Professional Documents
Culture Documents
c3.4 Exam Questions
Uploaded by
haquangminh haiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
c3.4 Exam Questions
Uploaded by
haquangminh haiCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer all the questions.
1. During the electrolysis of molten potassium chloride, what is made at the cathode?
A chlorine
B hydrogen
C potassium
D potassium hydroxide
Your answer
[1]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 1 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
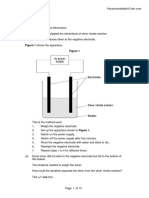
2(a). Meena electrolyses copper sulfate using copper electrodes.
Look at the diagram. It shows the apparatus she uses.
She investigates the change in mass at each electrode before and after the electrolysis.
Look at Meena's method.
1. Using a balance, measure the mass of the copper cathode and copper anode.
2. Set up the apparatus and run the electrolysis for 30 seconds.
3. Remove the copper cathode and the copper anode and immediately place them on the balance and
measure their masses again.
What improvements could you make to Meena's experiment?
Explain your answers.
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 2 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
[4]
(b). Meena finds that
the cathode gains mass
the anode loses mass.
Explain these observations in terms of the reactions at each electrode.
[2]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 3 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
3(a). Molten aluminium oxide contains Al3+ and O2– ions.
The electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide makes aluminium and oxygen.
(i) Write the balanced symbol equation for the electrode reaction that happens at the cathode.
Use the symbol e- to represent an electron.
[1]
(ii) Solid aluminium oxide cannot be electrolysed.
Explain why.
[1]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 4 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
(b). Copper is also made by electrolysis of copper sulfate solution.
Look at the diagram of the apparatus used in this electrolysis.
Describe what you would see at each of the electrodes.
At the anode:
At the cathode:
[2]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 5 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
4(a). Molten (liquid) potassium chloride can be electrolysed.
Potassium is made.
Manjit investigates the mass of potassium made when molten potassium chloride is electrolysed.
She always uses a current of 10.3 amps.
She does the electrolysis for different lengths of time.
Look at the graph of her results.
What is the total mass of potassium made in 30 minutes?
____________________________ g
[1]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 6 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
(b). Manjit electrolyses molten potassium chloride for 120 minutes.
She uses a current of 20.6 rather than 10.3 amps.
Predict the mass of potassium made.
[2]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 7 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
5(a). Molten (liquid) salts can be electrolysed.
Sanjay does an electrolysis experiment using potassium bromide.
Solid potassium bromide cannot be electrolysed.
Molten (liquid) potassium bromide can be electrolysed. It makes two products.
(i) Write down the names of the two products made during this electrolysis.
[2]
(ii) Explain why molten (liquid) potassium bromide can be electrolysed.
[1]
(b). Molten (liquid) potassium chloride can be electrolysed.
It makes potassium.
Sanjay investigates the mass of potassium made when molten potassium chloride is electrolysed.
He always uses a current of 10.3 amps.
He changes how long, in minutes, he does the electrolysis.
Look at the graph of his results.
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 8 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
(i) What mass of potassium is made after 30 minutes?
______________ g
[1]
(ii) Sanjay electrolyses molten potassium chloride for 300 minutes.
Predict the mass of potassium made.
______________ g
[1]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 9 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
6(a). This question is about electrolysis.
Joel's teacher investigates the electrolysis of melted sodium chloride.
Look at the apparatus he uses.
Sodium chloride contains sodium ions, Na+, and chloride ions, Cl−.
(i) Chloride ions, Cl−, react at the anode.
Chlorine gas, Cl2, and electrons are the products.
Write a balanced symbol equation for the electrode process at the anode.
Use e− to show an electron.
[2]
(ii) Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity, but melted sodium chloride does conduct electricity.
Explain why.
[2]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 10 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
(b). Joel passes an electric current through copper(II) sulfate solution.
Joel does four experiments.
Joel changes either the time or the current.
Copper is made at the cathode.
He measures how much copper is made in each experiment.
Experiment Current in amps Time in minutes Mass of copper made in
g
1 0.15 5 0.20
2 0.30 5 0.40
3 0.15 10 0.40
4 0.60 10 1.60
Joel concludes that the amount of copper made is proportional to both the current and to the time.
Show how the results support this conclusion.
[2]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 11 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
7(a). During the electrolysis of sodium bromide solution, bromide ions make bromine molecules.
Complete the equation for this reaction.
[1]
(b). Explain why this reaction is an example of oxidation.
[1]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 12 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
8. Pure copper is used for electrical wiring.
The copper is purified by electrolysis.
The diagram shows the apparatus used to purify copper.
Complete the labels on the diagram.
Choose your answers from the list.
copper sulfate solution
dilute sulfuric acid
impure copper anode
impure copper cathode
pure copper anode
pure copper cathode
[2]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 13 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
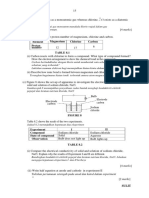
9(a). Joel's teacher investigates the electrolysis of four liquids.
The first liquid he uses is melted sodium chloride.
Look at the apparatus he uses.
The table shows the products made.
Liquid Product at cathode Product at anode
lead bromide lead bromine
lead iodide lead iodine
sodium chloride sodium _____________________
potassium iodide _____________________ iodine
[2]
(i) Complete the table.
(ii) Sodium chloride contains sodium ions, Na+, and chloride ions, Cl –.
Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity, but melted sodium chloride does conduct electricity.
Explain why.
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 14 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
[2]
(b). Joel passes an electric current through copper(II) sulfate solution.
Joel does four experiments.
Joel changes either the time or the current.
Copper is made at the cathode.
He measures how much copper is made in each experiment.
Experiment Current in amps Time in minutes Mass of copper made in g
1 0.15 5 0.20
2 0.30 5 0.40
3 0.15 10 0.40
4 0.60 10 1.60
Joel concludes that the amount of copper made is proportional to both the current and to the time.
Show how the results support this conclusion.
[2]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 15 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
10. Anita investigates the electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution (brine).
Look at the diagram. It shows the apparatus she uses.
What is the name of gas X?
Choose your answer from the list.
carbon dioxide
hydrogen
hydrogen chloride
oxygen
answer
[1]
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 16 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
11.
Look at the diagram. It shows the apparatus used to purify copper.
What is the name of the process used to purify copper?
Choose from the list.
crystallisation
electrolysis
eutrophication
neutralisation
thermal decomposition
answer _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ [1]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 17 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
1 C 1
Total 1
2 a electrolysis needs to run for longer than 30 4
seconds (1)
otherwise insufficient change at electrodes
(1)
after electrolysis anode and cathode need
to be washed (1) and then dried (1) before
measuring the mass
b copper is deposited at the cathode (1) 2 ALLOW higher level answers in terms of
copper anode dissolves / copper ions half equations
produced at anode (1) e.g. at cathode Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu (1)
–
e.g. at anode Cu → Cu2+ + 2e– / Cu – 2e →
2+
Cu (1)
Total 6
3 a i 1 ALLOW any correct multiple
DO NOT ALLOW & or and instead of +
ii Ions cannot move (1) 1 IGNORE electrons cannot move
b Anode: bubbles / effervescence (1) 2 Both correct descriptions but at wrong
Cathode: Brown / salmon pink deposit / electrodes
layer / coating (1)
Total 4
4 a 7.5 (g) (1) 1 allow 7.4 to 7.6
Examiner's Comments
This question focused on the electrolysis of
molten potassium chloride.
Most candidates were able to interpret the
graph and give an answer of 7.5 g.
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 18 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
b LOOK FOR ANSWER FIRST OF ALL 2 allow ecf answer to (a) × 8 e.g. 60.8 if 7.6g
IF mass = 60 g AWARD 2 MARKS and 59.2 if 7.4
idea that must multiply (7.5) by 4 / idea that
must multiply (30) by 2 / idea that must allow ecf
multiply (7.5) by 8 (1)
Examiner's Comments
This question focused on the electrolysis of
molten potassium chloride.
Candidates were able to use their result to
get an answer of 60.0 g. Some candidates
used Q=It in their answer and went through
complex calculations even remembering
96500 to get the correct answer. Other
candidates used the correct method of
appreciating that the current was doubled
and the time quadrupled so that overall the
mass will be 8 times the original mass.
Total 3
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 19 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
5 a i potassium (1) 2 allow K (1)
i bromine (1) allow Br2 (1)
do not allow bromide
Examiner's Comments
The products were usually correctly
identified as potassium and bromine.
Bromide was a common error.
ii ions can move / ions go to electrodes (1) 1 allow ions move to anode / ions move to
cathode (1)
do not allow electrons can move
Examiner's Comments
A very common misconception was that
molten potassium bromide can be
electrolysed because the electrons can
move.
b i 7.5 (g) (1) 1 allow 7.4 to 7.6 (1)
Examiner's Comments
Most candidates correctly interpreted the
graph and scored the marks.
ii 75 (g) (1) 1 allow ecf from (i) i.e. 10 x answer to (i)
Examiner's Comments
Most candidates correctly interpreted the
graph and scored the marks.
Total 5
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 20 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
6 a i 2Cl? ? Cl2 + 2e? / 2Cl? ? 2e? ? Cl2 2 allow = instead of ?
not and or & instead of +
formulae correct including electrons (1) allow any correct multiples including
fractions
balancing — dependent on correct allow e? or e for electrons
formulae (1) allow 2Cl? ? e? ? Cl2 + e? for two marks
allow one mark for correct balanced
equation with minor errors of case,
subscript and/or superscript eg
2CL? ? Cl2 + 2e?
allow one mark for Cl? ? e? ? Cl / Cl? ? Cl +
e?
allow one mark for 2Cl? ? Cl2
Examiner's Comments
Candidates found the electrode reaction
challenging and often candidates had the
electrons on the wrong side of the equation
or had the formula of chlorine incorrect. A
small proportion of candidates did not
attempt this question.
ii solid sodium chloride has ions in fixed 2 allow solid does not have free ions
positions / ions do not move in a solid (1) ignore electrons cannot move in a solid
liquid sodium chloride has ions that move allow liquid sodium chloride has free ions
(1) not electrons can move in a liquid
allow if no other marks scored award one
mark for particles can move in a liquid but
not in a solid / liquid has mobile charge
carriers but solid does not
Examiner's Comments
Candidates often appreciated that the
charge carrier could not move in a solid but
could move in a liquid, however most
candidates referred to electrons rather than
ions as the charge carrier.
b 2 allow reference to the correct data in the
table to identify which experiments they are
using
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 21 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
experiments 1 and 3 show that as time allow when the time doubles and the
doubles mass (of copper made) doubles current stays the same the mass doubles
(1)
experiments 3 and 4 show that as the
current quadruples, the mass also
quadruples (1)
OR
experiments 1 and 2 show that as current allow when the current doubles and the
doubles mass (of copper made) doubles time stays the same the mass doubles
(1)
allow if no other marks awarded then as
time and current increase the mass (of
copper) increases for one mark
Examiner's Comments
In this evaluation question many
candidates could use the data to show that
as current increases so does the mass and
as the time increases so does the mass
but were less confident at explaining why
this indicated direct proportionality. Only
the best answers referred to the
experiment numbers in their explanations.
Candidates did not always choose sets of
experiments where only one variable
changed and as a result did not justify the
patterns they were describing.
Total 6
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 22 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
7 a 2Br? - 2e? ? Br2(1) 1 allow any correct multiple, including
fractions
not any additional symbols, other than
balancing
Examiner's Comments
Most candidates correctly balanced the
equation.
b (oxidation because) electrons are lost 1 allow oxidation number of Br increases (1)
(from Br ?) (1) not bromine (atoms) lose electrons
but allow ions lose electrons (1)
Examiner's Comments
Most candidates explained that oxidation is
loss of electrons. Candidates who did not
gain credit either stated that electrons were
gained, or suggested that the wrong
species was losing electrons, e.g. bromine
loses electrons.
Total 2
8 2 all three labels correct scores 2 marks
one or two labels correct scores 1 mark
Examiner's Comments
Many candidates scored both marks.
Candidates who only scored 1 mark
usually correctly identified the electrolyte
as copper sulfate solution.
Total 2
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 23 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
9 a i chlorine (1) 2 allow Cl2 / Cl / CL
not chloride
potassium (1)
allow K
Examiner's Comments
Generally well known, but a few gave "
chloride“ as their answer instead of
chlorine.
ii solid sodium chloride has ions in fixed 2 Ignore electrons cannot move in a solid
positions / ions do not move in a solid (1) allow solid has no free ions
liquid sodium chloride has ions that move allow liquid sodium chloride has free ions
(1) NOT electrons can move in a liquid
if no other mark scored 1 mark for particles
cannot move in a solid but can move in a
liquid / liquid has mobile charge carriers
but solid does not for one mark
Examiner's Comments
Very few correct answers here. Common
errors were to discuss moving electrons or
that there is space for the electricity to get
through the liquid.
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 24 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
b experiments 1 and 3 show that as time 2 allow reference to the correct data in the
doubles mass (of copper made) doubles table to identify which experiments they are
(1) using
experiments 3 and 4 show that as the allow when the time doubles and the
current quadruples, the mass also current stays the same the mass doubles
quadruples (1)
OR
experiments 1 and 2 show that as current
doubles mass (of copper made) doubles
(1)
allow when the current doubles and the
time stays the same the mass doubles
allow if no other marks awarded then as
time and current increase the mass (of
copper) increases for one mark
Examiner's Comments
Few candidates scored 2 marks here;
many candidates were able to score a
mark for explaining that as the time and
current were increased, the mass of
copper deposited increased.
Total 6
10 hydrogen (1) 1 allow correct answer ticked, circled or
underlined in list if answer line is blank
Examiner's Comments
??Most candidates correctly identified gas
X as hydrogen. Hydrogen chloride was the
most common misconception.
Total 1
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 25 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Mark Scheme
Question Answer/Indicative content Marks Guidance
11 electrolysis (1) 1 allow other ways of indicating correct
response eg ringing or ticking the correct
answer but answer on answer line takes
precedence
Examiner's Comments
Electrolysis was the most common correct
answer.
Total 1
© OCR 2018. You may photocopy this page. 26 of 26 Created in ExamBuilder
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- Remember That You Can Search Using "Edit"!: GCSE Questions and AnswersDocument112 pagesRemember That You Can Search Using "Edit"!: GCSE Questions and AnswerskhujistaNo ratings yet
- C6 Hard QPDocument25 pagesC6 Hard QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework Questionservaldi0% (1)
- Chemistry Olympiad 2015 Tutorial Worksheet (ACJC Prelims 2014/P3/2 (B), (C) )Document5 pagesChemistry Olympiad 2015 Tutorial Worksheet (ACJC Prelims 2014/P3/2 (B), (C) )Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesElectrolysisBijoy SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry HandoutDocument13 pagesElectrochemistry HandoutSabeen Ahmed/TCHR/EKNNCNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Electrolysis QPDocument31 pages4.3 Electrolysis QPrjczzbclqhwipmsdlfNo ratings yet
- Section A: Summary Notes: Application of Redox Reactions 1 September 2015Document9 pagesSection A: Summary Notes: Application of Redox Reactions 1 September 2015Moses AhmedNo ratings yet
- C4 Chemical Changes HTDocument72 pagesC4 Chemical Changes HTMadhavi OchaniNo ratings yet
- Exampro - Acids and AlkalisDocument72 pagesExampro - Acids and AlkalisMadhavi OchaniNo ratings yet
- 10 Extracting MetalsDocument23 pages10 Extracting MetalsRigen AlamNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 4 QPDocument8 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 4 QPChemist Mohamed MohyNo ratings yet
- G10 CHEMISTRY P2 (2 Copies)Document8 pagesG10 CHEMISTRY P2 (2 Copies)Straight As StudyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Part 2 PDFDocument17 pagesChemistry Part 2 PDFHooi MinNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument19 pagesElectrolysisFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- SelasaDocument3 pagesSelasaMelor DihatiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 ICSE Electrolysis TestDocument2 pagesClass 10 ICSE Electrolysis Testaman.mourya383No ratings yet
- Electrolysis Homework PupilDocument8 pagesElectrolysis Homework Pupilnicole.fiorentini.almeidaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 03 - ElectrochemistryDocument10 pagesUNIT 03 - ElectrochemistryabhilashNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 7 QPDocument9 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 7 QPaliayanraza5No ratings yet
- Metals, Electrolysis, Energy Change Topical TestDocument5 pagesMetals, Electrolysis, Energy Change Topical TestCharles Allon YapNo ratings yet
- Actual Repeat Paper 2013Document10 pagesActual Repeat Paper 2013Jasmeet Kaur SandhuNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Mock Exam Topics 1 To 5, 9, 10Document6 pagesCIE IGCSE Mock Exam Topics 1 To 5, 9, 10Jenkins CK TsangNo ratings yet
- HL Paper3Document23 pagesHL Paper3dilemNo ratings yet
- C6a HW - Electrolysis PrinciplesDocument4 pagesC6a HW - Electrolysis PrinciplesAvaani MalhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: Lattice Energy: Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 19: Lattice Energy: Homework QuestionsSalar Ardebili50% (2)
- Gems Genesis: 9caieDocument4 pagesGems Genesis: 9caieBhavya darjiNo ratings yet
- Latihan ElektrolisisDocument17 pagesLatihan ElektrolisisFika KarimNo ratings yet
- Bengkel Ambang SPM 2009paper 2Document31 pagesBengkel Ambang SPM 2009paper 2Mimi MaliniNo ratings yet
- 2019 TJC h2 Chem Prelim p3 QPDocument16 pages2019 TJC h2 Chem Prelim p3 QPaliciaNo ratings yet
- VJC H2 Chem P3Document13 pagesVJC H2 Chem P3clarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- Term End Examination - November 2012 Course: CHY101 - Engineering Chemistry Slot: E2 Class NBR: 2330 / 2335 / 2338 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Document3 pagesTerm End Examination - November 2012 Course: CHY101 - Engineering Chemistry Slot: E2 Class NBR: 2330 / 2335 / 2338 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100ncNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesAssignment # 2 ElectrolysisRashard AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Chem PP1 BP 10 QP Kcse PredictionDocument66 pagesChem PP1 BP 10 QP Kcse PredictionASUMANI MWACHAJIONo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014Document5 pagesLXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014HNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Moles and Equations: Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 1: Moles and Equations: Homework QuestionsareebNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Electrochemistry LQDocument15 pagesPast Paper Electrochemistry LQapi-3739994100% (1)
- Structure - Bonding Carbon 1 QPDocument24 pagesStructure - Bonding Carbon 1 QPtertianerima101No ratings yet
- HL Paper2Document36 pagesHL Paper2Sharon ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1718 V2 EoS1 Past PaperDocument12 pagesChemistry 1718 V2 EoS1 Past PaperjcyNo ratings yet
- Topic 9: Oxidation and Reduction (7 Hours) : Assessment Statement Obj Teacher's NotesDocument3 pagesTopic 9: Oxidation and Reduction (7 Hours) : Assessment Statement Obj Teacher's NotesHaleyNo ratings yet
- Revision Test Electrolysis OlevelsDocument5 pagesRevision Test Electrolysis OlevelsMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument28 pagesMy TestkrisnuNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument80 pagesMetalsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 6 QPDocument9 pagesRate of Reaction 6 QPmalak tahaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesElectrochemistryzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- 8 Electricity and Chemical Change: Core CurriculumDocument3 pages8 Electricity and Chemical Change: Core CurriculumSumathi ShangkarNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Acids Bases and Salts Questions Teacher - Co .KeDocument9 pagesForm 4 Acids Bases and Salts Questions Teacher - Co .KeMikeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Chemical Cells and ElectrolysisDocument6 pages3 - Chemical Cells and Electrolysisapi-3700944100% (1)
- Electrolysis QPDocument14 pagesElectrolysis QPSartaj KabirNo ratings yet
- CHPT 11-13Document42 pagesCHPT 11-13Charles Borromeo LiNo ratings yet
- 12 Electrochemistry Assignment-1Document4 pages12 Electrochemistry Assignment-1Yashraj NarwariyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2000 Paper 1+ansDocument13 pagesChemistry 2000 Paper 1+ansapi-38240030% (2)
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry ElectrochemistryMagic Mind. TamilNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ElectrochemisrtyDocument7 pagesUnit 3 ElectrochemisrtyRahgul M.S.50% (2)
- Unit 3 ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesUnit 3 ElectrochemistrySapna 2704No ratings yet
- Cape Chem U2 P1 06Document14 pagesCape Chem U2 P1 06Daniella SalandyNo ratings yet
- Ea7145df 2Document5 pagesEa7145df 2KevinNo ratings yet
- 0450 s10 Ms 13Document11 pages0450 s10 Ms 13Ashmit BeraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/22The Engineer GuyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21shabanaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23shabanaNo ratings yet
- June 2021 Question Paper 11Document12 pagesJune 2021 Question Paper 11haquangminh haiNo ratings yet
- Lab4 F15 Si DiodeDocument15 pagesLab4 F15 Si DiodeJohn MarkNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Department Tracking Sheet OriginalCHARM2Document128 pagesLaboratory Department Tracking Sheet OriginalCHARM2Charmaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Clippers and ClampersDocument8 pagesClippers and Clamperspuneeth kumarNo ratings yet
- Sealand Equipment GuideDocument5 pagesSealand Equipment GuidePool Jaime Quispe CordovaNo ratings yet
- Diy AquariumsDocument108 pagesDiy Aquariumshalo_bing100% (2)
- Mua prc007 en - 12042009Document73 pagesMua prc007 en - 12042009sachinsaklani23No ratings yet
- Ahmedabad BRTSDocument3 pagesAhmedabad BRTSVishal JainNo ratings yet
- Project: Study On Building Construction Using Foam ConcreteDocument5 pagesProject: Study On Building Construction Using Foam ConcreteAzhagesanNo ratings yet
- Obturator / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument97 pagesObturator / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Monitoração E Diagnósticos de Pára-Raios A ZnoDocument7 pagesMonitoração E Diagnósticos de Pára-Raios A ZnoRamón MirelesNo ratings yet
- Tutoria Radio MobileDocument11 pagesTutoria Radio MobileGanti Nama Aja LahNo ratings yet
- Laporan Hasil Praktik Bahasa Inggris Dengan Tamu Asing Di Pantai KutaDocument12 pagesLaporan Hasil Praktik Bahasa Inggris Dengan Tamu Asing Di Pantai KutaEnal MegantaraNo ratings yet
- Lisa-Operation Manual: Installation and Operation Instructions (Part B)Document41 pagesLisa-Operation Manual: Installation and Operation Instructions (Part B)majdNo ratings yet
- Detection of Food AdulterationDocument10 pagesDetection of Food AdulterationDavara Paresh R.No ratings yet
- Well Control Daily Checklist Procedure VDocument13 pagesWell Control Daily Checklist Procedure VmuratNo ratings yet
- Penetapan Kadar Sakarin, Asam Benzoat, Asam Sorbat, Kofeina, Dan Aspartam Di Dalam Beberapa Minuman Ringan Bersoda Secara Kro...Document13 pagesPenetapan Kadar Sakarin, Asam Benzoat, Asam Sorbat, Kofeina, Dan Aspartam Di Dalam Beberapa Minuman Ringan Bersoda Secara Kro...Wisnu WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Wide Flange BeamDocument4 pagesLab 6 - Wide Flange BeamJanithNo ratings yet
- Berk-2009-Journal of Forensic SciencesDocument9 pagesBerk-2009-Journal of Forensic SciencesClaudio NovaesNo ratings yet
- An Open Letter To Annie Besant PDFDocument2 pagesAn Open Letter To Annie Besant PDFdeniseNo ratings yet
- (Ronald Weed, John Von Heyking (Eds.) ) Civil ReligiDocument375 pages(Ronald Weed, John Von Heyking (Eds.) ) Civil ReligiskaspeNo ratings yet
- Math Model Qs by NRBDocument4 pagesMath Model Qs by NRBapi-3825027No ratings yet
- Tesla in ChinaDocument9 pagesTesla in ChinaÁi Nhân Huỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Zener Diodes and Transient Voltage Suppressors Quarter 3, 1998 SG274 - D Rev 16Document8 pagesZener Diodes and Transient Voltage Suppressors Quarter 3, 1998 SG274 - D Rev 16Imraan RamdjanNo ratings yet
- m1340008 Dark FutureDocument220 pagesm1340008 Dark Futurejkj1176100% (1)
- Reviewer 3RD Exam FinalDocument14 pagesReviewer 3RD Exam FinalReane Romblon GerozagaNo ratings yet
- DIO 20. ZAŠTITA PRI RADU I SMJEŠTAJ POSADE Jan 2015Document44 pagesDIO 20. ZAŠTITA PRI RADU I SMJEŠTAJ POSADE Jan 2015Samo SpontanostNo ratings yet
- MCM (ENGLISH) Product SheetDocument4 pagesMCM (ENGLISH) Product SheetArdi PratamaNo ratings yet
- SDLP in Science July 18 2019Document5 pagesSDLP in Science July 18 2019Pinky MarieNo ratings yet
- Каталог Remeza - 2015 Ганновер 2015 PDFDocument32 pagesКаталог Remeza - 2015 Ганновер 2015 PDFbinhleduc36No ratings yet