Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15 Ishan Bajpai
Uploaded by
Kylo RenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
15 Ishan Bajpai
Uploaded by
Kylo RenCopyright:
Available Formats
IJRMET Vol.
5, Issue 1, November 2014 - April 2015 ISSN : 2249-5762 (Online) | ISSN : 2249-5770 (Print)
Comparative Study of Torsen Differential
Ishan Bajpai
Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, R.K.G.I.T, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India
Abstract A. Comparison With Open Differential
The main objective of the study is to compare theTorsen differential In an open differential the drive axle connection is designed to
with various other types of conventional differentials which are deliver equal torque to both the wheels. This arrangement will not
commonly used in automobiles. The comparison is based on support any substantial torque difference between the drive axle
various parameters like working mechanism, design, sensitivity and, as a consequence, offer very little resistance to differentiation.
etc. For example, if one of the wheel falls in poor traction region then
this differential will transfer maximum torque to the other wheel
Keywords resulting in ‘spin up’ of the wheel having poor traction. Thus the
Invex Gearing, Elementary Gears, Side Gears, Differential vehicle gets stuck and cannot overcome the traction difference
Housing, Bias Ratio problem. So, an open differential is limited to work when the car
is approaching a turn in order to differentially distribute the torque
I. Introduction to the two wheels. When comparing it with Torsen differential,the
The differential is a common mechanical device preferred to be Torsen dominance over the open differential as it can easily come
used in automobiles. The basic purpose of a differential is to up the traction difference on the two wheels by its invex gearing
transmit the power to the wheels while allowing them to rotate mechanism, where if any of the wheel falls in a poor traction
at different speeds.Though it seems a simple mechanism but still region the speed change will be transferred to the worm wheel,
there are many of its types, each with its own specific property which in turn transfer the speed change to its adjacent worm
and mechanism.Torsen is also a type of differential invented and wheel, since they are connected with spur gears (as explained
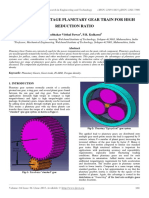
patented by Gleason in 1958, as shown in fig 1. Just like others in2.1 Invex gearing), this leads to locking of the whole drive
it works on the principle of transmission of torque and power mechanism into one system (as by the principle of worm and
through meshing of gears but unlikely the mechanism of Torsen worm gear ,explained in section 2). Hence, the wheel with poor
of controlling torque and traction differs technically. traction receives high torque and the vehicle can overcome the
traction difference problem.
II. The Working Principle
Every differential works on the simple principle of transfer of B. Comparision With Locking Differential
power and load from one gear to the other. Torsen also works The locking differential is almost similar to open differential but
on the same principal but what differentiates it with others is with an inherent mechanism to lock the two axles when a traction
the use of worm and worm gear assembly in its operation. Its difference occurs, just like the Torsen. When a wheel falls in a
principle is simple i.e. a rotating worm gear can rotate the worm poor traction region, this differential locks both of the axle (as
wheel but rotating worm wheel cannot spin the worm gear. This understood by its name “locking”) into a single unit and the vehicle
principle is the reason for its quick sensitivity to any change in can overcome the traction difference problem. But as the Torsen
torque output. also works on locking the axles then what is the difference in
using it?. The answer lies in the design and reactiveness of the
A. Invex Gearing mechanism. The locking type has a clumsy and heavy design
Invex gearing in a Torsen differential includes a gear train setup comprising of cam plate, friction discs and an engagement
arrangement (refer to fig 2.) comprised of two or more pairs of mechanism. Where the engagement mechanism is designed to
satellite gears (called ‘element gears’) in mesh with central helical work on an occurrence of a minimum traction difference, by
gears (called ‘side gears’).The pairs of element gears are connected engaging itself with the cam plate and friction discs. , resulting
with each other by means of two spur tooth engagement. Generally, in axle locking.
to transmit and handle the torque coming from the engine, an When comparing the sensitivity of the differentials i.e. how
overall set of 6 element gears is used but this number can vary quickly it responds to the change in traction between the wheels,
depending upon the torque capacity and space requirement. Torsen leads over the locking type as the respond is quick
whereas the locking differential takes time for its engagement
B. Torque Bias Ratio mechanism to work. Thus when comparing it on an overall basis,
Bias ratio is the maximum torque ratio which a particular differential the Torsenbeing compact in design, suits best for quick respond
design can support. It is expressed as quotient of higher torque to traction difference.
(i.e. in the higher axle) to the lower torque (i.e. in the lower axle)
proportioned to unity. A ‘4:1’ TBR means the Torsen differential C. Comparison With Limited-Slip Differential
can deliver the wheel having better traction, four times the amount Limited slip differential(refer to fig 3.) or LSD are provided
supported by lower traction wheel. with pre-loaded friction clutches to oppose the transfer of torque
between the axles.The friction pre-load represents a minimum
III. Comparision With Conventional Differentials magnitude of resistance which must be overcome to permit any
Even though all conventional differentials serves the same purpose relative motion between the drive axles which may interfere with
of providing better traction and torque to the wheels at all allowable the operation of anti-lock braking system. Also, since frictional
conditions still ,speaking technically, none of them can be pointed forces are continually active the friction clutches tends to wear,
to be perfectly efficient for every condition resulting in deterioration of intended differential performance.
On the other hand the bias ratio characteristic of the Torsen
74 International Journal of Research in Mechanical Engineering & Technology w w w. i j r m e t. c o m
ISSN : 2249-5762 (Online) | ISSN : 2249-5770 (Print) IJRMET Vol. 5, Issue 1, November 2014 - April 2015
differential instantly reacts to unequal traction conditions by
delivering an increased amount of torque to the drive wheel having
better traction before the other drive wheel exceeds the limit of
traction available to that wheel. Hence, technically the Torsen
shows better result in relation with the sensitivity and traction
control of the wheels.
IV. Conclusion
The Torsen differential exhibits a torque biasing
characteristic,compact design and high sensitivity of reacting
instantlyto traction problems. The TBR property of the Torsen
makes it possible to distribute the torque unevenly between the
wheels. Thus it is found to be better than any other conventional
differential that are discussed in this paper.
References
[1] H. Crouse, Williams – Automotive Mechanics, Tata McGraw- Fig. 2:
Hill Education,1951.
[2] Heitner, Joseph- Automotive Mechanics, Principle and
Practises, 2014.
[3] Wikipedia.org, Torsen, [Online] Available: http://
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torsen
[2] Renlist.com, The strange geometry of Gleason’s impossible
differential [Online] Available: http://members.rennlist.
com/951_racerx/ps84gleason.html
[3] Learningengineering.org, Torsen differential, How it
works? [Online] Available: http://www.learnengineering.
org/2014/11/Torsen-Differential.html
[4] Wikipedia.org, Locking differential, [Online] Available:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Locking_differential
[5] Wikipedia.org, Limited-Slipdifferential, [Online]
Available: http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Limited-slip_
differential
Fig. 3:
Mr. Ishan Bajpai is pursuing his
bachelor’s degree from Mechanical
engineering from R.K.G.I.T
Ghaziabad, India. He has done various
courses in designing like solidworks
and ansys, as well as provided training
in that field to other institution and
undertaken various projects, one of
them being under SAE India and also
works as a core committee member
under a NGO. His areas of interest
includes Designing, Research and
Development, Automobileetc. to name a few.
Fig. 1:
w w w. i j r m e t. c o m International Journal of Research in Mechanical Engineering & Technology 75
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Traction Control ArticleDocument8 pagesTraction Control ArticledromakiNo ratings yet
- Torsen Differential White PaperDocument8 pagesTorsen Differential White PaperPadmAnabhNo ratings yet
- Farm Machinery - Tractors - A Collection of Articles on the Operation, Mechanics and Maintenance of TractorsFrom EverandFarm Machinery - Tractors - A Collection of Articles on the Operation, Mechanics and Maintenance of TractorsNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Influence of Inter - Wheel Differentiak of 4WD VehicleDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of The Influence of Inter - Wheel Differentiak of 4WD VehicleRajeevNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Gearbox Noise and Vibration: Measurement, Signal Analysis, Signal Processing and Noise Reduction MeasuresFrom EverandVehicle Gearbox Noise and Vibration: Measurement, Signal Analysis, Signal Processing and Noise Reduction MeasuresNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Influence of Inter-Wheel Differentials On The Kinetic and Dynamic of 4WD VehicleDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of The Influence of Inter-Wheel Differentials On The Kinetic and Dynamic of 4WD VehicleNguyen Van QuyenNo ratings yet
- Effect of Coupling Types On Rotor VibrationDocument14 pagesEffect of Coupling Types On Rotor VibrationMarwa BouslemaNo ratings yet
- Comparison With Other Types of DifferentialsDocument6 pagesComparison With Other Types of DifferentialskaduNo ratings yet
- PRESENTION 2 MPPDocument28 pagesPRESENTION 2 MPPKhairul SyahreelNo ratings yet
- Design of The Differential For A Truck Brand Ford Model Ranger 1998Document22 pagesDesign of The Differential For A Truck Brand Ford Model Ranger 1998Mishu MalesNo ratings yet
- No Backlash DrivesDocument28 pagesNo Backlash Drivesmustafa taiforNo ratings yet
- Unit 14Document58 pagesUnit 14Parul SinghNo ratings yet
- Initial Report Anti Reverse DiffDocument53 pagesInitial Report Anti Reverse Diffvinay muleyNo ratings yet
- Limited-Slip Differential WikiDocument7 pagesLimited-Slip Differential WikiMariano MartinNo ratings yet
- Design of Automotive DifferentialDocument8 pagesDesign of Automotive DifferentialDeepak ChachraNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Reverse Locking of Differential MechanismDocument12 pagesFabrication of Reverse Locking of Differential MechanismKabilanCrazeeNo ratings yet
- Design Manufacturing Analysis of Differential Crown Gear and Pinion For MFWD AxleDocument8 pagesDesign Manufacturing Analysis of Differential Crown Gear and Pinion For MFWD AxleVinay Prasad NNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - 1: AIM: Study of Various Types of Gear Boxes Such As Industrial Gear Box, SynchromeshDocument3 pagesExperiment No - 1: AIM: Study of Various Types of Gear Boxes Such As Industrial Gear Box, SynchromeshParas KumbalwarNo ratings yet
- Damping in A Rolling Bearing Arrangement-SkfDocument7 pagesDamping in A Rolling Bearing Arrangement-Skfmick.pride81No ratings yet
- Clutch Palte - 1Document48 pagesClutch Palte - 1pramo_dassNo ratings yet
- ClutchDocument9 pagesClutchAndryanNo ratings yet
- KSRTC Final ReportDocument47 pagesKSRTC Final ReportBoby Thomas100% (1)
- Differential Selection ReportDocument6 pagesDifferential Selection ReportMichael Epshtein50% (2)
- Friction ClutchDocument7 pagesFriction ClutchJenifer DassNo ratings yet
- Final Drive and DifferentialDocument9 pagesFinal Drive and DifferentialVasantha SeelanNo ratings yet
- Design Failure Analysis and Optimization f0cbdf05Document8 pagesDesign Failure Analysis and Optimization f0cbdf05Afiq IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Backlash (Engineering) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesBacklash (Engineering) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediadarkruseNo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation of Planetary Transmission WDocument8 pagesDesign and Calculation of Planetary Transmission Wkarnail singh dhimanNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: Chassis Body and TransmissionDocument9 pagesLearning Outcomes: Chassis Body and Transmissionprem pravashNo ratings yet
- Differential Pocket Study Guide Ugears STEM Lab deDocument15 pagesDifferential Pocket Study Guide Ugears STEM Lab deChittaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Differential Unit Locking SystemDocument19 pagesAutomatic Differential Unit Locking SystemPradeep Gs100% (1)
- Automobile EngieeringDocument28 pagesAutomobile EngieeringYogesh Kumar GaurNo ratings yet
- Backlashvs LostMotion PDFDocument4 pagesBacklashvs LostMotion PDFjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- STC TRS Conv 03 Supplement Mech PDFDocument83 pagesSTC TRS Conv 03 Supplement Mech PDFZahoor Ahmed100% (1)
- AdhesionDocument82 pagesAdhesionriajulNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument24 pagesClutchesRom XenonNo ratings yet
- Design of ClutchesDocument37 pagesDesign of ClutchesRintu MazumderNo ratings yet
- Transmission SystemDocument51 pagesTransmission SystemPethurajNo ratings yet
- DiffDocument10 pagesDiffMoti LemiNo ratings yet
- Differetials & Solid AxlesDocument34 pagesDifferetials & Solid AxlesAkshay ChandrasNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-05 at 1.43.52 PMDocument25 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-05 at 1.43.52 PMTabish Naik 39No ratings yet
- Coupling - WikipediaDocument40 pagesCoupling - WikipediaManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Counter Shaft Usi PDFDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Counter Shaft Usi PDFLuis Angel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Balancing FundamentalsDocument16 pagesBalancing FundamentalsAHNo ratings yet
- Differential 150313145700 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument16 pagesDifferential 150313145700 Conversion Gate01 PDFmharitmsNo ratings yet
- Rotating Machine: Cogs Torque TransmissionDocument1 pageRotating Machine: Cogs Torque TransmissionJomariBobadillaNo ratings yet
- Continuously Variable TransmissionDocument33 pagesContinuously Variable Transmissionsk9145100% (1)
- Construction of A Constant Mesh Gear BoxDocument21 pagesConstruction of A Constant Mesh Gear BoxAmare Eshetie0% (1)
- Designe GearDocument8 pagesDesigne GearSaveli Paul FlorinNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Spur Gear Using Composite MaterialDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Spur Gear Using Composite MaterialIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- BrakeDocument13 pagesBrakeBaby SinghNo ratings yet
- Capter Four Drives: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument116 pagesCapter Four Drives: Department of Mechanical EngineeringabebawalemkerNo ratings yet
- AT6501 QBDocument8 pagesAT6501 QBSahayaraj GabrielNo ratings yet
- Clutch DesignDocument12 pagesClutch Designmos3ad2006No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: ObjectivesDocument27 pagesChapter - 1: ObjectivesjeyNo ratings yet
- Clutches and BrakesDocument10 pagesClutches and BrakesKhaloud Mahdi Al-JasmiNo ratings yet
- CouplingDocument5 pagesCouplingAnonymous 0v9zwXz6hFNo ratings yet
- DOM Short Answer QuestionsDocument14 pagesDOM Short Answer Questionskalyan saiNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document11 pagesWeek 3Kylo RenNo ratings yet
- Sample MSD PaperDocument2 pagesSample MSD PaperKylo Ren0% (1)
- Hypothesis Testing of Age & Gender Vs Covid 19 Deaths in MaharashtraDocument8 pagesHypothesis Testing of Age & Gender Vs Covid 19 Deaths in MaharashtraKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Suhane 2018Document10 pagesSuhane 2018Kylo RenNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Fire ExtinguisherDocument14 pagesCatalogue Fire ExtinguisherKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Encoder Data SheetDocument13 pagesEncoder Data SheetKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Effect of Different Loads On Fatigue Strength of 1040 Steel Materials After Design and Manufacturing of Rotating-Bending Fatigue Test DeviceDocument8 pagesEffect of Different Loads On Fatigue Strength of 1040 Steel Materials After Design and Manufacturing of Rotating-Bending Fatigue Test DeviceKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Simulation of Steam Power Cycles UsiDocument7 pagesThermodynamic Simulation of Steam Power Cycles UsiKylo RenNo ratings yet
- FEM-supported Simulation of Chip Formation and Ow in Gear Hobbing of Spur and Helical GearsDocument10 pagesFEM-supported Simulation of Chip Formation and Ow in Gear Hobbing of Spur and Helical GearsKylo RenNo ratings yet
- Jedinger Alexander 2015Document91 pagesJedinger Alexander 2015Kylo RenNo ratings yet
- 横屏车型 大众车系产品列表20220711 2Document13 pages横屏车型 大众车系产品列表20220711 2max.mustermannNo ratings yet
- Dv15Tis: Mechanical System Fuel SystemDocument2 pagesDv15Tis: Mechanical System Fuel SystemBùi Xuân ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Removal & Installation: Engine Cylinder Head Assembly - Service Information - HR VDocument13 pagesRemoval & Installation: Engine Cylinder Head Assembly - Service Information - HR VkavindaNo ratings yet
- 600 HDocument16 pages600 HOscar Marino Campo BonellNo ratings yet
- How To Repair Small Engines PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Repair Small Engines PDFStephane Durel MbidaNo ratings yet
- Camshaft1 PDFDocument3 pagesCamshaft1 PDFVladimirNo ratings yet
- PDF Toyota Starlet Ep82 Service Manual PDFDocument2 pagesPDF Toyota Starlet Ep82 Service Manual PDFArmando Amar50% (8)
- Pulsar NS200 & AS200 BSIII BSIV Combined - SPCDocument106 pagesPulsar NS200 & AS200 BSIII BSIV Combined - SPCgastonNo ratings yet
- Icml'S Rhino RX: Design and EngineeringDocument3 pagesIcml'S Rhino RX: Design and EngineeringNiteesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Isi Brosur 2019 180219Document1 pageIsi Brosur 2019 180219bang nalNo ratings yet
- Heavy Vehicle Inspection Checklist TemplateDocument2 pagesHeavy Vehicle Inspection Checklist TemplateAhmed IsmaielNo ratings yet
- Renault Magnum Dxi13 Wiring ManualDocument354 pagesRenault Magnum Dxi13 Wiring ManualBoris rojas100% (2)
- LW800KN: Outline DimensionsDocument4 pagesLW800KN: Outline Dimensions余No ratings yet
- Practical - QP - R - 2017 - AT8411 - OK - AT 8411-4.4Document3 pagesPractical - QP - R - 2017 - AT8411 - OK - AT 8411-4.4Palani VelNo ratings yet
- Ducati Monster 600 Engine AssignmentDocument56 pagesDucati Monster 600 Engine AssignmentJuan Lopez100% (2)
- s590 t4 Maintenance ChartDocument1 pages590 t4 Maintenance ChartKleon TriantafillidisNo ratings yet
- 950h mxl00417Document13 pages950h mxl00417Mahmmod Al-Qawasmeh100% (1)
- Model Engine Development: by Gordon CornellDocument6 pagesModel Engine Development: by Gordon CornellNitsam7No ratings yet
- dp4 Pricelist PDFDocument207 pagesdp4 Pricelist PDFMissoum TerrasNo ratings yet
- Mack-Aro de Fuego 45-Sb213042Document5 pagesMack-Aro de Fuego 45-Sb213042cpaolinodNo ratings yet
- Conventional, Tricycle and Tandem (Landing Gears)Document3 pagesConventional, Tricycle and Tandem (Landing Gears)Sergio Pingol100% (1)
- C7.1 Parts ManualDocument78 pagesC7.1 Parts ManualMarcelo L Zamora93% (14)
- 2008 Ski Doo Rev XP Shop Manual PDFDocument553 pages2008 Ski Doo Rev XP Shop Manual PDFRaphael LabontéNo ratings yet
- 2106T0642 TK70 Concrete PumpDocument128 pages2106T0642 TK70 Concrete Pumpviemey1952100% (3)
- Cummins Isf2.8 Spare Parts CatalogDocument8 pagesCummins Isf2.8 Spare Parts CatalogChen Caroline100% (1)
- Transmission Identification GuideDocument14 pagesTransmission Identification Guidecampollano14100% (1)
- Auto Manual Cars Utility VehiclesDocument40 pagesAuto Manual Cars Utility VehiclesMohan RajNo ratings yet
- PH Svel29bDocument53 pagesPH Svel29bاشرينكيل مسونكيلNo ratings yet
- tp99124 PDFDocument20 pagestp99124 PDFDieselkNo ratings yet
- 1.jan - 21Document65 pages1.jan - 21mani01kandanNo ratings yet