-to-start light
The WAIT-TO-START (WTS) lamp is yellow and is illuminated
during the preheat time that takes place when the keyswitch is in the
ON position during cold weather starting. To minimize cranking time
during cold weather starting, the engine should not be cranked until
the WAIT-TO-START lamp has been extinguished.
page 30/53 Chapter IV – ed. 10-2004
Control instruments Operation and maintenance manual
Engine generaI Information
The QSB engine control system is an electronically operated fuel control
system that also provides many operator and vehicle or equipment
features.
The base functions of the control system include fueling and timing
control, limiting the engine speed operating range between the low and
high idle set points and reducing exhaust emissions while optimizing
engine performance.
The control system uses inputs from the operator and its sensors to
determine the fueling and timing required to operate at the desired
engine speed.
The electronic control module (ECM) is the control center of the
system. It processes all of the inputs and sends commands to the fuel
system and engine control devices.
The ECM performs diagnostic tests on most of its circuits and will
activate a fault code if a problem is detected in one of these circuits.
Along with the fault code identifying the problem, a snapshot of engine
operating parameters at the time of fault activation is also stored in
memory.
Some fault codes will cause a diagnostic lamp to activate to signal the
driver.
The control system utilizes a number of sensors to provide information
on engine operating parameters. These sensors include:
1. Coolant Temperature Sensor
2. Intake Air Temperature Sensor
3. Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor
4. Oil Pressure Sensor
5. Engine Speed/Position Sensor
6. Water-in-Fuel Sensor.
Chapter IV – ed. 10-2004 page 31/53
Operation and maintenance manual Control instruments
Engine Protection System
The QSB engines are equipped with an engine protection system. The
system monitors critical engine temperatures and pressures, and will
log diagnostic faults when an over or under normal operation condition
occurs. If an out-of range condition exists, and engine derate action is
to be initiated, the operator will be alerted by an in-cab WARNING
lamp. The WARNING lamp will blink or flash when out-of-range
conditions continue to get worse. When the red STOP lamp is
illuminated, the driver must pull to the side of the road, when it is safe
to do so, to reduce the possibility of engine damage.
The engine protection system monitors the following data:
• Coolant temperature
• Coolant level (opt)
• Oil pressure
• Intake manifold temperature
• Engine overspeed
• OEM pressure (opt)
NOTE: Engine power and speed will be gradually reduced,
depending on the level of severity of the observed condition.
Diagnostic Fault Codes
The QSB control system can show and record operation anomalies that
present themselves as fault codes. These codes will make
troubleshootjng easier. The fault codes are recorded in the ECM. They
can be read using the fault lamps in the cab panel .
NOTE: Not all engine or QSB control system anomalies are shown as
fault codes.
There are two types of fault codes:
• Engine electronic control system fault codes
• Engine protection system fault codes
All fault codes recorded will either be active (fault code is
active at the moment) or inactive (fault code that was active at some
time but is not presently active).
Some, but not all, of the electronic fault codes will light a lamp when
they are active.
page 32/53 Chapter IV – ed. 10-2004
Control instruments Operation and maintenance manual
To check for active engine electronic fuel system and engine protection
system fault codes, turn the keyswitch to the OFF position and move the
diagnostic switch to the ON position.
Turn the vehicle keyswitch to the ON position.
If no active fault codes are recorded, both warning and stop lamps will
come on and stay on.
If active fault codes are recorded, both warning and stop lamps will
come on momentarily, then begin to flash one code of the recorded
faults.
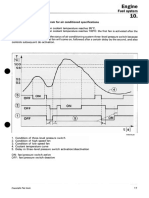
The fault code will flash in the following sequence:
First, a WARNING (yellow) lamp will flash. There will be a short 1 or 2
second pause after which the number of the recorded fault code will
flash in the STOP (red) lamp. There will be a 1 or 2 second pause
between each number. When the number has finished flashing in red,
a yellow lamp will appear again. The fault code will repeat in the same
sequence.
The lamps flash each fault code 3 times before advancing to the next
code. To skip to the next fault code, move the idle speed adjust switch
momentarily to the positive (+) position. You can go back to the
previous fault code by momentarily moving the idle speed adjust switch
to the negative (-) position. If only one active fault is recorded, the QSB
control system will continuously display the same fault code when
either + or -switch is depressed.
Fault Code Snapshot Data
Additional fault code information can be obtained by using the INSITE
service tool. The snapshot data records the value or state of the control
system sensors and switches at the time a fault occurred. These data
are stored for the first occurrence of the fault, since it was last cleared,
and the most recent occurrence. These data can be very valuable
when trying to recreate or determine engine operating conditions at the
time of a fault.
The ECM communicates with INSITE service tool through on SAE
J1939 datalink. The datalink connector is placed inside the electric
connection box near the batteries housing.
Chapter IV – ed. 10-2004 page 33/53
You might also like
- Caterpillar 3126 HEUI Engine: Mvp-Ef Service ManualDocument18 pagesCaterpillar 3126 HEUI Engine: Mvp-Ef Service ManualDarwin PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Cummins Diesel Engine Fault Code GuideDocument20 pagesCummins Diesel Engine Fault Code GuideSy Demba100% (1)
- Caterpillar 3126 HEUI Engines: Mvp-Er Service ManualDocument6 pagesCaterpillar 3126 HEUI Engines: Mvp-Er Service ManualJesus Almanzar SantosNo ratings yet
- Activity Report: Diesel EngineDocument19 pagesActivity Report: Diesel EngineDim lordwin HacutinaNo ratings yet
- quick guide DSE4520- ENDocument7 pagesquick guide DSE4520- ENdaneNo ratings yet
- DisplayDocument2 pagesDisplaybilmon selviantoNo ratings yet
- Engine Diagnostics Guide for B5254TDocument30 pagesEngine Diagnostics Guide for B5254TFlorin AgaiNo ratings yet
- Volvo Engine MY04B5254T2-S40 PDFDocument29 pagesVolvo Engine MY04B5254T2-S40 PDFJohn DeenyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Fault CodesDocument11 pagesDiagnostic and Fault CodescristianNo ratings yet
- OMM - Gauges and IndicatorsDocument3 pagesOMM - Gauges and Indicatorsjordan navarroNo ratings yet
- Cummins Diesel Engine Fault Code Guide (First Used On 1563, 1566, 1567, 1568, 1570 and Up)Document22 pagesCummins Diesel Engine Fault Code Guide (First Used On 1563, 1566, 1567, 1568, 1570 and Up)stefan corjuc100% (1)
- Calculation of Fuel Quantity Cylinder BalancingDocument1 pageCalculation of Fuel Quantity Cylinder Balancinguser1No ratings yet
- Cat Eng-Er Serv PDFDocument25 pagesCat Eng-Er Serv PDFGiapy Phuc TranNo ratings yet
- 559 Fault CodeDocument4 pages559 Fault Codeabdelbagi ibrahim100% (1)
- Service 3126Document18 pagesService 3126jrrodrigueza293% (15)
- EMT3-C10186 Manual (Rev. 1) W E-Stop and Throttle Pot (71610)Document17 pagesEMT3-C10186 Manual (Rev. 1) W E-Stop and Throttle Pot (71610)Matias Contreras Köbrich100% (2)
- Code Reason EffectDocument3 pagesCode Reason EffectAhmedmahNo ratings yet
- Gauges and IndicatorsDocument3 pagesGauges and Indicatorsbenjir shuvoNo ratings yet
- Bosch 5.2.1 Engine Management SystemDocument34 pagesBosch 5.2.1 Engine Management Systemolyga mgolNo ratings yet
- Engine Design Guide 2015 DGDocument7 pagesEngine Design Guide 2015 DGAu GroupsNo ratings yet
- Tier3 ElectricDocument10 pagesTier3 ElectricLuong Nguyen Danh100% (1)
- InternshipDocument45 pagesInternshipPrakashRaiNo ratings yet
- Volvo - My05 07B5254T S40V50C70C30Document30 pagesVolvo - My05 07B5254T S40V50C70C30sharck04100% (1)
- DTN0004 PID Idle ControlDocument3 pagesDTN0004 PID Idle ControlshayNo ratings yet
- Product News: Engine Monitoring System (EMS) For Caterpillar Industrial EnginesDocument16 pagesProduct News: Engine Monitoring System (EMS) For Caterpillar Industrial Enginesmohammad hazbehzadNo ratings yet
- FORD EXPLORER 91-99 Códigos de FallaDocument16 pagesFORD EXPLORER 91-99 Códigos de Fallagian marco llamojaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection System ExplainedDocument22 pagesFuel Injection System ExplainedZeke KazamiNo ratings yet
- Manual Services 3126B PDFDocument14 pagesManual Services 3126B PDFdiony182100% (1)
- 4 AfeDocument36 pages4 AfeJuan ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Introduction of PowerCom Genset Controls for 320-625KVA NodesDocument8 pagesIntroduction of PowerCom Genset Controls for 320-625KVA NodesTaz UddinNo ratings yet
- ISUZU 4JJ1 Function, Structure, Operation of EngineDocument40 pagesISUZU 4JJ1 Function, Structure, Operation of EnginePHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ100% (14)
- Reaprendizaje de Sistemas AntirroboDocument8 pagesReaprendizaje de Sistemas AntirrobochovyNo ratings yet
- TE Series Power Unit Controller Start InstructionsDocument13 pagesTE Series Power Unit Controller Start InstructionsFrances SalongaNo ratings yet
- 13a Multipoint Fuel Injection (Mpi)Document246 pages13a Multipoint Fuel Injection (Mpi)Pafuncio de AlecrimNo ratings yet
- Siemens MS43 SystemsDocument26 pagesSiemens MS43 SystemszefrenchNo ratings yet
- Ecu 750 Instruction ManualDocument8 pagesEcu 750 Instruction ManualAu GroupsNo ratings yet
- 3126 HeuiDocument26 pages3126 HeuiBradley LodderNo ratings yet
- On-Board Diagnostics Ii SystemDocument266 pagesOn-Board Diagnostics Ii Systemvadim vadimNo ratings yet
- Fiat Barchetta: EngineDocument20 pagesFiat Barchetta: EngineHallex OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Outboard Warning System FeaturesDocument3 pagesOutboard Warning System FeaturesMartin A Gomez RNo ratings yet
- ENGINE CONTROLS RELEARN PROCEDURESDocument8 pagesENGINE CONTROLS RELEARN PROCEDURESsimpsonrl80% (10)
- Function, Structure, Operation of Engine Null (4JK1)Document36 pagesFunction, Structure, Operation of Engine Null (4JK1)jonathan100% (3)
- 151Document3 pages151AhmedmahNo ratings yet
- Error Code Volvo TruckDocument130 pagesError Code Volvo Truckandra50% (2)
- Sistema de Control de EmisionesDocument45 pagesSistema de Control de EmisionesDavid ParariNo ratings yet
- Yanmar CANplus 600 Operation and Troubleshooting PDFDocument40 pagesYanmar CANplus 600 Operation and Troubleshooting PDFJozefNo ratings yet
- 2001 Kia Optima Fuel SystemDocument136 pages2001 Kia Optima Fuel SystemJorge EspinoNo ratings yet
- S 6476Document5 pagesS 6476mnezami100% (1)
- BccontDocument78 pagesBccontIonut GrozaNo ratings yet
- Page 9 of 22Document1 pagePage 9 of 22mNo ratings yet
- RENR2223-13 Oil RenewalDocument24 pagesRENR2223-13 Oil RenewalJACOB MUDONHINo ratings yet
- SKI-DOO Diagnostic and Fault Codes (SUMMIT X) - Shop Manual - 04cchhAAA - SM11Y015S21 - enDocument4 pagesSKI-DOO Diagnostic and Fault Codes (SUMMIT X) - Shop Manual - 04cchhAAA - SM11Y015S21 - enSkorost SkorostNo ratings yet
- Ecp ManualDocument22 pagesEcp Manualகோவி கோபால் ஆர்ட்ஸ்100% (1)
- ASE L2 Composite Vehicle 2007Document0 pagesASE L2 Composite Vehicle 2007Anil YarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Sensor and SystemDocument30 pagesElectronic Sensor and SystemDammiam Gatica100% (2)
- Base Control System DescriptionDocument2 pagesBase Control System Descriptionwilfredo escobar gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Automotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)From EverandAutomotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Windscreen Wiper PDFDocument7 pagesWindscreen Wiper PDFmazizNo ratings yet
- Ecos System Description GMK 4075: Error CodesDocument31 pagesEcos System Description GMK 4075: Error CodesMohamed RashedNo ratings yet
- Steer OverviewDocument1 pageSteer OverviewmazizNo ratings yet
- Joystick GMKDocument8 pagesJoystick GMKmazizNo ratings yet
- Join Megamas Training for Basic H2S Safety CourseDocument3 pagesJoin Megamas Training for Basic H2S Safety CoursemazizNo ratings yet
- ZF As Tronic DescriptionDocument24 pagesZF As Tronic DescriptionBienvenu MassouanguiNo ratings yet
- Project 0: Cloud & Web Service EnvironmentDocument3 pagesProject 0: Cloud & Web Service EnvironmentAbdelkrim LamraouiNo ratings yet
- Accident Detection For Automobiles Switch and Buzzer: AbstractDocument2 pagesAccident Detection For Automobiles Switch and Buzzer: AbstractgiufugiNo ratings yet
- The National Academies PressDocument149 pagesThe National Academies PressERRAMESH1989No ratings yet
- Sims 2 Ultimate Collection Resolution GuideDocument8 pagesSims 2 Ultimate Collection Resolution GuidePat TyNo ratings yet
- Viscosity of OilsDocument4 pagesViscosity of OilsJa Phe TiNo ratings yet
- IEEE Xplore - Enterprise Information Security Architecture A Review of Frameworks, Methodology, and Case StudiesDocument2 pagesIEEE Xplore - Enterprise Information Security Architecture A Review of Frameworks, Methodology, and Case StudiesHugo PagolaNo ratings yet
- Rotating Machineries - Aspects of Operation and Maintenance (PDFDrive)Document110 pagesRotating Machineries - Aspects of Operation and Maintenance (PDFDrive)paulo cesar hernandez mijangosNo ratings yet
- Multiple Vacancies With MENAISCO in Jazan - Saudi ArabiaDocument5 pagesMultiple Vacancies With MENAISCO in Jazan - Saudi ArabiaViiq Corpse GrinderNo ratings yet
- CISSP Review QuestionsDocument87 pagesCISSP Review QuestionsGsk SkNo ratings yet
- Working With Geo Media ProfessionalDocument978 pagesWorking With Geo Media ProfessionalJacob WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Arco en C Siemens Polymobil 3 MS EngDocument34 pagesArco en C Siemens Polymobil 3 MS EngAzucena RivasNo ratings yet
- FdeosinfoDocument18 pagesFdeosinfowhacky LiloNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument10 pagesIlovepdf MergedAnisha SapraNo ratings yet
- Rizwan Habib / Roll - 131: Online Travel Agency (OTA)Document13 pagesRizwan Habib / Roll - 131: Online Travel Agency (OTA)rizwan_habibNo ratings yet
- Features: CC CC IN PeakDocument3 pagesFeatures: CC CC IN PeakRobson DiasNo ratings yet
- Project DirectionDocument1 pageProject DirectionAnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Fame TechnologiesDocument144 pagesFame TechnologiesYoheswaran GnanavelNo ratings yet
- Data Privacy GovernanceDocument22 pagesData Privacy GovernanceSimarNo ratings yet
- Interior DesignDocument13 pagesInterior DesignHajar SuwantoroNo ratings yet
- Esp8285 Datasheet enDocument29 pagesEsp8285 Datasheet enJohn GreenNo ratings yet
- Railml® 3 Simple Example Step Part 2: Interlocking Railml® 3.1 Tutorial Simple Example Step-By-Step Part 2: Interlocking StepDocument68 pagesRailml® 3 Simple Example Step Part 2: Interlocking Railml® 3.1 Tutorial Simple Example Step-By-Step Part 2: Interlocking Steptap.jackson6255No ratings yet
- Hitachi - AssignmentDocument6 pagesHitachi - AssignmentPraveena IvanaNo ratings yet
- Build A Double Bazooka Antenna (K3DAV Version)Document11 pagesBuild A Double Bazooka Antenna (K3DAV Version)Steven BaynesNo ratings yet
- Java Programming Chapter 3 GUI With JavafxDocument15 pagesJava Programming Chapter 3 GUI With JavafxShimelis KassaNo ratings yet
- Adrián Lugo Bendezú (Senior, University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Campus) Mentor: Tristan Goulden (AOP)Document1 pageAdrián Lugo Bendezú (Senior, University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Campus) Mentor: Tristan Goulden (AOP)jpNo ratings yet
- FOB2-3 TS - Technical Manual - Section 2 - Installation SpecificationsDocument10 pagesFOB2-3 TS - Technical Manual - Section 2 - Installation SpecificationsmaghraouiNo ratings yet
- b0700bp CDocument90 pagesb0700bp Cyoucef hamzaNo ratings yet
- Primary Storage Types & RAM MemoryDocument4 pagesPrimary Storage Types & RAM Memoryhehehehe100% (1)
- Huawei LTE CountersDocument14 pagesHuawei LTE CountersRocky33% (3)
- Communications Engineering Mastery Test 8 ECE Pre-BoardDocument35 pagesCommunications Engineering Mastery Test 8 ECE Pre-BoardXyNo ratings yet