Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New PSA Test
Uploaded by
Xahid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageNew PSA Test
Uploaded by
XahidCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
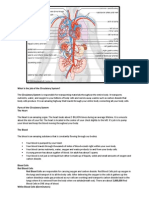
Blood is an important fluid that keeps us alive. We cannot live without it.
The heart pumps blood to all
parts of the body and brings them oxygen and food. At the same time blood carries all the substances
we don't need away from us. Blood fights infections, keeps our body temperature the same and carries
chemicals that control body functions. Finally, blood has substances that repair broken blood vessels so
that we don't bleed to death. Plasma is the liquid part of our blood. It makes up about 50-60% of it.
Plasma consists mostly of water but many other substances are in it. It contains dissolved food,
chemicals that control our growth and do other jobs, proteins, minerals and waste products. Red blood
cells look like flat round discs. They contain haemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen to the body and
gives blood its red colour. Each drop of blood has about 300 million of these red cells. White blood cells,
also called leukocytes, fight infections and harmful substances that invade the body. Most of these cells
are round and colourless. They have different sizes and shapes. White blood cells are not as numerous as
red ones. For every 700 red blood cells there is only one white blood cell. Platelets are tiny bodies that
are much smaller than red blood cells. They stick to the edges of a cut and form blood clots to stop
bleeding. The blood of a normal adult has about 2trillion platelets. The circulatory system carries blood
to all parts of your body. The heart pumps blood through big blood vessels called arteries and veins. In
our body there are also millions of small blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen, food and other
substances pass through the thin walls of these capillaries into the tissue. When you inhale air oxygen
passes through your lungs and and is picked up by haemoglobin which transports it to your whole body.
It is released into cells which produce energy. In return cells produce carbon dioxide which enters your
blood stream and is transported back to your lungs where it is exhaled. Food also reaches your body by
means of blood. It is digested in your stomach and important substances like fat, sugar, proteins,
vitamins and minerals are separated. These nutrients enter your blood stream and are moved to the
cells and muscles where they are needed in order to give you energy or fuel. The work of the muscles
and other tissue creates heat. Blood is the transporting system which carries heat throughout your body
and warms you. The things that you don't need are transported to your intestines and kidneys and leave
your body again. White blood cells play an important role in your immune system. When harmful
substances invade your body an alarm goes off and white blood cells are activated. Then they work to
destroy the invaders. They fight off viruses, harmful bacteria and begin anti-body production. Blood also
carries hormones to places where they are needed. When a hormone reaches a part of the body it
controls growth, how the body uses food and other things. You would bleed to death from a small cut if
your blood didn't clot. When a blood vessel breaks platelets rush to the damaged area and stick to one
another, forming a plug. Blood cells come from bone marrow. They begin as stem cells and then develop
into red or white blood cells, or platelets. They don't live forever and must be replaced by new ones. Red
blood cells live an average of 120days before wearing out. Then they are captured and destroyed in the
liver and spleen. Platelets live only for about 10days. The amount of blood in your body depends on your
size, weight and the altitude at which you live. An adult who weighs 80 kg has about 5 litres of blood, a
40 kg child about half the amount. People who live in high areas where the air is thinner need more
blood to deliver more oxygen to the body.
You might also like
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- What Is BloodDocument1 pageWhat Is BloodAygül HaciyevaNo ratings yet
- Blood WorksheetDocument2 pagesBlood WorksheetCarlos OsorioNo ratings yet
- Iii. Patient and His Illness A. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIii. Patient and His Illness A. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemFeba VARGHESENo ratings yet
- Blood WorksheetDocument5 pagesBlood Worksheetapi-296199660100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemJeffrey ErazoNo ratings yet
- A New Cancer Treatment: High Blood Pressure - A Silent KillerDocument3 pagesA New Cancer Treatment: High Blood Pressure - A Silent KillerUulAmrelNo ratings yet
- Blood ReadingDocument2 pagesBlood Readingapi-383564780No ratings yet
- The Components and Functions of BloodDocument2 pagesThe Components and Functions of BloodNana AhsanahNo ratings yet
- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia - Patho, Anatomy, and Diagnostic TestDocument66 pagesAcute Myelogenous Leukemia - Patho, Anatomy, and Diagnostic TestCharles Kevin L. Bataga33% (3)
- CirculatoryDocument9 pagesCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- Bone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorDocument6 pagesBone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorIanne Sandra SorrosaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemcatchivanNo ratings yet
- 5h-7-Thomas Lee Research Report Final March 2014Document3 pages5h-7-Thomas Lee Research Report Final March 2014api-251921674No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument3 pagesAnatomyKim CarpioNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Blood PC3Document4 pagesReading Comprehension Blood PC3Erik J. Roshan FloresNo ratings yet
- Main Components of Blood ExplainedDocument3 pagesMain Components of Blood ExplainedWild RoseNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lymphatic SystemJohn Lendel Maramo LunarNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Circulatory System)Document18 pagesGen Bio (Circulatory System)Kit KathNo ratings yet
- Teks BloodDocument2 pagesTeks BloodFazrie WahyuNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transport and Blood CirculationDocument10 pagesCirculatory System: Transport and Blood Circulationadriann strakerNo ratings yet
- Structured Task of FishewDocument6 pagesStructured Task of FishewDaisy KavinskyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartDocument6 pagesCirculatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartVance CeballosNo ratings yet
- The Body Systems - For MergeDocument57 pagesThe Body Systems - For MergeNicole DouglasNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyRamon PerroneNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System2Document9 pagesCirculatory System2Wajeeha AsifNo ratings yet
- Function of The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- B SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurDocument10 pagesB SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurMicaela Marcela Baldwin BarrigaNo ratings yet
- Blood: What Is It and Why Is It Important?Document31 pagesBlood: What Is It and Why Is It Important?Stelio SapatoruNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - BloodDocument7 pagesIGCSE - Bloodmubasherkatbar562No ratings yet
- Blood: What Is It and Why Is It Important?Document31 pagesBlood: What Is It and Why Is It Important?vallalNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System (Blood)Document57 pagesCirculatory System (Blood)Trisha NideaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of DengueDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Dengueciarkai_18No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Pathophysiology of AnemiaDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Pathophysiology of AnemiaDarlen Rabano88% (8)
- Presentation CSDocument21 pagesPresentation CSJeffreyYtienzaNo ratings yet
- ABT Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument85 pagesABT Anatomy & PhysiologyABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Biotecaaaaaaaah AnswerDocument2 pagesBiotecaaaaaaaah AnswerAldrin MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemMarco DadoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Transporting Nutrients & Oxygen Throughout the BodyDocument12 pagesThe Circulatory System: Transporting Nutrients & Oxygen Throughout the BodySonny BudimanNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Science 6 Arianne S. de Guzman 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Document3 pagesAssignment in Science 6 Arianne S. de Guzman 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Allana PonceNo ratings yet
- The Circulation of BloodDocument3 pagesThe Circulation of BloodTykmeto UrHartNo ratings yet
- Life Process Part 2 2Document32 pagesLife Process Part 2 2Anin BertNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemGlen MillarNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument1 pageCardiovascularBea H DulatreNo ratings yet
- Names and Functions of The Human AnatomiesDocument92 pagesNames and Functions of The Human AnatomiesShania Kate Ledesma ManabatNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in MammalsDocument8 pagesCirculatory System in MammalsObiora Ekene HilaryNo ratings yet
- Lec. (1) Medical PhysiologyDocument4 pagesLec. (1) Medical Physiologysic 20162085No ratings yet
- The Human Body: 25 Fantastic Projects Illuminate How the Body WorksFrom EverandThe Human Body: 25 Fantastic Projects Illuminate How the Body WorksNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument8 pagesBloodnn nnNo ratings yet
- Heart Structure and Blood Circulation Pathways in AnimalsDocument8 pagesHeart Structure and Blood Circulation Pathways in AnimalsKNo ratings yet
- Circulation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceDocument29 pagesCirculation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceHasan Mahmud Maruf 1621513630No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument92 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyzaneta.szuckaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular SytemDocument37 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular Sytemsophiapelayo326No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemkristineNo ratings yet
- Año de la lucha contra la corrupción y la impunidad en el EcuadorDocument5 pagesAño de la lucha contra la corrupción y la impunidad en el EcuadorHelen Salazar SagasteguiNo ratings yet
- How Blood WorksDocument11 pagesHow Blood Worksalexandruleconiuc6199No ratings yet
- Assignment in Science 6 John Marvin V. Sarile 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Document2 pagesAssignment in Science 6 John Marvin V. Sarile 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Allana PonceNo ratings yet
- Transportation NotesDocument12 pagesTransportation NotesavanishNo ratings yet
- Let's Go WalkaboutDocument1 pageLet's Go WalkaboutXahidNo ratings yet
- Let's Go WalkaboutDocument1 pageLet's Go WalkaboutXahidNo ratings yet
- 100 Opposite Words-1 PDFDocument5 pages100 Opposite Words-1 PDFMumtaz Ali Bukhari50% (2)
- Let's Go WalkaboutDocument1 pageLet's Go WalkaboutXahidNo ratings yet
- Visa Company PortalDocument1 pageVisa Company PortalXahidNo ratings yet
- Visa Company PortalDocument1 pageVisa Company PortalXahidNo ratings yet
- FIA (1200+ MCQs) Past test MCQs from VU exams Dec 2021Document109 pagesFIA (1200+ MCQs) Past test MCQs from VU exams Dec 2021Muntazir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Interview PSA KhanewalDocument1 pageInterview PSA KhanewalXahidNo ratings yet
- Interview PSA KhanewalDocument1 pageInterview PSA KhanewalXahidNo ratings yet
- Eng509 Recent Quiz 3Document57 pagesEng509 Recent Quiz 3XahidNo ratings yet
- ENG509 QUIZ (03-04) .PDF Version 1 (1) - 1Document69 pagesENG509 QUIZ (03-04) .PDF Version 1 (1) - 1XahidNo ratings yet
- 516 Finalterm Notes-1Document15 pages516 Finalterm Notes-1XahidNo ratings yet
- Edu305 Final Term PapersDocument16 pagesEdu305 Final Term PapersXahidNo ratings yet
- ENG509 QUIZ 03 Lesson (23-25)Document26 pagesENG509 QUIZ 03 Lesson (23-25)XahidNo ratings yet
- ??-All Sim Save Balance CodesDocument4 pages??-All Sim Save Balance CodesXahidNo ratings yet
- Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology Volume 71 Issue 6 2014 (Doi 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.06.015) Bronsnick, Tara Murzaku, Era Caterina Rao, Babar K. - Diet in DermatologyDocument12 pagesJournal of The American Academy of Dermatology Volume 71 Issue 6 2014 (Doi 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.06.015) Bronsnick, Tara Murzaku, Era Caterina Rao, Babar K. - Diet in Dermatologyxjorgwx100% (1)
- MMDST screening test evaluates child developmentDocument1 pageMMDST screening test evaluates child developmentCee Kaye GeeNo ratings yet
- Semen ExaminationDocument33 pagesSemen ExaminationDr.Vasant86% (7)
- Meridian System ExplainedDocument34 pagesMeridian System ExplainedYaqueli Mayta100% (2)
- Terapi LintahDocument3 pagesTerapi LintahDevi FitriNo ratings yet
- A Practical Handbook of Pancha Karma ProceduresDocument92 pagesA Practical Handbook of Pancha Karma ProceduresfatagiuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Farsalinos Study On Diacetyl in E-LiquidDocument1 pageDr. Farsalinos Study On Diacetyl in E-LiquidRuss WishtartNo ratings yet
- Reiki I ShodenDocument47 pagesReiki I ShodenSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- He NetherlandsDocument13 pagesHe NetherlandsDaniel LaoatenNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Concepts 2013: Consensus and ConcernsDocument99 pagesShoulder Concepts 2013: Consensus and ConcernsMichel HovsepianNo ratings yet
- From Start To Phase 1 in 30 Months - Insilico MedicineDocument9 pagesFrom Start To Phase 1 in 30 Months - Insilico MedicinejeanNo ratings yet
- (Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-1 Batch 3 2018 PDFDocument93 pages(Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-1 Batch 3 2018 PDFKomang Sudiase50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan of Integument SystemDocument27 pagesNursing Care Plan of Integument SystemAlfianGafar67% (3)
- 2020 Medical GuidelinesDocument406 pages2020 Medical Guidelinesanitn2020No ratings yet
- AVES SBFP Forms - 5A - 1 40 DAYS 2019 2020Document1 pageAVES SBFP Forms - 5A - 1 40 DAYS 2019 2020Kristian MagdoboyNo ratings yet
- Moya MoyaDocument5 pagesMoya MoyaNick Junior100% (1)
- Characteristics of Dubai's IR-DRGsDocument61 pagesCharacteristics of Dubai's IR-DRGstimvrghs123100% (1)
- Nortriptyline Tablets Prescribing InformationDocument10 pagesNortriptyline Tablets Prescribing InformationMirza MarufNo ratings yet
- List of Medical Professionals by SpecialtyDocument5 pagesList of Medical Professionals by SpecialtyRomina ParedesNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Critical CareDocument6 pagesCase Study On Critical CareJude Micko Bunyi AlipitNo ratings yet
- 00 Librocasosclinicosodontopediatra 2017Document146 pages00 Librocasosclinicosodontopediatra 2017Abigail Guillén PinoNo ratings yet
- Johnson & Johnson's Effective PR Saved TylenolDocument8 pagesJohnson & Johnson's Effective PR Saved Tylenolkusumawi2311No ratings yet
- Ryan Martin Ko, M.DDocument54 pagesRyan Martin Ko, M.DDhaval Makwana100% (2)
- Volunteer Orientation CheckListDocument1 pageVolunteer Orientation CheckListIsabella TNo ratings yet
- Preserving and Improving Memory As We Age: Proven Approaches Include Healthful Habits and Some Do-It-Yourself StrategiesDocument4 pagesPreserving and Improving Memory As We Age: Proven Approaches Include Healthful Habits and Some Do-It-Yourself StrategiesChrismoonNo ratings yet
- BHU M.SC SyllabiDocument422 pagesBHU M.SC Syllabiridip2009100% (1)
- Bioethics LectureDocument40 pagesBioethics LecturejeshemaNo ratings yet
- Ob Supplement Handout by DR - Chris SorianoDocument33 pagesOb Supplement Handout by DR - Chris SorianoHedley Chua75% (4)
- July 24 orDocument1 pageJuly 24 orนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Disc DiseaseDocument3 pagesDegenerative Disc DiseaseNikolas LawrenceNo ratings yet