Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics 1.6
Uploaded by
KurtilicioussOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics 1.6
Uploaded by
KurtilicioussCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
PHYSICS
Conclusion
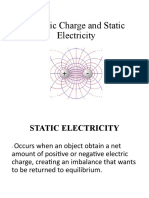
The majority of objects are electrically neutral, meaning they have an equal number of positive and negative
charges. One needs to change the charge balance between positive and negative charges in order to charge
an object. There are three means of achieving this: friction, conduction, and induction.
The charging by friction method is when material is rubbed with certain materials to gain an electric charge. One
example from the activity is the interaction between balloons rubbed on wool. There is a net transfer of
electrons from the wool to the balloon. Before rubbing, both balloon and wool were electrically neutral. It seems
that balloon has a greater affinity for additional electrons than wool, hence the transfer of electrons from the
wool to the balloon. Placing the balloon on its original place, after it has been rubbed enough times to the wool,
it becomes attracted to the wool. On the contrast, when bringing the two balloons closer to each other, the
balloons repel each other. This explains the interaction between objects with identical and opposite charges.
Like charges repel, unlike charges attract.
The charging by conduction method requires contacting a conductive material with a charged particle. When a
negatively charged rod is touched to the metal ball of the electroscope, some of the excess electrons on the rod
that are repelled by the close proximity of their neighboring excess electrons move over to the metal ball. The
metal ball and the negative rod share some of the excess of electrons that the charged rod previously had.
Both have some of the excess and hence both are negatively charged. Therefore, when a positively charged
rod is used, some of the free electrons on the metal ball of the electroscope are attracted over to the positive
rod to reduce some of its deficit of electrons. The electroscope and the rod share the deficit of electrons that the
rod previously had, and both have a positive charge.
Lastly, the induction charging is when after a material has been charged by rubbing, it may be used to charge
another material by a method which requires no contact between the two materials. For example from the
activity a negatively charged rod is brought near the electroscope and you touch the electroscope with your
finger, keeping the negative rod in place, electrons are induced to vacate the electroscope and flow through
your finger. When your finger is removed, the electroscope is left with a deficit of electrons and, therefore, a
positive charge. The leaves will remain apart even when the negative rod is removed.
You might also like
- Static Electricity: Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology & ConceptsDocument77 pagesStatic Electricity: Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology & ConceptsDERRICKKEANNo ratings yet
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electric Charge ExplainedDocument51 pagesElectric Charge ExplainedMarl Allen ReyesNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Direct Current PDFDocument76 pagesElectrostatics - Direct Current PDFRita UmutoniNo ratings yet
- 9 - Static Electricity CombinedDocument57 pages9 - Static Electricity CombinedAli khan7No ratings yet
- 51 52 Derivative of Exponential FunctionsDocument3 pages51 52 Derivative of Exponential FunctionsDan AvrukhNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Lesson 1 PDFDocument85 pagesQ3 - Lesson 1 PDFTimothy Francisco100% (1)
- Electric Charge and Field ForcesDocument3 pagesElectric Charge and Field ForcesAhmet UlusoyNo ratings yet
- The Special Theory of Relativity. Anadijiban DasDocument225 pagesThe Special Theory of Relativity. Anadijiban DasMarioNo ratings yet
- CV BasarabNicolescuDocument93 pagesCV BasarabNicolescuBasarab Nicolescu100% (3)
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument37 pagesElectric Forces and Electric FieldsJennifer Magango100% (1)
- International Islamic University Malaysia Course OutlineDocument5 pagesInternational Islamic University Malaysia Course Outlinebelkhair ahmed100% (2)
- Charging Processes-G7Document20 pagesCharging Processes-G7hmoncatar.bulNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The Phenomena and Properties of Stationary or SlowDocument6 pagesElectrostatics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The Phenomena and Properties of Stationary or SlowfunandruinsNo ratings yet
- Capitelli M., Bruno D., Laricchiuta A. - Fundamental Aspects of Plasma Chemical Physics. Transport - 2013 PDFDocument364 pagesCapitelli M., Bruno D., Laricchiuta A. - Fundamental Aspects of Plasma Chemical Physics. Transport - 2013 PDFNelson EspinelNo ratings yet
- Electr Ic Forces Charge Interactions: Opposites (+/-) Attract and Likes (+/+ or - / - ) RepelDocument8 pagesElectr Ic Forces Charge Interactions: Opposites (+/-) Attract and Likes (+/+ or - / - ) Repelapi-27085921No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledMMann, Ryan Philip A.No ratings yet
- Electricity: Introductio NDocument17 pagesElectricity: Introductio NPavelNo ratings yet
- Electricity 01 - Electric ChargeDocument16 pagesElectricity 01 - Electric ChargeAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive ChargeDocument6 pagesELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive Chargecatherine SitatiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electric CircuitsDocument54 pagesTopic 2 Electric CircuitsMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- 115 PPT Electrostatics Origin Electrostatics CapacitanceDocument67 pages115 PPT Electrostatics Origin Electrostatics CapacitanceErojo, Kyeane Red N.No ratings yet
- 1st WeekDocument5 pages1st WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 - Module 1Document31 pagesGeneral Physics 2 - Module 1Nicole anne loredoNo ratings yet
- Charging by FrictionDocument33 pagesCharging by FrictionlostgirlNo ratings yet
- Phy CHP 1 NotesDocument33 pagesPhy CHP 1 Notesayaan ahmedNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY AT RESTDocument27 pagesELECTRICITY AT RESTRomel PanisNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Document33 pagesElectric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Maryam MehekNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument44 pagesPhysics ProjectAvnish TewariNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields ExplainedDocument16 pagesElectric Charges and Fields ExplainedAishwarya AishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Charging Bodies and ElectroscopeDocument23 pagesCharging Bodies and Electroscoperajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Charging by ConductionDocument7 pagesCharging by Conductionimanuelsukarno0% (1)
- Phy2 Unit Test 1Document21 pagesPhy2 Unit Test 1JACOB SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Kaunas University of TechnologyDocument8 pagesFaculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Kaunas University of TechnologyDar MudasirNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument4 pagesElectric ChargeDis DoodNo ratings yet
- Triboelectric Series and Induction ChargingDocument6 pagesTriboelectric Series and Induction ChargingDanielle Danica Alcuizar BaguioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 - 10 Electric ChargeDocument4 pagesChapter 0 - 10 Electric ChargeshengNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicsジョンNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument7 pagesPhysics NotesSoe ThiriNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeDocument19 pagesElectrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeManishKumarNo ratings yet
- Conduction and InductionDocument29 pagesConduction and Inductionalkinani.faithNo ratings yet
- Handout Static Electricity S3Document16 pagesHandout Static Electricity S3SUKU BUNGANo ratings yet
- Physics ResearchDocument4 pagesPhysics ResearchYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: An Interactive Module For BGSCE Physics Created by Mrs. C. Saunders - NeelyDocument18 pagesStatic Electricity: An Interactive Module For BGSCE Physics Created by Mrs. C. Saunders - NeelyChristanique McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument3 pagesReviewer in PhysicsBeatrice MararacNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 2022 KatikamuDocument24 pagesElectrostatics 2022 KatikamuWAFULA BRIAN OKANYANo ratings yet
- Electrostatic InductionDocument1 pageElectrostatic InductionArpit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges Physics SSS 1Document14 pagesElectric Charges Physics SSS 1aliutunde3495No ratings yet
- Electrostatic InductionDocument25 pagesElectrostatic InductionPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Charging ProcessesDocument23 pagesDifferent Types of Charging ProcessesRiah VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics CH1 Part - 1Document24 pagesElectrostatics CH1 Part - 1Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- PPT-Course 1-2-Charge Force Field Gaus PotentialDocument63 pagesPPT-Course 1-2-Charge Force Field Gaus PotentialRaul AtofaneiNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document5 pagesTask 1Marfe Salamat ManilaNo ratings yet
- Grounding - The Removal of A ChargeDocument3 pagesGrounding - The Removal of A ChargeimanuelsukarnoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GP2Document40 pagesLesson 1 GP2lovlegin diongNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument4 pagesStatic ElectricityMuhammad Wasil KhanNo ratings yet
- AP Lec 1Document14 pagesAP Lec 1Muhammad HaziqNo ratings yet
- Pearson CH 19 Sec 1 21-22Document20 pagesPearson CH 19 Sec 1 21-22Ghala AlholiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 7 Notesyooh9814No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument10 pagesPhysicsHuidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- DraftDocument3 pagesDraftgubajanajNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargesDocument31 pagesElectric ChargesJeorge QuiboyNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 7 Unit 8Document31 pagesPhysics Grade 7 Unit 8kidanemariam HabtemariamNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge FundamentalsDocument12 pagesElectric Charge FundamentalsKainat MusawarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics SS1Document6 pagesElectrostatics SS1OlusolaNo ratings yet
- Mass MovementDocument4 pagesMass MovementKurtilicioussNo ratings yet
- What Is Catholicism? - History, Tradition & Beliefs: Where Did The Roman Catholic Church Come From?Document2 pagesWhat Is Catholicism? - History, Tradition & Beliefs: Where Did The Roman Catholic Church Come From?KurtilicioussNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Mitigation Mass MovementDocument8 pagesPrevention and Mitigation Mass MovementKurtilicioussNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Mitigation Mass MovementDocument8 pagesPrevention and Mitigation Mass MovementKurtilicioussNo ratings yet
- Precautionary MeasuresDocument8 pagesPrecautionary MeasuresKurtilicioussNo ratings yet
- Mass MovementDocument4 pagesMass MovementKurtilicioussNo ratings yet
- Maths Teacher Resume TemplateDocument1 pageMaths Teacher Resume TemplateKurtilicioussNo ratings yet
- Input and Output in Damped Quantum Systems by Gardiner Collett PRA 1985 Paper ID V Imp Quantum Core PhysRevA.31.3761Document14 pagesInput and Output in Damped Quantum Systems by Gardiner Collett PRA 1985 Paper ID V Imp Quantum Core PhysRevA.31.3761Raktim HalderNo ratings yet
- Normal and Tangential Components of AccelerationDocument8 pagesNormal and Tangential Components of AccelerationihtishamqabidNo ratings yet
- Deal or No DealDocument33 pagesDeal or No Dealjenefer agustina magoraNo ratings yet
- Ginsberg ErrataDocument8 pagesGinsberg ErrataBenjamín AdolfNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts: Space Time MassDocument6 pagesFundamental Concepts: Space Time MassShahood MustafaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Matrix InversionDocument17 pagesMethods of Matrix InversionPaawanDubalNo ratings yet
- Section 3-9: Chain Rule: For Problems 1 - 51 Differentiate The Given Function. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6Document5 pagesSection 3-9: Chain Rule: For Problems 1 - 51 Differentiate The Given Function. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6Alglen GeronaNo ratings yet
- Charged ParticlesDocument19 pagesCharged Particlesjonan_evansNo ratings yet
- Strauss PDEch 1 S 1 P 01Document8 pagesStrauss PDEch 1 S 1 P 01Walter Torres MontesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure LecturesDocument31 pagesAtomic Structure LecturesHaibat Sultan StationeryNo ratings yet
- ME 1501 Computer Aided Design 2020 Odd Semster Tutorial Sheet No. 1Document1 pageME 1501 Computer Aided Design 2020 Odd Semster Tutorial Sheet No. 1Prateek ShivhareNo ratings yet
- MAT 435 Chapter 3: Functions of Two and Three Variables: 1 y X 3) Y, X (FDocument8 pagesMAT 435 Chapter 3: Functions of Two and Three Variables: 1 y X 3) Y, X (FlancaugilaNo ratings yet
- M 1.2 RMDocument16 pagesM 1.2 RMk thejeshNo ratings yet
- PS6Document9 pagesPS6cptudorNo ratings yet
- Jackson 5.11 Homework Problem SolutionDocument4 pagesJackson 5.11 Homework Problem SolutionJulia CesarNo ratings yet
- Derivative Rules and TechniquesDocument16 pagesDerivative Rules and TechniqueslegoNo ratings yet
- Biot Equations of MotionDocument2 pagesBiot Equations of MotionSriram GullapalliNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Chemical Physics Volume 20 Issue 4 1952 (Doi 10.1063 - 1.1700516) McClure, Donald S. - Spin-Orbit Interaction in Aromatic MoleculesDocument6 pagesThe Journal of Chemical Physics Volume 20 Issue 4 1952 (Doi 10.1063 - 1.1700516) McClure, Donald S. - Spin-Orbit Interaction in Aromatic MoleculesJustin MdNo ratings yet
- PDE Textbook (101 150)Document50 pagesPDE Textbook (101 150)ancelmomtmtcNo ratings yet
- European Organization For Nuclear ResearchDocument10 pagesEuropean Organization For Nuclear Researchutam555No ratings yet
- Question Bank MathDocument82 pagesQuestion Bank MathnimiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic EquilibriumDocument4 pagesThermodynamic EquilibriumtechzonesNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A Rigid Body: DM D D DM DFDocument3 pagesDynamics of A Rigid Body: DM D D DM DFAlessio ScarabelliNo ratings yet
- Classical Fields NotesDocument203 pagesClassical Fields NotesCassianoNo ratings yet
- Entanglement Made SimpleDocument4 pagesEntanglement Made SimpleMilan BasuNo ratings yet