Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Structure of An Egg 35
Uploaded by
alvimd1290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesThe document describes the structure of an egg. It discusses the air cell that forms when the egg cools after laying, located at the larger end of the egg. It also describes the chalazae, which are ropes of egg white that hold the yolk in the center and attach it to the eggshell membrane, with more prominent chalazae indicating a fresher egg.
Original Description:
Original Title
The structure of an Egg 35
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the structure of an egg. It discusses the air cell that forms when the egg cools after laying, located at the larger end of the egg. It also describes the chalazae, which are ropes of egg white that hold the yolk in the center and attach it to the eggshell membrane, with more prominent chalazae indicating a fresher egg.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 35
Uploaded by
alvimd129The document describes the structure of an egg. It discusses the air cell that forms when the egg cools after laying, located at the larger end of the egg. It also describes the chalazae, which are ropes of egg white that hold the yolk in the center and attach it to the eggshell membrane, with more prominent chalazae indicating a fresher egg.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
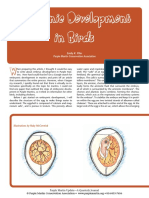
The structure of an Egg
3. Air cell
n air space forms when the contents of the eggcoolandcontractafterlaying.Theaircellisgenerally
A
located between the external and inner membranes at the egg's larger end and represents the crater
frequently seen at the end of a hard-boiled egg. The air cell grows as the egg periods.
The structure of an Egg
5. Chalazae
paque ropes of egg white, the chalazae hold the yolkin
O
the center of the egg. Like little anchors, they attach the
yolk covering to the eggshell membrane. The more
prominent they are, the fresher the egg will be.
You might also like
- Exercise5 Mature OvumDocument7 pagesExercise5 Mature OvumleyNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE5 MATURE OVUM1dddddddDocument4 pagesEXERCISE5 MATURE OVUM1dddddddbingchillingNo ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 34Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 34alvimd129No ratings yet
- Veterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 6Document3 pagesVeterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 6john benedickNo ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 15Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 15alvimd129No ratings yet
- EggDocument3 pagesEggIsmail DzaficNo ratings yet
- Eggs p6 Cracking Open InstructionsDocument1 pageEggs p6 Cracking Open InstructionsAqua AvilaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 23Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 23alvimd129No ratings yet
- Exercise 7 - The Avian EggDocument5 pagesExercise 7 - The Avian EggSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- Avian Hens EggDocument1 pageAvian Hens EggAthena NocetoNo ratings yet
- Gr10 EggStructureDocument14 pagesGr10 EggStructureLenLen PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Practical No 2Document16 pagesPractical No 2Jannat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Composition of An EggDocument16 pagesStructure and Composition of An EggRosalyn DelfinNo ratings yet
- Physical Structure and Composition of EggsDocument37 pagesPhysical Structure and Composition of EggsAre Em GeeNo ratings yet
- Embryology, Types of EggDocument21 pagesEmbryology, Types of EggHoney krishnaNo ratings yet
- Foldings of Embryo Foetal Period 1Document22 pagesFoldings of Embryo Foetal Period 1Riya SinghNo ratings yet
- Online Notebook Orange VariantDocument20 pagesOnline Notebook Orange VariantKiara Alexzine Samantha MalakiNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Diagram Labelling SampleDocument2 pagesIELTS Reading Diagram Labelling SampleManu SehgalNo ratings yet
- Burung Matin PDFDocument2 pagesBurung Matin PDFRiskian Alfaro BabtistaNo ratings yet
- Adm Format Tle 10 CookeryDocument19 pagesAdm Format Tle 10 CookeryMay Ann Guinto100% (2)
- Diagram Label Completion General 2Document3 pagesDiagram Label Completion General 2Abd UllahNo ratings yet
- AnimalsDocument9 pagesAnimalssolomon MekonninNo ratings yet
- Prepare Egg DishesDocument62 pagesPrepare Egg DishesKhan TanNo ratings yet
- Embryology-Lecture Notes-I Different Types of Eggs With ExamplesDocument8 pagesEmbryology-Lecture Notes-I Different Types of Eggs With ExamplesWilfordNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Eggs With Example PDFDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Eggs With Example PDFAniruddh JhanwarNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10: Perform Mise en Place (Egg Dishes)Document20 pagesCookery 10: Perform Mise en Place (Egg Dishes)Mary Ann Valenzuela BusaniaNo ratings yet
- Practical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectDocument6 pagesPractical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectAfridi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 202004080636590834shailie Egg StructureDocument4 pages202004080636590834shailie Egg Structuretame4217No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 25Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 25alvimd129No ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document14 pagesLesson 1Elizabeth ReyesNo ratings yet
- The EggDocument6 pagesThe Eggapi-262572717100% (1)
- Human Development Days 1-4Document43 pagesHuman Development Days 1-4Kriztine Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Egg Composition and StructureDocument28 pagesEgg Composition and StructuregwenstefanabagNo ratings yet
- Vi Semester B. SC Zoology Practicals Study of Embryological Slides Frog BlastulaDocument11 pagesVi Semester B. SC Zoology Practicals Study of Embryological Slides Frog BlastulaSuchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: Egg InoculationDocument15 pagesExperiment No. 2: Egg InoculationILHAM BAGUS DARMA .NNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants: Cape Biology Unit 1Document19 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants: Cape Biology Unit 1Santhiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Mangile's Pigeon Pages: The 'Egg Hatching' ProcessDocument6 pagesMangile's Pigeon Pages: The 'Egg Hatching' ProcessMariale Arauz RizoNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology of Frog: SpermDocument21 pagesDevelopmental Biology of Frog: SpermRavindra MadurNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology of Frog: SpermDocument21 pagesDevelopmental Biology of Frog: SpermRavindra MadurNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Chick EmbryoDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Chick EmbryoMiel MercadoNo ratings yet
- Parts of An Egg 2Document9 pagesParts of An Egg 2Limüel Trillana ÜNo ratings yet
- B10 - ReproductionDocument5 pagesB10 - Reproductionpiechloe597No ratings yet
- Cleavage Partitions The Zygote Into Many Smaller CellsDocument10 pagesCleavage Partitions The Zygote Into Many Smaller CellssispulieNo ratings yet
- Physical Structure and Composition of Eggs: Reported By:group 2Document13 pagesPhysical Structure and Composition of Eggs: Reported By:group 2Kathlyn S. Bendaña100% (1)
- VANA2210 LaboratoryAcivity6Document3 pagesVANA2210 LaboratoryAcivity6Leticia Rose SunicoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 - Gross Morphology of The Chick EmbryoDocument5 pagesExercise 8 - Gross Morphology of The Chick EmbryoSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- Incubator BasicsDocument13 pagesIncubator BasicsSelva Mara CoutoNo ratings yet
- Type of EggDocument4 pagesType of EggFina NafrillaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Ovule and TypesDocument10 pagesStructure of Ovule and TypesJemson KhundongbamNo ratings yet
- Frog EmbryologyDocument8 pagesFrog EmbryologyklumabanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Answer KeyDocument7 pagesReproductive System Answer Keyapi-209542414No ratings yet
- Embyology UG Part II Note 2 - Development of Amphioxus Drprity Mam2Document8 pagesEmbyology UG Part II Note 2 - Development of Amphioxus Drprity Mam2Adwika DeoNo ratings yet
- 3Gr10 EggStructureDocument23 pages3Gr10 EggStructureLenLen PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Ana 209Document15 pagesAna 209ADELAJA SAMUELNo ratings yet
- If You Must Print:: Please Print at Least 6 Slides Per PageDocument15 pagesIf You Must Print:: Please Print at Least 6 Slides Per PagebongkoNo ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 37Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 37alvimd129No ratings yet
- Extra Embryonic Membranes E-ContentDocument25 pagesExtra Embryonic Membranes E-ContentLydia Angel HartonoNo ratings yet
- Structure of GametesDocument4 pagesStructure of Gametesapi-481318101No ratings yet
- EggLayingHensPres PDFDocument62 pagesEggLayingHensPres PDFkalaiarasi ravichandranNo ratings yet
- Pigeons - A Collection of Articles on the Origins, Varieties and Methods of Pigeon KeepingFrom EverandPigeons - A Collection of Articles on the Origins, Varieties and Methods of Pigeon KeepingNo ratings yet
- قواعد تحقيق الحلم عربي الجزء الثانيDocument21 pagesقواعد تحقيق الحلم عربي الجزء الثانيalvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 37Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 37alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 47Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 47alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 25Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 25alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 26Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 26alvimd129No ratings yet
- WJ - Teen Depression Rose Sharply During The Pandemic, But Treatment Didn't FollowDocument3 pagesWJ - Teen Depression Rose Sharply During The Pandemic, But Treatment Didn't Followalvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 6Document1 pageThe Structure of An Egg 6alvimd129No ratings yet
- The Structure of An Egg 27Document2 pagesThe Structure of An Egg 27alvimd129No ratings yet
- Depression Page 3Document1 pageDepression Page 3alvimd129No ratings yet
- Depraion Page 1Document1 pageDepraion Page 1alvimd129No ratings yet
- 01 Academic IELTS - A To Z INSTRUCTION (Hand Written Note)Document41 pages01 Academic IELTS - A To Z INSTRUCTION (Hand Written Note)alvimd129No ratings yet
- SelfDocument1 pageSelfalvimd129No ratings yet
- Academic IELTS - SPEAKING (Hand Written Note)Document3 pagesAcademic IELTS - SPEAKING (Hand Written Note)alvimd129No ratings yet
- Academic IELTS - LISTENING (Hand Written Note)Document14 pagesAcademic IELTS - LISTENING (Hand Written Note)alvimd129No ratings yet