Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pratt & Whitney Standard Practices Manual (PN 585005)
Uploaded by
Paul FisherOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pratt & Whitney Standard Practices Manual (PN 585005)
Uploaded by
Paul FisherCopyright:
Available Formats
Previous Pageblock Return to Previous Menu Next Pageblock
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
Task 70−44−01−330−100−001:
1. General Plating Procedures
A. Part Hardness
(1) For several plating SPOPs, it is necessary that the
repair source know the hardness of the part before the
start of the repair. The hardness is used to select
the applicable operations in these SPOPs. The CIR or
Engine Manual repair will give the hardness of the part
in the repair. Thus, for these repairs, it is not
necessary to do a test for part hardness.
B. Degreasing With SPOP 209
(1) Degrease the part with SPOP 209 whenever possible.
Refer to 70−21−00, SPOP−209 (Task 70−21−00−110−041).
(2) Protect all such degreased parts and plated surfaces
with a corrosion inhibitor in SPOP 5. Refer to
70−21−00, SPOP−05 (Task 70−21−00−110−048).
C. Demagnetization
NOTE: It is important to do a check of each steel part or
test panel for magnetization and, if necessary, to
demagnetize the part or panel before plating.
(1) Demagnetization Test
(a) With a magnetic field strength indicator, test
each steel part or test panel for magnetization.
Move the meter over all areas of the part or test
panel, especially the faces and rims of flanges
on parts and all projections from the main body.
The magnetic field strength indicator (or use a
unit with equivalent features and safeguards) is
available from the Tool And Equipment Source Code
Index. Refer to 70−91−00, General−02 (Task
70−91−00−990−002) for the source name/address
identified by this number.
5V126
(b) Read the meter.
1 If the maximum meter reading is no more
than ±3 Gauss, then it is not necessary to
demagnetize the part or test panel.
#70−44−01 Page 901
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/11
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
2 If the maximum meter reading is more than ±3
Gauss, then demagnetize the part or test panel.
(2) Demagnetization Procedure
(a) Pass the part or test panel through the full
length of the demagnetizer.
(b) Hold the part or test panel close to the top or
sides of the demagnetizer.
(c) Withdraw the part or test panel slowly.
(d) Rotate circular parts while withdrawing.
(e) Remove the part or test panel straight away from
the demagnetizer. Do not turn current off until
the part or test panel is at least three feet
(0.91 m) from the demagnetizer.
(f) Do the demagnetization test again. If necessary,
do the procedure and test again until you get
satisfactory results.
D. Masking
NOTE: Refer to SPOP 36 in 70−44−01, SPOP−36 (Task
70−44−01−330−008) for specific masking application
and removal procedures.
(1) For masking, you can use a mechanical mask (neoprene or
other rubber−like materials), masking tape, lacquer,
wax, or chemical or waterborne maskants. The choice of
materials depends mainly on the temperature of, and the
length of time in, the solutions. For example,
(a) Wax must be insoluble in solutions in which it is
used and must adhere to parts being plated without
staining the underlying metal. See the specific
details given in SPOP 36. Refer to 70−44−01,
SPOP−36 (Task 70−44−01−330−008).
(b) Standard lacquer will withstand a 200°F (93°C)
immersion for a short period after which it is not
reliable above 130°F (54°C).
1 Special lacquers are available which will
withstand higher temperatures in acid
solutions.
#70−44−01 Page 902
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/11
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
2 Lacquer is not suitable in alkaline solutions
operated at a temperature of 160°F (71°C) or
more.
3 Use lacquer which will air dry to touch in less
than 30 minutes after spraying at 30 − 50 psi
(206.8 − 344.7 kPa) and be ready for use after
an air dry of two hours.
4 Lacquer must be insoluble in plating solutions
and adhere to part without staining underlying
metal after immersion for one and one−half
minutes in an alkaline cleaning solution (such
as PS 101, PS 117, PS 201, PS 211, PS 344, SPS
119−1, SPS 133, SPS 134, or SPS 199) or for
three hours in any plating solution.
5 After plating, you can remove lacquer if
you put it fully in, or wash it, with hot
degreasing fluid, or you can loosen it if you
put it fully in a hot alkaline cleaner until
the lacquer can be blown off with an airblast.
(c) Waterborne maskant has restrictions as to its use.
Refer to the Masking Procedures in SPOP 36 in
70−44−01, SPOP−36 (Task 70−44−01−330−008).
(2) In general, silver plated parts are masked with wax and
lacquer, and tin plated parts are masked with tape.
Use rubber masks when a large number of parts are to be
plated.
(3) Deterioration with age or usage is another factor in
the choice of materials.
(a) Phenolite and Micarta fixtures wear out and rubber
loses its elasticity after lengthy immersion in
silver plating solutions.
(b) Shapes, sizes, and surfaces also determine the
choice of masking material.
NOTE: Do not use lacquer (which shrinks when
drying) for inside diameter surfaces or
for flat ring surfaces where there is no
adherence when an edge has lacquer on it.
E. Cleaning
#70−44−01 Page 903
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
(1) Parts must be fully clean for a good plating bond.
(a) Examine the part frequently for water breaks.
Where there are water breaks, do the subsequent
steps:
1 Use a tampico brush (GA 55−1 or GA 56−1) or a
nylon brush (GA 55−2 or GA 56−2) and one of
the subsequent materials to remove the water
breaks:
a A paste of pumice (PMC 3001) and water
b A cleaning solution that you used to clean
the part. For example:
· PS 101
· PS 117
· PS 201
· PS 211
· PS 344
· SPS 119−1
· SPS 133
· SPS 134
· SPS 199
2 Flush the part with clean water.
3 Do this procedure again, as necessary.
a The part is fully clean when you see no
water breaks.
(2) Compressed air used for cleaning and drying must
not exceed 30 psig (206.8 kPa), as specified by the
Occupational Safety and Health Act. (Federal Register,
Part 2, 1910.242 General, Paragraph B.)
F. Agitation
(1) Plating solutions with exception of strike solutions
must be agitated.
G. Baking
(1) Temperature and time are the most critical factors in
baking.
#70−44−01 Page 904
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
(a) The time necessary at each specified temperature
begins only when the total load is at the
specified temperature.
(b) When no other time tolerances are specified, the
specified baking time is the minimum permitted.
(c) Temperature ranges are absolute and tolerances do
not apply.
H. Bond Testing Silver Plated Parts
(1) Baking Before Bond Test
(a) It must be determined that all high speed steel
or stainless steel parts to be subjected
to shotpeening or chisel test have been
stress−relieved before bond testing by baking at
approximately 375°F (191°C) for two hours following
plating process.
(2) Shotpeening Test
NOTE: The shotpeening test does not apply to repairs
that require silver flash plating.
(a) Degrease parts with SPOP 209 and, with sufficient
layers of PMC 4270 masking tape, or equivalent,
or mechanical masks, mask all areas not to be
shotpeened. Refer to 70−21−00, SPOP−209 (Task
70−21−00−110−041). Use steel shot conforming to
SAE specification S−170 and adjust air pressure
as indicated by results obtained on test strips.
Once a week, test 100 gram sample of shot taken
from shot nozzle to determine that shot meets size
standards. Record results.
(b) Inspect all parts for thickness of silver; use
a Magne−Gage or Fischer scope MMS Sigmascope
(602−156) with a water−resistant ESD2 probe
(602−308), or equivalent.
NOTE: This equipment (or use units with
equivalent features and safeguards) is
available from the Tool And Equipment
Source Code Index. Refer to 70−91−00,
General−02 (Task 70−91−00−990−002) for the
#70−44−01 Page 905
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
source names/addresses identified by these
numbers.
EQ018
61325
1 Reject any part that has plate thickness of
less than 0.004 inch (0.102 mm), more than
0.027 inch (0.686 mm) or variation in thickness
of more than 0.005 inch (0.127 mm).
2 Mark each acceptable piece, with its maximum
plate thickness and arrange pieces in groups
within which there is variation of not more
than 0.005 inch (0.127 mm).
(c) Shotpeen each group to minimum arc for maximum
thickness of that group as shown in Figure 901.
Adjust peening intensity by test on an Almen A2
gage.
NOTE: This equipment (or use units with
equivalent features and safeguards) is
available from the Tool And Equipment
Source Code Index. Refer to 70−91−00,
General−02 (Task 70−91−00−990−002) for the
source name/address identified by this
number.
0CJ83
1 Process a test strip before starting each lot
and again every hour thereafter if lot is
continuous.
2 Poor silver bond will be indicated by blisters
or ruptures.
(3) Chisel Test
(a) Apparatus
1 0.250 inch (6.350 mm) or 0.500 inch (12.700 mm)
blade chisel. See Figure 902.
2 Knife
3 Pointed pick
#70−44−01 Page 906
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
4 Bench vise
5 Hammer
6 6 − 10X magnifying glass.
(b) Test of Plate 0.002 Inch (0.051 mm) Thick or Over
1 Clamp part in vise allowing access to an
area of excess plate such as would be built
up on the edges of the part. Hold chisel
almost parallel (or tangent) to the excess
plated surface. Tap the chisel with a hammer
until blade edge has penetrated plate to the
interface of plate and base metal. Continue
tapping so that chisel shears or cuts plate at
interface, but stop before reaching edge of any
intended plate envelope. If possible, repeat
at five additional locations.
2 If plate has separated or lifted from base
metal or from strike beyond the sides or
ends of the actual shear path, bond is
unsatisfactory.
(c) Test of Plate under 0.002 Inch (0.051 mm) Thick
1 Under magnification, in an area outside the
required plate area, and using a knife or razor
blade held at an angle of 10 to 20 degrees to
the surface being tested, cut through the
deposit to the base metal and attempt to lift
plate from the base metal. If possible, repeat
at five additional locations.
2 If plate has separated from the base metal
or the strike at any location, bond is
unsatisfactory.
I. Bond Test for Soft Nickel Plated Parts
(1) Chisel Test
(a) This test is identical to the chisel test
described under Bond Testing Silver Plated Parts.
The bond requirements for soft nickel plate are
the same as those shown for silver plate.
#70−44−01 Page 907
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
J. Bend Test for Silver, Chromium, Electroless Nickel, and Soft
Nickel Plated Parts
(1) Plated test panels of an alloy representative of the
part base can be used as an alternative to the chisel
test to determine plate adhesion.
(2) Acceptable panels will show no separation of the
plating from the base metal when examined at 6 − 10X
magnification after being bent through an angle of 180
degrees around a diameter equal to the thickness of the
specimen.
(3) Bend the panel until the panel fractures.
(4) Formation of cracks which do not result in flaking or
blistering of the plate is acceptable.
K. Shotpeening
(1) Types of Shot
(a) Refer to 70−41−02, SPOP−501 (Task
70−41−02−380−019).
(2) Equipment − Airblast Machine, Wheelabrator−Frye or
Rotor Blast Machine
(a) Degrease all parts with SPOP 209. Refer to
70−21−00, SPOP−209 (Task 70−21−00−110−041).
(b) Mask all areas which are not to be
shotpeened. Refer to 70−44−01, SPOP−36 (Task
70−44−01−330−008).
(c) Shotpeen all areas to be peened to the specified
intensity.
NOTE: At any time during processing, test piece
may be run to determine if parts are being
shotpeened to requirements.
(d) Remove all necessary masking.
(e) Visually inspect shotpeened surface. Surfaces on
which peening is required shall have peened or
hammered appearance. If coverage of shotpeened
areas is not complete, part must be shotpeened
again.
#70−44−01 Page 908
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
(f) Holes and edges of parts must be free from rolled
metal.
(g) Check for embedded shot.
(3) Clean
(a) Remove remaining shot by blowing off with air.
(4) Preservation
(a) Preserve the parts, as necessary, with
SPOP 5. Refer to 70−21−00, SPOP−05 (Task
70−21−00−110−048).
L. Flash Plating
(1) Wherever flash plating is recommended, thickness is
understood to be approximately 0.0001 inch (0.0025 mm).
M. Solutions
(1) Solution numbers referenced throughout text are Pratt &
Whitney numbers and are keyed to numbers in Section
70−44−02.
(2) Parts may be immersed in certain solutions either with
or without application of current. Do not assume, for
example, that an immersion in an electrolytic cleaner
makes use of current necessary. Be sure that such use
of current is specifically requested.
N. Tools And Equipment
Name Source Code
Almen Gage 0CJ83
Magne−Gage EQ018
or
Fischer Scope MMS Sigmascope (602−156) with 61325
a water−resistant ESD2 probe (602−308)
* Refer to 70−91−00, General−02 (Task 70−91−00−990−002)
for specific information on location of source
name/address.
#70−44−01 Page 909
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
O. Care Of Equipment And Work Area
CAUTION: DO NOT USE EQUIPMENT THAT WILL ARC AND CAUSE
ENGINE PARTS TO BURN. DAMAGE BY AN ARC OR
BURN WILL MAKE THE PART UNSERVICEABLE.
IF A PART ARC BURNS, IT IS NECESSARY TO
FIND OUT THE CAUSE AND TAKE CORRECTIVE
ACTION. REFER TO 70−31−00, GENERAL−01 (Task
70−31−00−200−001) FOR DEFINITIONS.
(1) Tools, fixtures, containers, and benches must be kept
clean at all times since these items directly affect
the part as it is processed and may be indicative of
quality of work.
NOTE: Fixtures used for cadmium and nickel−cadmium
plating must be stripped of cadmium deposits
before each use.
(2) It is not permissible to smoke, eat, or store food in
and around the processing lines.
(3) It is important to label the contents of all open
surface tanks and identify those containing hazardous
materials with a standard "CAUTION" sign.
(4) To prevent process errors that can cause damage to
parts or coating, label chemical solution tank(s) with
the SPOP or approved process.
P. Maintenance Of The Electroless Nickel Controller By The
Plating Department
(1) Calibrate the colorimeter each time the controller is
started up.
(2) One time each week, examine the pH meter with a
known standard solution; then report any problems to
department supervision.
(3) Measure monthly the replenishment pump rates and make
any necessary adjustments.
(4) One time each week, examine all tubing and fittings for
leakage; then replace any tubing that shows wear or
leakage.
#70−44−01 Page 910
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
(5) Pump clean water until all the nickel solution in the
line has been pumped out.
NOTE: This cleaning step takes approximately three
minutes to do.
(6) Stop the pump.
(7) Replace the tube in the replenishment drum.
Q. Rinsing
(1) When plating SPOP instructions say "Clean water rinse",
it means to put the part fully in a tank of clean
water.
Task 70−44−01−330−100−002:
2. Machining Preparation For Nickel Plate Repairs
A. General
(1) For each snap diameter repair on a disk, hub, or rotor
shaft, the fillet radius of the undercut made in
preparation for nickel plating must not be smaller than
the original snap diameter fillet radius, and neither
the undercut nor its fillet radius may extend into the
adjacent face surface.
Task 70−44−01−330−100−003:
3. Stripping Plasma Spray, Flame Spray, Flame Plate, High Velocity
Oxy−Fuel, And Electrodeposited Coatings
A. General
(1) Pratt & Whitney no longer recommends to use only grit
blasting to strip (remove) coatings from parts in
repairs. Grit blasting can cause unequal or too much
stock loss. Stripping (removal) procedures such as
grinding, machining, chemical stripping/blasting and
water−jet are alternatives that are less aggressive.
Refer to 70−46−01, SPOP−535 (Task 70−46−01−340−014)
for the recommended grind and single−point machine
methods (procedures) for plasma and other thermal spray
coatings. Machining or grinding is an effective method
for the removal of plasma spray, flame spray, flame
plate, and other thermal spray coatings from parts.
#70−44−01 Page 911
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
Bond Testing Chart
Figure 901
(Task 70−44−01−330−100−001)
#70−44−01 Page 912
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
Silver Bond Test Chisel
Figure 902
(Task 70−44−01−330−100−001)
R
R #70−44−01 Page 913
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 DEC 1/12
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
(2) In many instances, the coatings can be more easily and
economically stripped (removed) or degraded by chemical
or water−jet stripping methods. Recommended methods
are identified as follows and in Figure 903 (Sheet 1)
thru Figure 903 (Sheet 3).
Method
SPOP Letter Description
44 A Sodium Carbonate−Tartrate
Stripping Solution
45 B Molten Salt Bath
48 E Nickel Strip Salt − Sodium Cyanide
Solution
50 F Nitric Acid Solution
51 G Caustic Soda Solution
53 H Nickel Strip Solution
301 I Hydrochloric Acid Solution
304 J Nitric−Sulfuric Acid Solution
317 L Acidic Peroxide Solution
R 319 R Stripping Solution
322 P Water−Jet Stripping
324 M Nitric/Inhibited Phosphoric,
Alkaline Permanganate Solution
326 N Nitric Acid Solution
CAUTION: DO NOT USE METHODS A, B, C, OR D TO STRIP
COATINGS FROM CAST MATERIAL, MOST IMPORTANTLY
TURBINE VANES, UNLESS PERMITTED BY SPECIFIC
REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS.
(3) Figure 903 shows the methods that will strip or degrade
the coatings in the list without damage to the base
metal. For coatings that are not in the table, use
conventional machining, grinding or, where specified,
grit blasting to strip the coating.
#70−44−01 Page 914
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 DEC 1/12
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
(a) The chemical solutions in each stripping method
that is underlined in Figure 903 do not strip the
coating, but will degrade the coating sufficiently
to make it possible for the blasting procedures
specified in the method to strip the coating.
(b) Each method that is in parentheses in Figure 903
does not fully strip the coating by itself, but
removes the underlayer or bond coat of multi−layer
coatings where the edges of the bond coat are
in contact with the stripping solution; this
undermines the top coat. Chip off (remove with a
tool) the undermined top coat from time to time to
increase the speed of the procedure.
(c) Method P does not strip PWA 53−5; use Method M or
grind to strip PWA 53−5. Method P can be used to
strip all other coatings in Figure 903 from the
base materials shown.
(4) Figure 903 puts nickel alloy base materials into two
material classes as Nickel−Base Alloys or Nickel−Base
Super Alloys for stripping method identification.
Tables 901 thru 903 give a list of the materials
that are in each of these classes. In general, the
materials in the nickel−base alloy class are wrought,
nonhardenable alloys, which include the widely used
wrought types of Hastelloy X and 600−series Inconel,
while the materials in the nickel−base super alloy
class include both cast nickel−base alloys (notably
turbine materials) and all age−hardenable nickel−base
alloys, which are usually of the wrought type.
CONDITION:
Code Description
AC AS CAST
ANN ANNEALED
SC SINGLE CRYSTAL
SOL SOLUTION HEAT TREATED
SP SOLUTION AND PRECIPITATION HEAT TREATED
SR STRESS−RELIEVED
SSP SOLUTION, STABILIZATION, AND PRECIPITATION HEAT TREATED
#70−44−01 Page 915
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
FORM:
Code Description
AT SEAMLESS TUBING
B BARSTOCK
DS DIRECTIONALLY SOLIDIFIED
F FORGING
P PLATE
PC INVESTMENT CAST
R RINGS
S SHEET
ST STRIP
WDT WELDED AND DRAWN TUBING
WT WELDED TUBING
AMS PWA Trade Name Condition
5540 P,S,ST ANN
5580 AT 1060* AT Inconel 600 ANN
−−−− 1070* AT ANN
5665 B,F,R 1062** WDT ANN
5536 P,S,ST 1038 P,S,ST HASTELLOY X SOL
5754 B,F,R −−−− SOL
5587 AT 5588 WDT 1066 WDT SOL
5666 B,F,R −−−− Inconel 625 ANN
−−−− 1069** AT SOL
5599 P,S,ST 1072*** WDT SOL
5530 S 5750 B,F,R −−−− HASTELLOY C SOL
5715 B,F,R −−−− Inconel 601 ANN
5870 P,S,ST −−−− ANN
−−−− 1045 S Nicroloy 165Y SOL
5711 B,F,R 1055 B,F,R HASTELLOY S SOL
−−−− 1198 Haynes 242 SP
* Superseded by AMS 5580
** Superseded by AMS 5581, Type 1
Wrought Nonhardenable Nickel−Base Alloys
Table 901
#70−44−01 Page 916
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
AMS PWA Trade Name Condition
*** Superseded by AMS 5581, Type 1 for tubing with diameters of
less than one inch (25.4 mm). AMS 5581, Type 2 can be used for
tubing with diameters of one inch (25.4 mm) or greater. If PWA
1072 is specified, use the latest revision of AMS 5581, Type 1 or
2, as applicable.
Wrought Nonhardenable Nickel−Base Alloys
Table 901 (Continued)
AMS PWA Trade Name Condition
5702 B,F,R 1025 B,F,R Inconel 706 SOL
5703 B,F,R 1026 B,F,R Inconel 706 SSP
5606 P,S,ST 1043 P,S,ST Inconel 706 SOL
5662 B,F,R 1009 B,F Inconel 718 SOL
5663 B,F,R 1010 B,F Inconel 718 SP
5664 B,F,R −−−− Inconel 718 SOL
−−−− 1065 WDT Inconel 718 ANN
5589 AT 1085 B,F Inconel 718 SOL
5596 P,S,ST −−−− Inconel 718 SOL
5597 P,S,ST −−−− Inconel 718 SOL
5542 P,S,ST 1063 WDT Inconel X−750 SOL
5582 AT −−−− Inconel X−750 SOL
5667 B,F,R −−−− Inconel X−750 SOL
5671 B,F,R −−−− Inconel X−750 SOL
5598 P,S,ST 1031 S Inconel X−750 SOL
5668 B,F,R 1192 Inconel 909 SP
5670 B,F,R 1199 Thermospan SOL
5660 B,F 5661 1003 B,F Incoloy 901 SSP
B,F
−−−− 1022 F Incoloy 901 SP
−−−− 1024 F Incoloy 901 SP
−−−− 1047 F Incoloy 901 SP
Wrought Age−Hardenable Nickel−Base Super Alloys
Table 902
#70−44−01 Page 917
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
AMS PWA Trade Name Condition
5708 B,F 7471 −−−− WASPALOY SOL
Bolt
5709 B,F 686 B,F 92 Bolt WASPALOY SSP
5706 B,F,R −−−− WASPALOY SOL
5707 B,F,R −−−− WASPALOY SSP
5704 F 1005 F 1007 F WASPALOY SSP
−−−− 1016 F 1027 F WASPALOY SSP
5544 P,S,ST −−−− WASPALOY ANN
5586 WT 1057 F WASPALOY ANN
−−−− 1013 F Astroloy SSP
−−−− 1021 B 93 Bolt Astroloy SSP
−−−− 1023 B,F Astroloy SR
−−−− 1041 S Astroloy SR
−−−− 1051 F Astroloy SP
−−−− 1071 WDT Astroloy SR
−−−− 689 B,F Udimet 700 SSP
−−−− 1019 B,F Udimet 700 SSP
−−−− 1028 F IN 100 SP
−−−− 1058 F Modified IN 100 SSP
−−−− 1073 F Modified IN 100 SSP
−−−− 1074 F Modified IN 100 SSP
−−−− 1106 Modified IN 100 SSP
−−−− 1100 IN 100 IMP SSP
−−−− 1112 Modified SSP
Waspaloy
−−−− 1113 Modified SSP
Waspaloy
Wrought Age−Hardenable Nickel−Base Super Alloys
Table 902 (Continued)
AMS PWA Trade Name Condition
−−−− 661 PC Inconel 600 AC
5390 PC −−−− Hastelloy X AC
−−−− 649 PC Inconel 718 ANN
−−−− 652 PC Waspaloy SSP
Cast Nickel−Base Super Alloys
Table 903
#70−44−01 Page 918
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 JUN 1/10
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
AMS PWA Trade Name Condition
5391 PC 655 PC Inconel 713C AC
5397 PC 658 PC IN 100 AC
−−−− 1422 DS Mar−M 200 + Hf SOL
−−−− 663 PC B−1900 AC
−−−− 1455 PC B−1900 AC
−−−− 1447 PC Mar−M 247 AC
−−−− 1426 DS −−−− SOL
−−−− 1451 PC Inconel 738 SOL
−−−− 1456 PC Inconel 792 SOL
−−−− 1480 SC −−−− SOL
5384 PC 1483 SC Udimet 500 SP
−−−− 1484 SC −−−− SOL
−−−− 1487 SC −−−− SOL
Cast Nickel−Base Super Alloys
Table 903 (Continued)
R
R #70−44−01 Page 919
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 DEC 1/12
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
Stripping Methods For Flame Spray, Plasma Spray, Flame Plate,
High Velocity Oxy−Fuel, And Electrodeposited Coatings
Figure 903 (Sheet 1)
(Task 70−44−01−330−100−003)
#70−44−01 Page 920
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 DEC 1/12
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
Stripping Methods For Flame Spray, Plasma Spray, Flame Plate,
High Velocity Oxy−Fuel, And Electrodeposited Coatings
Figure 903 (Sheet 2)
(Task 70−44−01−330−100−003)
#70−44−01 Page 921
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 DEC 1/12
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
Pratt & Whitney
STANDARD PRACTICES MANUAL (PN 585005)
PLATING PROCEDURES − REPAIR−00
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
Stripping Methods For Flame Spray, Plasma Spray, Flame Plate,
High Velocity Oxy−Fuel, And Electrodeposited Coatings
Figure 903 (Sheet 3)
(Task 70−44−01−330−100−003)
#70−44−01 Page 922
EFFECTIVITY −ALL REPAIR−00 DEC 1/12
000
P&W Proprietary - Subject to further restrictions on the cover page.
Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3).
You might also like
- SP7041M03T46 000 A PDFDocument5 pagesSP7041M03T46 000 A PDFPedro Casimiro GámizNo ratings yet
- Soft Natural Rubber Lining: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesSoft Natural Rubber Lining: Technical Data SheetArmanda SiryogiawanNo ratings yet
- WBEpoxyCoating Data SheetDocument2 pagesWBEpoxyCoating Data SheetkaleshNo ratings yet
- Triflex ™ 3-Layer Combinations: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesTriflex ™ 3-Layer Combinations: Technical Data SheetSantosh JayasavalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material Specification: Controlled Document at Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesEngineering Material Specification: Controlled Document at Page 1 of 6erik0007No ratings yet
- Ford ABS Plating Spec.Document7 pagesFord ABS Plating Spec.Pieter100% (2)
- Surface Preparation & Paint Procedure (RevB)Document19 pagesSurface Preparation & Paint Procedure (RevB)Mohd Taufiq IsmailNo ratings yet
- Durability of Coating Repair Systems For Offshore Services - Eurocorr 2014Document17 pagesDurability of Coating Repair Systems For Offshore Services - Eurocorr 2014ANIBALLOPEZVEGA100% (1)
- SECTION 09980 Thin Film Polymer Floor Sealer Part 1 - General 1.01Document2 pagesSECTION 09980 Thin Film Polymer Floor Sealer Part 1 - General 1.01Eng CivilNo ratings yet
- Jotafloor EP SL Uni - Abrasion & Impact ResistDocument6 pagesJotafloor EP SL Uni - Abrasion & Impact Resistangelito bernalNo ratings yet
- Durashield 110 61Document6 pagesDurashield 110 61huicholeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledRodrigo LeanosNo ratings yet
- WSS M99P32 D1Document6 pagesWSS M99P32 D1jose luisNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Highway Materials (4300-468-568)Document9 pagesAssignment 3 - Highway Materials (4300-468-568)Mir Shahnewaz ArefinNo ratings yet
- Test Block No. 2 Acc. To EN ISO 3452-3 (Order No. 9992.100) : Description, Application and Handling of TheDocument1 pageTest Block No. 2 Acc. To EN ISO 3452-3 (Order No. 9992.100) : Description, Application and Handling of TheSowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- Holiday Testing ProcedureDocument1 pageHoliday Testing ProcedureSyed Zakiuddin100% (2)
- TMT 035 Nde 04Document14 pagesTMT 035 Nde 04rameshqcNo ratings yet
- 24T3 Series TDSDocument5 pages24T3 Series TDSFernando CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Chemflake Special Application GuideDocument10 pagesChemflake Special Application GuideMohanadNo ratings yet
- Resist 86: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesResist 86: Technical Data SheetantonyfmNo ratings yet
- Abstract of ASTM F1136 1998Document3 pagesAbstract of ASTM F1136 1998Jesse ChenNo ratings yet
- 23T3 SeriesDocument5 pages23T3 SeriesEliana FLTNo ratings yet
- Application Guide Phenoline Tank ShieldDocument10 pagesApplication Guide Phenoline Tank ShieldNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- AG 462 Jota Armour Euk GBDocument10 pagesAG 462 Jota Armour Euk GBEirikJohansenNo ratings yet
- MORTH 1600 2 Acrylic Elastomeric CoatingDocument4 pagesMORTH 1600 2 Acrylic Elastomeric CoatingRameshNo ratings yet
- Ti01f06a03-01en 001Document5 pagesTi01f06a03-01en 001haisamsarwarNo ratings yet
- Sikatack Panel: Panel Adhesive For Ventilated FaçadesDocument2 pagesSikatack Panel: Panel Adhesive For Ventilated FaçadeselpibematadorNo ratings yet
- SP7011M00D01 000 ADocument30 pagesSP7011M00D01 000 APedro Casimiro GámizNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument12 pagesPDFThamaraikani ManiNo ratings yet
- PDS Intergard 906Document4 pagesPDS Intergard 906SUBHOMOYNo ratings yet
- Penguard Express MIO Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesPenguard Express MIO Technical Data SheetGurdeep Sungh AroraNo ratings yet
- TDS Penguard Pro JotunDocument5 pagesTDS Penguard Pro JotunLuka BornaNo ratings yet
- Jotun - Penguard FC (Second Coat)Document5 pagesJotun - Penguard FC (Second Coat)Satria IstanaNo ratings yet
- AutoRecovery Save of SOW - Sand Blsting and Recoating of HPCMS TECHNICON Rev9 (AutoRecovered)Document6 pagesAutoRecovery Save of SOW - Sand Blsting and Recoating of HPCMS TECHNICON Rev9 (AutoRecovered)MotswalediNo ratings yet
- Jotaprime Mastic 80 AGDocument8 pagesJotaprime Mastic 80 AGMuthu Sivarama Krishnan Nallaiah100% (2)
- GMW - 4707-2002 Corrosion Protective Coating Zinc Plating OrganicDocument3 pagesGMW - 4707-2002 Corrosion Protective Coating Zinc Plating Organichorse888No ratings yet
- Final SOW-HVOF Coating On Boiler ChannelDocument29 pagesFinal SOW-HVOF Coating On Boiler ChannelCorrosion FactoryNo ratings yet
- Chemflake SpecialDocument10 pagesChemflake SpecialNabeel K SNo ratings yet
- Paint Specification For Marine BargeDocument6 pagesPaint Specification For Marine BargeNsidibe Michael EtimNo ratings yet
- DTD 5509 Aircraft Material SpecificationDocument5 pagesDTD 5509 Aircraft Material SpecificationMateen AhmadNo ratings yet
- Tankguard StorageDocument5 pagesTankguard StorageBiju_PottayilNo ratings yet
- Marathon XHB: Technical Data Sheet Application GuideDocument9 pagesMarathon XHB: Technical Data Sheet Application GuideDamar WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Powder Coat Performance Spec WSS M70J5 C1Document9 pagesPowder Coat Performance Spec WSS M70J5 C1Michal BílekNo ratings yet
- Arm Grout HF66 VDocument3 pagesArm Grout HF66 VRajesh GiriNo ratings yet
- 407ASB407ASB22128Document10 pages407ASB407ASB22128camiloguayazanNo ratings yet
- Jotamastic 70Document9 pagesJotamastic 70Muhammad HanafiNo ratings yet
- TDS Marathon 1000 XHBDocument5 pagesTDS Marathon 1000 XHBSyamsul MaripNo ratings yet
- Smarter Building Systems SBS-R30 Insulating Paint InstructionsDocument5 pagesSmarter Building Systems SBS-R30 Insulating Paint InstructionsJJ Sherem MoraNo ratings yet
- Neoprene Lining: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesNeoprene Lining: Technical Data SheetinfoNo ratings yet
- Marathon 1000GF Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesMarathon 1000GF Technical Data SheetGurdeep Sungh AroraNo ratings yet
- FILMTEC™ Membranes: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesFILMTEC™ Membranes: Product Data SheetAshish GulrandheNo ratings yet
- Return To TOC: Dowty Propellers Standard Practices ManualDocument18 pagesReturn To TOC: Dowty Propellers Standard Practices ManualNicolás PiratovaNo ratings yet
- Tds - Jotun - Guard Classic EtDocument3 pagesTds - Jotun - Guard Classic Etvijh van niemannNo ratings yet
- Marathon: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesMarathon: Technical Data SheetOkinawa TeakNo ratings yet
- Trim Assembly, Enclosed Luggage WSS-M15P32-D Compartment Covering 1. ScopeDocument11 pagesTrim Assembly, Enclosed Luggage WSS-M15P32-D Compartment Covering 1. Scopeerik0007No ratings yet
- Penguard Express PDFDocument5 pagesPenguard Express PDFImam SitumeangNo ratings yet
- WSS M16J19 BDocument10 pagesWSS M16J19 BJuan Angel DechimaNo ratings yet
- Functional Polymer Coatings: Principles, Methods, and ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Polymer Coatings: Principles, Methods, and ApplicationsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Chromium Finishing Questionnaire - 0Document72 pagesChromium Finishing Questionnaire - 0Paul FisherNo ratings yet
- Cisco 95-0669-01 - C1-1Document15 pagesCisco 95-0669-01 - C1-1Paul FisherNo ratings yet
- Cisco 95-0669-01 - C1-1Document15 pagesCisco 95-0669-01 - C1-1Paul FisherNo ratings yet
- Astme3 01Document12 pagesAstme3 01Paul FisherNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesChemistry Notesraifaisal9267% (12)
- TA308 616configurationDocument1 pageTA308 616configurationJesus AvilaNo ratings yet
- Eng Pipe DesignDocument12 pagesEng Pipe DesignEsapermana Riyan100% (1)
- BLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914Document304 pagesBLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914fantasmaNo ratings yet
- Calculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFDocument10 pagesCalculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Microscope MaintenanceDocument2 pagesMicroscope MaintenanceCharlyn KeithNo ratings yet
- Modern Views Catalogue/Sotheby's BenefitDocument36 pagesModern Views Catalogue/Sotheby's BenefitStudio AdjayeNo ratings yet
- Feature Writing EnglishDocument2 pagesFeature Writing EnglishAldren BababooeyNo ratings yet
- Ieee 802Document3 pagesIeee 802M Zubair AslamNo ratings yet
- M1-Safety StandardsDocument9 pagesM1-Safety StandardscarlNo ratings yet
- Ays 082914 3331 PDFDocument18 pagesAys 082914 3331 PDFFabian R. GoldmanNo ratings yet
- Gold Advanced Progress Test 5Document6 pagesGold Advanced Progress Test 5BernardNo ratings yet
- Jib Crane Assembly ManualDocument76 pagesJib Crane Assembly ManualRobert Cumpa100% (1)
- From Science To God by Peter RussellDocument6 pagesFrom Science To God by Peter RussellFilho adulto pais alcolatrasNo ratings yet
- 10 - Enzymes - PPT - AutoRecoveredDocument65 pages10 - Enzymes - PPT - AutoRecoveredFaith WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Diels-Alder Reaction: MechanismDocument5 pagesDiels-Alder Reaction: MechanismJavier RamirezNo ratings yet
- TR189 Kathuria PDFDocument168 pagesTR189 Kathuria PDFuqiNo ratings yet
- Stress Management PPT FinalDocument7 pagesStress Management PPT FinalAdarsh Meher100% (1)
- Marriage HalldocxDocument50 pagesMarriage HalldocxBalaji Kamalakannan100% (2)
- Eoi QAMDocument6 pagesEoi QAMPeeyush SachanNo ratings yet
- 5 Years High and Low PointsDocument7 pages5 Years High and Low PointsNaresh Kumar VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- The Ecological Effects of Eucalyptus PDFDocument97 pagesThe Ecological Effects of Eucalyptus PDFgejuinaNo ratings yet
- En LF Drivers 10nw76 8Document3 pagesEn LF Drivers 10nw76 8ChrisNo ratings yet
- Macleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusDocument2 pagesMacleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusSIMONE BLAIRNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Mid Term Exam 2014Document8 pagesChemistry Mid Term Exam 2014Adham TamerNo ratings yet
- Fluid Solids Operations: High HighDocument20 pagesFluid Solids Operations: High HighPriscilaPrzNo ratings yet
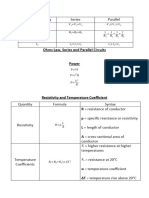
- EET - Formulas - Christmas TermDocument3 pagesEET - Formulas - Christmas TermJMDNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016Document3 pages1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016api-292307509No ratings yet
- Digital Trail Camera: Instruction ManualDocument20 pagesDigital Trail Camera: Instruction Manualdavid churaNo ratings yet
- Sindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionDocument192 pagesSindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionNea Tan100% (1)