Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise 3
Uploaded by
Banny SaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 3
Uploaded by
Banny SaiCopyright:
Available Formats
CENTRE OF MASS Page # 55
Exercise - III Subjective Problem
1. The mass of an uniform ladder of length l increases 6. In the arrangement, mA = 2 kg and mB = 1 kg. String is light
uniformly from one end A to the other end B, and inextensible. Find the acceleration of centre of mass of
(a) Form an expression for linear mass density as a function both the blocks. Neglect friction everywhere.
of distance x from end A where linear mass density 0. The
density at one end being twice that of the other end. 7. A small cube of mass m slides down a circular path of radius
(b) find the position of the centre of mass from end A. R cut into a large block of mass M. M rests on a table and
both blocks move without friction. The blocks initially are at
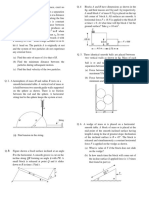
2. Find the distance of centre of mass of a uniform plate having rest and m starts from the top of the path. Find the velocity v of
semicircular inner and other boundaries of radii a and b from the cube as it leaves the block.
the centre O. m
R
M
a
b
O 8. A (trolley + child) of total mass 200 kg is moving with a
uniform speed of 36 km/h on a frictionless track. The child of
3. A thin sheet of metal of uniform thickness is cut into the mass 20 kg starts running on the trolley from one end to the
shape bounded by the line x = a and y = ± k x2, as shown. other (10 m away) with a speed of 10 ms–1 relative to the trolley
Find the coordinates
y of the centre of mass. in the direction of the trolley's motion and jumps out of the
trolley with the same relative velocity. What is the final speed
y=kx2 of the trolley? How much has the trolley moved from the time
x the child begins to run?
a
y=–kx2 9. In the figure shown the spring is compressed by ‘x0’ and
released. Two blocks ‘A’ and ‘B’ of masses ‘m’ and ‘2m’
respectively are attached at the ends of the spring. Blocks are
4. Two balls of equal masses are projected upwards simulta- kept on a smooth horizontal surface and released.
neously, one from the ground with speed 50 m/s and other k
from a 40m high tower with initial speed 30 m/s. Find the A B
maximum height attained by their centre of mass.
(a) Find the speed of block A by the time compression of the
5. In the figure shown, when the persons A and B exchange
spring is reduced to x0/2.
their positions, then
(b) Find the work done by the spring on ‘A’ by the time com-
pression of the spring reduced to x0/2.
A B
10. The figure showns the force versus time graph for a par-
m1 M m2 ticle.
(i) Find the change in momentum p of the particle (ii)
Find the average force acting on the particle
2m
m1=50kg, m2 = 70kg, M = 80 kg
100 N
(i) the distance moved by the centre of mass of the system
is__________.
t(a)
(ii) the plank moves towards_________ 0 0.2 0.4
(iii) the distance moved by the plank is _________.
(iv) the distance moved by A with respect to ground is 11. A force F acts on an object (mass = 1kg) which is initially
____________ at rest as shown in the figure. Draw the graph showing the
(v) the distance moved by B with respect to ground is momentum of the object varying during the time for which the
____________. force acts.
394,50 - Rajeev Gandhi Nagar Kota, Ph. No. : 93141-87482, 0744-2209671
IVRS No : 0744-2439051, 52, 53, www. motioniitjee.com, info@motioniitjee.com
CENTRE OF MASS Page # 56
with which the second particle begins to move if the direction of
F(N) u is, (a) along BA, (b) at an angle of 120° with AB, (c) perpen-
dicular to AB. In each case calculate (in terms of m and u) the
5
impulsive tension in the string.
18. Two particle P of mass 2m and Q of mass m are subjected
to mutual force of attraction and no other act on them. At time
t = 0, P is at rest at a fixed O and Q is directly moving away
50 100 t(ms) from O with a speed 5 u. At a later instant when t = T before
any collision has taken place Q is moving towards O with speed
u.
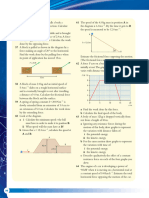
12. A man hosing down his driveway hits the wall by mistake. (a) Find in terms of m and u the total work done by the forces of
Knowing that the velocity of the stream is 25 m/s and the cross- attraction during the time interval 0 t T.
sectional area of the stream is 300 mm2, determine the force (b) At the instantt = T, impulses of magnitude J and K and
exerted on the wall. Assume that streamstrikes wall horizon- applied to P and Q bringing them to rest. Find the values of J
tally and after striking the wall, stream comes to rest. Also find and K
the pressure exerted on the wall by stream.
19. A block of mass m moving with a velocity v, enters a region
where it starts colliding with the stationary dust particles. If the
desnsity of dust particles is , & all colliding particle stick to its
front surface of cross-sectional area A. The velocity of block
after it has covered a distance x in this region is
__________________.
13. A bullet of mass m strikes an obstruction and deviates off at
60° to its original direction. If its speed is also changed from u 20. A football approaches a player at v = 12 m/s. At what speed
to v, find the magnitude of the impulse acting on the bullet. u and in which direction should the player’s foot move in order
to stop the ball upon contact? Assume that the mass of the
14. A neutro intially at rest, decays into a proton, an electron foot is much greater than that of the ball and that the collision
and an antineutrio. The ejected electron has a momentum of p1 is elastic.
= 1.4 × 10–28 kg-m/s and the antineutrino p2 = 6.5 × 10–27 kg-m/
s. Find the recoil speed of the proton (a) if the electron and the 21. Three carts move on a frictioless track with inertias and
antineutrino are ejected along the the same direection and (b) if velocities as shown. The carts collide and stick together after
they are ejected along perpendicular direction. Mass of the pro- successive collisions.
ton mp = 1.67 × 10–27 kg.
m1 = 2 kg m2 = 1 kg m3 = 2 kg
15. A steel ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from a height of 4 m v1 = 1 m/s v2 = 1 m/s v3 = 2 m/s
on to a horizontal heavy steel slab. The collision is elastic and
the ball rebounds to its original height. A B C
(a) Calculate the impulse delivered to the ball during impact.
(b) If the ball is in contact with the slab for 0.002 s, find the (a) Find loss of mechanical energy when B & C stick together.
average reaction force on the ball during impact. (b) Find magnitude of impulse experienced by A when it sticks
to combined mass (B & C).
16. A particle A of mass 2 kg lies on the edge of a table of
height 1m. It is connected by a light inelastic string of length 22. A sphere of mass m1 in motion hits directly another sphere
0.7 m to a second particle B of mass 3 kg which is lying on the of mass m2 at rest and sticks to it, the total kinetic energy after
table 0.25 m from the edge (line joining A & B is perpendicular collision is 2/3 of their total K.E. before collision. Find the ratio
to the edge). If A is pushed gently so that it start falling from of m1 : m2.
table then, find the speed of B when it starts to move. Also find
the imulsive tension in the string at that moment. 23. A body is thrown vertically upwards from ground with a speed
of 10 m/s. If coefficient of restitution of ground, e = 1/2. Find
17. Two particles, each of mass m, are connected by a light (a) the total distance travelled by the time it almost stops.
inextensible string of length 2l. Initially they lie on a smooth (b) time elapsed (after the ball has been thrown) when it is at
horizontal table at points A and B distant l apart. The particle at its subsequent maximum height for the third time.
A is projected across the table with velocity u. Find the speed
394,50 - Rajeev Gandhi Nagar Kota, Ph. No. : 93141-87482, 0744-2209671
IVRS No : 0744-2439051, 52, 53, www. motioniitjee.com, info@motioniitjee.com
CENTRE OF MASS Page # 57
24. A ball of mass 'm' is suspended by a massless string of A
2kg
length '' from a fixed point. A ball of mass 2m strikes in the 90°
direction of = 45° from horizontal and sticks to it. 1.5 m
(a) What should be the initial velocity of 2m so that system
4 kg
deflects by = B
2
(b) If at = 60° the stirng is cut then what will be the velocity (b) the maximum displacement of B after the impact.
at highest point of trajectory.
28. A small block of mass 2m initially rests at the bottom of a
fixed circular, vertical track, which has a radius of R. The con-
tact surface between the mass and the loop is frictionless. A
2m bullet of mass m strikes the block horizontally with initial speed
v0 and remain embedded in the block as the block and the
bullet circle the loop. Determine each of the following in terms
45° m
m, v0, R and g.
25. A ball is thrown horizontally from a cliff 10 m high with a
R
velocity of 10 m/s. It strikes the smooth ground and rebounds
as shown. The coefficient of restitution e for collision with the
ground e = 1/ 2 . Find
10 m/s
m, v0
(a) The speed of the masses immediately after the impact.
(b) The minimum initial speed of the bullet if the block and the
(a) velocity of ball just before striking ground. bullet are to successfully execute a complete ride on the loop.
(b) angle of velocity vector with horizontal before striking.
(c) angle of velocity vector with horizotal after striking. 29. A Cart of total mass M0 is at rest on a rough horizontal
(d) range of ball after first collision. road. It ejects bullets at rate of kg/s at an angle with the
horizontal and at velocity 'u' (constant) relative to the cart. The
26. A wedge free to move of mass 'M' has one face making an coefficient of friction between the cart and the ground is .
angle with horizotnal and is resting on a smooth rigid floor. A Find the velocity of the cart in terms of time 't'. The cart moves
particle of mass 'm' hits the inclined face of the wedge with a with sliding.
horizontal velocity v0. It is observed that the particle rebounds
in vertical direction after impact. Neglect friction between par-
ticle and the wedge & take M = 2m, v0 = 10 m/s, tan = 2, g
= 10 m/s2
M
(a) Determine the coefficient of restitution for the impact.
(b) Assume that the inclined face of the wedge is sufficiently
long so that the particle hits the same face once more during
its downward motion. Calculate the time elapsed between the
two impacts.
27. A sphere A is released from rest in the position shown and
strikes the block B which is at rest. If e = 0.75 between A and
B and k = 0.5 between B and the support, determine
(a) the velocity of A just after the impact
394,50 - Rajeev Gandhi Nagar Kota, Ph. No. : 93141-87482, 0744-2209671
IVRS No : 0744-2439051, 52, 53, www. motioniitjee.com, info@motioniitjee.com
You might also like
- Edtpa Elm Planning Commentary SandovalmarinaDocument9 pagesEdtpa Elm Planning Commentary Sandovalmarinaapi-251346191100% (3)
- Technical Drawing GuideDocument26 pagesTechnical Drawing GuideB.i. Shahed0% (1)
- Physics Assignment Sheet Topic: (Collision & Centre of Mass) SECTION BDocument6 pagesPhysics Assignment Sheet Topic: (Collision & Centre of Mass) SECTION Brebel rocksNo ratings yet
- SINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONDocument5 pagesSINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper IDocument12 pagesPhysics Paper IMOHAMMED ASIF100% (3)
- Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-2 1683019532469Document6 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-2 1683019532469SAHIL KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886Document10 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- ShashiBhushanTiwariClass11 (WWW - Jeebooks.in) 2 1Document27 pagesShashiBhushanTiwariClass11 (WWW - Jeebooks.in) 2 1Mohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum - Level 3Document8 pagesEnergy and Momentum - Level 3Kusharg rahejaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Problems: Problems I: Introductory Problems & Collisions in One DimensionDocument4 pagesIntroductory Problems: Problems I: Introductory Problems & Collisions in One DimensionDiego ForeroNo ratings yet
- Assignment#01 TNS (Centre of Mass)Document7 pagesAssignment#01 TNS (Centre of Mass)ashutosh paridaNo ratings yet
- Com and CollisionsDocument6 pagesCom and Collisionsarun2006No ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Mechanics 3 SolutionDocument10 pagesAssignment 3 - Mechanics 3 SolutionVincent haNo ratings yet
- 7 EXERCISE 4 - CompleteDocument6 pages7 EXERCISE 4 - CompleteQusai SaifyNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass Problems & SolutionsDocument15 pagesCentre of Mass Problems & SolutionsSiddharth Acharya100% (1)
- Inc JR.C - Cta-01 - 08-08-21 - QPDocument12 pagesInc JR.C - Cta-01 - 08-08-21 - QPpraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains Level: PHYSICS - Work Energy and PowerDocument8 pagesJee Mains Level: PHYSICS - Work Energy and PowerAnju MohtaNo ratings yet
- Narayana Educational Society: Star SuperDocument2 pagesNarayana Educational Society: Star SuperAkshith IsolaNo ratings yet
- 5 AS EnergyDocument3 pages5 AS EnergyfdadsfNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Momentum and Energy ProblemsDocument6 pagesMechanics Momentum and Energy ProblemsTrần Hoàng ViệtNo ratings yet
- Class XI Jee Advanced Paper FinalDocument9 pagesClass XI Jee Advanced Paper Finaldheeraj ShahNo ratings yet
- WORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedDocument7 pagesWORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Centre of Mass, Basic Home Work Sheet-3Document3 pagesNK C SI R: Centre of Mass, Basic Home Work Sheet-3Yash DhokeNo ratings yet
- NLM 8Document2 pagesNLM 8Ramesh BadamNo ratings yet
- (Centre of Mass, Momentum & Collision) Exercise-IDocument4 pages(Centre of Mass, Momentum & Collision) Exercise-IAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Com Sub Q PDFDocument4 pagesCom Sub Q PDFAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Momentum & CollisionDocument5 pagesAssignment - Momentum & CollisionKalpan ShahNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet WPEDocument9 pagesPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferNo ratings yet
- COM Location, Momentum Conservation & Impulse in One ShotDocument123 pagesCOM Location, Momentum Conservation & Impulse in One ShotSanjog KhuranaNo ratings yet
- P2. Growth-Phase-1 & 2 - JA - 01-10-2023Document12 pagesP2. Growth-Phase-1 & 2 - JA - 01-10-2023Tanay1 MitraNo ratings yet
- 1978 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1Document4 pages1978 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1dawnNo ratings yet
- 1979 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1. (A)Document4 pages1979 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1. (A)dawnNo ratings yet
- Work, Power & Energy (Question)Document4 pagesWork, Power & Energy (Question)Harika NKNo ratings yet
- Collisions-New Tutorial SheetDocument3 pagesCollisions-New Tutorial SheetSuyog PatilNo ratings yet
- 1976 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1Document4 pages1976 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1dawnNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Document4 pagesIndonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- F Wedge+Pseudo 18 07 2021 TestDocument2 pagesF Wedge+Pseudo 18 07 2021 TestAryanNo ratings yet
- Assignment UNIT 1Document4 pagesAssignment UNIT 1Abhi WaliaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Mechanics 3 SolutionDocument10 pagesAssignment 3 - Mechanics 3 SolutionSamriddhi SinglaNo ratings yet
- Two yr CRP 224_B-lot_Ph-I_Paper-1_PhysicsDocument5 pagesTwo yr CRP 224_B-lot_Ph-I_Paper-1_Physicsjdhmyj2zchNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3-Centre of MassDocument6 pagesAssignment-3-Centre of MassSwarnalatha SwarnalathaNo ratings yet
- Center of Mass and Collision - Practice Sheet - JEE ChallengersDocument8 pagesCenter of Mass and Collision - Practice Sheet - JEE ChallengersSHREYANSH RAINo ratings yet
- Advanced HandoutDocument8 pagesAdvanced Handoutparthkalra1981No ratings yet
- 04 11 23 09 - 42 - 26 AmDocument4 pages04 11 23 09 - 42 - 26 Amjindalipad10No ratings yet
- 06 - Work Energy and PowerDocument5 pages06 - Work Energy and PowerMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- Momentum Problem Set PDFDocument3 pagesMomentum Problem Set PDFNirmaan ShankerNo ratings yet
- Review Practice Sheet - KM, Lom, WpeDocument7 pagesReview Practice Sheet - KM, Lom, WpeSaksham PanghalNo ratings yet
- Dakshana Class 11th Unit Test 4 - Circular Motion and Conservation of MomentumDocument3 pagesDakshana Class 11th Unit Test 4 - Circular Motion and Conservation of MomentumullasagwNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocument7 pagesUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNo ratings yet
- 136 - Centre+of+Mass,+Exercise-4 (B) @unacademyplusdiscountsDocument2 pages136 - Centre+of+Mass,+Exercise-4 (B) @unacademyplusdiscountsYash DhokeNo ratings yet
- Centre of MassDocument8 pagesCentre of Massgskpraveen86No ratings yet
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf_extractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf_extractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Physics by Mista SirDocument5 pagesPhysics by Mista SirSatish PatelNo ratings yet
- Eamcet '13 PDFDocument44 pagesEamcet '13 PDFAmaan YousufNo ratings yet
- Paper - 1 (Question Paper) - 5 PDFDocument22 pagesPaper - 1 (Question Paper) - 5 PDFSaumya MundraNo ratings yet
- PS 320 - Classical Mechanics Reynolds ProblemsDocument14 pagesPS 320 - Classical Mechanics Reynolds ProblemsSK MishraNo ratings yet
- Conserving Momentum, Collisions and ImpulseDocument2 pagesConserving Momentum, Collisions and Impulsemayank singhNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet - 23 - (Rotation-2) - (AM) - Date - 11.8.2008Document10 pagesAssignment Sheet - 23 - (Rotation-2) - (AM) - Date - 11.8.2008Pranjal SinghalNo ratings yet
- Momento Linear e Centro de Massa: Resolução de Problemas de MecânicaDocument4 pagesMomento Linear e Centro de Massa: Resolução de Problemas de MecânicaThales FreireNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet on Work, Energy and PowerDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet on Work, Energy and PowerGaming baseNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum (Practice Questions)Document34 pagesConservation of Momentum (Practice Questions)SakshamNo ratings yet
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorFrom EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 HOTs Question BankDocument29 pagesCBSE Class 10 HOTs Question BankBanny SaiNo ratings yet
- C.O.M & CollisionDocument42 pagesC.O.M & CollisionBanny SaiNo ratings yet
- Particles NewDocument101 pagesParticles NewBanny SaiNo ratings yet
- PP NotesDocument252 pagesPP NotesAravind KondamudiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7th Jan Shift-2 PDFDocument16 pagesMathematics 7th Jan Shift-2 PDFBanny SaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 PDFDocument13 pagesLecture6 PDFBanny SaiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Series JMS/CDocument12 pagesMathematics: Series JMS/CNikshay HansNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7th Jan Shift-1Document15 pagesMathematics 7th Jan Shift-1Banny SaiNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Differntiation & Integration Formulae.Document1 pageClass Xii - Differntiation & Integration Formulae.Mandeep Singh Plaha59% (22)
- Physics v1 PDFDocument18 pagesPhysics v1 PDFHagNo ratings yet
- 14 Computer Science NewDocument6 pages14 Computer Science NewRekhaBhandariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetDocument4 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetSumit Dhall74% (50)
- Physics 9th Jan Shift-1 PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics 9th Jan Shift-1 PDFBanny SaiNo ratings yet
- Free Fall DrawingDocument2 pagesFree Fall DrawingBanny SaiNo ratings yet
- notebook1-JEEMAIN GURU PDFDocument258 pagesnotebook1-JEEMAIN GURU PDFChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 - Number SystemsDocument15 pages1 - Number Systemskaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Izzard, C. F.-The Surface-Profile of Overland-FlowDocument10 pagesIzzard, C. F.-The Surface-Profile of Overland-Flowjosue.angelo9459No ratings yet
- Topic 1: Conic Sections Subtopic: 1.1 Introduction To Conic Sections 1.2 Circles Learning OutcomesDocument35 pagesTopic 1: Conic Sections Subtopic: 1.1 Introduction To Conic Sections 1.2 Circles Learning OutcomesAravind Ravi100% (1)
- Electrical: ElectronicDocument100 pagesElectrical: ElectronicIver SanchezNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Simulation of The Orthogonal Cutting Based On AbaqusDocument5 pagesFinite Element Simulation of The Orthogonal Cutting Based On AbaqusBalaji Venkateshwaran PanchatsaramNo ratings yet
- Stability and Plant WideDocument150 pagesStability and Plant WideAlifDzakiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1.EE 2A Stem Midterms. LM 1Document11 pagesThermodynamics 1.EE 2A Stem Midterms. LM 1mery9jean9lasamNo ratings yet
- Formula 2 PFDocument32 pagesFormula 2 PFAnwar HossainNo ratings yet
- Calculus Released Exam 2003 Scoring WorksheetDocument6 pagesCalculus Released Exam 2003 Scoring WorksheetvingtsNo ratings yet
- CS401 Homework 1Document2 pagesCS401 Homework 1mohammadnh2002No ratings yet
- Lab 2 Basic CMOS AmplifiersDocument5 pagesLab 2 Basic CMOS AmplifiersJatinKumarNo ratings yet
- Karnataka 2nd Puc Mathematics Board Exam Question Paper Eng Version-March 2018 PDFDocument7 pagesKarnataka 2nd Puc Mathematics Board Exam Question Paper Eng Version-March 2018 PDFVinod MNNo ratings yet
- Activity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsDocument84 pagesActivity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsSze Siu Pui100% (2)
- G3 - Math - Study - Guide - 2nd - Midterm TestDocument8 pagesG3 - Math - Study - Guide - 2nd - Midterm Testphuongnguyen21022k5.ewaNo ratings yet
- Stats Chap10Document63 pagesStats Chap10Sameh SalahNo ratings yet
- 16 17 CILLI RobertoDocument81 pages16 17 CILLI RobertosandroNo ratings yet
- 07 - Workbook Part 2 - Business StatisticsDocument158 pages07 - Workbook Part 2 - Business StatisticsvNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument152 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignosamahNo ratings yet
- Detect Structural Damage Using ANN & Modal DataDocument8 pagesDetect Structural Damage Using ANN & Modal DataSri NNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Sample PaperDocument21 pagesSSC CGL Sample PaperPraveen ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- NARAYANA IIT ACADEMY JR.IIT CO SUPER CHAINA & SUPER CHAINA N120/MAINS QP KEY & SOLUTIONDocument12 pagesNARAYANA IIT ACADEMY JR.IIT CO SUPER CHAINA & SUPER CHAINA N120/MAINS QP KEY & SOLUTIONYugandher BadanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Flow Through Packed BedsDocument5 pagesExperiment 5: Flow Through Packed BedsBianca BelmonteNo ratings yet
- NCSE Math 2018 SolutionDocument15 pagesNCSE Math 2018 SolutionDexter B50% (2)
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Fin6381.001.09f Taught by Alain Bensoussan (Axb046100)Document4 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Fin6381.001.09f Taught by Alain Bensoussan (Axb046100)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Complex Structure Based On AutoCAD VBADocument3 pages3D Modeling of Complex Structure Based On AutoCAD VBAInnovative Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Basic Java Chapter 4Document9 pagesBasic Java Chapter 4zyrus-mojica-6477No ratings yet
- Complex identities and inequalitiesDocument2 pagesComplex identities and inequalitiesnastasescuNo ratings yet
- Cad 1264355Document17 pagesCad 1264355Ogunbiyi OlalekanNo ratings yet