Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Structure of An Egg 25
The Structure of An Egg 25
Uploaded by
alvimd1290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe document describes the internal structure of an egg. It discusses the internal and external membranes between the shell and albumen that provide defense against bacteria. It also describes the chalazae, which are plaques of egg white that hold the yolk in the center of the egg like anchors attaching the yolk covering to the eggshell membrane. The more prominent the chalazae, the fresher the egg.
Original Description:
Original Title
The structure of an Egg 25
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the internal structure of an egg. It discusses the internal and external membranes between the shell and albumen that provide defense against bacteria. It also describes the chalazae, which are plaques of egg white that hold the yolk in the center of the egg like anchors attaching the yolk covering to the eggshell membrane. The more prominent the chalazae, the fresher the egg.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 25
The Structure of An Egg 25
Uploaded by
alvimd129The document describes the internal structure of an egg. It discusses the internal and external membranes between the shell and albumen that provide defense against bacteria. It also describes the chalazae, which are plaques of egg white that hold the yolk in the center of the egg like anchors attaching the yolk covering to the eggshell membrane. The more prominent the chalazae, the fresher the egg.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
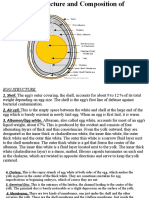
The structure of an Egg
2. Internal and external membranes
ocatedbetweentheshellandalbumenoftheegg,these
L
two transparent protein membranes give an effective
defenseagainstbacterialinvasion.However,youwillfind
them unexpectedly strong, If you haul these cloaks.
They're composed incompletely of keratin, a protein in
mortal hair.
The structure of an Egg
5. Chalazae
paque ropes of egg white, the chalazae hold the yolkin
O
the center of the egg. Like little anchors, they attach the
yolk covering to the eggshell membrane. The more
prominent they are, the fresher the egg will be.
You might also like
- Prepare Egg DishesDocument62 pagesPrepare Egg DishesKhan TanNo ratings yet
- Topic: Fertilization: Print Self Learning MaterialDocument9 pagesTopic: Fertilization: Print Self Learning MaterialNihalNo ratings yet
- Egg Composition and StructureDocument28 pagesEgg Composition and StructuregwenstefanabagNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 pagesExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Physical Structure and Composition of Eggs: Reported By:group 2Document13 pagesPhysical Structure and Composition of Eggs: Reported By:group 2Kathlyn S. Bendaña100% (1)
- Structure of An Ovum Structure and Function of A SpermDocument25 pagesStructure of An Ovum Structure and Function of A SpermTiffany Joy QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 23Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 23alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 24Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 24alvimd129No ratings yet
- Veterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 6Document3 pagesVeterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 6john benedickNo ratings yet
- Gr10 EggStructureDocument14 pagesGr10 EggStructureLenLen PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- EggDocument3 pagesEggIsmail DzaficNo ratings yet
- Group Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 2Document3 pagesGroup Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 2Kayl Dustin MalalisNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7 - The Avian EggDocument5 pagesExercise 7 - The Avian EggSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE 2 - OogenesisDocument4 pagesLAB EXERCISE 2 - OogenesisGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Structure of GametesDocument4 pagesStructure of Gametesapi-481318101No ratings yet
- Practical No 2Document16 pagesPractical No 2Jannat FatimaNo ratings yet
- 3Gr10 EggStructureDocument23 pages3Gr10 EggStructureLenLen PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT 6 PHYSIOLOGY OF PREGNANCYDocument98 pagesReproduction PPT 6 PHYSIOLOGY OF PREGNANCYlisanames.23No ratings yet
- Online Notebook Orange VariantDocument20 pagesOnline Notebook Orange VariantKiara Alexzine Samantha MalakiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 - Embryology LabDocument3 pagesExercise 3 - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Practical ProgrammingDocument3 pagesPractical ProgrammingSubramanian AnanthanarayananNo ratings yet
- DLP Week 1 - Cookery 12Document6 pagesDLP Week 1 - Cookery 12Christine PinedaNo ratings yet
- Exercise5 Mature OvumDocument7 pagesExercise5 Mature OvumleyNo ratings yet
- Adm Format Tle 10 CookeryDocument19 pagesAdm Format Tle 10 CookeryMay Ann Guinto100% (2)
- EXERCISE5 MATURE OVUM1dddddddDocument4 pagesEXERCISE5 MATURE OVUM1dddddddbingchillingNo ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 35Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 35alvimd129No ratings yet
- Avian Hens EggDocument1 pageAvian Hens EggAthena NocetoNo ratings yet
- Cookery 12 Prepare Egg Dishes Learning Outcome 1 To 4Document91 pagesCookery 12 Prepare Egg Dishes Learning Outcome 1 To 4d5g5szsyy4No ratings yet
- Physical Structure and Composition of EggsDocument22 pagesPhysical Structure and Composition of EggsDe ShangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document14 pagesLesson 1Elizabeth ReyesNo ratings yet
- Practical No 1Document13 pagesPractical No 1Jannat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Physical Structure and Composition of EggsDocument8 pagesPhysical Structure and Composition of EggsSantos, Glorifhel C.No ratings yet
- Physical Structure and Composition of EggsDocument37 pagesPhysical Structure and Composition of EggsAre Em GeeNo ratings yet
- City of Malaybalay: San Isidro College Integrated Basic EducationDocument3 pagesCity of Malaybalay: San Isidro College Integrated Basic EducationJessie Cris GumonayNo ratings yet
- Tips On The Structure Composition and Properties of The Egg ZucamiDocument12 pagesTips On The Structure Composition and Properties of The Egg ZucamiGrecia LopezNo ratings yet
- Physical Structure and Composition of EggsDocument31 pagesPhysical Structure and Composition of EggsCatherine Bercasio Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 OogenesisDocument7 pagesActivity 2 OogenesisHILARY PARAGAS. CORUÑANo ratings yet
- Developmental GeneticsDocument20 pagesDevelopmental GeneticsProjjal SanyalNo ratings yet
- Structure and Composition of An EggDocument16 pagesStructure and Composition of An EggRosalyn DelfinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - TleDocument12 pagesLesson 1 - TleJhon Anthony CatinoyNo ratings yet
- AM G09: FertilizationDocument60 pagesAM G09: FertilizationTURPIAS RamelynNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Eggs With Example PDFDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Eggs With Example PDFAniruddh JhanwarNo ratings yet
- Embryology-Lecture Notes-I Different Types of Eggs With ExamplesDocument8 pagesEmbryology-Lecture Notes-I Different Types of Eggs With ExamplesWilfordNo ratings yet
- (Unit 4) Human GametesDocument8 pages(Unit 4) Human GametesHanif AlfarizkiNo ratings yet
- 202004080636590834shailie Egg StructureDocument4 pages202004080636590834shailie Egg Structuretame4217No ratings yet
- Type of EggDocument4 pagesType of EggFina NafrillaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10 The Avian Egg PDFDocument3 pagesExercise 10 The Avian Egg PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint - EGGSDocument39 pagesPowerpoint - EGGSkrestina lacamraNo ratings yet
- Look at The Diagrams Identity The Testes and Ovaries. What Do They Have in Common Although They Are Found in Two Separate Systems?Document15 pagesLook at The Diagrams Identity The Testes and Ovaries. What Do They Have in Common Although They Are Found in Two Separate Systems?PATRICIA BROOKSNo ratings yet
- 1 Egg & Egg Cookery LectureDocument15 pages1 Egg & Egg Cookery LectureErin DelavinNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Nursing Care of The Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildDocument24 pagesUnit I: Nursing Care of The Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildBlaise Anne InocNo ratings yet
- Structure of An EggDocument6 pagesStructure of An EggJeissa LaraNo ratings yet
- Practical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectDocument6 pagesPractical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectAfridi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Biology: Find and Fuse: Unsolved Mysteries in Sperm - Egg RecognitionDocument11 pagesBiology: Find and Fuse: Unsolved Mysteries in Sperm - Egg RecognitionFlavio NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2 Oogenesis: WMSU-ISMP-GU-002.00Document6 pagesActivity No. 2 Oogenesis: WMSU-ISMP-GU-002.00Ferhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- Human Sex Cells Worksheet SupportDocument2 pagesHuman Sex Cells Worksheet SupportJohanna UrwinNo ratings yet
- Part 1 EggDocument46 pagesPart 1 EggKyejean BayubayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07 Infertility TRANSDocument5 pagesChapter 07 Infertility TRANSTiffany Joy QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Cytoskeleton: AP BiologyDocument29 pagesThe Cell: Cytoskeleton: AP BiologyMaria Fareed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- قواعد تحقيق الحلم عربي الجزء الثالثDocument26 pagesقواعد تحقيق الحلم عربي الجزء الثالثalvimd129No ratings yet
- قواعد تحقيق الحلم عربي الجزء الثانيDocument21 pagesقواعد تحقيق الحلم عربي الجزء الثانيalvimd129No ratings yet
- خوابوں کو سچا بنانے کے اصول- اردو حصہ 2Document21 pagesخوابوں کو سچا بنانے کے اصول- اردو حصہ 2alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 37Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 37alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 47Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 47alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 26Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 26alvimd129No ratings yet
- Rules To Make Dreams True - English P1Document20 pagesRules To Make Dreams True - English P1alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 27Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 27alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 34Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 34alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 6Document1 pageThe Structure of An Egg 6alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 13Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 13alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 12Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 12alvimd129No ratings yet
- Depraion Page 1Document1 pageDepraion Page 1alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 35Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 35alvimd129No ratings yet
- WJ - Teen Depression Rose Sharply During The Pandemic, But Treatment Didn't FollowDocument3 pagesWJ - Teen Depression Rose Sharply During The Pandemic, But Treatment Didn't Followalvimd129No ratings yet
- Depression Page 3Document1 pageDepression Page 3alvimd129No ratings yet
- Academic IELTS - LISTENING (Hand Written Note)Document14 pagesAcademic IELTS - LISTENING (Hand Written Note)alvimd129No ratings yet
- SelfDocument1 pageSelfalvimd129No ratings yet
- 01 Academic IELTS - A To Z INSTRUCTION (Hand Written Note)Document41 pages01 Academic IELTS - A To Z INSTRUCTION (Hand Written Note)alvimd129No ratings yet
- Academic IELTS - SPEAKING (Hand Written Note)Document3 pagesAcademic IELTS - SPEAKING (Hand Written Note)alvimd129No ratings yet