Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cyto Unit 2 Transes
Uploaded by
Eunice PillejeraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cyto Unit 2 Transes
Uploaded by
Eunice PillejeraCopyright:
Available Formats
MLS 108: CTYOGENETICS
BSMT 2 | 1st Semester | S.Y. 2023-2024
UNIT 2: DNA STRUCTURE (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID)
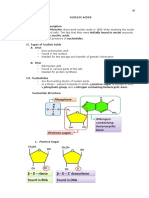
• A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic
DNA STRUCTURE acids (RNA and DNA).
• Nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either
ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a
phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base
• The bases used in DNA are Adenine (A), Cytosine
(C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T)
NITROGENOUS BASES:
Adenine-Thymine, Cytosine-Guanine
GE
• PURINES
– Pure as “AG” (silver)
– 2 of them= 2 ringed structure
-is composed of chains of nucleotide which is comprised of • PYRIMIDINES
the ff: – Cut the “pie” (py)
– 1 ringed structure
1. Phosphate group
2. Sugar group (Deoxyribose) 5- carbon sugar CHARGAFF’S RULE
3. Nitrogenous bases
NUCLEOTIDE • States that DNA from any cell of all organisms
should have a 1:1 ratio (base Pair Rule) of
pyrimidine and purine bases and, more specifically,
that the amount of Guanine is equal to cytosine
and the amount of adenine is equal to thymine.
• Nucleotides are the building block of DNA and RNA.
They contain genetic information.
• The phosphate group together with the sugar
group forms the backbone to which the bases are
attached.
• Nitrogenous bases are the part of DNA that stores
information and gives DNA the ability to encode
phenotype-visible traits.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________ 1
Prepared by: Eunice Y. Pillejera | BSMT 2A
MLS 108: CTYOGENETICS
BSMT 2 | 1st Semester | S.Y. 2023-2024
UNIT 2: DNA STRUCTURE (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID)
POLARITY OF THE DNA STRAND
• DIRECTIONALITY: ANTI-PARALLEL
TO GENETICS (Oriented in the
opposite direction)
• On one end, the DNA strand will have a 5’-phosphate and
on the opposite end, a 3’- hydroxyl group
• Hydrogen bonds can be broken, and the DNA trand is
separated by heating the DNA molecule (denaturation)
• MELTING TEMPERATURE(Tm): (52-58°C) the emperature
at which one strand of the DNA duplex will dissociate to
become single stranded and indicates the duplex stability.
;will depend on GC content; the HIGHER the GC Content,
the HIGHER the (Tm) required to denature that DNA.
CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY
REPLICATION- the process by which the genome’s DNA is
copied in cells. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or
replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter
cell ends up with its complete genome.
TRANSLATION- involves the synthesis of a protein from an
mRNA template, converting the mRNA code to an amino
acid sequence within a protein
TRANSCRIPTION- the process of transcribing a plaece of
DNA into RNA. The enzyme involved in the transcription
process is RNA polymerase
_______________________________________________________________________________________________ 2
Prepared by: Eunice Y. Pillejera | BSMT 2A
You might also like
- HHMI - The p53 Gene and CancerDocument4 pagesHHMI - The p53 Gene and CancerThe vegetal saiyanNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument58 pagesTranscription and Translationkevin_ramos007No ratings yet
- Preclinical Biochemistry and Medical Genetics Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Biochemistry and Medical Genetics Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1No ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument75 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionFENo ratings yet
- Transes - Nucleic Acid by GetteDocument6 pagesTranses - Nucleic Acid by GetteDUQUE, GEORGETTE FLOREANNE L.No ratings yet
- MacromoleculesDocument91 pagesMacromoleculesSabali NewtonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Gene RegulationDocument35 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Gene RegulationDrew TaryeeNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein - Transcription and TranslationDocument11 pagesFrom Gene To Protein - Transcription and TranslationELOISA N. CASANENo ratings yet
- Epigenetics and Chromatin RemodellingDocument30 pagesEpigenetics and Chromatin RemodellingMaya BerriesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On DNA and RNA AnswersDocument3 pagesWorksheet On DNA and RNA AnswersBenjamin SalernoNo ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument23 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationAleksandar KlingNo ratings yet
- Written Work 2Document5 pagesWritten Work 2Jellie May RomeroNo ratings yet
- DBT BET Question Paper 2009 With Answer KeyDocument22 pagesDBT BET Question Paper 2009 With Answer KeyAbhay Kumar100% (3)
- Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesNucleic AcidsJM MatiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesChapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsSofeaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Store and Transmit Hereditary InformationDocument28 pagesNucleic Acids Store and Transmit Hereditary InformationSerap BayramNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument69 pagesNucleic AcidsKinjal BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- 202003271457480855monisha Basics of DNADocument67 pages202003271457480855monisha Basics of DNANelecaupNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture 9 - Nucleic AcidsDocument35 pagesBiology Lecture 9 - Nucleic Acidsamritabehera2222No ratings yet
- 1.nucleic Acid Chemistry and Gene Manipulation IntroDocument85 pages1.nucleic Acid Chemistry and Gene Manipulation Introshruti shahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument21 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerabcdeniselimNo ratings yet
- 2.2. DNA RNA Transcr TranslatDocument35 pages2.2. DNA RNA Transcr TranslatClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance 1Document17 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance 1SNIGDHA APPANABHOTLANo ratings yet
- 2nd - Sem - BPharma - Nucleic Acid NotesDocument55 pages2nd - Sem - BPharma - Nucleic Acid NotesDeep MaliNo ratings yet
- DnaDocument36 pagesDnafyou56939No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Chemistry LectureDocument31 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistry LectureHoque Mohammed Newaz Shoriful100% (1)
- DNA, RNA, and The Flow of InformationDocument31 pagesDNA, RNA, and The Flow of InformationSasa AbassNo ratings yet
- L1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentDocument29 pagesL1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Pre-Class AssignmentDocument56 pagesLearning Objectives: Pre-Class AssignmentEden ManggaNo ratings yet
- 3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryDocument90 pages3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryMajd HallakNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesNucleic Acidsbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- DNA STRUCTURE LectureDocument44 pagesDNA STRUCTURE Lectureevacarlina1721No ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Supercoiling L1Document8 pagesDNA Structure and Supercoiling L1ellieNo ratings yet
- Cyto PL2Document17 pagesCyto PL2Danielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument7 pagesMolecular GeneticsSiti Hajar RevillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Structure of Nucleotide and Neuclic AcidsDocument21 pagesLecture 1 Structure of Nucleotide and Neuclic AcidsSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts - MacromoleculesDocument49 pagesBasic Concepts - MacromoleculeskasomaisaackNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna 11Document70 pagesDna Rna 11L CuevasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 & 4: DNA, Genes, Chromatin Learning ObjectivesDocument65 pagesLecture 3 & 4: DNA, Genes, Chromatin Learning ObjectivesAli Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesNucleic Acidslim.angelyne0126No ratings yet
- Central Dogma - Part 1Document29 pagesCentral Dogma - Part 1akilroberto17No ratings yet
- DNA RNA Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesDNA RNA Protein Synthesisjohairah merphaNo ratings yet
- CH1131 - Biomolecular Engineering - Week 2 - Transcription Translation - Aug 18 21 2015Document49 pagesCH1131 - Biomolecular Engineering - Week 2 - Transcription Translation - Aug 18 21 2015joshuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 DNA Structure, DNA Library, DNA IsolationDocument45 pagesLecture 5 DNA Structure, DNA Library, DNA IsolationDr.Fahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Properties of DNADocument21 pagesProperties of DNAakshif KhanNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic GenomesDocument50 pagesEukaryotic GenomesturkiNo ratings yet
- Material Review of Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesMaterial Review of Nucleic AcidIrvandar NurviandyNo ratings yet
- FHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesFHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionLeena AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 2 CH DNA - Structure - Replication - 2022Document50 pages2 CH DNA - Structure - Replication - 2022aswinarumugam2003No ratings yet
- 04 Nucleic AcidsDocument45 pages04 Nucleic AcidsNash DeniegaNo ratings yet
- LecturerDocument42 pagesLectureratef.salman.grNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna-101Document30 pagesDna Rna-101Hazel SioseNo ratings yet
- DNA and Genetic EngineeringDocument43 pagesDNA and Genetic EngineeringBlessy Anne GabeloNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument62 pagesStructure of DNANikki SStarkNo ratings yet
- Sandra Central DogmaDocument82 pagesSandra Central Dogmakaren milloNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- The Nucleic AcidsDocument94 pagesThe Nucleic Acidsmeklit birhanuNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Information StorageDocument29 pagesNucleic Acids: Information StorageAbrar Mohi-ud-DinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - DNA The Molecular of InheritanceDocument28 pagesChapter 8 - DNA The Molecular of InheritanceNguyễn ChiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: A. DnaDocument9 pagesNucleic Acids: A. DnaJeyan BoncavilNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA 3Document28 pages2.3 Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA 3Moza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - Structure of NucleotidesDocument26 pagesNucleic Acids - Structure of Nucleotidesits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Compared AutosavedDocument35 pagesDNA and RNA Compared Autosavedfranzpersonal810No ratings yet
- Case 1 SummeryDocument11 pagesCase 1 SummeryTtNo ratings yet
- Mic180 - Chapter 7 - Nucleic Acid - EditedDocument59 pagesMic180 - Chapter 7 - Nucleic Acid - EditedNur ShahirahNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Dna & RnaDocument3 pages1.5 Dna & RnaNURIN ALIS BINTI FADZIL MoeNo ratings yet
- Cape1 DNA2Document48 pagesCape1 DNA2Matt BarhamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Nucleic Acid (2) - Doc Viliran 06/11/09Document162 pagesChemistry of Nucleic Acid (2) - Doc Viliran 06/11/09lowellaNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument31 pagesGenetic MaterialANBC- 24- Safa AfreenNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Fourth EditionDocument17 pagesMolecular Biology: Fourth Editionفقوش عبودNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis HomeworkDocument5 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis HomeworkKarla Long100% (1)
- Microbiology PDFDocument26 pagesMicrobiology PDFAladin herzALLAHNo ratings yet
- The Genetics of Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument3 pagesThe Genetics of Sickle Cell AnemiaJuhany MusaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisDocument34 pagesChapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisPikuNo ratings yet
- Parte 2 BioDocument150 pagesParte 2 BioPâmella PicançoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology 2nd Edition Clark Test BankDocument25 pagesBiotechnology 2nd Edition Clark Test BankCameronAllenmtwei100% (58)
- chemistry-technical-document-CHTD 500 v1 Revo 07jul2016 PDFDocument27 pageschemistry-technical-document-CHTD 500 v1 Revo 07jul2016 PDFMoni Becerra WongNo ratings yet
- Nsejs Exam Solutions Paper 2019Document27 pagesNsejs Exam Solutions Paper 2019EDat UthuberNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument21 pagesAn Introduction To BiotechnologyBrayan Trujillo rojasNo ratings yet
- Ms. Rima DessaiDocument46 pagesMs. Rima DessaiSanghaviNo ratings yet
- Biology of CancerDocument19 pagesBiology of CancerAbaixo Joaquim Jacinto RosseNo ratings yet
- Cell Determination and DifferentiationDocument19 pagesCell Determination and DifferentiationDrAbhilasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper-03 (For 2014)Document5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Paper-03 (For 2014)cbsestudymaterialsNo ratings yet
- ProkariatesDocument24 pagesProkariatesteja prasadNo ratings yet
- Biology and Genetics PDFDocument8 pagesBiology and Genetics PDFPrincess Angie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisjNo ratings yet
- DNA Activity SheetDocument9 pagesDNA Activity SheetGu Jun PyoNo ratings yet
- 9700 w15 QP 13Document16 pages9700 w15 QP 13Hew Li Yang100% (1)
- Amity Institute of Biotechnology In-House Training Report-2020Document27 pagesAmity Institute of Biotechnology In-House Training Report-2020Tony BernardNo ratings yet