Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transmission Media
Uploaded by
Catherine KiwalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transmission Media
Uploaded by
Catherine KiwalaCopyright:
Available Formats
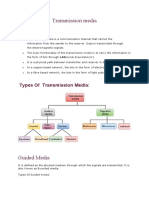
TRANSMISSION MEDIA
Transmission medium is a communication channel that carries information from the sending
device to the receiving device.
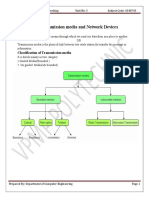
Classification of Transmission Media:
Guided Media
It is defined as the physical medium through which the signals are transmitted. It is also
known as Bounded media.
Types of Guided media:
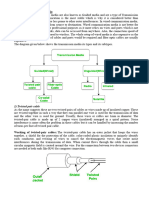
Twisted pair:
Twisted pair is a physical medium made up of a pair of cables twisted with each other. A
twisted pair cable is cheap as compared to other transmission media. Installation of the
twisted pair cable is easy, and it is a lightweight cable. The frequency range for twisted
pair cable is from 0 to 3.5KHz.
A twisted pair consists of two insulated copper wires arranged in a regular spiral pattern.
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
The degree of reduction in noise interference is determined by the number of turns per foot.
Increasing the number of turns per foot decreases noise interference.
Types of Twisted pair:
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
Refers to a pair of wires that are twisted around each other to minimize interference. Telephone
and Ethernet cables are common examples of UTP wires.
Advantages of Unshielded Twisted Pair:
o It is cheap.
o Installation of the unshielded twisted pair is easy.
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
o It can be used for high-speed LAN.
Disadvantage:
o This cable can only be used for shorter distances because of attenuation.
Shielded Twisted Pair
A shielded twisted pair is a cable that contains a mesh surrounding the wire that allows
the higher transmission rate.
Advantages of Shielded Twisted Pair
1. Cheaper than fibre optic cables
2. Easy to install
3. The shield allows for higher transmission rates
Disadvantages of Shielded Twisted Pair
1. It is more expensive as compared to UTP and coaxial cable.
2. It has a higher attenuation rate.
Attenuation is the reduction of the amplitude of a signal, electric current, or other oscillation.
Coaxial Cable
o Coaxial cable is very commonly used transmission media, for example, TV wire is
usually a coaxial cable.
o The name of the cable is coaxial as it contains two conductors parallel to each
other.
o It has a higher frequency as compared to Twisted pair cable.
o The inner conductor of the coaxial cable is made up of copper, and the outer
conductor is made up of copper mesh. The middle core is made up of non-
conductive cover that separates the inner conductor from the outer conductor.
o The middle core is responsible for the data transferring whereas the copper mesh
prevents from the EMI (Electromagnetic interference).
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
Coaxial cable is of two types:
1. Baseband transmission: It is defined as the process of transmitting a single
signal at high speed.
2. Broadband transmission: It is defined as the process of transmitting multiple
signals simultaneously.
Advantages of Coaxial cable:
o The data can be transmitted at high speed.
o It has better shielding as compared to twisted pair cable.
o It provides higher bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Coaxial cable:
o It is more expensive as compared to twisted pair cable.
o If any fault occurs in the cable causes the failure in the entire network.
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
Fibre Optic
Fiber optics are thin glass or plastic fibers used to transmit data via light. A fiber optic cable
consists of a bundle of optical fibers that can transmit information over long distances and at
high bandwidth.
The core is the actual glass fiber that the light travels through, and the cladding is wrapped
around the core to ensure the light signals cannot escape the fiber.
Outside appearance Inside are multiple glass fibres
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
Advantages of fibre optic cables
o Better bandwidth
o Higher transmission speeds due to better bandwidth
o Longer transmission distances
A fibre optic cable is a low power loss medium, meaning you can achieve higher
bandwidths over greater transmission distances. Fibre optic cables can reach 10’s
of kilometres in distance compared to the maximum 100-metre distance that is
the limit of copper cables.
o Greater flexibility. Fibre is flexible, can bend easily and resists most corrosive
elements that often attack copper cables.
o Stronger security. Fibre optic cable keeps data secure. It does not radiate signals
and is very difficult to tap without your knowledge. It has higher physical security
as all hardware and electronics can be installed in one central location, unlike
copper systems, where equipment is required to be installed within distribution
locations throughout a facility.
o Fibre optic cables are lighter to carry from one place to another unlike copper
cables such as coaxial and twisted pair.
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
Unguided Media
Unguided transmission media are methods that allow the transmission of data by
use of non physical means. Examples of this include microwave, radio or infrared.
1. Radio waves: The radio waves can be defined as electromagnetic waves which can
be used to transmit the information in any direction without having any restriction. The
radio waves can travel in any direction. In radio waves transmission, there is no necessity
that the sending antenna and receiving antenna should be aligned, the signals can be
transmitted to any receiving antenna. One of the best examples of radio waves signal is
FM radio.
Radio waves application:
o The radio waves are used where there is a requirement of sending the same
information to multiple users from a single source.
o The applications of radio waves are television, FM radio, and cordless phone.
2. Microwave: The microwave is unidirectional. In this transmission, whenever the
signals are transmitted through an antenna, the signals can make narrow to focus to a
particular point. And in this transmission, there is a requirement of proper alignment of
sending antenna and receiving antenna.
Microwave application:
o The unicast transmission becomes easier using microwave transmission.
In computer networking, unicast is a one-to-one transmission from one point in the network
to another point; that is, one sender and one receiver, each identified by a network address
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
o The microwaves are used in satellite network communication and wireless LANs.
3. Infrared waves: These types of waves are used when there is a requirement to have
communication for shorter distances. As the frequency is very high for infrared waves,
the signals cannot penetrate through walls. Infrared communication can be done for
long-range also depending on the requirements. The infrared waves can be intervening
if the sun rays fall on it as the sunrays also have infrared waves.
Infrared application:
o The data transmission quality for the infrared is comparatively higher than other
types of electromagnetic waves.
o Used in computer system components to have communication between them.
Assignment
Explain advantages and disadvantages of unguided transmission media.
Reference
https://www.javatpoint.com/unguided-transmission-media
https://www.educba.com/unguided-media-transmission/
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
© ICT department www.msmcnamagunga.ac.ug
You might also like
- VFD House Electrical Equipment Operation ManualDocument21 pagesVFD House Electrical Equipment Operation ManualJohn SimancaNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi 3000gt Workshop Manual Vol 2Document738 pagesMitsubishi 3000gt Workshop Manual Vol 2mohanngp100% (1)
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument132 pagesCathodic Protectionpeyman_tNo ratings yet
- Hands On 1988 07Document100 pagesHands On 1988 07Harald DasselNo ratings yet
- SEEE Society Electrical Engineering Book CollectionDocument5 pagesSEEE Society Electrical Engineering Book CollectionJames BondNo ratings yet
- SATIP-P-113-01 Rev 8 Final Induction Motor PDFDocument3 pagesSATIP-P-113-01 Rev 8 Final Induction Motor PDFSabheeh AliNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- MediaDocument19 pagesMediaDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Iec 62852-2014Document86 pagesIec 62852-2014grauNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Transmission MediaDocument9 pagesUnit1-Transmission MediaManmohan K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document28 pagesUnit 2Atharv KhadatareNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument31 pagesTransmission MediaMOHAMED FAAIZNo ratings yet
- Unshielded Twisted PairDocument17 pagesUnshielded Twisted Pairjone apkNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Notes: What Is Communication Media?Document18 pagesData Communication Notes: What Is Communication Media?ychokhatNo ratings yet
- Assignment of NetworkingDocument13 pagesAssignment of NetworkingJyoti BhanotNo ratings yet
- 170 Transmission MediaDocument39 pages170 Transmission Mediahauwauibrahimmagaji532No ratings yet
- Types of Transmission MediaDocument8 pagesTypes of Transmission MediaUterus Xbox er f u. RNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document70 pagesUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNo ratings yet
- What Is Transmission MediaDocument12 pagesWhat Is Transmission MediaMuneeza AlizaNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediumDocument12 pagesTransmission MediumSuryanshuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Physical LayerDocument22 pagesUNIT 2 Physical Layervasundhara kaleNo ratings yet
- Guided Transmission MediaDocument6 pagesGuided Transmission MediaKunal MhatreNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument14 pagesTransmission MediaMacloud KamulaNo ratings yet
- CN-lecture9 Trans MediaDocument6 pagesCN-lecture9 Trans MediaⲤʟᴏᴡɴᴛᴇʀ ᏀᴇɪꜱᴛNo ratings yet
- What is Transmission Media? Classification and TypesDocument7 pagesWhat is Transmission Media? Classification and TypestomakobNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document84 pagesUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education: CertificateDocument18 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education: CertificateSanket ParabNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 CCNDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 CCNsajjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Transmission MediaDocument24 pagesChapter 3 - Transmission MediaTawanda MukuteNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibre Communication With Overview 1.pdf 2Document97 pagesOptical Fibre Communication With Overview 1.pdf 2ahmedNo ratings yet
- COM 122 Introduction To Internent Lecture Note 3Document8 pagesCOM 122 Introduction To Internent Lecture Note 3Elijah OlusegunNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media Types and CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesTransmission Media Types and CharacteristicsRonit SahuNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument7 pagesAdvantages of Optical Fiber Communicationmohammadanas7686No ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument33 pagesTransmission MediaAshish ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument7 pagesData Transmissionantonially24No ratings yet
- SLM - Example Networks, Transmission MediaDocument24 pagesSLM - Example Networks, Transmission MediaPSRILATHANo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument5 pagesResearchNicole BernalNo ratings yet
- Mbalenhle Ndaba ICT1532: The Advantages of The Twisted Pair Cable AreDocument4 pagesMbalenhle Ndaba ICT1532: The Advantages of The Twisted Pair Cable AreMbali NdabaNo ratings yet
- Idresss sir#6OKDocument17 pagesIdresss sir#6OKDil NawazNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking NotesDocument13 pagesComputer Networking Notesanamayasharma2953No ratings yet
- Study of Transmission Media Shaheen OldDocument34 pagesStudy of Transmission Media Shaheen OldAmit Pasi0% (1)
- DCC Unit2Document76 pagesDCC Unit2Omkar mahamuniNo ratings yet
- PHY LAYER FUNCS & MEDIADocument26 pagesPHY LAYER FUNCS & MEDIAalish shrsethaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media ManualDocument10 pagesTransmission Media ManualVarun RankajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3_networkingDocument9 pagesChapter 3_networkingninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- Types of Transmission Media: Twisted Pair, Coaxial, Fiber OpticDocument9 pagesTypes of Transmission Media: Twisted Pair, Coaxial, Fiber Opticpratyay dhondNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Guided: Transmission Capacity Depends Critically On The Medium, The Length, andDocument10 pagesTransmission Media: Guided: Transmission Capacity Depends Critically On The Medium, The Length, andMONEER THAMEERNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer: Transmission Media - Guided Transmission MediaDocument185 pagesPhysical Layer: Transmission Media - Guided Transmission MediaDeepika SheshabutterNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument12 pagesTransmission MediaJatin RajputNo ratings yet
- Networking Notes (Grade-12 CBSE Computer Science)Document32 pagesNetworking Notes (Grade-12 CBSE Computer Science)Adil DanadNo ratings yet
- Guided and Unguided Media Part-2Document32 pagesGuided and Unguided Media Part-2vinamra MishraNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediumDocument5 pagesTransmission MediumQUSI E. ABDNo ratings yet
- Example: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneDocument33 pagesExample: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- CableDocument26 pagesCableHrithik ReignsNo ratings yet
- RASHAD MAHMOOD Instructor Guide on Network Cabling TypesDocument24 pagesRASHAD MAHMOOD Instructor Guide on Network Cabling TypesRashad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument14 pagesTransmission MediaCONSTANTINOSNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument6 pagesTransmission Mediamahar.nomi1039No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Transmission Media Network Devices1Document27 pagesUnit 3 Transmission Media Network Devices1Amruta ShingoteNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Wired MediaDocument5 pages1.5 Wired Mediayabocew846No ratings yet
- unit 2Document15 pagesunit 2sahilNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer and Its Design Issues Chapter-3Document10 pagesPhysical Layer and Its Design Issues Chapter-3Amir SilwalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: TheoryDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 1: TheoryAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Notes-Transmission MediaDocument22 pagesNotes-Transmission MediaRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Applications of NetworkDocument20 pagesApplications of NetworkJom JerryNo ratings yet
- Trans Miss On MediaDocument13 pagesTrans Miss On Mediahatim44026No ratings yet
- INFORMATIONDocument15 pagesINFORMATIONJANELIA MARTINNo ratings yet
- Guided vs Unguided Transmission Media TypesDocument6 pagesGuided vs Unguided Transmission Media TypesAbdirahman ElmiNo ratings yet
- Maximum Efficiency and Output of Class-F Power AmplifiersDocument5 pagesMaximum Efficiency and Output of Class-F Power AmplifierscemshitNo ratings yet
- TOOLS FOR SERVICING ELECTRIC AND HYBRID VEHICLESDocument25 pagesTOOLS FOR SERVICING ELECTRIC AND HYBRID VEHICLESL ESNo ratings yet
- Itu-T: Surge Protective Component Application Guide - Gas Discharge TubesDocument42 pagesItu-T: Surge Protective Component Application Guide - Gas Discharge TubesDanny NjomanNo ratings yet
- Public Safety Standards for Power CapacitorsDocument2 pagesPublic Safety Standards for Power CapacitorsmaninderpreetNo ratings yet
- ECEN 454: Digital Integrated Circuit DesignDocument36 pagesECEN 454: Digital Integrated Circuit DesignJoe KingNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Temperature ControllerDocument8 pagesIntelligent Temperature ControllerDhp CiaNo ratings yet
- WurilotonutenabenowaDocument2 pagesWurilotonutenabenowavikash kushwahaNo ratings yet
- L 207Document2 pagesL 207miltongrimiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Power System Harmonics On Transformer Loading Capability and Hot Spot TemperatureDocument4 pagesEffect of Power System Harmonics On Transformer Loading Capability and Hot Spot TemperatureJorge EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Bang Gia LK (1) - DTDocument22 pagesBang Gia LK (1) - DTTri Nang HuynhNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: HEF4519B MSIDocument4 pagesData Sheet: HEF4519B MSIGoodLookingPirateNo ratings yet
- AM Modulator: Experiment TheoryDocument14 pagesAM Modulator: Experiment Theorycluj24No ratings yet
- Photodiode and LIGHT Emitting DiodeDocument38 pagesPhotodiode and LIGHT Emitting DiodekaneeshaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5_ Electricity and magnetism – IB PhysicsDocument18 pagesTopic 5_ Electricity and magnetism – IB PhysicsVinisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- SCT 013 Series - YHDCDocument1 pageSCT 013 Series - YHDCLucian MarcNo ratings yet
- LM 567Document9 pagesLM 567Juan Chin Pérez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 System CabinetDocument1 page3.1 System CabinetBoualem AisNo ratings yet
- EC203 Solid State Devices CourseDocument2 pagesEC203 Solid State Devices CoursehimaNo ratings yet
- Protel DXP TutorialDocument123 pagesProtel DXP TutorialMarkNo ratings yet
- NEE2202 PARALE LabWorkNo.1Document16 pagesNEE2202 PARALE LabWorkNo.1Ricelle Ann ParaleNo ratings yet
- TLB Ethernet TCP Ip User ManualpdfDocument51 pagesTLB Ethernet TCP Ip User Manualpdfing.sergio.raga.1992No ratings yet
- STS - (3000K, 6000K) - H1 Smart Transformer Station Installation Guide (Malaysia, BGMC)Document79 pagesSTS - (3000K, 6000K) - H1 Smart Transformer Station Installation Guide (Malaysia, BGMC)Miguel Bejarano PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Electromagnetic Waves in Open Media: Carlos Arley MendezDocument10 pagesTask 1 - Electromagnetic Waves in Open Media: Carlos Arley Mendezjair jimenezNo ratings yet