Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amino Acids
Uploaded by
shane.surigaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amino Acids
Uploaded by
shane.surigaoCopyright:
Available Formats
SURIGAO, SHANE MISSY G.
BSN1-A
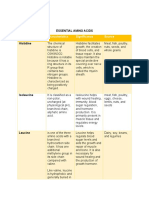
ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS
AMINO ACIDS FUNCTION DIETARY SOURCES
PHENYLALANINE It is needed for the synthesis of Phenylalanine is found in most
proteins, catecholamines and protein-containing foods such as
melanin. milk, eggs, cheese, nuts,
soybeans, chicken, beef, pork,
beans and fish.
VALINE It promotes muscle growth and Valine is found mainly in protein
tissue repair. food sources, such as meats,
fish, soy, and dairy.
THREONINE It mainly serves as a substrate High threonine foods include
for protein synthesis, lean beef, chicken, pork, tuna,
particularly mucin. tofu, beans, milk, cheese, green
peas, eggs, seeds, and nuts.
TRYPTOPHAN The body uses Tryptophan to Tryptophan is present in most
help make melatonin and protein-based foods or dietary
serotonin. proteins. It is particularly
plentiful in chocolate, oats, dried
dates, milk, yogurt, cottage
cheese, red meat, eggs, fish.
METHIONINE It can regulate metabolic Methionine is an essential amino
processes, the innate immune acid found in high quantities in
system and digestive functioning average American diet such as
in mammals. nuts, beef, lamb, cheese, turkey,
pork, fish, shellfish, soy, eggs,
dairy, and beans.
LEUCINE It can regulate several cellular Fortunately, plenty of healthy,
processes such as protein tasty foods contain leucine,
synthesis , tissue regeneration including eggs, seeds, oats,
and metabolism. legumes, and spirulina, and
they're all easy to incorporate
into your diet.
LYSINE To help the body absorb High-lysine foods include
calcium. poultry, fish, shrimp, shellfish,
pork, beef, soy, nuts, seeds,
eggs, beans, and lentils.
ISOLEUCINE It helps in growth, immunity, Isoleucine is plentiful in meat,
protein metabolism, fatty acid fish, poultry, eggs, cheese
metabolism and glucose lentils, nuts and seeds.
transportation.
NON-ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS
AMINO ACIDS FUNCTION DIETARY SOURCES
GLYCINE Glycine is essential for building Examples of foods that are high
muscle mass and the formation in glycine are bone broth,
of stretchy, flexible cartilage, poultry skin, seafood, meat and
which is particularly important legumes.
as we get older.
ALANINE Alanine is an amino acid that is As with the other amino acids ,
used to make proteins. It is used excellent sources of alanine
to break down tryptophan and include meat and poultry, fish,
vitamin B-6. It is a source of eggs, and dairy products.
energy for muscles and the
central nervous system.
SERINE L-serine plays an essential role Serine is found in soybeans, nuts
in a broad range of cellular (especially peanuts, almonds,
functions including protein and walnuts), eggs, chickpeas,
synthesis, neurotransmission, lentils, meat, and fish (especially
and folate and methionine cycles shellfish).
and synthesis of sphingolipids,
phospholipids, and sulfur
containing amino acids.
TYROSINE Neurotransmitters help nerve Tyrosine is found in soy
cells communicate and influence products, chicken, turkey, fish,
mood. Tyrosine also helps peanuts, almonds, avocados,
produce melanin, the pigment bananas, milk, cheese, yogurt,
responsible for hair and skin cottage cheese, lima beans,
color. pumpkin seeds, and sesame
seeds.
CYSTEINE This is the main protein in nails, It's found in beta-keratin. This is
skin, and hair. Cysteine is the main protein in nails, skin,
important for making collagen. and hair.
It affects skin elasticity and
texture. Cysteine has antioxidant
properties.
ASPARAGINE Asparagine is needed to produce They are found in huge amounts
many proteins but also plays as plant proteins. Plant sources
other roles. Asparagine helps to include whole grains, soy, nuts,
break down toxic ammonia legumes, asparagus, seeds, and
within cells potatoes.
ASPARTIC It helps make other amino acids It is produced in the body and
and some nucleotides. provided by dietary sources
including beef, poultry, dairy
products, and seed sprouts.
GLUTAMIC ACID Glutamic acid is an amino acid In a healthy diet, most glutamic
used to form proteins. In the acid is obtained through the
body, it turns into glutamate. consumption of meats, poultry,
fish, eggs, and dairy products, as
well as a few high protein
vegetable sources.
GLUTAMINE The functions of glutamine are Dietary sources of glutamine
many and include: substrate for include plant and animal
protein synthesis, anabolic proteins such as beef, pork,
precursor for muscle growth, poultry, milk, yogurt, ricotta
acid-base balance in the kidney, cheese, cottage cheese, raw
substrate for ureogenesis in the spinach, raw parsley, and
liver, cabbage.
PROLINE Proline plays important roles in The primary sources are
protein synthesis and structure, protein-rich foods including
metabolism (particularly the meat, fish, and dairy.
synthesis of arginine,
polyamines, and glutamate via
pyrroline-5-carboxylate), and
nutrition, as well as wound
healing, antioxidative reactions,
and immune responses.
You might also like
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument26 pagesVitamins and MineralsAisha Doll100% (1)
- Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrient (Vitamins) Needed For Key SourcesDocument4 pagesVitamins and Minerals: Nutrient (Vitamins) Needed For Key SourcesKevin Carl A. CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Protein EssentialsDocument49 pagesProtein Essentialsarun100% (2)
- OrganicAthlete Vegan Meal PlanDocument44 pagesOrganicAthlete Vegan Meal PlanOrganicAthlete90% (10)
- Black Soldier Fly Larvae, An Alternative For AquacultureDocument23 pagesBlack Soldier Fly Larvae, An Alternative For Aquaculturebsffarming100% (2)
- Micronutrients For HealthDocument4 pagesMicronutrients For HealthIsaac GoldNo ratings yet
- Indusdrial Visit in SSP PVT LTD FaridabadDocument16 pagesIndusdrial Visit in SSP PVT LTD FaridabadkedarnathvishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- No7 PreviewDocument17 pagesNo7 Previewumetnost1No ratings yet
- Vegetal Vs Mineral OilsDocument6 pagesVegetal Vs Mineral OilsDark CenobiteNo ratings yet
- Foods To Enjoy, Foods To Toss: For AutoimmunityDocument20 pagesFoods To Enjoy, Foods To Toss: For AutoimmunityrafilhouseNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Classification of Nutrients NutritionDocument33 pagesWEEK 3 Classification of Nutrients NutritionLaida PaguitalNo ratings yet
- Soal Procedure Tex1 PendampinganDocument7 pagesSoal Procedure Tex1 PendampinganBella HasnaNo ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica MannapackDocument7 pagesFicha Técnica Mannapackcamilo guzman100% (1)
- ESSENTIALDocument3 pagesESSENTIALYo1No ratings yet
- INGREDIENTSDocument17 pagesINGREDIENTSPaulo BacayNo ratings yet
- For Protein !: Say C HeeseDocument4 pagesFor Protein !: Say C HeeseJuan Sebastian CeleitaNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument4 pagesProteinEly gyNo ratings yet
- Types of Nutrients CONSUMER CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesTypes of Nutrients CONSUMER CHEMISTRYkeijeiNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument8 pagesAmino AcidsKatherine BellezaNo ratings yet
- Food Rich in ProteinDocument1 pageFood Rich in ProteinJazzmin Rae BarbaNo ratings yet
- What Is NutrientsDocument11 pagesWhat Is NutrientsRichard DerbyNo ratings yet
- Food Science & NuitritionDocument13 pagesFood Science & NuitritionACANo ratings yet
- Essential Amino Acids: Arab British Academy For Higher EducationDocument3 pagesEssential Amino Acids: Arab British Academy For Higher Educationstranieri08No ratings yet
- Feed Source and NutritionDocument17 pagesFeed Source and Nutritionj.cortez.525157No ratings yet
- Proteins - En, Food, Nutrition, Proteins, Vegetarian - Glogster EDU - Interactive Multimedia PostersDocument1 pageProteins - En, Food, Nutrition, Proteins, Vegetarian - Glogster EDU - Interactive Multimedia PostersClara BlancaNo ratings yet
- The Body Needs Many MineralsDocument3 pagesThe Body Needs Many MineralsTendekai GwatidzoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids TableDocument2 pagesAmino Acids Tableswarna.khare2574No ratings yet
- List of Amino AcidsDocument1 pageList of Amino AcidsHazrin RezzaNo ratings yet
- Tle ActivityDocument4 pagesTle ActivityManayam CatherineNo ratings yet
- Nutri (Minerals)Document83 pagesNutri (Minerals)Juliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- 2-Amino AcidsDocument8 pages2-Amino AcidsJaysette SNNo ratings yet
- Macrominerals: Major Minerals Mineral Function SourcesDocument2 pagesMacrominerals: Major Minerals Mineral Function Sourcesgelsa dragonNo ratings yet
- Obesity Management: UNIQUE PAPER CODE: 12555261Document26 pagesObesity Management: UNIQUE PAPER CODE: 12555261Dhritiraj KalitaNo ratings yet
- Formatted Food N Nutrition EVS Notes 27th AugDocument5 pagesFormatted Food N Nutrition EVS Notes 27th AugGauravNo ratings yet
- Protein Heat TreatmentDocument17 pagesProtein Heat TreatmentU H T 2No ratings yet
- Nutri PeDocument4 pagesNutri PeDaniel ArshNo ratings yet
- IAMS Proactive Health Dry Dog FoodDocument1 pageIAMS Proactive Health Dry Dog FoodEnchanting PetsNo ratings yet
- Plant Based Protein SeminarDocument41 pagesPlant Based Protein SeminarRitika ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Types of MeatDocument9 pagesTypes of MeatAna Marie AllamNo ratings yet
- Yeast Makes The Ecosystem More Favorable For Growth Due To The YeastDocument2 pagesYeast Makes The Ecosystem More Favorable For Growth Due To The YeastAizaz HassanNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument10 pagesProteinkg7484231No ratings yet
- Types of MeatDocument9 pagesTypes of MeatRA Tumacay0% (1)
- Food NutritionsDocument3 pagesFood NutritionsMopiyNo ratings yet
- 320 FeedstuffsDocument4 pages320 FeedstuffsGawum LoicNo ratings yet
- Masing, A.G. (CHE 403) Assignment 2Document6 pagesMasing, A.G. (CHE 403) Assignment 2Andrea Gail MasingNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ProteinsDocument30 pagesGroup 2 ProteinslaarnieNo ratings yet
- Water-Soluble Vitamins (Sanchez, Gonzales and Rojas)Document9 pagesWater-Soluble Vitamins (Sanchez, Gonzales and Rojas)CHELSEE VALENTINA SANCHEZ MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document5 pagesActivity 3Lucía ChabletNo ratings yet
- Vetn 2016 7 5 273 277Document5 pagesVetn 2016 7 5 273 277nick olisNo ratings yet
- Protein Content in Animal Feed Is A Critical Component For The Efficient Food Conversion of The AnimalDocument2 pagesProtein Content in Animal Feed Is A Critical Component For The Efficient Food Conversion of The AnimalLincolnNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Function Food SampleDocument3 pagesNutrition Function Food SampleAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Macro and Micro NutientsDocument11 pagesMacro and Micro NutientsPramodNo ratings yet
- Suplemento CorderoDocument10 pagesSuplemento CorderoRubiNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Function Deficiency Symptoms Toxicity Symptoms SourcesDocument1 pageNutrient Function Deficiency Symptoms Toxicity Symptoms SourcesSatyam AnandNo ratings yet
- 1.proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats, Their Role in Human NutritionDocument19 pages1.proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats, Their Role in Human NutritionFazil KfNo ratings yet
- Pork 101: Nutrition Facts and Pork 101: Nutrition Facts and Health Effects Health EffectsDocument12 pagesPork 101: Nutrition Facts and Pork 101: Nutrition Facts and Health Effects Health EffectsPhoenix Liebe JeffNo ratings yet
- Boe Flip ClassDocument14 pagesBoe Flip Classrohitrajww4No ratings yet
- High Protein in FoodsDocument5 pagesHigh Protein in Foodssourav.surNo ratings yet
- Nutritionforall - Soy Protein Isolate Manufacturers in IndiaDocument19 pagesNutritionforall - Soy Protein Isolate Manufacturers in IndiaNaina AhujaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Physical Activity and NutritionDocument5 pagesUnit3 Physical Activity and NutritionJames Andrei LeonidaNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument6 pagesNutritionrkjoseph1410No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument23 pagesVitaminsYumul, Jewel B.No ratings yet
- He4 Module1Document8 pagesHe4 Module1Shane Daughty Serdoncillo GarciaNo ratings yet
- HakdogDocument10 pagesHakdogcotaabdulnabelNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument11 pagesVitaminVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- SM 6 NutritionDocument10 pagesSM 6 Nutritionrahul royNo ratings yet
- Geography Minerals Project Nikhila DurbhakulaDocument4 pagesGeography Minerals Project Nikhila DurbhakulaNikki DNo ratings yet
- A Review of Forage Soybean Production - Quality and Yield - A Growing CultureDocument8 pagesA Review of Forage Soybean Production - Quality and Yield - A Growing CulturegegarborNo ratings yet
- Bioteh. Cresterea Animalelor PDFDocument168 pagesBioteh. Cresterea Animalelor PDFFlorin100% (1)
- Research Alternative For Dairy ProductsDocument5 pagesResearch Alternative For Dairy Productspanjee moyanNo ratings yet
- Cxxxv. Sources Urease: NEW OF For Determination of UreaDocument6 pagesCxxxv. Sources Urease: NEW OF For Determination of Ureaandi batikNo ratings yet
- Bello Que 2002Document27 pagesBello Que 2002Ahmed IsmailNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Soyabean Milk and ItDocument22 pagesPreparation of Soyabean Milk and Itniki dadhichNo ratings yet
- Tumour Inhibitors From PlantsDocument59 pagesTumour Inhibitors From PlantsAlishba Mushtaq100% (1)
- Best Muscle Building Foods - Muscle Building Diet - Foods To Build MuscleDocument10 pagesBest Muscle Building Foods - Muscle Building Diet - Foods To Build MuscleThe Fitness LevelsNo ratings yet
- Technical Article Onf Extrusion Process For Preparation of Instant CerealDocument10 pagesTechnical Article Onf Extrusion Process For Preparation of Instant Cerealgurusamy kandasamyNo ratings yet
- African Sales Trading Agency LTD Feasibility StudyDocument35 pagesAfrican Sales Trading Agency LTD Feasibility StudyMustapha AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Globalization On Japanese Food Culture and Health EssayDocument18 pagesEffects of Globalization On Japanese Food Culture and Health EssayCherise Fuselier83% (6)
- LegumesDocument3 pagesLegumesValerieNo ratings yet
- FDA Organic Food RecallsDocument23 pagesFDA Organic Food RecallsAnonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument17 pagesChemistryVishal KamalakannanNo ratings yet
- Kriti IndiaDocument7 pagesKriti IndiaPrabhat PahanNo ratings yet
- th9901 SoyabeenDocument91 pagesth9901 SoyabeenelanthamizhmaranNo ratings yet
- BASF and Solidaridad Team Up To Empower Brazilian Farmers To Foster BiodiversityDocument2 pagesBASF and Solidaridad Team Up To Empower Brazilian Farmers To Foster Biodiversitymikeskordilis1No ratings yet
- Overview of Crop Agriculture - John Bryan GregorioDocument11 pagesOverview of Crop Agriculture - John Bryan GregorioArts IanNo ratings yet
- Kenta DocumentDocument1 pageKenta DocumentVincent OktavianNo ratings yet
- Soya IndustryDocument33 pagesSoya IndustrySheel HansNo ratings yet
- 8 2 Introduction To Biodiesel ProductionDocument7 pages8 2 Introduction To Biodiesel ProductionshawonscribdNo ratings yet