Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pas 12
Uploaded by
Sacedon, Trishia Mae C.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pas 12
Uploaded by
Sacedon, Trishia Mae C.Copyright:
Available Formats
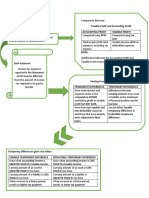
PAS 12 – ACCOUNTING FOR INCOME • the carrying amount of a liability is
TAXES lower than its tax base (CAL < TBA)
Note: Tax base is the amount attributable to
the asset or liability for tax purposes
Accounting Income – is the net income
before deducting income tax expense. Recognition of Deferred Tax Liability
Taxable Income – income for the period Shall be recognized for all taxable
determined in accordance with the rules temporary differences
established by the taxation authorities upon
Exception: When taxable temporary
which income taxes are payable or
differences arises from:
recoverable.
• goodwill resulting from business
combination and which is non-
Permanent Differences deductible for tax purposes
• initial recognition of an asset or
• items of revenue and expenses which
liability in a transaction that is not a
are included in either in accounting
business combination and affects
income or taxable income but will
neither accounting income nor
never be included in the other
taxable income
• pertain to non-deductible expenses
• undistributed profit of subsidiary,
and non-taxable revenue
associate or joint venture when:
• do not give rise to either deferred tax
- the parent, investor or venturer is
asset or liability
able to control the timing of the
Temporary Differences reversal of the temporary
difference
• differences between the carrying
- it is probable that the temporary
amount of an asset or liability and its
difference will not reverse in the
tax base
foreseeable future
• include timing differences
• give rise to either deferred tax asset Temporary differences that technically are
or liability not timing differences but nevertheless give
rise to deferred tax liability:
Timing Differences
• asset is revalued upward and no
• differences between accounting
equivalent adjustment is made for tax
income and taxable income that
purposes
originate in one period and reverse in
• the carrying amount of investment in
one or more subsequent periods
subsidiary, associate or joint venture
is higher than its tax base because
the subsidiary, associate or joint
Taxable Temporary Difference
venture has not distributed its entire
• temporary difference that will result income to the parent or investor
in future TAXABLE amount in • the cost of a business combination
determining taxable income of future that is accounted for as an
periods when the carrying amount of acquisition is allocated to the
the asset or liability is recovered or identifiable assets and liabilities
settled acquired at fair value and no
equivalent adjustment is made for tax
Deferred Tax Liability is the amount of
purposes
income tax payable in future periods with
respect to a taxable temporary difference.
Deferred tax liability arises from the Deductible Temporary Difference
following:
• temporary difference that will result
• the accounting income is higher than in future DEDUCTIBLE amount in
the taxable income because of timing determining taxable income of future
differences (AI > TI) periods when the carrying amount of
• the carrying amount of an asset is the asset or liability is recovered or
higher than its tax base (CAA > TBA) settled
Deferred Tax Asset is the amount of income Presentation of Deferred Tax Liability and
tax recoverable in future periods with Deferred Tax Asset
respect to deductible temporary difference
Presentation in the Statement of Financial
and operating loss carry forward.
Position
Deferred tax asset arises from the
• Deferred tax assets and deferred tax
following:
liabilities are presented separately as
• the taxable income is higher than the noncurrent assets and noncurrent
accounting income because of timing liabilities, respectively.
differences (TI > AI)
Presentation in the Statement of
• the tax base of an asset is higher than
Comprehensive Income
its carrying amount (TBA > CAA)
• the tax base of a liability is lower than • Current and deferred taxes are
its carrying amount (TBA < CAL) usually recognized in profit or loss.
Recognition of Deferred Tax Asset
Shall be recognized for all deductible Tax consequences are accounted for in the
temporary differences and operating loss same way as the related transactions or
carry forward when it is probable that events. Thus, if a transaction is recognized
taxable income will be available against in profit or loss, its tax effect is also
which the deferred tax asset can be used recognized in profit or loss. If a transaction
is recognized outside profit or loss, the tax
Temporary differences that technically are
effect is also recognized outside profit or
not timing differences but nevertheless give
loss (e.g., in other comprehensive income
rise to deferred tax asset:
or directly in equity).
• asset is revalued downward and no
Taxes recognized in other comprehensive
equivalent adjustment is made for tax
income:
purposes
• the tax base of an investment in • Revaluation of property, plant and
subsidiary, associate or joint venture equipment.
is higher than its carrying amount • Exchange differences arising on the
because the subsidiary, associate or translation of the financial
joint venture has suffered continuing statements of a foreign corporation.
losses in the current and prior years
Taxes recognized directly in equity:
• financial asset is carried at fair value
which is less than cost but no • Adjustment to the opening balance of
equivalent adjustment is made for tax retained earnings resulting from a
purposes change in accounting policy or
correction of a prior-period error.
• Amounts arising on initial recognition
Measurement of Income Tax Expense of the equity component of a
compound financial instrument.
Current Tax Liability And Current Tax Asset
• measured using the tax rate that has
been enacted and effective at the end Accounting for Current Taxes
of the reporting
An entity uses relevant tax laws in
Deferred Tax Liability And Deferred Tax computing for its current taxes. Unpaid
Asset current taxes are recognized as current tax
liability, e.g., income tax payable. Excess
• measured using the tax rate that has
tax payments over the current tax due are
been enacted by the end of the
recognized as current tax asset, e.g.,
reporting period and expected to
prepaid income tax.
apply to the period when the asset is
realized or the liability is settled
Income Tax Expense = Current Tax Expense
+ Deferred Tax Expense
You might also like
- Pas 12 Income TaxesDocument4 pagesPas 12 Income TaxesFabrienne Kate Eugenio Liberato100% (1)
- Ia2 16 Accounting For Income TaxDocument55 pagesIa2 16 Accounting For Income TaxJoyce Anne Garduque100% (1)
- Deferred TaxDocument16 pagesDeferred TaxErick NuescaNo ratings yet
- Accounting FinalsDocument10 pagesAccounting FinalsrixaNo ratings yet
- Punjab Chemicals - Apr 2014Document20 pagesPunjab Chemicals - Apr 2014Duby Rex100% (1)
- IAS 12 - Income TaxesDocument1 pageIAS 12 - Income TaxesFeras ShreimNo ratings yet
- Factsheet IAS12 Income TaxesDocument14 pagesFactsheet IAS12 Income TaxesMira EbreoNo ratings yet
- Cfas - FinalsDocument9 pagesCfas - FinalsawitakintoNo ratings yet
- Ias 12Document5 pagesIas 12Ahmed NiazNo ratings yet
- Pas 12Document5 pagesPas 12elle friasNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at A Glance: IAS 12 Income TaxesDocument4 pagesIfrs at A Glance: IAS 12 Income Taxeslina_siscanu6356No ratings yet
- Income Tax: Cabria Cpa Review CenterDocument4 pagesIncome Tax: Cabria Cpa Review CenterMaeNo ratings yet
- 34 Accounting For Income Tax Intermediate Accounting 2 - CompressDocument4 pages34 Accounting For Income Tax Intermediate Accounting 2 - CompressKIMBERLY BEZARNo ratings yet
- Income Taxes Lang HehezDocument8 pagesIncome Taxes Lang HehezDiana Rose BassigNo ratings yet
- Ias 12Document2 pagesIas 12Philemon FatunbiNo ratings yet
- Far.119 Income TaxDocument4 pagesFar.119 Income Taxjhon tupagNo ratings yet
- PAS 12 INCOME TAXES Cont With ProbsDocument8 pagesPAS 12 INCOME TAXES Cont With ProbsFabrienne Kate Eugenio Liberato100% (1)
- Pas 12Document2 pagesPas 12JennicaBailonNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On IAS 12 - Income TaxesDocument2 pagesConcept Map On IAS 12 - Income TaxesRey OnateNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 12Document37 pagesInd AS 12Amal P TomyNo ratings yet
- Classroom Notes 6382Document2 pagesClassroom Notes 6382THRISHIA ANN SOLIVANo ratings yet
- ToA 10 Income Tax StudentDocument4 pagesToA 10 Income Tax Studentlana del reyNo ratings yet
- Bdo Ias 12Document1 pageBdo Ias 12thamsanqamanciNo ratings yet
- Income Taxes (IAS 12)Document15 pagesIncome Taxes (IAS 12)Mahir RahmanNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument12 pagesAccounting For Income Taxglrosaaa cNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Accounting For Other LiabilitiesDocument21 pagesChapter 4 - Accounting For Other Liabilitiesjeanette lampitoc0% (1)
- Income Taxes Far Reviwer NotesDocument15 pagesIncome Taxes Far Reviwer Notesabb.reviewersNo ratings yet
- Ia2 16 Accounting For Income TaxDocument57 pagesIa2 16 Accounting For Income TaxLawrence NarvaezNo ratings yet
- IAS 12 Income TaxDocument43 pagesIAS 12 Income TaxMinal BihaniNo ratings yet
- 16-Acctg For Income TaxDocument56 pages16-Acctg For Income TaxCherry MirabuenoNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument6 pagesAccounting For Income TaxGirl Lang AkoNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument4 pagesAccounting For Income TaxMjhayeNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Taxes On IncomeDocument69 pagesAccounting For Taxes On Incomesơn hảiNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - Income TaxDocument6 pagesModule 10 - Income TaxLuiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument23 pagesAccounting For Income TaxMelissa Jane ViveroNo ratings yet
- Accounting For ItDocument7 pagesAccounting For ItAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Pas 12 Income TaxesDocument3 pagesPas 12 Income TaxesR.A.No ratings yet
- Income TaxDocument13 pagesIncome TaxMohammad AnikNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Cebu Cpar Center Inc. Unit 103, MGA Arcade, A.C. Cortes Ave., Mandaue CityDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Cebu Cpar Center Inc. Unit 103, MGA Arcade, A.C. Cortes Ave., Mandaue CityNhel AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Ind As 12: Income Taxes: Current Tax Temporary Difference: TaxableDocument2 pagesInd As 12: Income Taxes: Current Tax Temporary Difference: Taxablechandrakumar k pNo ratings yet
- Income Tax: Full PFRS, Prfs For Smes & Pfrs For SesDocument15 pagesIncome Tax: Full PFRS, Prfs For Smes & Pfrs For SesChara etangNo ratings yet
- 1 Income TaxesDocument95 pages1 Income TaxesJoven LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Tax: Technical KnowledgeDocument45 pagesAccounting For Income Tax: Technical KnowledgeCharlene de LaraNo ratings yet
- 11 Income-Tax Lecture-NotesDocument6 pages11 Income-Tax Lecture-NotesandreamrieNo ratings yet
- 201.04 Accounting For Income Taxes (IAS-12)Document16 pages201.04 Accounting For Income Taxes (IAS-12)Biplob K. SannyasiNo ratings yet
- Luspe - AC54 - Unit IX - Summary NotesDocument4 pagesLuspe - AC54 - Unit IX - Summary NotesEDMARK LUSPENo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Taxes: June 6, 2020Document18 pagesAccounting For Income Taxes: June 6, 2020Andrea Marie CalmaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Tax: Technical KnowledgeDocument42 pagesAccounting For Income Tax: Technical KnowledgeAngela Miles DizonNo ratings yet
- Advanced Financial ch1Document13 pagesAdvanced Financial ch1bikilahussenNo ratings yet
- CH16 Accounting For Income TaxDocument5 pagesCH16 Accounting For Income Taxeyayaya blablablaNo ratings yet
- 15.515 Financial Accounting Preliminary Final ReviewDocument21 pages15.515 Financial Accounting Preliminary Final ReviewAnant AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PAS 12 Income TaxesDocument12 pagesPAS 12 Income Taxeshjihjbj,iljNo ratings yet
- Income TaxesDocument11 pagesIncome TaxesamNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Accounting: Interacctgii BSA22A1 Online ModuleDocument17 pagesIncome Tax Accounting: Interacctgii BSA22A1 Online Module11 LamenNo ratings yet
- Income TaxesDocument10 pagesIncome TaxesLohraine DyNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting - Advanced - Deferred Tax - Where To Recognise Deferred Tax AdjustmentsDocument7 pagesFinancial Reporting - Advanced - Deferred Tax - Where To Recognise Deferred Tax AdjustmentsTami ChitandaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledGayathri DhandapaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - IAS 12Document54 pagesChapter 13 - IAS 12Bahader AliNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document20 pagesTopic 4Ollid Kline Jayson JNo ratings yet
- HO1 - Accounting For Income TaxDocument5 pagesHO1 - Accounting For Income TaxCharlesNo ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting Period: Pas 10, Pas 12, and Pas 16 ObjectiveDocument5 pagesEvents After The Reporting Period: Pas 10, Pas 12, and Pas 16 ObjectiveMica DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- List SurnamesDocument1 pageList SurnamesSacedon, Trishia Mae C.No ratings yet
- FAMISANDocument4 pagesFAMISANSacedon, Trishia Mae C.No ratings yet
- Artist and ArtisanDocument7 pagesArtist and ArtisanSacedon, Trishia Mae C.No ratings yet
- Pas 8Document3 pagesPas 8Sacedon, Trishia Mae C.No ratings yet
- Panasonic1 DamanDocument7 pagesPanasonic1 DamanTarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Chap 13Document18 pagesChap 13N.S.RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Digital India in Agriculture SiddhanthMurdeshwar NMIMS MumbaiDocument4 pagesDigital India in Agriculture SiddhanthMurdeshwar NMIMS MumbaisiddhanthNo ratings yet
- O&M Module PDF File-1Document177 pagesO&M Module PDF File-1Strewbary BarquioNo ratings yet
- Assignment III - Descriptive QuestionsDocument2 pagesAssignment III - Descriptive QuestionsAndroid AccountNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Operating Management BesDocument5 pagesLesson 6 Operating Management BesMich ValenciaNo ratings yet
- ECON20063 TemplateDocument6 pagesECON20063 TemplateKristel LacaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Depreciation, Impairments and DepletionDocument24 pagesChapter 11: Depreciation, Impairments and DepletionRahat KhanNo ratings yet
- Business Cycles (BBA BI)Document19 pagesBusiness Cycles (BBA BI)Yograj PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Guidance Note On Accoounting For LeasesDocument22 pagesGuidance Note On Accoounting For LeasesANUSHA DAVENo ratings yet
- Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino ProgramDocument3 pagesPantawid Pamilyang Pilipino ProgramGercel Therese SerafinoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Results Analysis For WIP: Introduction and Configuration GuideDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Results Analysis For WIP: Introduction and Configuration GuidegildlreiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Managers-Unit-1Document21 pagesAccounting For Managers-Unit-1VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Scarcity, Opportunity Costs, and Production Possibilities CurvesDocument14 pagesScarcity, Opportunity Costs, and Production Possibilities CurvesAhmad Mahmuz ArroziNo ratings yet
- Coffee Shop Business Plan TemplateDocument12 pagesCoffee Shop Business Plan TemplateLanurias, Gabriel Dylan S.No ratings yet
- Value Added Tax PracticeDocument7 pagesValue Added Tax PracticeSelene DimlaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Internal Audit Plan For The CrewDocument4 pages2023 Internal Audit Plan For The CrewLateef LasisiNo ratings yet
- Growth, Poverty, and Income Distribution PovertyDocument6 pagesGrowth, Poverty, and Income Distribution PovertyMija DiroNo ratings yet
- Institute of Business Management and Research, Ips Academy, Indore Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesInstitute of Business Management and Research, Ips Academy, Indore Lesson PlanSushma IssacNo ratings yet
- 33 Money LessonsDocument37 pages33 Money Lessonsraj100% (3)
- Activity Based CostingDocument8 pagesActivity Based CostingAli AhmiiNo ratings yet
- Getting Paid Math 2.3.9.A1 PDFDocument3 pagesGetting Paid Math 2.3.9.A1 PDFLyndsey BridgersNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Ijcem 20180701 01Document21 pages10 5923 J Ijcem 20180701 01Atul SethNo ratings yet
- TNCT FragmentationDocument12 pagesTNCT FragmentationEdna CatubiganNo ratings yet
- The Ethical and Social Responsibilities of The Entrepreneur: Reported By: Berceles, Manuel, Toledo, VillanuevaDocument3 pagesThe Ethical and Social Responsibilities of The Entrepreneur: Reported By: Berceles, Manuel, Toledo, VillanuevaJojenNo ratings yet
- Tax 102 Prelim ExamDocument5 pagesTax 102 Prelim ExamDonna TumalaNo ratings yet
- Electronic PaymentDocument8 pagesElectronic Paymentqa diiNo ratings yet
- ACT450 - Fa20 - Project Deliverable PDFDocument10 pagesACT450 - Fa20 - Project Deliverable PDFHassan SheikhNo ratings yet