Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CLT Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Ali BissenovCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CLT Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Ali BissenovCopyright:
Available Formats
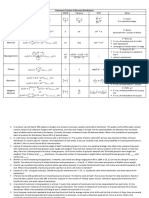
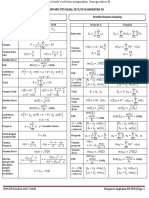
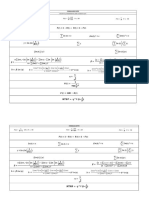
CLT “Cheat Sheet”
For Sample Means of Samples of Size 𝒏
Distribution of 𝑿 𝝁𝑿 𝝈𝑿 ̅
Distribution of 𝒙 𝝁𝑿̅ 𝝈𝑿̅
(general)
𝑿 ~ a distribution 𝑆𝐷(𝑿)
with expected value 𝜇𝑋 = 𝐸(𝑿) 𝜎𝑋 = 𝑆𝐷(𝑿) 𝑥̅ ~ normal(𝜇𝑋̅ , 𝜎𝑋̅ ) 𝜇𝑋̅ = 𝐸(𝑿) 𝜎𝑋̅ =
E(X) and standard √𝑛
deviation SD(X)
𝜎
𝑿 ~ normal(𝜇, 𝜎) 𝜇𝑋 = 𝜇 𝜎𝑋 = 𝜎 𝑥̅ ~ normal(𝜇𝑋̅ , 𝜎𝑋̅ ) 𝜇𝑋̅ = 𝜇 𝜎𝑋̅ =
√𝑛
𝛽
𝑿 ~ exponential(𝛽) 𝜇𝑋 = 𝛽 𝜎𝑋 = 𝛽 𝑥̅ ~ normal(𝜇𝑋̅ , 𝜎𝑋̅ ) 𝜇𝑋̅ = 𝛽 𝜎𝑋̅ =
√𝑛
√𝜆
𝑿 ~ Poisson(𝜆) 𝜇𝑋 = 𝜆 𝜎𝑋 = √𝜆 𝑥̅ ~ normal(𝜇𝑋̅ , 𝜎𝑋̅ ) 𝜇𝑋̅ = 𝜆 𝜎𝑋̅ =
√𝑛
𝑘𝑚 𝑚 𝑛 𝑚+𝑛−𝑘 𝑘𝑚 𝜎𝑋
𝑿 ~ hyper.(𝑚, 𝑛, 𝑘) 𝜇𝑋 = 𝜎𝑋 = √𝑘 ( )( )( ) 𝑥̅ ~ normal(𝜇𝑋̅ , 𝜎𝑋̅ ) 𝜇𝑋̅ = 𝜎𝑋̅ =
𝑚+𝑛 𝑚+𝑛 𝑚+𝑛 𝑚+𝑛−1 𝑚+𝑛 √𝑛
Distribution of 𝑿 𝝁𝑿 𝝈𝑿 ̂
Distribution of 𝒑 𝝁𝒑̂ 𝝈𝒑̂
√𝑝(1 − 𝑝)
𝑿 ~ binomial(1, 𝑝) 𝜇𝑋 = 𝑝 𝜎𝑋 = √𝑝(1 − 𝑝) 𝑝̂ ~ normal(𝜇𝑝̂ , 𝜎𝑝̂ ) 𝜇𝑝̂ = 𝑝 𝜎𝑝̂ =
√𝑛 ∗
Note! The values of 𝝁𝑿 and 𝝈𝑿 for the binomial case are expressed here for the case when 𝒏 = 𝟏 (that is, for a Bernoulli random variable).
This cheat sheet shows these values for 𝑛 = 1 to continue to emphasize the pattern seen when we are able to apply the CLT – specifically,
when we’re considering the distribution of 𝑝̂ , its expected value and standard deviation follow the same pattern as for the distribution of
𝑥̅ . That is, the expected value of 𝑝̂ is just the expected value of a binomial random variable with 𝑛 = 1, and the standard deviation of 𝑝̂ is
the standard deviation of a binomial random variable with 𝑛 = 1 divided by √𝑛∗ , where 𝑛∗ is the number of trials in the binomial scenario
you’re working with.
© 2018 Claudia Mahler
© 2018 Claudia Mahler
You might also like
- 215 Final Exam Formula SheetDocument2 pages215 Final Exam Formula SheetH.C. Z.No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Combinatorics MCQDocument57 pagesUnit 3 Combinatorics MCQFatherNo ratings yet
- Sample Mean R.V. ̅ : Bern/binDocument1 pageSample Mean R.V. ̅ : Bern/binAmelieNo ratings yet
- Statistic FormulasDocument4 pagesStatistic FormulasBasoko_LeaksNo ratings yet
- COR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution TablesDocument2 pagesCOR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution Tables19Y6C11 MEAGAN TSENG MEI-ENNo ratings yet
- BB113 Formula SheetDocument5 pagesBB113 Formula SheetmubbaahNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet MTE23Document1 pageFormula Sheet MTE23Meera AlhefaityNo ratings yet
- CQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DDocument15 pagesCQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DAmr AlShenawyNo ratings yet
- Parametric Families of Discrete DistributionsDocument2 pagesParametric Families of Discrete DistributionsByun BaekHyunNo ratings yet
- Exam FormulaSheetDocument1 pageExam FormulaSheetmqdghsxtrmNo ratings yet
- Rumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorDocument2 pagesRumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorAhmad Nur HadieNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula Sheetfexiko9727No ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument11 pagesAnalysisNISHANK KANSARANo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument8 pagesFormula SheetLionel HectorNo ratings yet
- Statistics Help Card FullDocument6 pagesStatistics Help Card FullBarbNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerchxrlslxrrenNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasMoshiurNo ratings yet
- Topic - Chapter 7 - Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument1 pageTopic - Chapter 7 - Continuous Probability Distributions23006122No ratings yet
- Statprob NotesDocument31 pagesStatprob NotesCatherine DitanNo ratings yet
- Ex 1 Two Hinge ArchDocument3 pagesEx 1 Two Hinge ArchchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- GB Academy Equation ListDocument16 pagesGB Academy Equation ListfaysalnaeemNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Final - ExamDocument1 pageFormula Sheet For Final - ExamFlávia PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Final - ExamDocument1 pageFormula Sheet For Final - ExamIsabel EirasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. One-Sample Hypothesis Tests Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 21 Aug, 2021)Document1 pageChapter 9. One-Sample Hypothesis Tests Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 21 Aug, 2021)aaxdhpNo ratings yet
- EC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesEC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFnormanNo ratings yet
- Formulario Series de FourierDocument2 pagesFormulario Series de FourierItzan Charbel Flores BravoNo ratings yet
- Laju ReaksiDocument2 pagesLaju ReaksiIzma YulianaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFDocument7 pagesEstimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- SM Notes (Unit 1,2,3,4 & 5)Document62 pagesSM Notes (Unit 1,2,3,4 & 5)culvertsNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetNikki Jean HonaNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBADocument5 pagesHoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBAeferrentiadcapNo ratings yet
- Eda FormulasDocument2 pagesEda FormulasLee Angus SantosNo ratings yet
- Univariate and Bivariate Data Analysis + ProbabilityDocument5 pagesUnivariate and Bivariate Data Analysis + ProbabilityBasoko_Leaks100% (1)
- 1.2 Discrete-Time Random Processes: 1.2.1 Sample Spaces and EventsDocument7 pages1.2 Discrete-Time Random Processes: 1.2.1 Sample Spaces and EventsÖmer Faruk DemirNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1-2 Frequency Distribution & Central TendencyDocument7 pagesLecture-1-2 Frequency Distribution & Central TendencyNafiul Alam SnigdhoNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability Distribution.Document10 pagesContinuous Probability Distribution.Hassan El-kholy100% (1)
- Appendix - Errors and UncertaintiesDocument2 pagesAppendix - Errors and UncertaintiesstevenwuminecraftNo ratings yet
- Sample Correlation Coefficient: X Value and Is Called The Simple Regression EquationDocument1 pageSample Correlation Coefficient: X Value and Is Called The Simple Regression EquationaaxdhpNo ratings yet
- All Formulae CH # 03Document2 pagesAll Formulae CH # 03abbas ZafarNo ratings yet
- WK 4-Tut 4 Notes-Expectation-UploadDocument4 pagesWK 4-Tut 4 Notes-Expectation-UploadJennifer YoshuaraNo ratings yet
- Formulas 2 T3 AY2020-21Document9 pagesFormulas 2 T3 AY2020-21deanNo ratings yet
- 9-Normal DistributionDocument28 pages9-Normal Distributionadamoh62No ratings yet
- Stat Cheatsheet (Ver.2)Document2 pagesStat Cheatsheet (Ver.2)memeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Normal DistributionDocument17 pagesLesson 8 Normal DistributionAeon Cadiz Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Laju ReaksiDocument2 pagesLaju ReaksiIzma YulianaNo ratings yet
- EXAM FormulaSheetDocument9 pagesEXAM FormulaSheetAbood RainNo ratings yet
- Data Shetet 7th .PDF UpgreadeDocument1 pageData Shetet 7th .PDF UpgreadeAbdallah LotfyNo ratings yet
- 课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalDocument2 pages课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalluoyifei1988No ratings yet
- Financial Statistics - Formula SheetDocument26 pagesFinancial Statistics - Formula Sheetale.ili.pauNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation With Constant CoefficientsDocument1 pageHomogeneous Linear Differential Equation With Constant CoefficientstumambingaleahNo ratings yet
- Calculus Topic 9Document10 pagesCalculus Topic 9Ceejay IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformDocument14 pagesLaplace TransformJohn RedaNo ratings yet
- Example of Implicit Method To Solve PdesDocument5 pagesExample of Implicit Method To Solve PdesKhayrouMezerregNo ratings yet
- Distributions Formulas (Formula Sheet)Document2 pagesDistributions Formulas (Formula Sheet)mariammaged981No ratings yet
- Wave Function ELearn 0923Document3 pagesWave Function ELearn 0923邱頌智No ratings yet
- Formulario MTBF Calcular La Probabilidad de Falla Estadística Por: . + .Document3 pagesFormulario MTBF Calcular La Probabilidad de Falla Estadística Por: . + .Eduardo Torres PinoNo ratings yet
- Credibility, Mahler & Dean (AutoRecovered)Document4 pagesCredibility, Mahler & Dean (AutoRecovered)Selly SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Stat 101Document21 pagesStat 101marvellousokezie6No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Random Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101From EverandRandom Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101No ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics: Dr.-Ing. Erwin Sitompul President UniversityDocument15 pagesProbability and Statistics: Dr.-Ing. Erwin Sitompul President UniversityRafay QayyumNo ratings yet
- Statistics CSS SyllabusDocument4 pagesStatistics CSS SyllabusGum Nam InsanNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS ProblemsDocument5 pagesSTATISTICS ProblemsA100% (1)
- SPBA102..Quantitative and Research Methods in BusinessDocument237 pagesSPBA102..Quantitative and Research Methods in Businessharipriya100% (2)
- Chapter 6Document16 pagesChapter 6Khay OngNo ratings yet
- Midterm Codes A - B 8.4.2022Document1 pageMidterm Codes A - B 8.4.2022Vũ Tiến HiếuNo ratings yet
- Lab Project 5: The Normal Approximation To Binomial DistributionDocument4 pagesLab Project 5: The Normal Approximation To Binomial DistributionjuanNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics and ProbabilityDocument49 pagesBasic Statistics and ProbabilityVikram SKNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 SolutionsDocument1 pageQuiz 2 SolutionsBilly bobNo ratings yet
- The Binomial Distribution 1Document83 pagesThe Binomial Distribution 1Priyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 RadiationDocument36 pagesChapter 3 Radiationlilmadhu100% (1)
- HAMZADocument4 pagesHAMZASyed HamzaNo ratings yet
- 5 Probability DistributionsDocument88 pages5 Probability Distributionsnatiphbasha2015No ratings yet
- Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument52 pagesDiscrete Probability DistributionsCiel CelizNo ratings yet
- BI348 Chapter11 Video65 CreatingRandomVariablesDocument106 pagesBI348 Chapter11 Video65 CreatingRandomVariableslazarpaladinNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument5 pagesBinomial DistributionGopalsamy SelvaduraiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biostatistics 8th Edition Rosner Solutions ManualDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Biostatistics 8th Edition Rosner Solutions Manualshanerussellqe03lw100% (17)
- Binomial Normal DistributionDocument47 pagesBinomial Normal DistributionGopal GuptaNo ratings yet
- B Sc-Maths PDFDocument34 pagesB Sc-Maths PDFNunna MaheshbabuNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Problem Set 1Document13 pagesSolutions To Problem Set 1Vinícius FernandoNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Discrete Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument59 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: Discrete Random Variables and Probability Distributionsfour threepioNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument8 pagesProbabilityNorbert LimNo ratings yet
- Sharon Lawner Weinberg Daphna Harel Sarah Knapp AbramowitzDocument696 pagesSharon Lawner Weinberg Daphna Harel Sarah Knapp AbramowitzNicole HartNo ratings yet
- Summary Statistics For BRM Pre MSC All Chapters For The ExamDocument44 pagesSummary Statistics For BRM Pre MSC All Chapters For The Examemmanuel emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument33 pagesLecture 8 - Continuous Probability DistributionsIsmadth2918388No ratings yet
- Double-Sampling Control Charts For AttributesDocument6 pagesDouble-Sampling Control Charts For AttributesIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Elementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Test BankDocument13 pagesElementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Test Bankjosephwisemrfisbtdcz100% (30)
- Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability DistributionsDocument115 pagesDiscrete Random Variables and Their Probability DistributionsJrNo ratings yet
- ICT114 Mathematics For Computing: Queueing Theory Algorithms and FlowchartsDocument56 pagesICT114 Mathematics For Computing: Queueing Theory Algorithms and FlowchartsDanny MannoNo ratings yet