Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phy Worksheet
Phy Worksheet
Uploaded by
7217 Mithil PatilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phy Worksheet
Phy Worksheet
Uploaded by
7217 Mithil PatilCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 4
Topic: Work and Energy
Question 1
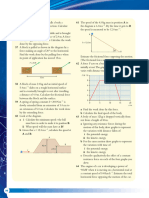
The figure below shows the free fall of a ball of mass m from positions A through B and C.
Initially, the ball is stationary at position A. It then drops through B and eventually to C on the ground.
a) Complete the table above by stating the magnitudes
Position Energy Explanation
UA = Because height is h
A
KA = Because v = 0
UB = Because height is (h – x)
B
KB = v2 = 2gx, since v2 – u2 = 2aS
UC = Because h = 0
of the gravitational potential energy U C
and kinetic energy K at each of the KC = v2 = 2gh, since v2 – u2 = 2aS
positions A, B and C respectively.
b) Assuming that no energy is transferred to the surroundings, state the sum of gravitational potential
energy (total energy) at positions A, B and C respectively.
Position Gravitational PE (U) Kinetic Energy (K) Total Energy
c) State the law of conservation of energy.
Question 2
The figure below illustrates a simple pendulum bob suspended using a string such that it is at a certain
height above the ground.
The pendulum bob is initially stationary at its mean position M.
a) When the bob is at rest at M, it has _______________________________________ ________________________ energy.
b) When the bob is pulled to position X,
i. Its height above the ground (increases / decreases / remains the same).
ii. Therefore its gravitational potential energy also (increases / decreases / remains the same).
c) When the bob is released from X, it returns to M.
i. The increased gravitational potential energy converts to _____________________ energy.
ii. At this position the kinetic energy is (maximum / minimum / zero).
d) Because the bob now has kinetic energy, it swings to the extreme position Y.
i. The kinetic energy of the bob at Y becomes (maximum / minimum / zero).
ii. This is because the kinetic energy is used to (increase / decrease) the gravitational potential
energy of the pendulum bob.
e) If there is air resistance,
i. The amplitude of the oscillations keeps on (increasing / decreasing ).
ii. This is because in every oscillation, some of the kinetic energy is converted into ____________
energy and _______________ energy.
f) If the air resistance is zero, the pendulum continues swinging _____________________.
Question 3
a) A ball has a mass of 0.5 kg. Dropped from a cliff top, the ball hits the sea below at a velocity of 10 m.s-1.
i. What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it is about to hit the sea? (25 J)
ii. What was the ball’s gravitational potential energy before it was dropped? (25 J)
iii. From what height was the ball dropped? (5 m)
b) A ball of mass 1.5 kg falls from a building whose height is 40 m. Calculate
i. The kinetic energy of the ball after 1 second. (75 J)
ii. The gravitational potential energy of the ball after 1 second (525 J)
You might also like
- Chapter 6 Work, Energy and PowerDocument12 pagesChapter 6 Work, Energy and PowerZhu Jiankun100% (1)
- Exercise WorkshopDocument5 pagesExercise WorkshopDanna SofíaNo ratings yet
- Standards For Low Voltage Embedded GenerationDocument26 pagesStandards For Low Voltage Embedded GenerationCliffNo ratings yet
- 2013-05-27 Voith Generators PDFDocument5 pages2013-05-27 Voith Generators PDFBruno OliveiraNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument40 pagesRevisionshrija nooporNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Work and EnergyDocument2 pagesSummative Test Work and EnergySha RonNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy Problems Worksheet 6Document3 pagesConservation of Energy Problems Worksheet 6Balkis MungurNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 4 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 4 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- PeKe RevisionmidtopicDocument4 pagesPeKe RevisionmidtopiccNo ratings yet
- Sample QuizDocument4 pagesSample QuizJohn Mark CabicunganNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document3 pagesExercise 3Banny SaiNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2013 SOLUtIONDocument7 pagesNsejs 2013 SOLUtIONAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.7 Work, Energy, Power and EfficiencyDocument12 pagesLesson 2.7 Work, Energy, Power and EfficiencyRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Work Energy Power and MachineDocument28 pages3.3 Work Energy Power and MachineGladys KNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, Power & MachinesDocument54 pagesWork, Energy, Power & MachinesYvonne NtinyariNo ratings yet
- P2 Energy ReviseDocument6 pagesP2 Energy ReviseSamuel ChenNo ratings yet
- FR MomentumDocument22 pagesFR MomentumJanel Edwards0% (1)
- DPP+ +WPE+one+shot+++mock+test+Document90 pagesDPP+ +WPE+one+shot+++mock+test+rahul kmNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics EnergyDocument5 pagesIGCSE Physics EnergySufyanNo ratings yet
- 242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarDocument21 pages242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarEffendi HabibieNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6-Ii (Heights & Distance)Document11 pagesChapter-6-Ii (Heights & Distance)Deepika PaulNo ratings yet
- Physics Test: A) Infinite B) Zero C) Positive (D) NegativeDocument3 pagesPhysics Test: A) Infinite B) Zero C) Positive (D) Negativebapasito969No ratings yet
- Worksheet Ch8Document3 pagesWorksheet Ch8polatgulec47No ratings yet
- Work Power and EnergyDocument8 pagesWork Power and Energyapi-275290316No ratings yet
- 242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarDocument21 pages242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarDhimas RimbangNo ratings yet
- 242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarDocument21 pages242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarsuidanoverniNo ratings yet
- hw7 ch8Document8 pageshw7 ch8faisalphyNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet For Grade 9Document4 pagesPhysics Worksheet For Grade 9Kassahun100% (1)
- HSSRptr-Chapter 6 Notes-Work, Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesHSSRptr-Chapter 6 Notes-Work, Energy and Powerbeatsof22No ratings yet
- 4 Friction (Wedge Friction)Document2 pages4 Friction (Wedge Friction)RAMAKANT RANA0% (1)
- Beban Terdistribusi PDFDocument18 pagesBeban Terdistribusi PDFDeni Juhana SuhermanNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.10 Understanding Work, Energy, Power and EfficiencyDocument12 pagesLESSON 2.10 Understanding Work, Energy, Power and Efficiencychekgu_2007No ratings yet
- Work, Power, Energy Review - KeyDocument4 pagesWork, Power, Energy Review - KeyRainNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - CH 5 Work and EnergyDocument25 pagesAP Physics 1 - CH 5 Work and EnergyNeil SolasNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power: FiitjeeDocument37 pagesWork Energy Power: Fiitjeekushagrajoshi69No ratings yet
- 期中复习答案Document14 pages期中复习答案IDKNo ratings yet
- 2nd LE - Set A PDFDocument12 pages2nd LE - Set A PDFLester Jason T. ChengNo ratings yet
- Physics An Algebra Based Approach 1st Edition Mcfarland Test BankDocument38 pagesPhysics An Algebra Based Approach 1st Edition Mcfarland Test Bankloganyjl9th100% (14)
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- F Wedge+Pseudo 18 07 2021 TestDocument2 pagesF Wedge+Pseudo 18 07 2021 TestAryanNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 LE2 ReviewerDocument14 pagesPhysics 71 LE2 ReviewerLoyd BascoNo ratings yet
- Physics An Algebra Based Approach 1St Edition Mcfarland Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesPhysics An Algebra Based Approach 1St Edition Mcfarland Test Bank Full Chapter PDFjonathanwelchjrcizmsdty100% (9)
- Chapter 8: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy: Answers To Even-Numbered Conceptual QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy: Answers To Even-Numbered Conceptual QuestionsRoger Lenin Maya MartinezNo ratings yet
- Impo. WpeDocument24 pagesImpo. WpeChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- PhysicssDocument4 pagesPhysicssmozajNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy Problems Worksheet 2Document3 pagesConservation of Energy Problems Worksheet 2Balkis MungurNo ratings yet
- Exercise Workshop PDFDocument5 pagesExercise Workshop PDFVANESSA ESPEJO LEAÑONo ratings yet
- 5 Worksheet (AS) Work Power and EnergyDocument3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) Work Power and EnergyMahad Asim100% (2)
- Electric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialDocument11 pagesElectric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialTshiamo MotaungNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument6 pagesEnergyapi-3806615No ratings yet
- LP Week 34 Science 8Document4 pagesLP Week 34 Science 8rommel mukayNo ratings yet
- ICSE Work Power Energy TestDocument2 pagesICSE Work Power Energy TestHarsh GulatiNo ratings yet
- 5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Almas TalibNo ratings yet
- Com and CollisionsDocument6 pagesCom and Collisionsarun2006No ratings yet
- AP FR Quiz #27 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument2 pagesAP FR Quiz #27 Simple Harmonic Motionbok choiNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Motion - 2 - Sec 3Document6 pagesTopical Test Motion - 2 - Sec 3Imam Akbar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Ai2TS-2 (XI) - Test - (18-12-2023) - Final PaperDocument21 pagesAi2TS-2 (XI) - Test - (18-12-2023) - Final Papertechnical yogeshNo ratings yet
- Pogil - Ke PeDocument4 pagesPogil - Ke Peapi-259781257No ratings yet
- Dynamo (Diogo, Fustiga, Pires, Cristo) (Modo de CompatibilidadeDocument7 pagesDynamo (Diogo, Fustiga, Pires, Cristo) (Modo de CompatibilidadefemacureNo ratings yet
- HYOSUNG Wind Turbine System: Wind Energy Business DivisionDocument6 pagesHYOSUNG Wind Turbine System: Wind Energy Business DivisionE. Javier Fernandez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- AP-chem Thermochemistry 2018-01-08Document285 pagesAP-chem Thermochemistry 2018-01-08Kashyap MuraliNo ratings yet
- The 9f PlatformDocument8 pagesThe 9f Platformsevero97No ratings yet
- SMC-3 Specs PDFDocument3 pagesSMC-3 Specs PDFManuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 Transformer PDFDocument50 pagesLecture6 Transformer PDFAhmad Akram100% (1)
- CB Techical RequirementDocument22 pagesCB Techical RequirementsoksopheaNo ratings yet
- Static Shunt CompensationDocument16 pagesStatic Shunt CompensationAlisha AnjumNo ratings yet
- Uncovering The Missing Secrets of MagnetismDocument99 pagesUncovering The Missing Secrets of MagnetismPuzzleMasterNo ratings yet
- CHEN403-Unit Operation 1 Fluid Flow and Mechanical Operations, 25th Edition-KA Gavhane-2015 PDFDocument381 pagesCHEN403-Unit Operation 1 Fluid Flow and Mechanical Operations, 25th Edition-KA Gavhane-2015 PDF521 Balaji ONo ratings yet
- Power For The People Stirling Engines For Domestic CHPDocument6 pagesPower For The People Stirling Engines For Domestic CHPAwais ChaudryNo ratings yet
- Improvised Hydroelectric GeneratorDocument29 pagesImprovised Hydroelectric GeneratorVincent LambanNo ratings yet
- Stat MechanicsDocument46 pagesStat MechanicsBala RajaNo ratings yet
- Unit 10Document2 pagesUnit 10Thảo PhươngNo ratings yet
- CET Datasheet Enclosure Systems 48Vdc-120VacDocument5 pagesCET Datasheet Enclosure Systems 48Vdc-120VacAlejandro Garcia MNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: MR Edd VillamorDocument25 pagesThermodynamics: MR Edd VillamorEdd VillamorNo ratings yet
- Totalenergies Marine Fuels The Drive For Cleaner Marine Fuels DigitalDocument23 pagesTotalenergies Marine Fuels The Drive For Cleaner Marine Fuels DigitalManuel RibeiroNo ratings yet
- 1ST Periodical Exam Sci. 8Document5 pages1ST Periodical Exam Sci. 8richardsamranoNo ratings yet
- Lb-Xp12-350-Pd-En-V1.3-201912 - EquivalenteDocument2 pagesLb-Xp12-350-Pd-En-V1.3-201912 - EquivalenteDaniel Oliveira Freitas RochaNo ratings yet
- Asco Series Nt320 Nuclear CatalogDocument4 pagesAsco Series Nt320 Nuclear CatalogJota JotaNo ratings yet
- Protein Adsorption Review by Vogler PDFDocument37 pagesProtein Adsorption Review by Vogler PDFMangesh PantawaneNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Manipulator Type ScaraDocument9 pagesDesign and Construction of A Manipulator Type ScaraHari Kirupakar100% (1)
- Forces Movement Shape and Momentumqp UnlockedDocument13 pagesForces Movement Shape and Momentumqp UnlockedPrerna JainNo ratings yet
- GEN - EDUC - Ultimate-With-AnsDocument132 pagesGEN - EDUC - Ultimate-With-AnsElromer S. TaripeNo ratings yet
- Free Energy Generation Using FlywheelDocument12 pagesFree Energy Generation Using FlywheelOshan IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Thermal Master 500Document2 pagesThermal Master 500cris melos0% (1)
- Cap3 - Advanced Charging System For Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles and Battery Electric VehiclesDocument21 pagesCap3 - Advanced Charging System For Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles and Battery Electric VehiclesMarceloViníciusdePaulaNo ratings yet
- Arf360d ManualDocument2 pagesArf360d ManualBalahur MironaNo ratings yet