Professional Documents
Culture Documents
????????? ??????? ???? ???????
Uploaded by
Safna SinanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
????????? ??????? ???? ???????
Uploaded by
Safna SinanCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Revision
1) Circle the correct options A, B, C & D.
1) To obtain large copper sulphate crystals, one should
____________________
(A) gently heat a saturated solution
(B) cool a hot saturated solution slowly
(C) heat a saturated solution strongly
(D) cool a hot saturated solution rapidly
2) The acid used in preserving food and for cooking_____________.
(A) hydrochloric acid
(B) nitric acid
(C) carbonic acid
(D) ethanoic acid
3) Which of the following substances is produced through crystallisation?
(A) Chlorine
(B) Silicon wafers
(C) Glass
(D) Gun powder
4) What ill happen to th pH value of an alkali when acid is slowly added
to it?
(A) It increases and then decreases
(B) It decreases
(C) It remains the same
(D) It increases
5) Which of the following substances has a pH value of more than 7?
(A) Methyl orange
(B) Hydrogen gas
(C) Calcium hydroxide
(D) Oxalic acid
6) Usually the first substance to be added to water in impounding
reservoirs is ____________
(A) chlorine
(B) fluorine
(C) aluminium sulphate
(D) lime
7) What is the pH value of pure water?
(A) 7
(B) 10
(C) 14
(D) 1
8) Which process can be used to obtain pure copper sulphate?
(A) Chromatography
(B) Sublimation
(C) Condensation
(D) Crystallisation
9) A substance that is 6 on the pH scale would be :
(A) strong alkali
(B) weak acid
(C) strong acid
(D) neutral
10) When an indicator is added to solutions of different pH values, it
should sow a change in ___________.
(A) colour
(B) volume
(C) state
(D) smell
Section B
1) Answer the following questions.
1) What is crystallisation?
𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐜𝐫𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐥𝐬
_________________________________________________________
2) What is desalination?
𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐫𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐬𝐚𝐥𝐭 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐰𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐫
_________________________________________________________
3) List three examples of an acid and their uses.
* 𝐂𝐢𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐜 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐡𝐞𝐚𝐥𝐭𝐡𝐲 𝐟𝐨𝐨𝐝
_________________________________________________________
* 𝐍𝐢𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐜 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐟𝐞𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐞𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐨𝐬𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐬
_________________________________________________________
* 𝐚𝐜𝐞𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐟𝐨𝐨𝐝 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐜𝐨𝐨𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠
_________________________________________________________
4) What is neutralisation?
𝐖𝐡𝐞𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐫𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭 𝐚𝐦𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐚𝐥𝐤𝐚𝐥𝐢 𝐚𝐫𝐞 𝐦𝐢𝐱𝐞𝐝
_________________________________________________________
𝐚 𝐧𝐞𝐮𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐨𝐟 𝐬𝐚𝐥𝐭 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐰𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐫 𝐢𝐬 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐜𝐞𝐝
_________________________________________________________
5) List three examples of alkalis and their uses.
𝐏𝐨𝐭𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐡𝐲𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐱𝐢𝐝𝐞 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐩𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐭 𝐫𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐝𝐲𝐞𝐬
_________________________________________________________
𝐒𝐨𝐝𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐡𝐲𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐱𝐢𝐝𝐞 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐞𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐬𝐨𝐚𝐩 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐰𝐚𝐬𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐩𝐨𝐰𝐝𝐞𝐫
_________________________________________________________
𝐀𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐚𝐦𝐦𝐨𝐧𝐢𝐚 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐟𝐞𝐭𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐫𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐜𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐧𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐥𝐢𝐪𝐮𝐢𝐝𝐬
_________________________________________________________
6) What is saturated solution?
𝐀_________________________________________________________
𝐬𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐬𝐨𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐢𝐬 𝐨𝐧𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐮𝐦
𝐚𝐦𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐯𝐞𝐝 𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐭𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐚 𝐠𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐧 𝐯𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐦𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐯𝐞𝐧𝐭
_________________________________________________________
𝐚𝐭 𝐚 𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫 𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐢𝐟 𝐞𝐱𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬
𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐭𝐞
2) Name the acid or alkali in each of the substance given below:
𝐂𝐢𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐜 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝
1) Oranges - ______________________________________________
𝐒𝐨𝐝𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐡𝐲𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐱𝐢𝐝𝐞
2) soap - _________________________________________________
𝐌𝐚𝐥𝐢𝐜 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝.
3) apples - ________________________________________________
3) Complete the following equations:
1) Hydrochloric acid + potassium 𝐏𝐨𝐭𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐜𝐡𝐥𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐝𝐞 + 𝐡𝐲𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐠𝐞𝐧
________________________
2) Sulphuric acid + sodium carbonate 𝐒𝐨𝐝𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐬𝐮𝐥𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐭𝐞 +
____________________
𝐰𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐫 + 𝐜𝐚𝐫𝐛𝐢𝐧 𝐝𝐢𝐨𝐱𝐢𝐝𝐞
____________________
3) Nitric acid + magnesium hydroxide 𝐌𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞 +
____________________
𝐰𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐫
____________________
4) Answer the following questions.
1) Copper chloride crystals can be made by adding excess copper
carbonate which is insoluble in water to hydrochloric acid.
1) Why was the copper carbonate in excess?
𝐓𝐨 𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐚𝐥𝐥 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 𝐡𝐚𝐬 𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐞𝐝
________________________________________________________
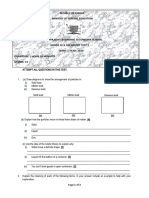
2) Label the diagram shown below:
𝐁𝐞𝐚𝐤𝐞𝐫
𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐢𝐧𝐠
𝐦𝐢𝐱𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞
𝐅𝐢𝐥𝐭𝐞𝐫 𝐩𝐚𝐩𝐞𝐫
𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐝𝐮𝐞
𝐅𝐮𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐥
𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐟𝐥𝐚𝐬𝐤
𝐅𝐢𝐥𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞
3) Describe how you could obtain pure dry crystals of copper chloride
from copper chloride solution?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Crystallisation -
We must pour the mixture into an evaporating dish and gently heat
the solution using a Bunsen burner.
When we see crystals starting to form, we have to remove the
evaporating dish from the heat and allow the solution to cool so that
the salt crystals become larger.
𝐅𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐥𝐲 𝐝𝐫𝐲 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐜𝐫𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐚 𝐬𝐨𝐟𝐭 𝐜𝐥𝐨𝐭𝐡
You might also like
- 06 Science WorksheetsDocument34 pages06 Science Worksheetspraveen mbvnNo ratings yet
- Respiration I QuestionsDocument79 pagesRespiration I QuestionsAayma MunirNo ratings yet
- Kasempa Boys Boarding Secondary School Grade 10 B Chemistry Test 2 TERM: 1 YEAR: 2019 Duration: 1 Hour 20 Minutes MARKS: 51Document3 pagesKasempa Boys Boarding Secondary School Grade 10 B Chemistry Test 2 TERM: 1 YEAR: 2019 Duration: 1 Hour 20 Minutes MARKS: 51Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Combined B7 Test 1 Beginner QP UnlockedDocument17 pagesAQA GCSE Combined B7 Test 1 Beginner QP Unlockedramloghun veer100% (1)
- GB 17395-2008ENgDocument35 pagesGB 17395-2008ENgGanesh Srinivasan100% (1)
- WS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESDocument4 pagesWS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Sagar PPT On Plastic As Soil StabilizerDocument20 pagesSagar PPT On Plastic As Soil StabilizerSagar78% (9)
- Doc PKG Vol II - O&M Manual (Rev 0)Document320 pagesDoc PKG Vol II - O&M Manual (Rev 0)Nermeen Elmelegae100% (1)
- SPE 189134 Economic Optimization of Water and Gas Shut Off Treatment in Oil WellsDocument16 pagesSPE 189134 Economic Optimization of Water and Gas Shut Off Treatment in Oil WellsEdgar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- PSV Thermal SizingDocument16 pagesPSV Thermal Sizingahmad santoso0% (1)
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیNo ratings yet
- Sep 2013Document28 pagesSep 2013Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- Std. X Chemistry PAPER IV ExtendedDocument8 pagesStd. X Chemistry PAPER IV ExtendedYashodhaNo ratings yet
- C Annual 2023Document12 pagesC Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 7 Revision Sheet - IIDocument2 pages7 Revision Sheet - IIsakshampaharia1No ratings yet
- General Revision 2Document6 pagesGeneral Revision 2Anbu SelvanNo ratings yet
- Chem 127 Exam 1 06Document11 pagesChem 127 Exam 1 06Glitch172No ratings yet
- Chemistry Test Review - Mar 2023Document4 pagesChemistry Test Review - Mar 2023rblxproNo ratings yet
- c9 Chemistry of The Atmosphere HTDocument66 pagesc9 Chemistry of The Atmosphere HTMadhavi OchaniNo ratings yet
- Yr 12 Chemistry Holiday HomeworkDocument8 pagesYr 12 Chemistry Holiday HomeworkEsam ELNOAMANYNo ratings yet
- Chem Paper 1 Pracs QPDocument21 pagesChem Paper 1 Pracs QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Amount of Substance Exam QsDocument15 pages1.2 Amount of Substance Exam QsEmoryNo ratings yet
- f.1 Chem Cycle 1 Term 3 2016Document10 pagesf.1 Chem Cycle 1 Term 3 2016Vincent AgumbaNo ratings yet
- Assesment For ChemistryDocument5 pagesAssesment For ChemistrymiraNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Chapter #: 6: Quantitative Chemistry - How Much? (Moles)Document26 pagesSubject: Chemistry Chapter #: 6: Quantitative Chemistry - How Much? (Moles)Haider Ali100% (2)
- Year 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesYear 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- D3 Chemical Formula QuizDocument1 pageD3 Chemical Formula QuizAtizado EricNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistryW. Joseph the chemistNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Acid Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesWorksheet Acid Bases and SaltswardaNo ratings yet
- Pollution Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesPollution Exam QuestionsArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- f.1 Chem Cycle 1 Term 3 2013Document7 pagesf.1 Chem Cycle 1 Term 3 2013Vincent AgumbaNo ratings yet
- WS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSDocument7 pagesWS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Quiz On SolubilityDocument1 pageQuiz On SolubilityShahiraNo ratings yet
- Quantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4Document37 pagesQuantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4KshitijNo ratings yet
- CH 26-27 Energy, Population & Sustainability Lesson 1: Traditional (Conventional) Energy Sources For SocietyDocument31 pagesCH 26-27 Energy, Population & Sustainability Lesson 1: Traditional (Conventional) Energy Sources For SocietyFe Pakias GullodNo ratings yet
- 4th Monthly Test Physical ScienceDocument2 pages4th Monthly Test Physical ScienceTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- WS 8 IG I Chemistry REDOX REACTIONDocument2 pagesWS 8 IG I Chemistry REDOX REACTIONRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Yr09 t2 2018Document12 pagesChemistry Yr09 t2 2018imanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Time Allowed: 1 Hour Paper 2 Theory Total Marks: /45Document10 pagesChemistry Time Allowed: 1 Hour Paper 2 Theory Total Marks: /45Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Naming Acids and Bases Worksheet NameDocument2 pagesNaming Acids and Bases Worksheet NameDeath BedNo ratings yet
- Module Science Pt3Document11 pagesModule Science Pt3lccjane8504No ratings yet
- Gasexchange Part 2Document66 pagesGasexchange Part 2/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 Question Paper Zeraki Achievers 10.0 July 2023Document10 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Question Paper Zeraki Achievers 10.0 July 2023vincent mosotaNo ratings yet
- Naming Practice 2Document1 pageNaming Practice 2Nicholas FerroniNo ratings yet
- Sep 2014Document28 pagesSep 2014Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- 10 AnalysinggraphsDocument27 pages10 Analysinggraphsttvstone1No ratings yet
- Set 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Document17 pagesSet 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 (Dry Lab) Formula and NomenclatureDocument2 pagesActivity No. 1 (Dry Lab) Formula and NomenclatureSumayyaNo ratings yet
- Test 2-P2Document8 pagesTest 2-P2Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Respiration & Pollution Worksheet 2022Document2 pagesRespiration & Pollution Worksheet 2022CSEC NOWNo ratings yet
- Carbonyls Ppqs NO ANSWERSDocument9 pagesCarbonyls Ppqs NO ANSWERSmariam saikNo ratings yet
- Chem 11 Total Review With Answers Key UpdateDocument28 pagesChem 11 Total Review With Answers Key Updatemelissa.figueroamoralesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Part 6Document38 pagesAtomic Structure Part 6xenaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 - Science Analytical Practice Test - Question KeyDocument21 pagesGrade 5 - Science Analytical Practice Test - Question KeySUNIL SONAWANENo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument4 pagesClassification of MatterDiana AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Using Resources - Paper 2 TESDocument28 pagesUsing Resources - Paper 2 TESYotos XdNo ratings yet
- Lonestar College - Kingwood General Chemistry 1411 Naming Compounds and ReactionsDocument3 pagesLonestar College - Kingwood General Chemistry 1411 Naming Compounds and ReactionsHân BảoNo ratings yet
- L13 1e-Calculating The RFM and Using Moles WiDocument7 pagesL13 1e-Calculating The RFM and Using Moles WiOMarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Paper 2Document8 pagesGrade 10 Paper 2jfkdmfmdfNo ratings yet
- WS 5 IG I Chemistry REACTING MASSES AND CHEMICALDocument4 pagesWS 5 IG I Chemistry REACTING MASSES AND CHEMICALRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- 6031 Q 2 SpecimenDocument16 pages6031 Q 2 Specimenmarume944No ratings yet
- Everything About WoolDocument31 pagesEverything About Woolletuongthuy2000No ratings yet
- Calculation of A 2-4 Oil CoolerDocument45 pagesCalculation of A 2-4 Oil CoolerAndre HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Xray Sedimentation 3Document17 pagesXray Sedimentation 3Ralph EvidenteNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument431 pagesSOMPradeepvenugopalNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Enquiry Committee Report 1954Document2 pagesPharmaceutical Enquiry Committee Report 1954sanjnu50% (2)
- Impeller TechnologyDocument4 pagesImpeller TechnologySagarNo ratings yet
- MSDS TriclosanDocument4 pagesMSDS TriclosanIvanie SilviaNo ratings yet
- Nyloprint Techn Data enDocument2 pagesNyloprint Techn Data enpatavioNo ratings yet
- Science MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Document10 pagesScience MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Apex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Methods of PurificationDocument5 pagesMethods of PurificationFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Particle ModelDocument4 pages5.1 Particle ModelKris_14No ratings yet
- M.pharm Second SemesterDocument1 pageM.pharm Second SemesternikuNo ratings yet
- N Butanol As An Extractant For Lactic Acid Recovery PDFDocument4 pagesN Butanol As An Extractant For Lactic Acid Recovery PDFKanungnit ChawongNo ratings yet
- Styro LutionDocument3 pagesStyro LutionGanesan TNo ratings yet
- Welding - Fissures DefectDocument12 pagesWelding - Fissures DefectthanhNo ratings yet
- NSO Sample Paper For Class 7Document12 pagesNSO Sample Paper For Class 7Helen RaniNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Carbon Steels in Monoethylene Glycol (51300-00498-Sg)Document13 pagesCorrosion of Carbon Steels in Monoethylene Glycol (51300-00498-Sg)Henny CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Aquatrac5 enDocument4 pagesAquatrac5 enTRIMECHNo ratings yet
- SOP 75v4 Specific-Gravity FinalDocument22 pagesSOP 75v4 Specific-Gravity FinalAldwiNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument16 pagesSummer Training ReportmohitNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing PresentationDocument18 pagesRemote Sensing PresentationShoaibNo ratings yet
- TrussDocument18 pagesTrussSYifa ShuhaIliNo ratings yet
- Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions #3Document7 pagesExothermic and Endothermic Reactions #3SubatomoNo ratings yet
- Dual Film RT Article PDFDocument7 pagesDual Film RT Article PDFRaja Muaz Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- 65ah - 12V - 6FM65 VISIONDocument2 pages65ah - 12V - 6FM65 VISIONBashar Salah100% (1)