Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STUDY GUIDE For GENERAL BIOLOGY Finals Google Docs
Uploaded by
Tisha Artagame0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesOriginal Title
STUDY-GUIDE-for-GENERAL-BIOLOGY-Finals-Google-Docs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesSTUDY GUIDE For GENERAL BIOLOGY Finals Google Docs
Uploaded by
Tisha ArtagameCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
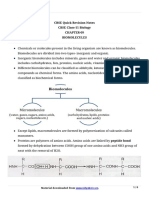
STUDY GUIDE for GENERAL Polysaccharides- starch(present in plants),
BIOLOGY (Finals) glycogen (present in animals), cellulose
(large amount)
BIOMOLECULES- substances that are monomer-monosaccharides
important in life. Lipids- molecules that contain hydrocarbons
-any of numerous substances that are and make up the building blocks of the
produced by cells and living organisms. structure and function of living cells.
Biomolecules have a wide range of sizes and -glycerol and 3 fatty acids- ester
structures and perform a vast array of bond
functions. - Include fats consisting of one fatty
bio=life acid molecule and three glycerol
molecule=substances molecules
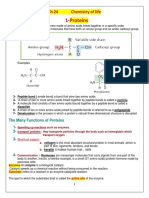
MONOMERS- building blocks of carbs, -Examples of lipids include fats, oils,
lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. waxes, certain vitamins (such as A, D, E and
-a molecule that can be bonded to K), hormones and most of the cell
other identical molecules to form a polymer. membrane that is not made up of protein.
POLYMERS- any of a class of natural or monomers-fatty acids and glycerol
synthetic substances composed of very large Proteins- large, complex molecules that
molecules, called macromolecules, which play many critical roles in the body. They do
are multiples of simpler chemical units most of the work in cells and are required
called monomers. Polymers make up many for the structure, function, and regulation of
of the materials in living organisms and are the body's tissues and organs.
the basis of many minerals and man-made Monomer-amino acids
materials. -dictates the chemical
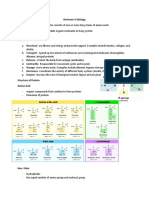
Carbohydrates- found in a wide array of properties of amino acids-variable side (R)
both healthy and unhealthy foods—bread, chai
beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, Nucleic Acids-large biomolecules that play
spaghetti, soft drinks, corn, and cherry pie. essential roles in all cells and viruses. A
-a biomolecule consisting of carbon major function of nucleic acids involves the
(C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, storage and expression of genomic
usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio information. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or
of 2:1 (as in water) DNA, encodes the information cells need to
-storage form of carbohydrates in make proteins.
animals is glycogen and in plants it is starch monomers-nucleotides
Monosaccharides- glucose (simplest), *nucleoside- A nucleoside is a compound
galactose, fructose (fruit sugar) that consists of a purine or pyrimidine base
Disaccharides- lactose (milk sugar), maltose combined with deoxyribose or ribose and is
(malt sugar), sucrose (table sugar) found especially in DNA or RNA
-Monomers of nucleoside-
nitrogenous base and pentose sugar
*Deoxyribose represents a pentose
-example of a DNA strand-
CTACCCGTCGGATTGTCT
complementary in mRNA is
GAUGGGCAGCCUAACUGA
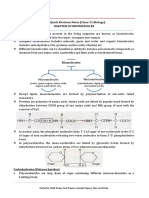
Enzymes- proteins that help speed up
metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our
bodies. They build some substances and Phospholipids(structure above)- major
break others down. All living things have membrane lipids that consist of lipid
enzymes. Our bodies naturally produce bilayers. This basic cellular structure acts as
enzymes. a barrier to protect the cell against various
-Without the presence of enzymes, environmental insults and more importantly,
the reactions necessary to sustain life would enables multiple cellular processes to occur
require higher temperatures in order to in subcellular compartments.
occur.
-The part of the enzyme where the
substrate binds is called the active site.
-When a substrate binds to the
enzyme's active site, an enzyme-substrate
complex is formed. What happens next is
that the substrate is broken down into
A- enzyme
products through catalysis reaction.
B- substrate
Example* carboxylation of ribulose
C- product
bisphosphate (RuBP)- catalyzed by
RuBisCO
Photosynthesis- uses sunlight to convert
water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and
high energy sugars
-In the overall equation for
photosynthesis, six molecules of carbon
dioxide and six molecules of water result in
a molecule of sugar and six molecules of
oxygen
X-substrate 1st step- excitement of an electron of
Y-active site chlorophyll a by a photon of light
When electrons in the reaction-center
chlorophyll become so excited; they escape
to a nearby primary electron acceptor
molecule
Light Dependent Reaction
-happens in the thylakoids
(photosystems I and II)
-products- ATP and NADPH and
oxygen
Light Independent Reaction- Calvin
Cycle
-happens in the stroma
Stroma-The Calvin cycle produces
sugar.
-product- glucose (C6H12O6)
NADP+ - role is to carry electrons during
photosynthesis
3 parts of ATP-adenine, ribose, and three
phosphate groups
Equation for photosynthesis-
6CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2.
You might also like
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of MacromoleculesDocument6 pagesMolecular Structure of MacromoleculesBon Joey BernestoNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesMacromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesYda TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument5 pagesBiology NotesFaith SNNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesNucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsMika Sophia GonzagaNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument14 pagesBioenergeticsmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- 1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pages1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeXIBG21SANIANo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology 1Document2 pagesReviewer in General Biology 1Moy ReyesNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesgeecyjane YguintoNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE–FINALS REVIEWERDocument18 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE–FINALS REVIEWERPrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six, GeneticsDocument10 pagesChapter Six, GeneticsHashim GhazoNo ratings yet
- Biochem PDFDocument7 pagesBiochem PDFNhư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Molecules of Life: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins & EnzymesDocument102 pagesMolecules of Life: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins & Enzymeskavya nandhiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lesson-1Document18 pagesBiochemistry Lesson-1Priyadarshini LenkaNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument5 pagesEnergy TransformationmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 Lesson 4Document28 pagesBio 1 Lesson 4sattNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryDocument8 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryJulian WolfgangNo ratings yet
- Biology AS Level Work - 2Document22 pagesBiology AS Level Work - 2Harry Sedgwick100% (3)
- Biomolecules Reviewer 2324Document7 pagesBiomolecules Reviewer 2324heraloesaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesShilpaNo ratings yet
- Biomacromolecules: Structure and FunctionDocument21 pagesBiomacromolecules: Structure and FunctionKerry JiangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. MirroredDocument17 pagesChapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. Mirroredapi-524244445No ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBNo ratings yet
- Biological Principles ReviewDocument18 pagesBiological Principles ReviewCharles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Biological Principles ReviewDocument18 pagesBiological Principles ReviewshashaNo ratings yet
- Cell Chemistry: Sri Wahyuni Biochemistry Department Faculty of Medicine Universitas MalikussalehDocument28 pagesCell Chemistry: Sri Wahyuni Biochemistry Department Faculty of Medicine Universitas Malikussalehviola septinaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingRuskin Jamir AquinoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FileDocument17 pagesChemistry FilePrakhar33% (3)
- Reviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDocument9 pagesReviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDanilo PerezNo ratings yet
- Essential Biomolecules: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins & Nucleic AcidsDocument27 pagesEssential Biomolecules: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins & Nucleic AcidsAceres John HenryNo ratings yet
- MCB 201 Biosynthesis of Biomolecules - MCB - 201Document10 pagesMCB 201 Biosynthesis of Biomolecules - MCB - 201Lena HasleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Biological MoleculesDocument28 pagesChapter 4 - Biological MoleculesshammmssNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument17 pagesChemistrySanjay soniNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument23 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentArchita PanchalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - BiomacromoleculesDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - BiomacromoleculesWafaaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2NDDocument5 pagesGen Bio 2NDZyren Joy SamillanoNo ratings yet
- General Biology NotesDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology NotesjeayNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument10 pagesBiological MacromoleculesKristine Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Biochem LectureDocument100 pagesBiochem Lectureana.tacbadNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document29 pagesModule 9Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology NotesDocument147 pagesClass 11 Biology NotesreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Document2 pagesAmino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Noviemae TuandaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES HandoutsDocument4 pagesBIOMOLECULES HandoutsJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument6 pagesPhysical ScienceCAYABAN, RISHA MARIE DV.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biological Molecules: SummaryDocument9 pagesChapter 2: Biological Molecules: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Reviewer Final 1Document5 pagesGen Bio Reviewer Final 1Emmanuelle CalleNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesHARSH PahwaNo ratings yet
- Plant vs Animal Cell ComparisonDocument2 pagesPlant vs Animal Cell ComparisonshsakinahNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - 054325Document18 pagesBiomolecules - 054325Baninla NerusNo ratings yet
- 87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9Document21 pages87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9SAMPATH SPNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PDFDocument5 pagesBiomolecules PDFgabo uyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument38 pagesUnit 2 NotesElen Mae PadugaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 pagesCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 1Document2 pagesBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument92 pagesBiological MacromoleculesAilen Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- BioChem LESSON 1 and 2Document8 pagesBioChem LESSON 1 and 2Elvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Document10 pagesBio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Kaeya's asscheeksNo ratings yet
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- European Journal of Internal MedicineDocument4 pagesEuropean Journal of Internal Medicinesamer battatNo ratings yet
- IT-02 Residential StatusDocument26 pagesIT-02 Residential StatusAkshat GoyalNo ratings yet
- HNM Announcement Flyer enDocument2 pagesHNM Announcement Flyer enJali SahiminNo ratings yet
- Orion C.M. HVAC Case Study-07.25.23Document25 pagesOrion C.M. HVAC Case Study-07.25.23ledmabaya23No ratings yet
- Application of Gis in Electrical Distribution Network SystemDocument16 pagesApplication of Gis in Electrical Distribution Network SystemMelese Sefiw100% (1)
- Comparative Media SystemsDocument10 pagesComparative Media SystemsJoram MutwiriNo ratings yet
- Sato Printer Api Reference DocumentDocument34 pagesSato Printer Api Reference Documentsupersteel.krwNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Noun ClauseDocument101 pagesUnit 7 Noun ClauseMs. Yvonne Campbell0% (1)
- IGNOU MBA MS-11 Solved AssignmentDocument5 pagesIGNOU MBA MS-11 Solved AssignmenttobinsNo ratings yet
- Red Lion Edict-97 - Manual PDFDocument282 pagesRed Lion Edict-97 - Manual PDFnaminalatrukNo ratings yet
- Radio Codes and ConventionsDocument2 pagesRadio Codes and Conventionsapi-570661298No ratings yet
- 01 - PV - RESCO 1d Workshop - S1 PDFDocument61 pages01 - PV - RESCO 1d Workshop - S1 PDFDeasy KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 (10) Capital Investment Analysis: ObjectivesDocument40 pagesChapter 25 (10) Capital Investment Analysis: ObjectivesJames BarzoNo ratings yet
- CD 1 - Screening & DiagnosisDocument27 pagesCD 1 - Screening & DiagnosiskhairulfatinNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks2018 PDFDocument1 pageSolidWorks2018 PDFAwan D'almightyNo ratings yet
- Batt ChargerDocument2 pagesBatt Chargerdjoko witjaksonoNo ratings yet
- Ip 19 3RD EditionDocument240 pagesIp 19 3RD EditionSumanta Bhaya100% (13)
- Inner Unit EstimateDocument35 pagesInner Unit EstimateMir MoNo ratings yet
- Why it's important to guard your free timeDocument2 pagesWhy it's important to guard your free timeLaura Camila Garzón Cantor100% (1)
- Cisco Series SWCFG Xe 16 12 XDocument416 pagesCisco Series SWCFG Xe 16 12 XWagner SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Audio Narration SINGLE Slide: Google Form in The Discussion ForumDocument2 pagesAudio Narration SINGLE Slide: Google Form in The Discussion Forumfast sayanNo ratings yet
- 2iccas2005 Paper 377Document5 pages2iccas2005 Paper 377Cristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- Divisional Chart-IDocument1 pageDivisional Chart-Iabhisek1987No ratings yet
- BSNL TrainingDocument25 pagesBSNL TrainingAditya Dandotia68% (19)
- Syllabus PTSV3Document21 pagesSyllabus PTSV3Pablito Quispe RuizNo ratings yet
- LESSON 9 Steam Generators 2Document12 pagesLESSON 9 Steam Generators 2Salt PapiNo ratings yet
- Deviser TV Analyser S7000: Bagian 1: Fungsi AnalyzerDocument15 pagesDeviser TV Analyser S7000: Bagian 1: Fungsi AnalyzerAlexander WieseNo ratings yet
- Gfk-1383a 05012Document108 pagesGfk-1383a 05012occhityaNo ratings yet
- Clock Al Ghadeer Setup GuideDocument4 pagesClock Al Ghadeer Setup Guideakberbinshowkat100% (2)
- DOJ OIG Issues 'Fast and Furious' ReportDocument512 pagesDOJ OIG Issues 'Fast and Furious' ReportFoxNewsInsiderNo ratings yet