Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microscopee
Uploaded by
anaodtohan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThe brightfield compound microscope uses two lens systems to magnify specimens placed on the stage under illumination. It has four objective lenses with increasing magnifications: scanner at 4x, low power at 10x, high power at 45x, and oil immersion at 100x. Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the eyepiece magnification, usually 10x, by the objective magnification. The oil immersion objective requires using immersion oil of refractive index 1.516 between the objective and specimen slide to improve resolution. Proper use of the microscope involves focusing with the coarse and fine adjustment knobs while changing between objectives.
Original Description:
Original Title
microscopee
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe brightfield compound microscope uses two lens systems to magnify specimens placed on the stage under illumination. It has four objective lenses with increasing magnifications: scanner at 4x, low power at 10x, high power at 45x, and oil immersion at 100x. Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the eyepiece magnification, usually 10x, by the objective magnification. The oil immersion objective requires using immersion oil of refractive index 1.516 between the objective and specimen slide to improve resolution. Proper use of the microscope involves focusing with the coarse and fine adjustment knobs while changing between objectives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesMicroscopee
Uploaded by
anaodtohanThe brightfield compound microscope uses two lens systems to magnify specimens placed on the stage under illumination. It has four objective lenses with increasing magnifications: scanner at 4x, low power at 10x, high power at 45x, and oil immersion at 100x. Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the eyepiece magnification, usually 10x, by the objective magnification. The oil immersion objective requires using immersion oil of refractive index 1.516 between the objective and specimen slide to improve resolution. Proper use of the microscope involves focusing with the coarse and fine adjustment knobs while changing between objectives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
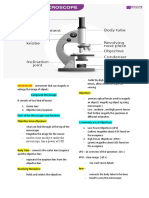
INTRODUCTION TO BRIGHTFIELD MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE LENSES
simplest type of compound microscope is the 1. SCANNER: Magnification: 4x
Brightfield compound microscope. 2. LOW POWER OBJECTIVE (LPO):
word “compound” from Brightfield Compound -Magnification: 10x
Microscope means “specimen positioned properly on -forms general outline or wider portion of the object.
the stage of a microscope and illuminated by a light 3. HIGH POWER OBJECTIVE (HPO):
-Magnification: 45x
source will be magnified by two-lens system.”
-longer than the LPO and it forms a bigger image if the
word “brightfield” means “magnified objects appear
object in focus.
as dark objects against a bright background.” A
-enlarge specimens are small under LPO.
sufficient contrast must exist between the magnified
4. OIL IMMERSION OBJECTIVE (OIO):
object and the brightfield background for the objects to -HIGHEST DEGREE OF MAGNIFICATION
be visible. -Magnification: 100x
THE PATH OF LIGHT -examine stained smear preparations of microorganisms
using immersion oil as their medium.
OCULAR LENS- image of the specimen is
Calculating the Total Magnification
magnified
- As “eyepiece” TOTAL MAGNIFICATION = Magnifying power of the eyepiece x
OBJECTIVE LENS- light rays Magnifying power of the objective used
CONDENSER-lenses that direct the light rays
Magnifying power of the eyepiece = 10
ILLUMINATOR- light source
Magnifying power of the objective used = 100 (OIO)
IMPORTANCE OF USING IMMERSION OIL
Correct Manipulation of Microscope
immersion oil has the same refractive index as the glass
slide 1. Place the specimen slide on the stage and secure it with the
IO is used, light rays do not refract stage clips. Arrange the portion of the slide to be examined
resolving power of the lenses. over the central opening stage.
2. Rotate the low power objective into place under the body
When oil is not used with an oil immersion objective
tube. You will feel a “click” when it is correctly place.
lens, the image becomes fuzzy, with poor resolution.
3. Raise the condenser as high as it will go.
HOW TO APPLY? 4. Rotate the coarse adjustment knob clockwise to bring down
the LPO close but not touching the slide, until the specimen
oil used in oil immersion is “CEDAR WOOD OIL”. is seen through the eyepiece.
refractive index is: 1.516. 5. Regulate the intensity of light by opening or closing the iris
diaphragm
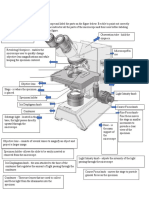
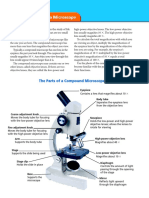
PARTS OF THE MICROSCOPE
6. Sharpen the focus by turning the fine adjustment knob.
Structural Components 7. Turn the LPO to HPO without elevating the body tube.
Notice that it will be almost in focus because most
1.HEAD/BODY-houses the optical parts microscopes are parfocal. Little adjustments with fine
2.ARM- supports the microscope head adjustment knob will only be needed to clearly view the
object in focus.
- carry microscope NOTE: The HPO has a smaller aperture than the LPO, hence
it will be necessary to open the iris diaphragm further in
3.BASE-supports the microscope and houses the illuminator
order to fill the objective aperture with light
Optical Components 8. To focus the oil immersion lens, swing the oil immersion
objective halfway towards the specimen in focus. Place a
1. EYEPIECE/OCULAR- remagnifies the image formed by the drop of immersion oil on the smear. Swing the oil immersion
objective lens; standard magnifying power is 10x. lens in place. Using the coarse adjustment, bring the
2. EYEPIECE TUBE- holds the eyepieces in place above objective down until it touches the oil. Find the object by
objective lenses. gently turning the coarse adjustment knob upwards.
3. OBJECTIVE LENSES- primary lenses magnifies specimen. Sharpen the focus with the fine adjustment knob.
4. NOSEPIECE-rotating turret
9. Compare the relative sizes from those seen under the LPO,
5. COARSE ADJUSTMENT KNOB- bigger wheel used to adjust
HPO, & OIO.
the LPO in focusing; initial focusing.
6. FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB- smaller wheel for final focusing 10. Clean the stage and the lenses after each use, before
of the specimen using HPO and OIO; make the specimen returning the microscope to the stockroom.
more vivid.
7. STAGE- slide/specimen is placed for focusing.
8. STAGE CLIPS- hold the slide in place
9. ILUMINATOR- light source
10. CONDENSER- collect and focus the light from illuminator
11. IRIS DIAPHRAGM- controls the amount of light
12. CONDENSER FOCUS KNOB- moves the condenser up or
down to control the lighting focus on the specimen.
You might also like
- 12 G Diagrama Electrico PDFDocument7 pages12 G Diagrama Electrico PDFcristian chuquicondor torres100% (2)
- LAB EXERCISE 2 Microscope AssDocument5 pagesLAB EXERCISE 2 Microscope AssArianne Jans MunarNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1 MicrosDocument7 pagesLab Exercise 1 MicrosaluapNo ratings yet
- Pc210lc-11 Sen06695-01 Circuit DiagramsDocument26 pagesPc210lc-11 Sen06695-01 Circuit DiagramsdatphuongNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lab Prelims PDFDocument15 pagesBacte Lab Prelims PDFRochellane Ramos PlasabasNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Kit List For KyoceraDocument83 pagesMaintenance Kit List For KyoceraEdgar EbarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Laboratory: Lab Report # 2 (MICROSCOPY)Document4 pagesMicrobiology Laboratory: Lab Report # 2 (MICROSCOPY)Kyla Nicole100% (1)
- Meiller Kipper Rear Tipper VOLVO - 0026 - 0115 - 083 - 6X4 - en - RusDocument23 pagesMeiller Kipper Rear Tipper VOLVO - 0026 - 0115 - 083 - 6X4 - en - RusGora FedotovNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 Microscope Anph111Document7 pagesLab Exercise 2 Microscope Anph111Den VerdoteNo ratings yet
- 1937 Enigma Manual - English Translation2Document5 pages1937 Enigma Manual - English Translation2R. EthierNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument30 pagesMicroscopy ReviewMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Selection Nfpa 14 & Nfpa 20Document38 pagesFire Pump Selection Nfpa 14 & Nfpa 20SIA PRESUPUESTOS100% (1)
- Bacte Lab - Prelim ExamDocument30 pagesBacte Lab - Prelim ExamDanielle Anne LambanNo ratings yet
- Microscope: Adelaide, Savero, & CharissaDocument12 pagesMicroscope: Adelaide, Savero, & CharissaPMIB Matrikulasi FKUI 2018/2019No ratings yet
- Transes-Micropara Lab PrelimsDocument4 pagesTranses-Micropara Lab Prelimsmikhyla.cardenoNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 MicrosDocument2 pagesPMLS 2 MicrosYlyza MarquezNo ratings yet
- A. Bonifacio Integrated School Supplemental Activities in Science 7 Second Quarter Week 1Document3 pagesA. Bonifacio Integrated School Supplemental Activities in Science 7 Second Quarter Week 1Rose Ann ChavezNo ratings yet
- Microscope Exp MarkingDocument5 pagesMicroscope Exp Markingjoybagga1910No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab NotesDocument24 pagesAnaphy Lab NotesBrylle MitchiNo ratings yet
- Microscope Usage and Handling Procedures: A. IntroductionDocument5 pagesMicroscope Usage and Handling Procedures: A. Introductiongrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- Eyepiece Objective Lenses Head Nosepiece: Proper Care and HandlingDocument1 pageEyepiece Objective Lenses Head Nosepiece: Proper Care and HandlingRafael SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 EDITED #1Document8 pagesExperiment 1 EDITED #1Ronel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument9 pagesScience NotesClaire MaeNo ratings yet
- Micp211 (Lab) ReviewerDocument2 pagesMicp211 (Lab) ReviewerMAV TAJNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab Activity 1Document6 pagesBiology Lab Activity 1Adrian Anthony Villaluz GasatayaNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument4 pagesZoologyLaylamaeNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument2 pagesMICROSCOPEErica Lumamba TabiosNo ratings yet
- Name: TAN, Julie Anne A. HHIS221 BSMT 2-Y1-1S: Ocular LensDocument2 pagesName: TAN, Julie Anne A. HHIS221 BSMT 2-Y1-1S: Ocular LensJulie Anne TanNo ratings yet
- HHIS221Document2 pagesHHIS221Julie Anne TanNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY SHEET ACT.1 LOQUIRE and GUIAPAR 1Document5 pagesLABORATORY SHEET ACT.1 LOQUIRE and GUIAPAR 1Mary Criscebel Kyla LoquireNo ratings yet
- Study of Compound Microsope: Aim of The Experiment PrincipleDocument4 pagesStudy of Compound Microsope: Aim of The Experiment PrincipleCHIRAJIT KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Tabalba 1 Y1 2 Microscope 1Document6 pagesTabalba 1 Y1 2 Microscope 1Shane V. Tabalba100% (1)
- Microscopy Hand NotesDocument10 pagesMicroscopy Hand NotesAmeeraNo ratings yet
- RK GoyalDocument2 pagesRK Goyalvyjain4573No ratings yet
- All About Microscope PresentationDocument11 pagesAll About Microscope Presentationearlyn angelie gopioNo ratings yet
- Lab Microscope ChartDocument2 pagesLab Microscope ChartFrankiesgirl6yrNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPEFelisa Pauline VallarNo ratings yet
- Study of Compound Microsope: Aim of The Experiment PrincipleDocument4 pagesStudy of Compound Microsope: Aim of The Experiment PrincipleCHIRAJIT KUNDUNo ratings yet
- The Microscope PDFDocument10 pagesThe Microscope PDFPrincess Angie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Unit 2 Topic 3 Cells, Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument74 pages3.1 Unit 2 Topic 3 Cells, Reproduction and DevelopmentAhmed AimanNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument4 pagesMICROSCOPEChelsea SebastianNo ratings yet
- Jeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFDocument3 pagesJeanne Erika Asio - Activity 1-Microscope PDFJeanne AsioNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroscopeDocument3 pages1 MicroscopeMary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- Histo Lab Exercise #1Document3 pagesHisto Lab Exercise #1Gela ReyesNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument65 pagesThe Cellsherylhanda45No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of A Microscope 2019Document18 pagesParts and Functions of A Microscope 2019Janielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesCompound Light MicroscopeCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- GenBio1 Quarter 3 (Inc)Document6 pagesGenBio1 Quarter 3 (Inc)carlosbolecheNo ratings yet
- SLHT Science 7 Q2 Week 1 (Ok)Document9 pagesSLHT Science 7 Q2 Week 1 (Ok)Sarah Mae TulodNo ratings yet
- Setting Up A Microscope For Use Putting Away A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesSetting Up A Microscope For Use Putting Away A MicroscopeAlexis PepitoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 ScriptDocument3 pagesScience 7 Scriptangeline vacalaresNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationDocument3 pagesInstruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationCyndel TindoyNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope: Objective Lenses CondenserDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope: Objective Lenses CondenserAnna Gabriela GuingonNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document15 pagesLab 3aizen3881No ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument4 pagesThe MicroscopeRyz DoctoraNo ratings yet
- K P Pathrose Vaidyan'S Kandamkulathy Vaidyasala Po Mala, KuzhurDocument2 pagesK P Pathrose Vaidyan'S Kandamkulathy Vaidyasala Po Mala, KuzhurANU M ANo ratings yet
- Microscope FinalDocument55 pagesMicroscope FinalpompocafeNo ratings yet
- Micp Lab Act # 01 MicrosDocument6 pagesMicp Lab Act # 01 MicrosEdel GapasinNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercises For BiologyDocument13 pagesLab Exercises For BiologyMari SoleiNo ratings yet
- Appendix B Using A Microscope PDFDocument2 pagesAppendix B Using A Microscope PDFJae GarcisoNo ratings yet
- Introduction:: The Use and Care of The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesIntroduction:: The Use and Care of The MicroscopeMohammad MalikNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument7 pagesMicrosJaeyun RuiNo ratings yet
- At Least 0.4 NM Apart Numerical ApertureDocument5 pagesAt Least 0.4 NM Apart Numerical ApertureRaffy FlandesNo ratings yet
- Microscope BasicsDocument7 pagesMicroscope Basicsuytud6tid67No ratings yet
- Dslr: The Beginners Guide to Master Camera & Improve (Learn How to Master the Art of Dslr Photography)From EverandDslr: The Beginners Guide to Master Camera & Improve (Learn How to Master the Art of Dslr Photography)No ratings yet
- Blood TypingDocument2 pagesBlood TypinganaodtohanNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture NotesDocument13 pagesVenipuncture NotesanaodtohanNo ratings yet
- CPH Lab - Vital Signs NotesDocument3 pagesCPH Lab - Vital Signs NotesanaodtohanNo ratings yet
- URINALYSISDocument5 pagesURINALYSISanaodtohanNo ratings yet
- Vivicam 4000 User ManualDocument83 pagesVivicam 4000 User ManualDeeNo ratings yet
- E Catalog Baru FIX 020123Document16 pagesE Catalog Baru FIX 020123luqman elektromedisNo ratings yet
- Kyocera Mita KM 2530 Km3530 KM 4030 Service ManualDocument688 pagesKyocera Mita KM 2530 Km3530 KM 4030 Service ManualJoel Wasserman50% (2)
- CatalogDocument2 pagesCatalogMai Văn BáchNo ratings yet
- Sma Sunny Central 500heDocument92 pagesSma Sunny Central 500heJayapavidranNo ratings yet
- Pipe SealsDocument32 pagesPipe SealsSekhil DevNo ratings yet
- ILC-single Line Volumetric SystemDocument74 pagesILC-single Line Volumetric Systemfahmi derbel100% (1)
- 2009 Venza - Block Heater - InstallManual - RevD - Combined2 - 2GR-FE, 1AR-FE - ENGDocument6 pages2009 Venza - Block Heater - InstallManual - RevD - Combined2 - 2GR-FE, 1AR-FE - ENGtilsidNo ratings yet
- Ma 110Document2 pagesMa 110Jari JokipiiNo ratings yet
- Bluelight-Photoelectric Diffuse Sensor With Background SuppressionDocument2 pagesBluelight-Photoelectric Diffuse Sensor With Background SuppressionKien Nguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- Oberdorfer N200MDocument2 pagesOberdorfer N200MJavier GarciaNo ratings yet
- Refrig Dryers - High Inlet Temperature Dryers D25IT-A To D170IT-ADocument2 pagesRefrig Dryers - High Inlet Temperature Dryers D25IT-A To D170IT-AChanNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)Document15 pagesProgrammable Logic Controllers (PLC)DEMEKE BEYENENo ratings yet
- Silver Streak and Blue Streak Repair Manual: All Rights Reserved, UJ BackusDocument20 pagesSilver Streak and Blue Streak Repair Manual: All Rights Reserved, UJ BackusRonNo ratings yet
- Stellar - Spare Parts ProposalDocument1 pageStellar - Spare Parts ProposalPaul CansinoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Lighting in A BuildingDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Lighting in A BuildingGaffur BoliyaNo ratings yet
- Control Cables Unarmoured PVC - Control Cable SpecificationDocument1 pageControl Cables Unarmoured PVC - Control Cable SpecificationWires Cable100% (1)
- Condensate and Seal Pots Model CP: ApplicationsDocument4 pagesCondensate and Seal Pots Model CP: Applicationsmadhu gawadeNo ratings yet
- MODULE II (A)Document65 pagesMODULE II (A)Nazeema TTNo ratings yet
- Manual de DobladoraDocument234 pagesManual de Dobladorajuan henaoNo ratings yet
- CC Edition 10/04 Simplex Fire Alarm System Design Standards D-2.1Document3 pagesCC Edition 10/04 Simplex Fire Alarm System Design Standards D-2.1s.m.arunNo ratings yet
- Apocolypse Food Prep - DAX TutorialDocument3 pagesApocolypse Food Prep - DAX TutorialyashwanthNo ratings yet
- Door Wired AxtraxDocument5 pagesDoor Wired Axtraxsoft42ansNo ratings yet
- What Is Memosens Digital Sensor TechnologyDocument3 pagesWhat Is Memosens Digital Sensor TechnologySab-Win DamadNo ratings yet