Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preface
Uploaded by
Alejandro ZagalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Preface
Uploaded by
Alejandro ZagalCopyright:
Available Formats
PREFACE
This is the third electronic edition of the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. In terms
of content, it follows the 81st Edition of the print Handbook, the first to be published in the
new millennium, and contains several updated and expanded tables:
- Fundamental Physical Constants (the new set of CODATA recommended values,
replacing the 1986 set)
- The Elements (descriptive texts on the occurrence, properties, history, and uses of all the
chemical elements)
- Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases (expanded by 50%)
- Dipole Moments (revised and expanded)
- Threshold Limits for Airborne Contaminants (including the most recent
recommendations)
Among the new topics covered in this edition are:
- Properties of Liquid Helium
- Electrical Conductivity of Water as a Function of Temperature and Pressure
- Bond Lengths in Organometallic Compounds
- Organic Magnets
- Pressure-Volume-Temperature Relationship for Polymer Melts
- Characteristics of Human Hearing
The Editor will appreciate suggestions on new topics for the Handbook and notification of
any errors. Address all comments to Editor, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC
Press, Inc., 2000 Corporate Blvd. N. W., Boca Raton, FL 33431. Comments may also be
sent by electronic mail to drlide@post.harvard.edu.
David R. Lide
Editor-
Editor-in-
in-Chief
May 1, 2000
This Edition is Dedicated to my Wife, Bettijoyce Breen Lide
Note on the Ordering of Chemical Compounds:
Compounds Most of the interactive tables are
ordered alphabetically by the adopted name of the substance (usually an IUPAC systematic
name). These tables can be sorted by molecular formula, common formula (for inorganic
compounds), or CAS Registry Number if desired. The text (pdf) displays follow the order
in the print version, which in most cases is by molecular formula in a modified Hill order.
In the Hill convention the molecular formula is written with C first, H second, and then all
© 2000 by CRC PRESS LLC
other elements in alphabetical order of their chemical symbols. The sequence of entries is
determined by the alphabetical order of elements in the molecular formula and the number
of atoms of each element, in ascending order, e.g., C3H7Cl, C3H7N, C3H7NO, C3H7NO2, etc.
In tables that include non-carbon compounds, all of those are listed first, followed by a
separate listing of compounds that do contain carbon. This is in contrast to the strict Hill
convention as followed by Chemical Abstracts Service, where the molecular formulas
beginning with A and B precede the formulas for carbon-containing compounds, while
those beginning with D... Z follow.
This work contains information obtained from authentic and highly regarded sources.
Reprinted material is quoted with permission, and sources are indicated. A wide
variety of references are listed. Reasonable efforts have been made
made to publish reliable
data and information, but the author and the publisher cannot accept responsibility
for the validity of all materials or for the consequences of their use.
© 2000 by CRC PRESS LLC
You might also like
- Comprehensive Organic Synthesis - Volume 4 (1991)Document1,293 pagesComprehensive Organic Synthesis - Volume 4 (1991)Sam West88% (8)
- Screening Test NEET/JEE FOUNATION AT KOTTAYAMDocument15 pagesScreening Test NEET/JEE FOUNATION AT KOTTAYAMfelixjamesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQs PPSCDocument92 pagesChemistry MCQs PPSCMuhammad Zain Kaleem100% (1)
- Handbook of Vapor Pressure: Volume 4: Inorganic Compounds and ElementsFrom EverandHandbook of Vapor Pressure: Volume 4: Inorganic Compounds and ElementsNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Functional Group ChemistryDocument176 pagesFunctional Group Chemistrylinhmung92% (13)
- US Navy NEETS - NAVEDTRA 14179 Module 07 Introduction To Solid-State Devices and Power SuppliesDocument287 pagesUS Navy NEETS - NAVEDTRA 14179 Module 07 Introduction To Solid-State Devices and Power SuppliesGeorges100% (2)
- Milne, George W. A - CRC Handbook of Pesticides-CRC Press (1995)Document411 pagesMilne, George W. A - CRC Handbook of Pesticides-CRC Press (1995)MillenaChristieNo ratings yet
- DP Chem Unit 1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsDocument6 pagesDP Chem Unit 1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Carl L. Yaws-Handbook of Thermodynamic Diagrams, Volume 1 - Organic Compounds C1 To C4 (Library of Physico-Chemical Property Data) (1996)Document366 pagesCarl L. Yaws-Handbook of Thermodynamic Diagrams, Volume 1 - Organic Compounds C1 To C4 (Library of Physico-Chemical Property Data) (1996)astriany50% (2)
- Naming CompoundsDocument60 pagesNaming CompoundsLorilieNo ratings yet
- Oxygenates in GasolineDocument303 pagesOxygenates in GasolinePhilip ShihNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, & MixturesDocument72 pagesElements, Compounds, & MixturesWendz ArominNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Hazardous Chemical PropertiesFrom EverandHandbook of Hazardous Chemical PropertiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- General Chemistry 1 Qt. 2 Week 5Document31 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Qt. 2 Week 5Nina Reca OmisolNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Inorganic Substances-De Gruyter (2018)Document1,817 pagesHandbook of Inorganic Substances-De Gruyter (2018)Samyak DholeNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 1: Organic Compounds C1 to C4From EverandHandbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 1: Organic Compounds C1 to C4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Richard M. Stephenson, Stanislaw Malanowski (Auth.) - Handbook of The Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds-Springer Netherlands (1987)Document560 pagesRichard M. Stephenson, Stanislaw Malanowski (Auth.) - Handbook of The Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds-Springer Netherlands (1987)Andina Indah SekararumNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 2: Organic Compounds C5 to C7From EverandHandbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 2: Organic Compounds C5 to C7No ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds PDFDocument17 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compounds PDFMuhammad Arshad0% (1)
- Organic NomenclatureDocument20 pagesOrganic NomenclatureJavier SolisNo ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature - WikipediaDocument11 pagesChemical Nomenclature - WikipediaJamella Jael Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios NomenclaturaDocument20 pagesEjercicios NomenclaturaJovenarellanoNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature: Blue Book Red Book Green Book Gold BookDocument9 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature: Blue Book Red Book Green Book Gold BookRakesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- I Basic Chemical IdeasDocument8 pagesI Basic Chemical IdeasTreeant PelonNo ratings yet
- Principles of Organic Synthesis 2th EditionDocument643 pagesPrinciples of Organic Synthesis 2th Editionminh leNo ratings yet
- Collection 4Document12 pagesCollection 4ohnestman4uNo ratings yet
- AL Chemistry Past Paper Essay Questions (1996 - 2001) Year 2001Document1 pageAL Chemistry Past Paper Essay Questions (1996 - 2001) Year 2001HEIHEI723No ratings yet
- Organic Compounds PDFDocument156 pagesOrganic Compounds PDFOana OnciucNo ratings yet
- Unit - IIDocument29 pagesUnit - IIPG ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques: Unit 12Document39 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques: Unit 12RosellaNo ratings yet
- A Mini ThesisDocument18 pagesA Mini ThesisarooojfataimaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Graphene OxideDocument13 pagesChemistry of Graphene Oxidenguyendktu100% (1)
- Class 9th ChemDocument41 pagesClass 9th Chemark217913No ratings yet
- Principles of Organic Synthesis 2th EditionDocument643 pagesPrinciples of Organic Synthesis 2th Editionbach2007No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry VL2xPA0Document11 pagesOrganic Chemistry VL2xPA0Maica GarampilNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 11Document34 pages07 Chapter 11M Zia Dogar100% (2)
- Física I. T3Document2 pagesFísica I. T3Simona FourtakNo ratings yet
- Física I. T3Document2 pagesFísica I. T3Simona FourtakNo ratings yet
- 1955 Book Reviews 6087: of ofDocument1 page1955 Book Reviews 6087: of ofسید حسین عارفیNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - (Philoid-IN) PDFDocument39 pagesChapter 5 - (Philoid-IN) PDFAruna WarkalNo ratings yet
- Langford LSPDocument119 pagesLangford LSPanakdamitNo ratings yet
- Binary Systems: Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds, Volume 1P2From EverandBinary Systems: Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds, Volume 1P2H. StephenNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques: Unit 12Document30 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques: Unit 12Sridipto GhoshNo ratings yet
- W1 D2 Q1 Gen Chem 1Document8 pagesW1 D2 Q1 Gen Chem 1Raymart Mesuga0% (1)
- Writing of Formulae and Balancing EquationsDocument8 pagesWriting of Formulae and Balancing EquationsKanzNo ratings yet
- Library Guide CSE StyleDocument3 pagesLibrary Guide CSE StyleRalfNo ratings yet
- What Is A Chemical Formula?Document1 pageWhat Is A Chemical Formula?Shanaia SapidaNo ratings yet
- TextbookDocument42 pagesTextbookAarzoo KaziNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Standard-State Entropies of Association For Aqueous Metal - Organic Complexes and Chelates at 25°C and 1 BarDocument23 pagesEstimation of Standard-State Entropies of Association For Aqueous Metal - Organic Complexes and Chelates at 25°C and 1 BarWilliam AgudeloNo ratings yet
- Organic Che-Some Basic PrinciplesDocument20 pagesOrganic Che-Some Basic PrinciplesFarhan Al ZayedNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Formula Writing and Naming Inorganic CompoundsDocument5 pagesActivity 1 - Formula Writing and Naming Inorganic CompoundsPrecious Mae Cuerquis Barbosa0% (1)
- 10.1201 b10908 PreviewpdfDocument76 pages10.1201 b10908 PreviewpdfGonzalo BustosNo ratings yet
- Module in (Ge-Ad: General CHEMISTRY (Organic) ) : Palawan State University Roxas Campus (Department Name) DepartmentDocument50 pagesModule in (Ge-Ad: General CHEMISTRY (Organic) ) : Palawan State University Roxas Campus (Department Name) DepartmentJohn Mark JuarezNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chemistry ReviewDocument4 pages1 - Chemistry ReviewAmmar KaziNo ratings yet
- II. Can We Unmuddle The Chemistry Textbook?Document12 pagesII. Can We Unmuddle The Chemistry Textbook?Dayana Salcedo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Inorganic Nomenclature PDFDocument2 pagesElementary Inorganic Nomenclature PDFPrecious Mae Cuerquis BarbosaNo ratings yet
- PDF 20231005 195926 0000Document20 pagesPDF 20231005 195926 0000UnKnOwn 0No ratings yet
- Organic CHMDocument39 pagesOrganic CHMsudeepjosephNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Drugs-Chemical Data, Structures and BibliographiesDocument1 pageDictionary of Drugs-Chemical Data, Structures and BibliographiesCesar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Organometallic - CompoundsDocument163 pagesOrganometallic - CompoundsAdeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Multi-Sulfur and Sulfur and Oxygen Five- and Six-Membered Heterocycles, Part 1From EverandMulti-Sulfur and Sulfur and Oxygen Five- and Six-Membered Heterocycles, Part 1David S. BreslowNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 3: Organic Compounds C8 to C28From EverandHandbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 3: Organic Compounds C8 to C28No ratings yet
- Yeoh 2012Document11 pagesYeoh 2012Alejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
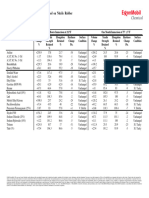
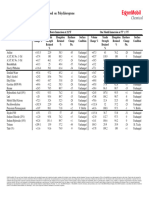
- Characteristics of Human HearingDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Human HearingAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Carcinogens: Substance Other Names Cas RNDocument5 pagesChemical Carcinogens: Substance Other Names Cas RNAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- Standard Atomic Weights (1995) : ReferenceDocument3 pagesStandard Atomic Weights (1995) : ReferenceAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- XE20-853U XE20-A0784: Steam Resistant Silicone ElastomerDocument2 pagesXE20-853U XE20-A0784: Steam Resistant Silicone ElastomerAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- Gough 2016Document19 pagesGough 2016Alejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- Ciir 1066 Res QcaDocument3 pagesCiir 1066 Res QcaAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- NBR Res QcaDocument3 pagesNBR Res QcaAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- NR Res QcaDocument3 pagesNR Res QcaAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- CR Res QcaDocument3 pagesCR Res QcaAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- Iir 065 Res QcaDocument3 pagesIir 065 Res QcaAlejandro ZagalNo ratings yet
- IX - WorkSheet-1 (MOLE) - With - Solution-1Document7 pagesIX - WorkSheet-1 (MOLE) - With - Solution-1hridhaan psuedopodiaNo ratings yet
- Building Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class XDocument13 pagesBuilding Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class Xloly62006No ratings yet
- Chemistry Contents Gr. 11 & 12Document9 pagesChemistry Contents Gr. 11 & 12milkiyasNo ratings yet
- Materi 6 Teori Kinetik Versi Bhs InggrisDocument7 pagesMateri 6 Teori Kinetik Versi Bhs InggrisNur Budi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Basic Terms in Polymer ScienceDocument25 pagesGlossary of Basic Terms in Polymer ScienceDownload_from_ScribdNo ratings yet
- Soil Water Class FinalDocument78 pagesSoil Water Class FinalVetri Vel PrakashNo ratings yet
- 16-Fundamentals + PromptsDocument1 page16-Fundamentals + PromptsAiesha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Structure of SolidsDocument16 pagesStructure of SolidsAnancy Reza Ngarbingan100% (1)
- IB SL Chemistry NotesDocument5 pagesIB SL Chemistry NotesArsh SheikhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Syllabus 8873) : Singapore-Cambridge General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Higher 1 (2024)Document49 pagesChemistry (Syllabus 8873) : Singapore-Cambridge General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Higher 1 (2024)mint :DNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding PDFDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding PDFsiddhant shuklaNo ratings yet
- S11196781 Exp 1 CH204Document7 pagesS11196781 Exp 1 CH204Shradha ChandraNo ratings yet
- Module 3A Chemical Formulae and Equations IIDocument5 pagesModule 3A Chemical Formulae and Equations IIMohd HafiezNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding in ElementsDocument31 pagesCovalent Bonding in ElementsOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- Spectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityDocument9 pagesSpectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityDr. Gazi Jahirul ISlamNo ratings yet
- Molecular Symmetry and Group Theory CartDocument1 pageMolecular Symmetry and Group Theory Cartdasalways4uNo ratings yet
- Crystallography - Solid MaterialsDocument18 pagesCrystallography - Solid MaterialsMehedi hasanNo ratings yet
- Visible Absorption Spectrum of IodineDocument10 pagesVisible Absorption Spectrum of IodinechristianNo ratings yet
- Causes of Hydrophobic InteractionsDocument3 pagesCauses of Hydrophobic InteractionsLucky LokeshNo ratings yet
- (Crossroads of Knowledge) Jacob Bull, Margaretha Fahlgren (eds.) - Illdisciplined Gender_ Engaging Questions of Nature_Culture and Transgressive Encounters-Springer International Publishing (2016).pdfDocument166 pages(Crossroads of Knowledge) Jacob Bull, Margaretha Fahlgren (eds.) - Illdisciplined Gender_ Engaging Questions of Nature_Culture and Transgressive Encounters-Springer International Publishing (2016).pdfbrunacjpereiraNo ratings yet
- BIOORG1 Syllabus 3-2012-13 PDFDocument4 pagesBIOORG1 Syllabus 3-2012-13 PDFSeth Andrew SalihNo ratings yet
- Electro NegativityDocument6 pagesElectro NegativityWarisha AkbarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Week 1 Gen Chem 2 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument30 pagesLesson 1 Week 1 Gen Chem 2 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsTwilightNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document53 pagesCH 05Mark BakalanNo ratings yet