Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Map Narrative Text
Uploaded by
Dinda NurkamilaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Map Narrative Text
Uploaded by
Dinda NurkamilaCopyright:
Available Formats
TYPES
1.) fable = a story that usally uses animals to teach moral lessons ( a fox and a grape) THE EXAMPLE OF WEST JAVA STORIES
2.) legend = a story which takes place within human history. Sangkuriang , Si kabayan, Lutung Kasarung, Situ
(tangkuban parahu, toba lake) Bagendit, and Ciung Wanara.
3.) myth = Stories that are based on tradition. (nyi roro kidul)
4.) fairy = is ashort story that belong to feature magic genre/folklore (cinderella)
5.) science fiction = a fictionalized story where in the plot are centered around
technology (space operah, star wars) THE EXAMPLE OF NATIONAL STORIES
Malin kundang, Timun mas, Si kancil,
LANGUAGE FEATURES Bawang merah & Bawang putih and kolor ijo
1.) Past tense = past tense is a tense that shows
you are talking about something that has already
happened. example : the cat died yesterday THE EXAMPLE OF INTERNATIONAL STORIES
2.) time connective = words that join phrases or pinocchio, willy wonka and the chocolate factory,
sentences together to help us understand when harry potter, snow white, and cinderella
something is happening. example : after, first,
eventually
3.) Qouted speech = a direct sentences. example :
roro jonggrang said, “i hate you!”
SOCIAL FUNCTION
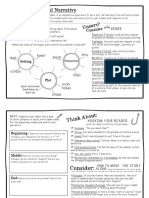
DEFINITION
Narrative text is a story or tale that
tells something imaginative essay or
NARRATIVE Social function of narrative text is to
amuse or entertain and to deal with actual or
vicarious experience in different ways.:
TEXT
something that only the creator
CHARACTERS
GENERIC STRUCTURE
•ORIENTATION : sets the scene: where and when
the story happened and introduces the
(group 4) character is participants presented as a role in a
narrative.
1.)Protagonist : refferred to as the main
participants of the story (who and what is character or hero.
involved in the story) 2.)Antagonist : is a character that represents
•COMPLICATION : Tells the beginning of the the opposition with protagonist
problems with leads to the crisis (climat) of the 3.)Deutragonist : the second most
main character. importantart after protagonist before
•RESOLUTION : when the problem (the crisis) is tritagonist
resolved either in a happy ending or in a sad 4.)Tritagonist : the third most important
(tragic)ending character after protagonist and deutragonist
ENDS
MORAL LESSONS ENDS is a final part of narrative text.
TYPES OF ENDING IS : happy ending, sad ending, resolved ending,
moral lessons is the lesson that narrative text teaches about how
unresolved ending, unexpected ending, expanded ending,
to behave in the world.
ambiquous ending
for example : you have to be patient to get what you want
You might also like
- 21ST Century Lit Chapter 1 Discussion NotesDocument7 pages21ST Century Lit Chapter 1 Discussion NotesKau BujoNo ratings yet
- Narrative Text - Infografis - KurmerDocument2 pagesNarrative Text - Infografis - KurmerCitra Arba RojunaNo ratings yet
- Readers: Reform For The PoorDocument6 pagesReaders: Reform For The PoorrosaNo ratings yet
- Narrative TeksDocument17 pagesNarrative TeksnatzyadeliaNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing FictionDocument28 pagesReading and Writing Fictiondowny FassionNo ratings yet
- Sastra Inggris Kelompok 4Document11 pagesSastra Inggris Kelompok 4bye xNo ratings yet
- SLG Eng1 5.1Document5 pagesSLG Eng1 5.1Christian MahusayNo ratings yet
- Lit - Elements HandoutDocument2 pagesLit - Elements HandoutDenise CañaNo ratings yet
- NarrativeDocument8 pagesNarrativeEvaNo ratings yet
- Narrative TextDocument23 pagesNarrative Text018-Diska LathifahNo ratings yet
- 41oe7s5pg Module 4 Creative WritingDocument14 pages41oe7s5pg Module 4 Creative WritingSteve Laurence PontilloNo ratings yet
- We Are Group 3!Document11 pagesWe Are Group 3!Ela LejoNo ratings yet
- Plot Elements - DisneyDocument23 pagesPlot Elements - DisneyssssssNo ratings yet
- Literary GenresDocument1 pageLiterary Genresf.evilla106No ratings yet
- I MA English Novel1Document25 pagesI MA English Novel1soundar12No ratings yet
- Old Testament Narrative: I. Meaning in The Text A. Levels of SignificationDocument11 pagesOld Testament Narrative: I. Meaning in The Text A. Levels of SignificationВладимир ПекићNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Lesson 1Document5 pagesUNIT 1 Lesson 1FonzyNo ratings yet
- The Craft of Fiction - Language IIDocument6 pagesThe Craft of Fiction - Language IIAmira AndinoNo ratings yet
- ProseDocument5 pagesProseAJ LlegoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Fiction: - Setting - Character - Plot - Point View - Theme - Symbolism - OtherDocument19 pagesElements of Fiction: - Setting - Character - Plot - Point View - Theme - Symbolism - OtherBaby Joan Alcazar100% (1)
- Plot and Plot Structure. Theoretical PreliminariesDocument36 pagesPlot and Plot Structure. Theoretical Preliminarieschernikka daryaNo ratings yet
- BAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryDocument11 pagesBAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryMutia ArumNo ratings yet
- FictionDocument3 pagesFictionmichelleanngonzales20No ratings yet
- CNF Lesson 1Document37 pagesCNF Lesson 1Jewel PascuaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quater Lesson 1Document65 pages2nd Quater Lesson 1Jomarie PauleNo ratings yet
- Micro Teaching MalefecintDocument9 pagesMicro Teaching MalefecintthouSANd foodNo ratings yet
- Elementsof FictionDocument30 pagesElementsof FictionTracy PattersonNo ratings yet
- Elements of Fiction: Setting Character Plot Point View Theme Symbolism OtherDocument17 pagesElements of Fiction: Setting Character Plot Point View Theme Symbolism OtherGoogle SucksNo ratings yet
- GE ELEC 02 HandoutDocument5 pagesGE ELEC 02 Handoutmic lobrinNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Q2 Week 3Document2 pages21st Century Q2 Week 3Mary Joy T CantorNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Q1W5Document39 pagesCreative Writing Q1W5Jhun Ar-Ar Roa RamosNo ratings yet
- Name: Anggita Fitri Yulidar Harahap Class: Bahasa Inggris 1 - PPG Daljab Um 2020 NIM: 203132776531Document5 pagesName: Anggita Fitri Yulidar Harahap Class: Bahasa Inggris 1 - PPG Daljab Um 2020 NIM: 203132776531Anggita HarahapNo ratings yet
- Narrative WritingDocument17 pagesNarrative WritingIULIA-MAGDALENA ARITONNo ratings yet
- Prosel 141109192045 Conversion Gate02Document19 pagesProsel 141109192045 Conversion Gate02Um ZainabNo ratings yet
- Mwa 2 FDDocument7 pagesMwa 2 FDapi-583798037No ratings yet
- LESSON 6 - Creative Writing ModuleDocument6 pagesLESSON 6 - Creative Writing ModuleAnmarie Bruno Ponlaon100% (1)
- BAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryDocument11 pagesBAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS Short StoryMutia ArumNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature 1Document8 pages21st Century Literature 1Zalamea, RyzaNo ratings yet
- Structures and Elements of ProseDocument19 pagesStructures and Elements of ProseJohn Lexter MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document18 pagesLesson 1Jaztine BacaniNo ratings yet
- Pyramidal Structure of A PlotDocument4 pagesPyramidal Structure of A PlotMarlou Castro AnteñeroNo ratings yet
- October 1, VIIIDocument16 pagesOctober 1, VIIIBirds HomeNo ratings yet
- Stories and Novels With Their KindsDocument20 pagesStories and Novels With Their KindsAaaNo ratings yet
- The Literature of The Philippines: (Fiction-Short Story)Document28 pagesThe Literature of The Philippines: (Fiction-Short Story)Angel YbanezNo ratings yet
- CNF LESSON 5-6 WEEK 5-6 ADocument45 pagesCNF LESSON 5-6 WEEK 5-6 AGuillermo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Novel Study Literary DevicesDocument5 pagesYear 10 Novel Study Literary Devicesapi-327257065No ratings yet
- Southeastern Mindanao Institute of Technology (SMIT), INC.: A. Elements of FictionDocument6 pagesSoutheastern Mindanao Institute of Technology (SMIT), INC.: A. Elements of FictionMars IndyNo ratings yet
- Creative WritingDocument17 pagesCreative Writingusagi GojoNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document32 pagesWeek 4Hannah CabatcanNo ratings yet
- Creative WritinDocument9 pagesCreative WritinadiksayyuuuuNo ratings yet
- Q4-HUMSS-Creative Writing-12-Week3Document4 pagesQ4-HUMSS-Creative Writing-12-Week3Joseph ClaveNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short Story Lesson PlanDocument60 pagesElements of A Short Story Lesson PlanMa. Clarissa MagatNo ratings yet
- 4B - Inglés B NS - Guion - Carranza - CesarDocument5 pages4B - Inglés B NS - Guion - Carranza - Cesar60287357No ratings yet
- Readings in Phil Lit Outline StoriesDocument26 pagesReadings in Phil Lit Outline StoriesBUEN, WENCESLAO, JR. JASMINNo ratings yet
- Elements of LiteratureDocument6 pagesElements of LiteratureYugal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 1) Types of CharactersDocument5 pages1) Types of Charactersvanessa joy cuevasNo ratings yet
- Plot and Structure: Irawati Pajrin PBI 4B SoreDocument12 pagesPlot and Structure: Irawati Pajrin PBI 4B SoreIrawati PajrinNo ratings yet
- Elements of ProseDocument40 pagesElements of Prosekate villanuevaNo ratings yet
- The VictorianDocument44 pagesThe VictorianSessylu TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Poets of Medieval EraDocument4 pagesPoets of Medieval EraLaiba ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Kafka BioDocument6 pagesKafka BioJohnNo ratings yet
- Zelda Medley SaxophoneDocument6 pagesZelda Medley SaxophoneSilvia TorresNo ratings yet
- Hedda Gabler Script AnalysisDocument2 pagesHedda Gabler Script AnalysisAlyssa EasterlyNo ratings yet
- Waiting For GodotDocument23 pagesWaiting For GodotIONELABNo ratings yet
- Final PPT FIGURES OF SPEECH DEMO TEACHING LAIRD SHEREIGNDocument25 pagesFinal PPT FIGURES OF SPEECH DEMO TEACHING LAIRD SHEREIGNMarvin PameNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century Literature TQ2Document4 pages21ST Century Literature TQ2Jundell DiazNo ratings yet
- Sentence Correction 2011 To 2016Document5 pagesSentence Correction 2011 To 2016ayub_baltic56% (9)
- Zad PDFDocument5 pagesZad PDFOrel BeilinsonNo ratings yet
- Tarikh e Masoodi (Mas'Udi) Tarjuma Muruj Al Zahab Wa Madin Al Jawahir Al Masoodi Jild-2 @Document429 pagesTarikh e Masoodi (Mas'Udi) Tarjuma Muruj Al Zahab Wa Madin Al Jawahir Al Masoodi Jild-2 @Faryal Yahya MemonNo ratings yet
- The Period Before ChaucerDocument6 pagesThe Period Before ChaucerDonald Jhey Realingo Morada100% (1)
- Essay Hooks ExamplesDocument4 pagesEssay Hooks Examplesdapysapowat2100% (2)
- Cinderella Story As Example of Narrative TextDocument2 pagesCinderella Story As Example of Narrative TextHikmatul Maghfiroh100% (1)
- Annexure - A - Contract AgreementDocument6 pagesAnnexure - A - Contract AgreementSameer ParmarNo ratings yet
- Anglo Saxon Period FULLDocument34 pagesAnglo Saxon Period FULLAulia AzharNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 Noc18 hs31 15Document3 pagesAssignment-1 Noc18 hs31 15Andrew KendallNo ratings yet
- A Definition of Translation TechniquesDocument7 pagesA Definition of Translation TechniquesMarkusMakuAldo100% (2)
- Cbse Worksheet 01 When I Set Out For Lyonnesse: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 2Document2 pagesCbse Worksheet 01 When I Set Out For Lyonnesse: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 2Meher KapoorNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Objectives:: Activity ADocument3 pagesTopic 3 Objectives:: Activity AJai GoNo ratings yet
- Chinese Mythology - An Introduction by Anne M. BirrellDocument268 pagesChinese Mythology - An Introduction by Anne M. BirrellMarlonNo ratings yet
- Superstitions and Beliefs Related To DeathDocument3 pagesSuperstitions and Beliefs Related To DeathHerbert Malayao HerboNo ratings yet
- Taijiquan 13 Powers v1 PDFDocument2 pagesTaijiquan 13 Powers v1 PDFconcretemanmcNo ratings yet
- Ganapati AtharvashirshaDocument16 pagesGanapati AtharvashirshaPhonetics laboratoryNo ratings yet
- Khaboris Manuscript - RTR Truth MediaDocument107 pagesKhaboris Manuscript - RTR Truth MediaTom Lacovara-Stewart RTR TruthMedia100% (2)
- JabberwockyDocument2 pagesJabberwockyapi-241172875No ratings yet
- Yeats Tarot and Golden Dawn - Kathleen RaineDocument30 pagesYeats Tarot and Golden Dawn - Kathleen Rainesrk777100% (8)
- 13 TH Age Landscape GM ScreenDocument4 pages13 TH Age Landscape GM ScreenQunariNo ratings yet
- (Eleni Hasaki) CeCeramic Kilns in Ancient Greece: Technology and Organization of Ceramic Workshopsramic Kilns of Ancient GreeceDocument591 pages(Eleni Hasaki) CeCeramic Kilns in Ancient Greece: Technology and Organization of Ceramic Workshopsramic Kilns of Ancient GreeceVahe Saryan100% (4)
- Introduction To Victorian Literature and The Physics of The ImponderableDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Victorian Literature and The Physics of The ImponderablePickering and Chatto100% (1)
- Thesis Writing by ZainDocument13 pagesThesis Writing by ZainZain Ul AbedienNo ratings yet