0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views5 pagesStatistics & Regression Analysis
The document provides analysis of data from 12 offices including total cost (Y) and number of clients (X).
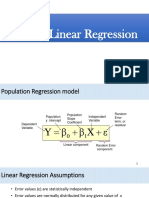
1) A linear regression model is assumed: Y = α + βX + ε. The error term ε captures unexplained variability in costs.
2) Estimates are calculated as: α = 1,175 (intercept), β = 43.75 (cost per client).
3) R-squared is 0.99, meaning the linear model explains 99% of the variability in total costs based on the number of clients.
Uploaded by
Munna ChoudharyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views5 pagesStatistics & Regression Analysis
The document provides analysis of data from 12 offices including total cost (Y) and number of clients (X).
1) A linear regression model is assumed: Y = α + βX + ε. The error term ε captures unexplained variability in costs.
2) Estimates are calculated as: α = 1,175 (intercept), β = 43.75 (cost per client).
3) R-squared is 0.99, meaning the linear model explains 99% of the variability in total costs based on the number of clients.
Uploaded by
Munna ChoudharyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5