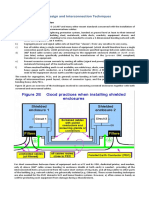
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BS7671 - Cable Installation Methods
Uploaded by
ant.gouldenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BS7671 - Cable Installation Methods
Uploaded by
ant.gouldenCopyright:
Available Formats
In the UK, common cable installation methods are outlined in BS 7671, also known as
the IET Wiring Regulations. These methods are classified with reference codes that
indicate how the cables are installed. Here are some of the most common methods:
Clipped Direct (Method C): Cables are clipped directly to a surface. This is a
common and straightforward method, often used for both indoor and outdoor
installations.
Conduit Systems (Method A): Cables are run through conduit, which provides
mechanical protection. This is typical in commercial or industrial installations
where additional protection against impact is necessary.
Trunking Systems (Method B): Cables are installed inside trunking, which is a type
of enclosed conduit. This method is often used in commercial buildings for ease of
access and cable management.
Underground Systems (Method D): Cables are buried underground, typically within
ducts. This method is used for external power supply lines.
Cable Tray (Method E): Cables are laid in cable trays, which are open on top. This
method is common in industrial environments where large numbers of cables are run
side by side.
Suspended or Elevated Systems (Method F): Cables are suspended, often above
ceilings or along walls, using supports or hangers.
Each installation method affects the current-carrying capacity of the cable, which
is detailed in the tables of BS 7671. For example, a cable clipped directly to a
wall will have a different current-carrying capacity than the same cable installed
in trunking. The selection of the installation method depends on various factors,
including the environmental conditions, mechanical protection required, and the
type of building.
For detailed guidance on cable installation methods, including the impact on
current-carrying capacity and other considerations, refer to Chapter 52 of BS 7671,
and specifically, Tables 52-3 to 52-10 provide details on current-carrying
capacities for different installation methods.
You might also like
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsFrom Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cable Reference Installation MethodsDocument2 pagesCable Reference Installation MethodsArshad TanoliNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom Systems-EC&MDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom Systems-EC&MJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Basics - of - Grounding and BondingDocument8 pagesBasics - of - Grounding and BondingSegun KehindeNo ratings yet
- Cable Laying and Pulling: Neutro À Terra June 2017Document5 pagesCable Laying and Pulling: Neutro À Terra June 2017Pradeep PooNoorNo ratings yet
- IEC Installation Reference MethodsDocument1 pageIEC Installation Reference MethodsJayagurunathanNo ratings yet
- Cable Reference Installation Methods - Open ElectricalDocument3 pagesCable Reference Installation Methods - Open ElectricalDoly DamanikNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation Lesson 17, 18, 19, and 20Document12 pagesElectrical Installation Lesson 17, 18, 19, and 20Sharon AmondiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom SystemsDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom SystemsSDE BSS KollamNo ratings yet
- Race WaysDocument4 pagesRace WaysJula CandorNo ratings yet
- Building Services Design: Electrical Installation (Higher)Document55 pagesBuilding Services Design: Electrical Installation (Higher)Zaharadeen Muhammad HamdanaNo ratings yet
- Installation Tips For Prefabricated Busbar Systems and Cables - EEPDocument7 pagesInstallation Tips For Prefabricated Busbar Systems and Cables - EEPkrit_kasemNo ratings yet
- What Engineers Should Know About Using Conduits in Power Substation DesignsDocument5 pagesWhat Engineers Should Know About Using Conduits in Power Substation DesignsManuel Henríquez SantanaNo ratings yet
- Electrical System of BuildingDocument86 pagesElectrical System of BuildingCatherineNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar: Bus Bars, Bus Duct, Cable Bus and CablesDocument29 pagesBus Bar: Bus Bars, Bus Duct, Cable Bus and CablesKhaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- EMCDocument10 pagesEMCTaner ErtürkNo ratings yet
- Compact Substation SolutionsDocument6 pagesCompact Substation SolutionsAnsul PrasadNo ratings yet
- Aerial Fiber Optic Cable OverviewDocument7 pagesAerial Fiber Optic Cable OverviewSted KingNo ratings yet
- Elsevier - A Technical Evaluation Framework For The Connection of DG To The Distribution NetworkDocument11 pagesElsevier - A Technical Evaluation Framework For The Connection of DG To The Distribution Networkstarmd3No ratings yet
- Telecom Earthing 2005Document13 pagesTelecom Earthing 2005Ats ByNo ratings yet
- Cables - Cable For Petrochemical Plants IEEESTANDARD1242Document10 pagesCables - Cable For Petrochemical Plants IEEESTANDARD1242cadtil100% (1)
- Tray and Ladder Practice GuideDocument73 pagesTray and Ladder Practice GuidemariusrotaruNo ratings yet
- Design Structured Cabling Systems and IT Network InfrastructuresDocument4 pagesDesign Structured Cabling Systems and IT Network InfrastructuresJm Garcia100% (1)
- Lecture 02 Workshop - Converted-1Document24 pagesLecture 02 Workshop - Converted-1Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringDocument15 pagesLearning Outcome: Estimating and Costing in Electrical EngineeringJEFFREY BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Reference Architecture Design Guide Part 3,0Document100 pagesReference Architecture Design Guide Part 3,0gurkan arif yalcinkayaNo ratings yet
- Structured Cabling System (SCS) : Web Proforum Tutorials The International Engineering Consortium 1/19Document19 pagesStructured Cabling System (SCS) : Web Proforum Tutorials The International Engineering Consortium 1/19Camilo R.Ortega M.No ratings yet
- Sistemi I IT Dhe TelefoniseDocument5 pagesSistemi I IT Dhe Telefonisedukagjin ramqajNo ratings yet
- AC Substation Detailed Design Guidelines Best Practice Dos and DontsDocument29 pagesAC Substation Detailed Design Guidelines Best Practice Dos and Dontsahmad shakeebNo ratings yet
- Grounding and Overvoltage Protection IP 16-4-1: ScopeDocument11 pagesGrounding and Overvoltage Protection IP 16-4-1: ScopeMara LiceoNo ratings yet
- Epri Capitulo12Document48 pagesEpri Capitulo12Juan Carlos Nizama Arrunategui100% (1)
- Cable Selection and Wiring SystemDocument34 pagesCable Selection and Wiring SystemMuhammad Faiz bin Ahmad Shafi0% (1)
- 3466 - Revised Solar PV Checklist - June 2017Document8 pages3466 - Revised Solar PV Checklist - June 2017Electricité & Instrumentation Gassi TouilNo ratings yet
- EMC Design and Interconnection Techniques: Cable Routing and ConnectionDocument27 pagesEMC Design and Interconnection Techniques: Cable Routing and ConnectionMurali MohanNo ratings yet
- Cable TrayDocument28 pagesCable Traykirink73No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom SystemsDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom SystemsrajuanthatiNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar ProtectionDocument9 pagesBus Bar ProtectionparameshvkrNo ratings yet
- Design Consideration of Electrical InstallationDocument29 pagesDesign Consideration of Electrical InstallationBhavarth Vaidya100% (4)
- Distribution in Low-Voltage Installations: Chapter EDocument8 pagesDistribution in Low-Voltage Installations: Chapter EMidhun VargheseNo ratings yet
- Towards A Meaningful Standard For PV Array Installation in AustraliaDocument4 pagesTowards A Meaningful Standard For PV Array Installation in AustraliaHon KiatNo ratings yet
- Trunking System of Electrical Systems76927 - 10 PDFDocument14 pagesTrunking System of Electrical Systems76927 - 10 PDFLeila Cherop100% (3)
- Chapter 2-Electrical Wiring CircuitsDocument43 pagesChapter 2-Electrical Wiring CircuitsyeabmotherNo ratings yet
- Specification Standard Grounding and Bonding 27 05 26 Part 1: GeneralDocument9 pagesSpecification Standard Grounding and Bonding 27 05 26 Part 1: GeneralDeny SafariNo ratings yet
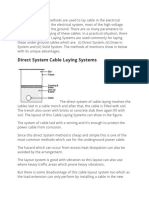
- Direct System Cable Laying SystemsDocument3 pagesDirect System Cable Laying SystemsDavid StuartNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom SystemsDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Grounding and Bonding Telecom SystemsanrpemNo ratings yet
- Earthing (Grounding) and Bonding Guidelines For Uniprise Solutions F/UTP Cabling SystemDocument11 pagesEarthing (Grounding) and Bonding Guidelines For Uniprise Solutions F/UTP Cabling Systemcharleselitb92No ratings yet
- Typical Telecom Earthing, Surge and LPDocument22 pagesTypical Telecom Earthing, Surge and LPAhmed BilalNo ratings yet
- Testing Bus DuctDocument3 pagesTesting Bus Ductlam9021No ratings yet
- He HeheDocument47 pagesHe HeheWinwinwin DeldeldeldelNo ratings yet
- 1383 A Practical Guide To Lightning Protection and Australia and NZDocument15 pages1383 A Practical Guide To Lightning Protection and Australia and NZandyhilbertNo ratings yet
- Grounding and BondingDocument47 pagesGrounding and BondingCharles BenwariNo ratings yet
- On The Insulation Co-Ordination Studies Using (Emtp)Document5 pagesOn The Insulation Co-Ordination Studies Using (Emtp)adauNo ratings yet
- Bộ Môn Hệ Thống Điện Khoa Điện-Đhbk ĐànẵngDocument46 pagesBộ Môn Hệ Thống Điện Khoa Điện-Đhbk ĐànẵngA3 Phòng Điều ĐộNo ratings yet
- Diary Report SirDocument14 pagesDiary Report SirNeeraj PurohitNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseFrom EverandDistribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electrical Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Practical Methods for Analysis and Design of HV Installation Grounding SystemsFrom EverandPractical Methods for Analysis and Design of HV Installation Grounding SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet