Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer
Uploaded by
chxrlslxrren0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThis document contains formulas for:
1) Calculating probabilities, means, variances, and standard deviations for probability distributions and sampling distributions.
2) Converting between random variables, standard scores, and z-scores.
3) Calculating population and sample characteristics like means, variances, standard deviations, and determining sample size for confidence intervals.
Original Description:
g11
Original Title
reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains formulas for:
1) Calculating probabilities, means, variances, and standard deviations for probability distributions and sampling distributions.
2) Converting between random variables, standard scores, and z-scores.
3) Calculating population and sample characteristics like means, variances, standard deviations, and determining sample size for confidence intervals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageReviewer
Uploaded by
chxrlslxrrenThis document contains formulas for:
1) Calculating probabilities, means, variances, and standard deviations for probability distributions and sampling distributions.
2) Converting between random variables, standard scores, and z-scores.
3) Calculating population and sample characteristics like means, variances, standard deviations, and determining sample size for confidence intervals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
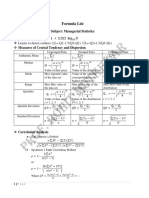
FORMULAS
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑠 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡 Variance of the sampling distribution of the
𝑃(𝐸) =
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑠 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 𝑠𝑝𝑎𝑐𝑒 sample means (with replacement)
Mean of the Probability Distribution ̅ ) ∙ (𝑋
𝜎2𝑥̅ = ∑[ 𝑃(𝑋 ̅ − 𝜇)2 ]
𝜇 = 𝐸(𝑋) = ∑(𝑋 ∙ 𝑃(𝑋)) Mean of the sampling distribution of the sample
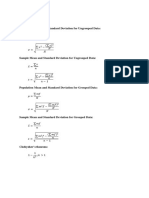
mean (without replacement)
Variance of the Probability Distribution
∑𝑋̅
𝜇𝑥̅ =
𝝈𝟐 = ∑[𝑿𝟐 ∙ 𝑷(𝑿)] − 𝝁𝟐 𝑛
Variance of the sampling distribution of the
Standard Deviation of the Probability Distribution
sample mean (without replacement)
𝝈 = √∑[𝑿𝟐 ∙ 𝑷(𝑿)] − 𝝁𝟐 ̅ − 𝜇𝑥̅ )2
∑(𝑋
𝜎𝑥̅2 =
𝑛
Converting a random variable x to a standard
normal variable z OR dealing with data from Standard Deviation of the sampling distribution
parameters of the sample mean (without replacement)
𝑥−𝜇
𝑧= ∑(𝑋̅ − 𝜇𝑥̅ )2
𝜎 𝜎𝑥̅ = √
𝑛
Converting standard normal variable z to
random variable x Convert the raw score to the standard score in
central limit OR dealing with data from sample
𝑥 = 𝑧𝜎 + 𝜇 mean
POPULATION MEAN 𝑥̅ − 𝜇
𝑧= 𝜎
∑𝑥
𝜇= √𝑛
𝑁
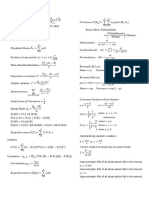
Lower limit : 𝐿𝐿 = 𝑋̅ − 𝐸
POPULATION VARIANCE
Upper limit: 𝑈𝐿 = 𝑋̅ + 𝐸
2
∑(𝑥 − 𝜇)2
𝜎 = 𝜎
𝑁 Margin of error: 𝐸 = 𝑍𝛼 ∙
2 √𝑛
POPULATION STANDARD DEVIATION
Length Of Confidence Interval:
∑(𝑥 − 𝜇)2 L = UL – LL 𝑜𝑟 𝐿 = 2𝐸
𝜎=√
𝑁
Determining Sample Size
SAMPLE MEAN
𝑧𝛼 𝜎 2
2
∑𝑥 𝑛=( )
𝑥̄ = 𝐸
𝑛
SAMPLE VARIANCE
∑(𝑥 − 𝑥̄ )2
𝑠2 =
𝑛−1
SAMPLE STANDARD DEVIATION
∑(𝑥 − 𝑥̄ )2
𝑠=√
𝑛−1
Combination of N (population size) objects
taken n (sample size) at a time.
𝑁!
𝐶
𝑁 𝑛
=
[𝑛! (𝑁 − 𝑛)!]
Mean of the sampling distribution of the sample
means. (with replacement)
𝜇𝑥̅ = ∑[𝑋̅ ∙ 𝑃(𝑋̅ )]
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- BB113 Formula SheetDocument5 pagesBB113 Formula SheetmubbaahNo ratings yet
- Random Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101From EverandRandom Fourier Series with Applications to Harmonic Analysis. (AM-101), Volume 101No ratings yet
- COR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution TablesDocument2 pagesCOR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution Tables19Y6C11 MEAGAN TSENG MEI-ENNo ratings yet
- 215 Final Exam Formula SheetDocument2 pages215 Final Exam Formula SheetH.C. Z.No ratings yet
- List of Formula - Managerial StatisticsDocument6 pagesList of Formula - Managerial Statisticsmahendra pratap singhNo ratings yet
- Exam FormulaSheetDocument1 pageExam FormulaSheetmqdghsxtrmNo ratings yet
- GB Academy Equation ListDocument16 pagesGB Academy Equation ListfaysalnaeemNo ratings yet
- CQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DDocument15 pagesCQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DAmr AlShenawyNo ratings yet
- Statprob NotesDocument31 pagesStatprob NotesCatherine DitanNo ratings yet
- QBM101 FormulasDocument4 pagesQBM101 FormulasDeveshNo ratings yet
- Mech 430 Final Formula Sheet UpdatedDocument12 pagesMech 430 Final Formula Sheet UpdatedSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Course Reference Sheet - Revision 2Document6 pagesCourse Reference Sheet - Revision 2mattbutler1401No ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasMoshiurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. One-Sample Hypothesis Tests Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 21 Aug, 2021)Document1 pageChapter 9. One-Sample Hypothesis Tests Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 21 Aug, 2021)aaxdhpNo ratings yet
- Statistic FormulasDocument4 pagesStatistic FormulasBasoko_LeaksNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - CSE - 381 PDFDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet - CSE - 381 PDFYasmine A. SabryNo ratings yet
- Stat Cheatsheet (Ver.2)Document2 pagesStat Cheatsheet (Ver.2)memeNo ratings yet
- Formula Help SheetDocument6 pagesFormula Help Sheetleah.efnNo ratings yet
- Univariate and Bivariate Data Analysis + ProbabilityDocument5 pagesUnivariate and Bivariate Data Analysis + ProbabilityBasoko_Leaks100% (1)
- Formula SheetDocument8 pagesFormula SheetLionel HectorNo ratings yet
- EC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesEC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFnormanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document13 pagesLecture 10YashikaNo ratings yet
- Mostly Harmless Statistics Formula Packet: Chapter 3 FormulasDocument10 pagesMostly Harmless Statistics Formula Packet: Chapter 3 FormulaskayNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics Cheat Sheet?Document7 pagesBusiness Statistics Cheat Sheet?Govind TrivediNo ratings yet
- STATISTICSDocument1 pageSTATISTICSCedrique PobreNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFDocument7 pagesEstimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- Formula StatistikDocument2 pagesFormula StatistikIkmal FaizienNo ratings yet
- Exam P Formula Sheet PDFDocument9 pagesExam P Formula Sheet PDFQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Standard Normal Distribution Critical Values, ZDocument3 pagesStandard Normal Distribution Critical Values, Zlbeard501No ratings yet
- Statistic PartCDocument12 pagesStatistic PartCAnkit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- EDA - FormulaDocument2 pagesEDA - FormulaLyka Mae MancolNo ratings yet
- SPFA01 6+Formula+SheetDocument3 pagesSPFA01 6+Formula+Sheettf9wgz2ysdNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Hypothesis TestingDocument6 pagesUnit 5: Hypothesis TestingKamlesh PariharNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula Sheetfexiko9727No ratings yet
- Measures of Location and Spread 2Document30 pagesMeasures of Location and Spread 2teeformeeNo ratings yet
- Sample Mean R.V. ̅ : Bern/binDocument1 pageSample Mean R.V. ̅ : Bern/binAmelieNo ratings yet
- All Formulae CH # 03Document2 pagesAll Formulae CH # 03abbas ZafarNo ratings yet
- List of Formula For Unit-3 and Unit-4Document7 pagesList of Formula For Unit-3 and Unit-4Hitika TeckaniNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBADocument5 pagesHoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBAeferrentiadcapNo ratings yet
- 课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalDocument2 pages课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalluoyifei1988No ratings yet
- Formulas 2 T3 AY2020-21Document9 pagesFormulas 2 T3 AY2020-21deanNo ratings yet
- Material To Lecture 2: Unit 5. Measures of Variation. Shape of Distribution Unit 6. Sample MethodDocument5 pagesMaterial To Lecture 2: Unit 5. Measures of Variation. Shape of Distribution Unit 6. Sample MethodДанила ДенисовNo ratings yet
- Formulas For The Final ExamDocument2 pagesFormulas For The Final ExamSebastian MercaderNo ratings yet
- FormulaSheet Test 1Document6 pagesFormulaSheet Test 1bestreview7No ratings yet
- Application of Partial Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesApplication of Partial Differential EquationsventhiiNo ratings yet
- CAT 2 Study Materials MAT 2001 PDFDocument12 pagesCAT 2 Study Materials MAT 2001 PDFsashidhar avuthuNo ratings yet
- Appendix - Errors and UncertaintiesDocument2 pagesAppendix - Errors and UncertaintiesstevenwuminecraftNo ratings yet
- CLT Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCLT Cheat SheetAli BissenovNo ratings yet
- 14 EDC Syed Irfan AliDocument9 pages14 EDC Syed Irfan AliRio YuwandiNo ratings yet
- Data Science Formula - Very ImpDocument6 pagesData Science Formula - Very Impcoloringcraft318No ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument11 pagesAnalysisNISHANK KANSARANo ratings yet
- Statistical InferenceDocument82 pagesStatistical InferenceSyed Umar Hayat Shirazi Al-HashmiNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference 2 Note 02Document7 pagesStatistical Inference 2 Note 02ElelanNo ratings yet
- Financial Statistics - Formula SheetDocument26 pagesFinancial Statistics - Formula Sheetale.ili.pauNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetNikki Jean HonaNo ratings yet
- Stat 115 FormulaDocument2 pagesStat 115 FormulaChisei MeadowNo ratings yet
- Formula of Chapter 1 - 5 (Statistics & Probability)Document5 pagesFormula of Chapter 1 - 5 (Statistics & Probability)adrian kwokNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression Formula Class 12Document2 pagesLinear Regression Formula Class 12surajsrivastavliluahNo ratings yet
- Cqe Sample ExamDocument17 pagesCqe Sample ExamnewdaoNo ratings yet
- Cpa f1.1 - Business Mathematics & Quantitative Methods - Study ManualDocument573 pagesCpa f1.1 - Business Mathematics & Quantitative Methods - Study ManualMarcellin MarcaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability PresentationDocument10 pagesStatistics and Probability PresentationJustine MactalNo ratings yet
- Deterministic PDFDocument8 pagesDeterministic PDFNigus AbebeNo ratings yet
- Erlang PDF GenerationDocument2 pagesErlang PDF GenerationChristopherNo ratings yet
- Catatan Statisktik FIXDocument59 pagesCatatan Statisktik FIXAndrian WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Event History and Survival Analysis - v3Document35 pagesEvent History and Survival Analysis - v3TommyyoNo ratings yet
- FE - Engineering Probability and StatisticsDocument22 pagesFE - Engineering Probability and StatisticsJuba W AllenNo ratings yet
- ch5 PDFDocument24 pagesch5 PDFcharu.iitdNo ratings yet
- Bus172-PracticeMid2 - With AnswerDocument3 pagesBus172-PracticeMid2 - With Answerprachee hossainNo ratings yet
- rr220105 Probability and StatisticsDocument10 pagesrr220105 Probability and StatisticsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 6592 - A1 QuestionsDocument14 pages6592 - A1 QuestionsYuhan KENo ratings yet
- Def Stan 00-970 Part 7-2Document159 pagesDef Stan 00-970 Part 7-2rokhgireh_hojjatNo ratings yet
- Random VariablesDocument7 pagesRandom VariablesHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- StatDocument16 pagesStatmariancantalNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression AnalysisDocument2 pagesCorrelation and Regression AnalysisKeshav karkiNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions: Prem Mann, Introductory Statistics, 9/EDocument110 pagesSampling Distributions: Prem Mann, Introductory Statistics, 9/EAfrin NaharNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Grade 11 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Grade 11 Statistics and ProbabilityLee C. Soriano100% (7)
- SFB Module I 2019Document37 pagesSFB Module I 2019Ashwani SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4.85 Actuarial ScienceDocument9 pages4.85 Actuarial Scienceratchagar aNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics 11th Edition Anderson Test BankDocument24 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics 11th Edition Anderson Test Bankjamesrichardxegfocajmd100% (13)
- 100% QM SourceDocument205 pages100% QM Sourcemoncarla lagonNo ratings yet
- R7220101-Probability & StatisticsDocument1 pageR7220101-Probability & StatisticslrploveNo ratings yet
- Random Variables PDFDocument64 pagesRandom Variables PDFdeelipNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and Random Processes: AppendixDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Probability and Random Processes: AppendixRajesh BathijaNo ratings yet
- Engr 0020 Exam 1 EquationsDocument2 pagesEngr 0020 Exam 1 EquationsZoeNo ratings yet
- CAMSHIFT Tracking Algorithm: CSE/EE 486: Computer Vision I Computer Project Report #: Project 5Document7 pagesCAMSHIFT Tracking Algorithm: CSE/EE 486: Computer Vision I Computer Project Report #: Project 5Engr EbiNo ratings yet
- ECON 2P91: Assignment #1Document7 pagesECON 2P91: Assignment #1Joel Christian MascariñaNo ratings yet
- Christian Heumann, Michael Schomaker Shalabh-Introduction To Statistics and Data Analysis With Exercises, Solutions and Applications in R-Springer (2017)Document453 pagesChristian Heumann, Michael Schomaker Shalabh-Introduction To Statistics and Data Analysis With Exercises, Solutions and Applications in R-Springer (2017)Marcelo Batelochi100% (3)
- Calculating Sample Size To Estimate, With Specified Precision, The Average For A Characteristic of A Lot or ProcessDocument5 pagesCalculating Sample Size To Estimate, With Specified Precision, The Average For A Characteristic of A Lot or ProcessRed RedNo ratings yet
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusFrom EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryFrom EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo ratings yet